STM32 Timer : Base Timer, Input Capture, PWM, Output Compare
http://www.cs.indiana.edu/~geobrown/book.pdf

An example of a basic timer is illustrated in Figure 10.1.
This timer has four components – a controller, a prescaler (PSC), an “auto-reload” register (ARR) and a counter (CNT).
The function of the prescaler is to divide a reference clock to lower frequency.
The STM32 timers have 16-bit prescaler registers and can divide the reference clock by any value 1..65535.
For example, the 24Mhz system clock of the STM32 VL Discovery
could be used to generate a 1 Mhz count frequency with a prescaler of 23 (0..23 == 24 values). T
he counter register can be configured to count up, down, or up/down and to be reloaded from the auto reload register
whenever it wraps around (an “update event”) or to stop when it wraps around.
The basic timer generates an output event (TGRO) which can be configured
to occur on an update event or when the counter is enabled (for example on a GPIO input).
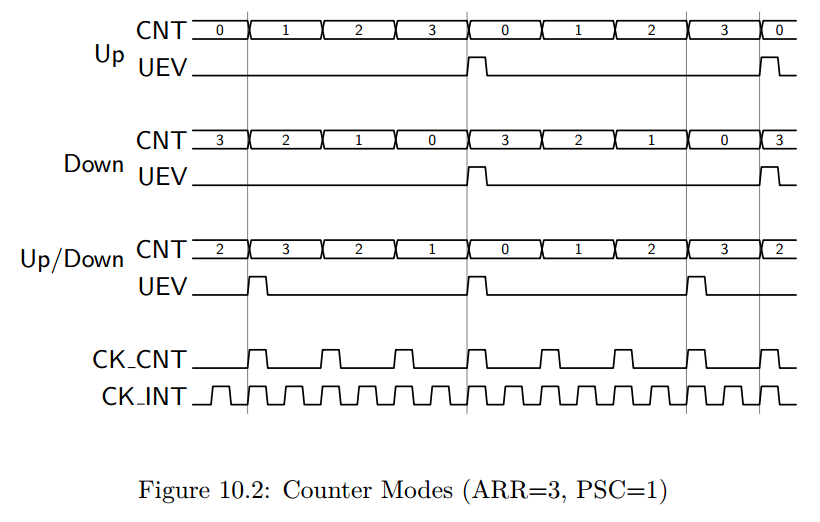
To understand the three counter modes consider Figure 10.2.
In these examples, we assume a prescaler of 1 (counter clock is half the internal clock), and a auto reload value of 3.
Notice that in “Up” mode, the counter increments from 0 to 3 (ARR) and then is reset to 0.
When the reset occurs, an “update event” is generated.
This update event may be tied to TRGO, or in more complex timers with capture/compare channels
it may have additional effects (described below).
Similarly, in “Down” mode, the counter decrements from 3 to 0 and then is reset to 3 (ARR).
In Down mode, an update “event” (UEV) is generated when the counter is reset to ARR.
Finally, in Up/Down mode, the counter increments to ARR, then decrements to 0, and repeats.
A UEV is generated before each reversal with the effect that the period in Up/Down mode
is one shorter than in either Up or Down mode.
Many timers extend this basic module with the addition of counter channels such as the one illustrated in Figure 10.3.
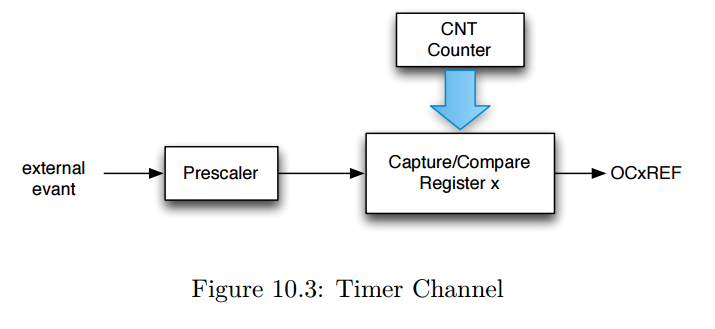
The “x” refers to the channel number – frequently, timers support multiple channels.
With this modest additional hardware, an output can be generated whenever the count register reaches a specific value
or the counter register can be captured when a specific input event occurs (possibly a prescaled input clock).
An important use of counter channels is the generation of precisely timed pulses.
There are two variations of this use – “one-pulse” pulses,
in which a single pulse is generated, and pulse width modulation, in which a series of pulses is generated with the counter UEV period.
The pulse width is controlled by the Capture/Compare Register (CCR).
For example, the channel output (OCxREF) may tied to whether the CNT register is greater (or less) than the Compare register.
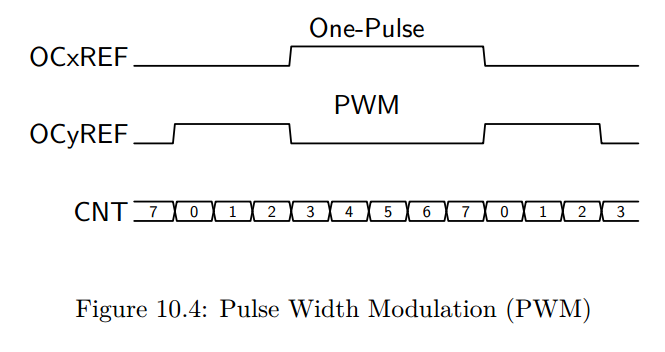
In Figure 10.4 we illustrate the use of two channels for one-pulse and PWM outputs.
Here we assume that the ARR is 7 and the CCR is 3.
In PWM mode, ARR controls the period, and CCR controls the pulse width (and hence the duty cycle).
In one-pulse mode, the pulse begins CCR cycles after an initial trigger event, and has a width of ARR-CRR.
It is possible to use multiple channels to create a set of synchronized, pulses beginning at precise delays from each other.
A timer channel may also be used to measure pulse widths – in effect decoding pwm signals.
There are many other configuration options for the STM32 timers including mechanisms
to synchronize multiple timers both to each other and to external signals.
In the remainder of this chapter we consider two timer applications including PWM output (Section 10.1),
input pulse measurement (Section 10.2).
In Chapter 13 we show how to use a timer to control DMA transfers for an audio player and
in Chapter 14 we use a timer to sample and analog input at regular intervals.
STM32 Timer : Base Timer, Input Capture, PWM, Output Compare的更多相关文章
- PIC32MZ tutorial -- Output Compare
Output Compare is a powerful feature of embedded world. The PIC32 Output Compare module compares the ...
- STM32 System and Timer Clock Configurations
STM32 System and Timer Clock Configurations I've started writing some software to drive a series of ...
- TIMER门控模式控制PWM输出长度
TIMER门控模式控制PWM输出长度 参照一些网友代码做了些修改,由TIM4来控制TIM2的PWM输出长度, 采用主从的门控模式,即TIM4输出高时候TIM2使能输出 //TIM2 PWM输出,由TI ...
- PIC32MZ tutorial -- Input Capture
Today I accomplish a simple application for PIC32MZ EC Starter Kit. This application uses Input Capt ...
- An Isolated DAC Using PWM Output
An Isolated DAC Using PWM Output Arduino‘s (ATmega328P) PWM outputs via analogWrite can be convenien ...
- 深入比特币原理(三)——交易的输入(input)与输出(output)
本节内容非常重要,如果你不能很好的掌握本节内容,你无法真正理解比特币的运行原理,请务必要学习清楚. 比特币的交易模型为UTXO(unspend transaction output),即只记录未花费的 ...
- Linux部署Django:报错 nohup: ignoring input and appending output to ‘nohup.out’
一.部署 Django 到远程 Linux 服务器 利用 xshell 通过 ssh 连接到 Linux服务器,常规的启动命令是 python3 manage.py runserver 但是,关闭 x ...
- STM32: TIMER门控模式控制PWM输出长度
搞了两天单脉冲没搞定,无意中发现,这个利用主从模式的门控方式来控制一路PWM的输出长度很有效. //TIM2 PWM输出,由TIM4来控制其输出与停止 //frequency_tim2:TIM2 PW ...
- STM32 Seminar 2007 -- Timer
随机推荐
- 第9月第30天 MVP
1. import UIKit struct Person { // Model let firstName: String let lastName: String } protocol Greet ...
- Anaconda+django写出第一个web app(十一)
今天我们来学习给页面添加一个Sidebar,根据Sidebar跳转到相应的tutorial. 打开views.py,编辑single_slug函数: def single_slug(request, ...
- NVIDIA / Intel 核芯显卡显示 + Nvidia 计算
今天折腾了好久intel集成显卡显示.最后好不容易才全部搞定,这里记录一下. 1. 首先在BIOS里是要打开Intel 核芯显卡的.我把它设置成了主显卡,显示器也接到核心显卡的口上. 重启后, I ...
- PHP+mysql系统报错:PHP message: PHP Warning: Unknown: Failed to write session data (files)
PHP+mysql系统报错:PHP message: PHP Warning: Unknown: Failed to write session data (files) 故障现象,后台页面点击没有 ...
- 关于sklearn,监督学习几种模型的对比
# K近邻,适用于小型数据集,是很好的基准模型,容易解释 from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier # 线性模型,非常可靠的首选算法,适用于 ...
- intelliJ 打包jar的多种方式
这里总结出用IntelliJ IDEA打包jar包的多种方式,以后的项目打包Jar包可以参考如下形式: 用IDEA自带的打包形式 用Maven插件maven-shade-plugin打包 用Maven ...
- Android开源库集合(工具)
图片加载框架: Glide https://github.com/bumptech/glide Android-Universal-Image-Loader https://github.com/no ...
- priority_queue<int>q;
priority_queue<int>q;//默认不递增q.size();//q中有几个元素q.pop();//删除队首q.top();//返回队首元素q.push();//在队列中插入一 ...
- 利用HTML5定位功能,实现在百度地图上定位(转)
原文:利用HTML5定位功能,实现在百度地图上定位 代码如下: 测试浏览器:ie11定位成功率100%,Safari定位成功率97%,(add by zhj :在手机上测试(用微信内置浏览器打开),无 ...
- 【Ray Tracing in One Weekend 超详解】 光线追踪1-7 Dielectric 半径为负,实心球体镂空技巧
今天讲这本书最后一种材质 Preface 水,玻璃和钻石等透明材料是电介质.当光线照射它们时,它会分裂成反射光线和折射(透射)光线. 处理方案:在反射或折射之间随机选择并且每次交互仅产生一条散射光线 ...
