【C++ Primer | 07】泛型算法
定制操作
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <numeric>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
template <typename Sequence>
inline ostream& println(Sequence const& seq)
{
for (auto const& elem : seq)
cout << elem << " ";
cout << endl;
return cout;
}
inline bool is_shorter(std::string const& lhs, std::string const& rhs)
{
return lhs.size() < rhs.size();
}
void elimdups(vector<string> &vs)
{
sort(vs.begin(), vs.end());
auto new_end = unique(vs.begin(), vs.end());
vs.erase(new_end, vs.end());
}
int main()
{
vector<", "Hi", "alan", "wang" };
elimdups(v);
stable_sort(v.begin(), v.end(), is_shorter);
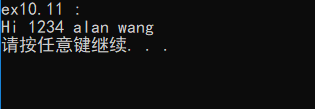
cout << "ex10.11 :\n";
println(v);
system("pause");
;
}
输出结果:
Exercise 10.14:
int main()
{
auto sum = [](int a, int b) {return a + b; };
cout << sum(, ) << endl;
;
}
Exercise 10.16
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
void elimdups(vector<string> &vs)
{
sort(vs.begin(), vs.end());
for (auto c : vs)
cout << c << " ";
cout << endl;
auto new_end = unique(vs.begin(), vs.end());
vs.erase(new_end, vs.end());
for (auto c : vs)
cout << c << " ";
cout << endl;
}
void biggies(vector<string> &vs, size_t sz)
{
elimdups(vs);
stable_sort(vs.begin(), vs.end(), [](string const& lhs, string const& rhs) {
return lhs.size() < rhs.size(); });
auto wc = find_if(vs.begin(), vs.end(), [sz](string const& s) {
return s.size() >= sz; });
for_each(wc, vs.end(), [](const string &s) {
cout << s << " ";
});
}
int main()
{
vector<string> v{
","hi~", "alan", "alan", "cp"
};
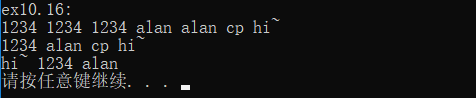
cout << "ex10.16: " << endl;
biggies(v, );
cout << endl;
system("pause");
;
}
输出结果:
Exercise 10.18、10.19
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
// from ex 10.9
void elimdups(vector<string> &vs)
{
sort(vs.begin(), vs.end());
auto new_end = unique(vs.begin(), vs.end());
vs.erase(new_end, vs.end());
for (auto it = vs.cbegin(); it != vs.end(); ++it)
cout << *it << " ";
cout << endl;
}
// ex10.18
void biggies_partition(vector<string> &vs, size_t sz)
{
elimdups(vs);
auto pivot = partition(vs.begin(), vs.end(), [sz](const string &s) {
return s.size() >= sz; }
);
for (auto it = vs.cbegin(); it != pivot; ++it)
cout << *it << " ";
}
// ex10.19
void biggies_stable_partition(vector<string> &vs, std::size_t sz)
{
elimdups(vs);
auto pivot = stable_partition(vs.begin(), vs.end(), [sz](const string& s) {
return s.size() >= sz; });
for (auto it = vs.cbegin(); it != pivot; ++it)
cout << *it << " ";
}
int main()
{
// ex10.18
vector<string> v{
"the", "quick", "red", "fox", "jumps", "over", "the", "slow", "red", "turtle"
};
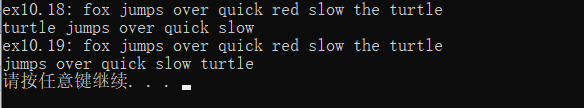
cout << "ex10.18: ";
vector<string> v1(v);
biggies_partition(v1, );
cout << endl;
// ex10.19
cout << "ex10.19: ";
vector<std::string> v2(v);
biggies_stable_partition(v2, );
cout << endl;
system("pause");
;
}
输出结果:
参数绑定
Exercise 10.22:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <functional>
using namespace std;
using namespace std::placeholders;
bool isLesserThanOrEqualTo6(const string &s, string::size_type sz)
{
return s.size() <= sz;
}
int main()
{
vector<string> authors{ "Mooophy", "pezy", "Queequeg90", "shbling", "evan617" };
cout << count_if(authors.cbegin(), authors.cend(), bind(isLesserThanOrEqualTo6, _1, )) << endl;
system("pause");
;
}
Exercise 10.24:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <functional>
using namespace std;
using namespace std::placeholders;
auto check_size(string const& str, size_t sz)
{
return str.size() < sz;
}
int main()
{
vector<, , , , , , , };
");
auto result = find_if(vec.begin(), vec.end(), bind(check_size, str, _1));
if (result != vec.end())
cout << *result << endl;
else
cout << "Not found" << endl;
system("pause");
;
}
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <functional>
using namespace std;
using namespace std::placeholders;
auto check_size(string const& str, size_t sz)
{
return str.size() < sz;
}
int main()
{
vector<int> vec{ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 };
string str("123456");
auto result = find_if(vec.begin(), vec.end(), bind(check_size, str, _1));
if (result != vec.end())
cout << *result << endl;
else
cout << "Not found" << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <functional>
using namespace std;
using namespace std::placeholders;
auto check_size(string const& str, size_t sz)
{
return str.size() < sz;
}
int main()
{
vector<int> vec{ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 };
string str("123456");
auto result = find_if(vec.begin(), vec.end(), bind(check_size, str, _1));
if (result != vec.end())
cout << *result << endl;
else
cout << "Not found" << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
【C++ Primer | 07】泛型算法的更多相关文章
- c++ primer 11 泛型算法
使用泛型算法必须包含头文件#inlucde <algorithm> 标准库还定义一组泛化的算术算法,其命名习惯与泛型算法相同,包含头文件#include <numeric> f ...
- C++ Primer : 第十章 : 泛型算法 之 只读、写和排序算法
大多数算法都定义在<algorithm>头文件里,而标准库还在头文件<numeric>里定义了一组数值泛型算法,比如accumulate. ● find算法,算法接受一对迭代 ...
- C++ Primer 5th 第10章 泛型算法
练习10.1:头文件algorithm中定义了一个名为count的函数,它类似find,接受一对迭代器和一个值作为参数.count返回给定值在序列中出现的次数.编写程序,读取int序列存入vector ...
- C++ Primer 读书笔记:第11章 泛型算法
第11章 泛型算法 1.概述 泛型算法依赖于迭代器,而不是依赖容器,需要指定作用的区间,即[开始,结束),表示的区间,如上所示 此外还需要元素是可比的,如果元素本身是不可比的,那么可以自己定义比较函数 ...
- 【足迹C++primer】30、概要(泛型算法)
概要(泛型算法) 大多数算法的头文件中定义algorithm在. 标准库也是第一个文件numeric它定义了一套通用算法. #include<iostream> #include<n ...
- 【C++ Primer | 07】常用算法
第一部分 常用泛型算法: find(beg, end, val); equal(beg1, end1, beg2); fill(beg, end, val); fill_n(beg, cnt, val ...
- [C++ Primer] : 第10章: 泛型算法
概述 泛型算法: 称它们为"算法", 是因为它们实现了一些经典算法的公共接口, 如搜索和排序; 称它们是"泛型的", 是因为它们可以用于不同类型的元素和多种容器 ...
- C++ Primer 学习笔记_45_STL实践与分析(19)--泛型算法的结构
STL实践与分析 --泛型算法的结构 引言: 正如全部的容器都建立在一致的设计模式上一样,算法也具有共同的设计基础. 算法最主要的性质是须要使用的迭代器种类.全部算法都指定了它的每一个迭代器形參可使用 ...
- C++ Primer笔记6_STL之泛型算法
1.泛型算法: 大多数算法定义在头文件algorithm中.标准库还在头文件numeric中定义了一组数值泛型算法 仅仅读算法: 举例: find函数用于找出容器中一个特定的值,有三个參数 int v ...
- C++ 泛型算法
<C++ Primer 4th>读书笔记 标准容器(the standard container)定义了很少的操作.标准库并没有为每种容器类型都定义实现这些操作的成员函数,而是定义了一组泛 ...
随机推荐
- python中// 和/有什么区别
python中// 和/有什么区别 通常C/C++中,"/ " 算术运算符的计算结果是根据参与运算的两边的数据决定的,比如: 6 / 3 = 2 ; 6,3都是整数,那么结果也就是 ...
- CGI,FastCGI,PHP-CGI与PHP-FPM区别详解【转】
CGI CGI全称是“公共网关接口”(Common Gateway Interface),HTTP服务器与你的或其它机器上的程序进行“交谈”的一种工具,其程序须运行在网络服务器上. CGI可以用任何一 ...
- 学习awk命令的使用
作者:邓聪聪 awk是行处理器: 相比较屏幕处理的优点,在处理庞大文件时不会出现内存溢出或是处理缓慢的问题,通常用来格式化文本信息 awk处理过程: 依次对每一行进行处理,然后输出 awk命令形式: ...
- 请求Jenkins链接返回403
使用python请求Jenkins链接,返回403 1.使用正确的账号密码(Jenkins -> 系统设置 -> 全局安全设置),该账户拥有访问该Jenkins链接的权限 2.代码中的账号 ...
- svn服务器的搭建备份和还原和svnmanager的使用
svn服务器的搭建备份和还原和svnmanager的使用 一.svn服务端软件的安装和配置 1.安装svn版本库软件 # yum install -y subversion 2.建立svn版本库数据存 ...
- Gitbook
2017年9月13日 17:12:20 星期三 gitbook 可以将markdown格式的文件编译成html格式 放在当前目录里的_book目录里(需要手动创建, 也可以指定编译后的html文件放到 ...
- 前端 ----关于DOM的操作的相关实例
关于DOM操作的相关案例 1.模态框案例 需求: 打开网页时有一个普通的按钮,点击当前按钮显示一个背景图,中心并弹出一个弹出框,点击X的时候会关闭当前的模态框 代码如下: <!DOCTYPE ...
- 解决:org.xml.sax.SAXParseException: 元素类型 "head" 必须由匹配的结束标记 "</head>问题
事件背景: 今天就碰到了这样的问题, org.xml.sax.SAXParseException: 元素类型 "head" 必须由匹配的结束标记 "</head&g ...
- mysql installer gentask怎么关闭
1 前言 安装mysql community版本的,可能经常会看到mysql installer gentask console框出现,有时候甚烦,我们并不需要它经常检测更新. 2 解决方案 开始/附 ...
- JS如何截取一段字符中,某一个字符的前面和后面的字符
比如这里的1992631934@qq.com如何获取到@前面的1992631934和@后面的qq.com js代码如下: var mail="1992631934@qq.com" ...
