LinkedHashMap结构get和put源码流程简析及LRU应用
原理这篇讲得比较透彻Java集合之LinkedHashMap。
本文属于源码阅读笔记,因put,get调用逻辑及链表维护逻辑复杂(至少网上其它文章的逻辑描述及配图,我都没看明白LinkedHashMap到底长啥样),所以以文字描述和手画逻辑图的方式来讲述源码逻辑,阅读时再辅以源码达到事半功倍的效果。
1.LinkedHashMap简要介绍。
LinkedHashMap继承hashMap,并维护一个双向链表保持有序(与haspmasp最重要的区别),accessOrder==true初始化时按访问顺序输出,默认按插入顺序输出,如下图所示,左边为Entry数组实现的hashtable存储结构,右边为双向链表结构,header为链表头,A离header最近可通过header.after访问, D离header最远为队尾,可通过header.before来访问,LRU删除最近最少使用时指的是A即header.after,新插入或者被访问(accessOrder为true)时先存储到左侧的hashtable中并将链表位置移动到D后面。左下方为put和get调用流程,右下为Entry中操作链表的方法remove,addBefore源码。
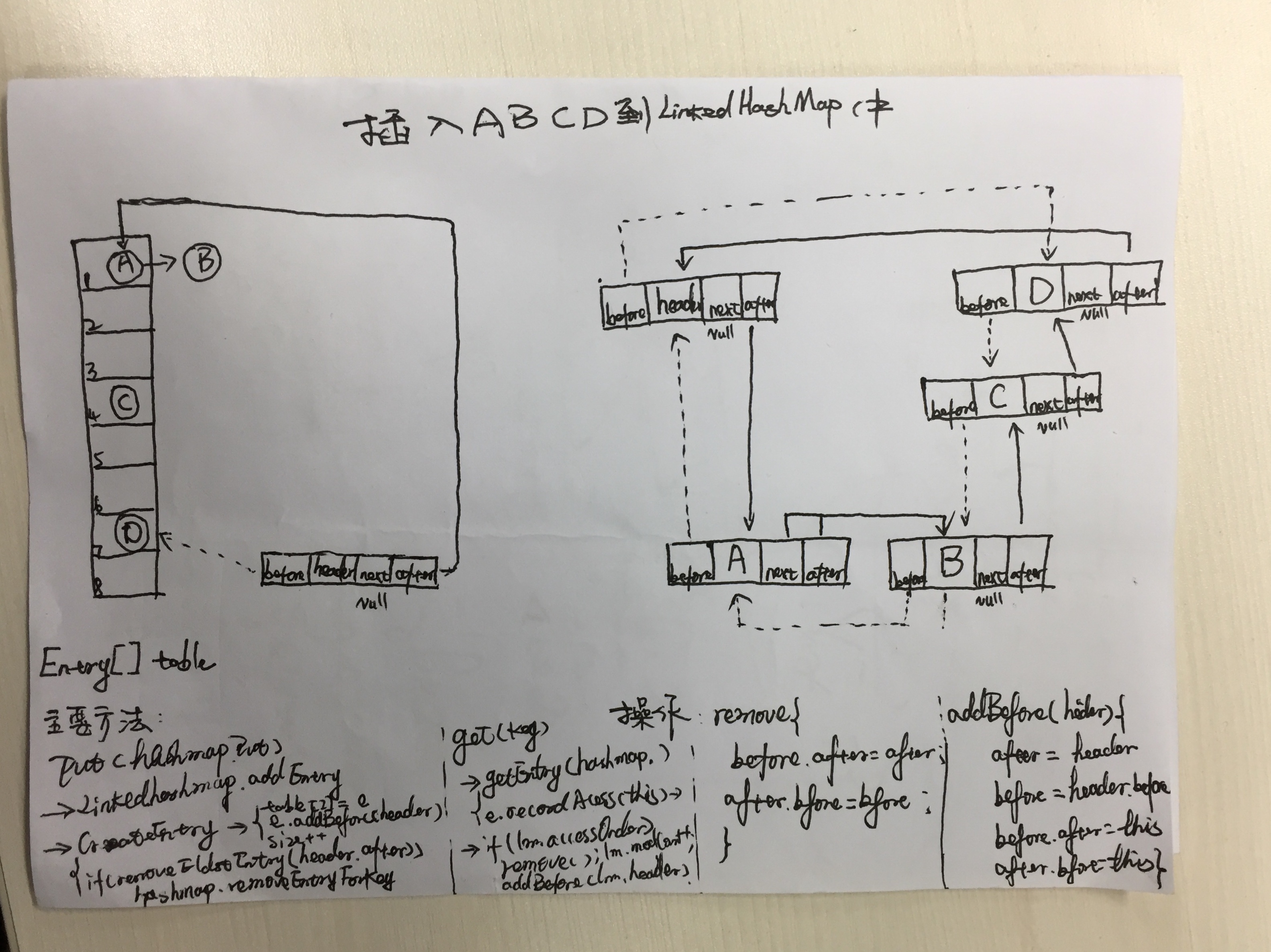
2.put及get和remove流程
put流程:HashMap.put(Object key)-->LinkedHashMap.addEntry(hash, key, value, i)(要么重写removeEldestEntry可删除元素达到维持固定长度,要么扩容判断(size>=threshold时扩容))-->LinkedHashMap.createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex)将Entry存储到tabel[Index]-->LinkedHashMap.中e.addBefore(header)将当前元素加到header的before,即链表队尾.
get流程:LinkedHashMap.get(key)-->HashMap.getEntry(key);get同时并记录访问LinkedHashMap中e.recordAccess(this)-->如果accessOrder==true,则调用LinkedHashMap.Entry.remove从链表this中删除e自己,LinkedHashMap.Entry.addBefore(header)把自己加入链表队尾,保持最远(离header最远,在队尾)最新。
remove流程:三种情况,一种为put时限制容量(重写removeEldestEntry)删除,HashMap.put-->LinkedHashMap.addEntry-->HashMap.removeEntryForKey(从hashTable中删除元素)-->LinkedHashMap.e.recordRemoval(this)-->LinkedHashMap.Entry.remove(将自己从链表删除中);第二种直接remove, HashMap.remove(object key)-->HashMap.removeEntryForKey后续与第一种情况相同。第三种,遍历器中删除,for(Iterator iterator=lru1.keySet().iterator();iterator.hasNext();) {iterator=iterator.next;iterator.remove();},HashMap.KeySet().iterator().newKeyIterator().KeyIterator().HashIterator().remove()-->HashMap.this.removeEntryForKey(current.key)后续与第一种情况相同。
说明:LinkedHashMap.Entry中remove及addBefore操作中的before,after,此二指针为Entry所有,当通过e.addBefore(header)调用时,before及after指的是当前调用实体Entry e的before,after指针,切勿以为是LinkedHashMap的成员,本人就是在找此二公初始化的地方时困惑了两天。header为LinkedHashMap私有属性,在LinkedHashMap.init()进行初始化并且不会被改变。
内部存储直接继承hashpMap,代码在hashpmap中,Entry[] table即hashtable来存,如上图左边,
public class HashMap<K,V>
extends AbstractMap<K,V>
implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, Serializable
{ transient Entry[] table;
static class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final K key;
V value;
Entry<K,V> next;
final int hash; /**
* Creates new entry.
*/
Entry(int h, K k, V v, Entry<K,V> n) {
value = v;
next = n;
key = k;
hash = h;
}
}
}
LinkedHashMap中对Entry进行继承并增加两个元素,before,after
public class LinkedHashMap<K,V>
extends HashMap<K,V>
implements Map<K,V>
{
//链表头
//初始化流程LinkedHashMap()-->super(initialCapacity, loadFactor)-->HashMap.HashMap()-->LinkedHashMap.init()
//-->header = new Entry<K,V>(-1, null, null, null);header.before = header.after = header;
private transient Entry<K,V> header;//header.hash=-1
//添加元素时,调用HashMap.put(Object key)-->LinkedHashMap.addEntry(hash, key, value, i)
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex);
// Remove eldest entry if instructed, else grow capacity if appropriate
Entry<K,V> eldest = header.after;
if (removeEldestEntry(eldest)) { //size>cachesize时删除最近最少使用元素
removeEntryForKey(eldest.key);
} else {
if (size >= threshold)
resize(2 * table.length);//扩容
}
}
private static class Entry<K,V> extends HashMap.Entry<K,V> {
// These fields comprise the doubly linked list used for iteration.
Entry<K,V> before, after;
Entry(int hash, K key, V value, HashMap.Entry<K,V> next) {
super(hash, key, value, next);
}
/**
* Removes this entry from the linked list.
*/
private void remove() {
before.after = after;
after.before = before;
}
/**
* Inserts this entry before the specified existing entry in the list.
*/
private void addBefore(Entry<K,V> existingEntry) {
after = existingEntry;
before = existingEntry.before;
before.after = this;
after.before = this;
}
/**
* This method is invoked by the superclass whenever the value
* of a pre-existing entry is read by Map.get or modified by Map.set.
* If the enclosing Map is access-ordered, it moves the entry
* to the end of the list; otherwise, it does nothing.
*/
void recordAccess(HashMap<K,V> m) {
LinkedHashMap<K,V> lm = (LinkedHashMap<K,V>)m;
if (lm.accessOrder) {
lm.modCount++;
remove();
addBefore(lm.header);
}
}
void recordRemoval(HashMap<K,V> m) {
remove();
}
}
}
3.LRU cache应用
Least Recently Used最近最少算法,重写removeEldestEntry方法并在初始化时传入accessOrder==true,实现cache,保持固定长度,并删除最近(离header最近,即header.after元素)最少(新加入或者被访问时都加到队尾header.before,最旧即最少访问的元素离header最近)使用的元素。
LinkedHashMap特别有意思,它不仅仅是在HashMap上增加Entry的双向链接,它更能借助此特性实现保证Iterator迭代按照插入顺序(以insert模式创建LinkedHashMap)或者实现LRU(Least Recently Used最近最少算法,以access模式创建LinkedHashMap)。
更多实现方式LRU缓存实现(Java),线程安全LRU缓存参考ConcurrentLinkedHashMap设计与代码解析
package hashmap_thread; import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.Map; /**
* @author pujiahong2006@163.com</br> Created By: 2018-12-17 下午6:22:17
*/
public class LRU_cache {
//cache大小
final static int cacheSize = 4;
//初始化LinkedHashMap,并传入参数accessOrder为true
//内部Entry[] table的长度capacity为2的N次方,且 capacity<initCapacity,此处initCapacity若为(cacheSize /0.75f) + 1时,
//扩容阈值threshold最大能等于cachesize,当size等于cachesize时会触发扩容,因此需扩大threshold,需扩大capacity,而扩大capacity必须是2的N次方,
//即最小(N为1)要扩大两倍,initCapacity需扩大两倍,经测算initCapacity=((cacheSize*2) /0.75f) + 1时能保证不扩容,
//但浪费空间太大,以cachesize=48来算,initCapacity=129,capacity=128,threshold=capacity*loadfactor=96,loadfactor=0.75f
//此处已重写removeEldestEntry,LinkedHashMap.addEntry时size<=48时,size<threshold=96没有触发扩容限值
//扩容就变为一个函数求解,threshold>cachesize时就不扩容,threshold=capacity*loadfactor,capacity=power(2,N)<initCapacity,
//initCapacity=Z*cacheSize+1,求解Z,最终Z=2/loadFactor
static Map lru1 = new LinkedHashMap<String, String>((int) Math.ceil((cacheSize*2) / 0.75f) + 1,
0.75f, true) {
@Override
//重写removeEldestEntry,维持默写size,超过时删除最近最少使用
protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry<String, String> eldest) {
return size() > cacheSize;
}
}; public void synchMap() {
lru1 = Collections.synchronizedMap(lru1); } public static void main(String[] args) {
lru1.put("11", "aa");
lru1.put("33", "cc");
lru1.put("00", "dd");
lru1.put("22", "hh");
lru1.put("66", "kk");//超过容量4的限制,删除近最少使用header.after元素11 lru1.get("00");//本来00排在33后,22前,但被访问后,移动到队尾header.before,即最远最新元素。 System.out.println(lru1); }
} 输出:
{33=cc, 22=hh, 66=kk, 00=dd}
LinkedHashMap结构get和put源码流程简析及LRU应用的更多相关文章
- .Net Framework4.5.2 源码命名空间简析
Miscosoft目前除.Net Core开源外,对于.Net4.5.1 , 4.5.2等后续版本同样开源.资源中包含sln,csproj等以方便我们在vs中打开它们,不过我们不能编译它,因为它缺少r ...
- 【原创】Ingress-Nginx-Controller的Metrics监控源码改造简析
一.背景 目前我们的生产环境一层Nginx已经容器化部署,但是监控并不完善,我们期望其具有Ingress-Nginx-Controller组件上报监控的数据.这样可以建立请求全链路的监控大盘.有利于监 ...
- Flask 源码流程,上下文管理
源码流程 创建对象 from flask import Flask """ 1 实例化对象 app """ app = Flask(__na ...
- ES6.3.2 index操作源码流程
ES 6.3.2 index 操作源码流程 client 发送请求 TransportBulkAction#doExecute(Task,BulkRequest,listener) 解析请求,是否要自 ...
- Eureka服务端源码流程梳理
一.简述 spring cloud三步走,一导包,二依赖,三配置为我们简化了太多东西,以至于很多东西知其然不知其所以然,了解底层实现之后对于一些问题我们也可以快速的定位问题所在. spring clo ...
- django-admin的源码流程
一.admin的源码流程 首先可以确定的是:路由关系一定对应一个视图函数 a.当点击运行的时候,会先找到每一个app中的admin.py文件,并执行 b.执行urls.py admin.site是什么 ...
- Django session 源码流程
流程 Django session源码流程 首先执行的是SessionMiddleware的init方法 import_module(settings.SESSION_ENGINE) 导入了一个 dj ...
- rest_framework解析器组件源码流程
rest_framework解析器组件源码流程 解析器顾名思义就是对请求体进行解析.为什么要有解析器?原因很简单,当后台和前端进行交互的时候数据类型不一定都是表单数据或者json,当然也有其他类型的数 ...
- 【转】ANDROID自定义视图——onMeasure,MeasureSpec源码 流程 思路详解
原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/a396901990/article/details/36475213 简介: 在自定义view的时候,其实很简单,只需要知道3步骤: 1.测量—— ...
随机推荐
- MySQL中int(M)和tinyint(M)数值类型中M值的意义
在一开始接触MySQL数据库时,对于int(M)及tinyint(M)两者数值类型后面的M值理解是最多能够插入数据库中的值不能大于M: 后来工作后,也是一边学习一边使用,之后的理解是其中的M的意思是插 ...
- 使用jquery.validation+jquery.poshytip做表单验证--未完待续
jqueryValidate的具体使用方法很多,这里就不在赘述,这一次只谈一下怎样简单的实现表单验证. 整片文章目的,通过JQvalidation按表单属性配置规则验证,并将验证结果通过poshyti ...
- itertools库 combinations() 和 permutations() 组合 和 排列选项的方法
combinations方法重点在组合,permutations方法重在排列. combinations和permutations返回的是对象地址,原因是在python3里面,返回值已经不再是list ...
- july 大神 要向他学习的东西(已学了)
交换礼物代码 库 permutations 库 product https://www.cnblogs.com/kaibindirver/p/10714375.html https://www.cnb ...
- Scala类与对象
类简介 简介 类是对象的蓝图.一旦你定义了类,就可以用关键字new根据类的蓝图创建对象.在类的定义里,可以放置字段和方法,这些被笼统地称为成员.对于字段,不管是val还是var定义的,都是指向对象的变 ...
- mysql下有符号数和无符号数的相关问题
最近自己的程序在调用mysql的存储过程传参给smallint类型变量的时候,总是出现out of range value的错误,刚开始用C数值转换方式的二进制位转换思路来思考时,总是觉得没什么问题, ...
- courator - create
0. retry policy RetryPolicy retryPolicy = new ExponentialBackoffRetry(3000,3); 1. client 1) recipes ...
- 在javascript中toString 和valueOf的区别
1.toString()方法:主要用于Array.Boolean.Date.Error.Function.Number等对象转化为字符串形式.日期类的toString()方法返回一个可读的日期和字符串 ...
- CCProxy
我在之前的博客里提到了用Teamviewer + CCProxy做内网穿透,当时只是简单提了一下,因为发现这种方式网速比较慢.今天又用到了它,虽然慢点,但是总比没的用好,哈哈哈.不得不感叹CCProx ...
- 理解Solr缓存及如何设置缓存大小
文献地址:http://wangdg.com/understanding-and-tuning-solr-cache/ 理解Solr缓存及如何设置缓存大小 为了得到最好的检索性能,Solr会在内存中缓 ...
