[BZOJ1576] [BZOJ3694] [USACO2009Jan] 安全路径(最短路径+树链剖分)
[BZOJ1576] [BZOJ3694] [USACO2009Jan] 安全路径(最短路径+树链剖分)
题面
BZOJ1576和BZOJ3694几乎一模一样,只是BZOJ3694直接给出了最短路树
给出一个n个点m条边的无向图,n个点的编号从1~n,定义源点为1。定义最短路树如下:从源点1经过边集T到任意一点i有且仅有一条路径,且这条路径是整个图1到i的最短路径,边集T构成最短路树。 给出最短路树,求对于除了源点1外的每个点i,求最短路,要求不经过给出的最短路树上的1到i的路径的最后一条边。
分析
求最短路树的过程略。
删掉了树上一个点i到父亲的边(即1到i路径上最后一条边)后,我们必须经过非树边才能到达i。贪心考虑,只经过一条非树边显然是最优的。
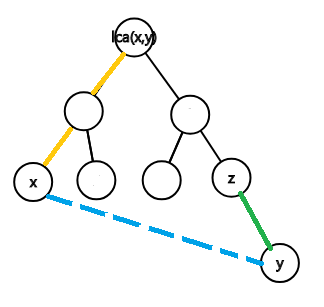
对于一条非树边(x,y) [图中蓝色虚线],它在树上对应一条路径(x,y).对于这条路径上的点z,在z往它父亲的边被删除后,我们可以走这样的路径1->x->y->z。1->x的距离显然为\(dist(x)\),x->y的距离为\(len(x,y)\),y->z的距离[绿线]是\(dist[y]-dist[z]\).因此到z的路径长度就是\(dist[x]+dist[y]+len(x,y)-dist[z]\)
注意到当z=lca(x,y)时,是不能从1->x->y->z的,因为z到父亲的边被删除后无法到达x.
那么方法就很明确了。对于每条边,我们用\(dist[x]+dist[y]+len(x,y)\)去更新路径(x,y)(不包含lca)上的点,每个点\(z\)求出\(min(dist[x]+dist[y]+len(x,y))\)。最后输出\(min(dist[x]+dist[y]+len(x,y))-dist[z]\)即可。路径修改,单点查询,可以用树链剖分解决。时间复杂度\(O(n \log^2 n)\)
代码
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#include<vector>
#define maxn 4000
#define maxm 100000
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
int n,m;
struct edge{
int from;
int to;
int next;
int len;
int type;
}E[maxm*2+5];
int head[maxn+5];
int esz=1;
void add_edge(int u,int v,int w,int t){
esz++;
E[esz].from=u;
E[esz].to=v;
E[esz].next=head[u];
E[esz].len=w;
E[esz].type=t;
head[u]=esz;
}
struct node{
int id;
ll dist;
node(){
}
node(int _id,ll _dist){
id=_id;
dist=_dist;
}
friend bool operator < (node p,node q){
return p.dist>q.dist;
}
};
bool vis[maxn+5];
ll dist[maxn+5];
void dijkstra(int s){
priority_queue<node>q;
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
memset(dist,0x3f,sizeof(dist));
dist[s]=0;
q.push(node(s,0));
while(!q.empty()){
int x=q.top().id;
q.pop();
if(vis[x]) continue;
vis[x]=1;
for(int i=head[x];i;i=E[i].next){
int y=E[i].to;
if(dist[y]>dist[x]+E[i].len){
dist[y]=dist[x]+E[i].len;
if(!vis[y]) q.push(node(y,dist[y]));
}
}
}
}
vector<int>T[maxn+5];
int deep[maxn+5];
int sz[maxn+5];
int fa[maxn+5];
int son[maxn+5];
int top[maxn+5];
int dfn[maxn+5];
int tim;
void dfs1(int x,int f){
sz[x]=1;
fa[x]=f;
deep[x]=deep[f]+1;
for(int i=0;i<T[x].size();i++){
int y=T[x][i];
if(y!=f){
dfs1(y,x);
sz[x]+=sz[y];
if(sz[y]>sz[son[x]]) son[x]=y;
}
}
}
void dfs2(int x,int t){
top[x]=t;
dfn[x]=++tim;
if(son[x]) dfs2(son[x],t);
for(int i=0;i<T[x].size();i++){
int y=T[x][i];
if(y!=fa[x]&&y!=son[x]){
dfs2(y,y);
}
}
}
struct segment_tree{
struct node{
int l;
int r;
ll val;
ll mark;
}tree[maxn*4+5];
void push_up(int pos){
tree[pos].val=max(tree[pos<<1].val,tree[pos<<1|1].val);
}
void build(int l,int r,int pos){
tree[pos].l=l;
tree[pos].r=r;
tree[pos].mark=INF;
tree[pos].val=INF;
if(l==r) return;
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
build(l,mid,pos<<1);
build(mid+1,r,pos<<1|1);
push_up(pos);
}
void push_down(int pos){
if(tree[pos].mark!=INF){
tree[pos<<1].mark=min(tree[pos<<1].mark,tree[pos].mark);
tree[pos<<1|1].mark=min(tree[pos<<1|1].mark,tree[pos].mark);
tree[pos<<1].val=min(tree[pos<<1].val,tree[pos].mark);
tree[pos<<1|1].val=min(tree[pos<<1|1].val,tree[pos].mark);
tree[pos].mark=INF;
}
}
void update(int L,int R,ll uval,int pos){
if(L<=tree[pos].l&&R>=tree[pos].r){
tree[pos].mark=min(tree[pos].mark,uval);
tree[pos].val=min(tree[pos].val,uval);
return;
}
push_down(pos);
int mid=(tree[pos].l+tree[pos].r)>>1;
if(L<=mid) update(L,R,uval,pos<<1);
if(R>mid) update(L,R,uval,pos<<1|1);
push_up(pos);
}
ll query(int L,int R,int pos){
if(L<=tree[pos].l&&R>=tree[pos].r){
return tree[pos].val;
}
push_down(pos);
int mid=(tree[pos].l+tree[pos].r)>>1;
ll ans=INF;
if(L<=mid) ans=min(ans,query(L,R,pos<<1));
if(R>mid) ans=min(ans,query(L,R,pos<<1|1));
return ans;
}
}S;
int lca(int x,int y){
while(top[x]!=top[y]){
if(deep[top[x]]<deep[top[y]]) swap(x,y);
x=fa[top[x]];
}
if(deep[x]>deep[y]) swap(x,y);
return x;
}
void update(int x,int y,ll val){
// printf("update %d->%d val=%d\n",x,y,val);
int tx=top[x],ty=top[y];
while(tx!=ty){
if(deep[tx]<deep[ty]){
swap(tx,ty);
swap(x,y);
}
S.update(dfn[tx],dfn[x],val,1);
x=fa[tx];
tx=top[x];
}
if(deep[x]>deep[y]) swap(x,y);
S.update(dfn[son[x]],dfn[y],val,1);//注意是son[x]而不是x,因为不包含lca
}
int main(){
int u,v,w,t;
scanf("%d %d",&n,&m);
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){
scanf("%d %d %d %d",&u,&v,&w,&t);
add_edge(u,v,w,t);
add_edge(v,u,w,t);
if(t==1){
T[u].push_back(v);
T[v].push_back(u);
}
}
dijkstra(1);
dfs1(1,0);
dfs2(1,0);
S.build(1,n,1);
for(int i=2;i<=esz;i+=2){
if(E[i].type==0){
int x=E[i].from;
int y=E[i].to;
update(x,y,dist[x]+dist[y]+E[i].len);
}
}
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){
ll ans=S.query(dfn[i],dfn[i],1);
if(ans==INF) printf("-1 ");
else printf("%lld ",ans-dist[i]);
}
}
[BZOJ1576] [BZOJ3694] [USACO2009Jan] 安全路径(最短路径+树链剖分)的更多相关文章
- 牛客练习赛26 E-树上路径 (树链剖分+线段树)
链接:https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/180/E 来源:牛客网 树上路径 时间限制:C/C++ 2秒,其他语言4秒 空间限制:C/C++ 262144K,其他语 ...
- BZOJ1576: [Usaco2009 Jan]安全路经Travel(树链剖分)
Description Input * 第一行: 两个空格分开的数, N和M * 第2..M+1行: 三个空格分开的数a_i, b_i,和t_i Output * 第1..N-1行: 第i行包含一个数 ...
- 树链剖分 - Luogu 3384【模板】树链剖分
[模板]树链剖分 题目描述 已知一棵包含N个结点的树(连通且无环),每个节点上包含一个数值,需要支持以下操作: 操作1: 格式: 1 x y z 表示将树从x到y结点最短路径上所有节点的值都加上z 操 ...
- SPOJ Query on a tree 树链剖分 水题
You are given a tree (an acyclic undirected connected graph) with N nodes, and edges numbered 1, 2, ...
- 树链剖分学习&BZOJ1036
题目传送门 树链剖分,计算机术语,指一种对树进行划分的算法,它先通过轻重边剖分将树分为多条链,保证每个点属于且只属于一条链,然后再通过数据结构(树状数组.SBT.SPLAY.线段树等)来维护每一条链. ...
- 【bzoj2238】Mst(树链剖分+线段树)
2238: Mst Time Limit: 20 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MBSubmit: 465 Solved: 131[Submit][Status][Discuss] ...
- bzoj3694: 最短路(树链剖分/并查集)
bzoj1576的帮我们跑好最短路版本23333(双倍经验!嘿嘿嘿 这题可以用树链剖分或并查集写.树链剖分非常显然,并查集的写法比较妙,涨了个姿势,原来并查集的路径压缩还能这么用... 首先对于不在最 ...
- 洛谷 P3384 【模板】树链剖分-树链剖分(点权)(路径节点更新、路径求和、子树节点更新、子树求和)模板-备注结合一下以前写的题目,懒得写很详细的注释
P3384 [模板]树链剖分 题目描述 如题,已知一棵包含N个结点的树(连通且无环),每个节点上包含一个数值,需要支持以下操作: 操作1: 格式: 1 x y z 表示将树从x到y结点最短路径上所有节 ...
- [bzoj3694]最短路_树链剖分_线段树
最短路 bzoj-3694 题目大意:给你一个n个点m条边的无向图,源点为1,并且以点1为根给出最短路树.求对于2到n的每个点i,求最短路,要求不经过给出的最短路树上的1到i的路径上的最后一条边. 注 ...
随机推荐
- Java的当中的泛型
Java当中的泛型 01 import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; public class Demo{ public static voi ...
- jQuery文档操作之克隆操作
语法: $(selector).clone(); 解释:克隆匹配的DOM元素 $("button").click(function(event) { //1.clone():克隆匹 ...
- CodeForces - 369E Valera and Queries(树状数组)
CodeForces - 369E Valera and Queries 题目大意:给出n个线段(线段的左端点和右端点坐标)和m个查询,每个查询有cnt个点,要求给出有多少条线段包含至少其中一个点. ...
- MySQL_8.0与5.7区别之账户与安全
一.创建用户和用户授权 MySQL5.7创建用户和用户授权命令可以同时执行 grant all privileges on *.* to 'Gary'@'%' identified by 'Gary@ ...
- JavaWeb-SpringBoot(抖音)_一、抖音项目制作
JavaWeb-SpringBoot(抖音)_一.抖音项目制作 传送门 JavaWeb-SpringBoot(抖音)_二.服务器间通讯 传送门 JavaWeb-SpringBoot(抖音)_三.抖音项 ...
- Git本地安装
1 Git简介 Git是一个开源的分布式版本控制系统,可以有效.高速的处理从很小到非常大的项目版本管理. Git是 Linus Torvalds 为了帮助管理 Linux 内核开发而开发的一个开放源码 ...
- 【CSS】三栏/两栏宽高自适应布局大全
页面布局 注意方案多样性.各自原理.各自优缺点.如果不定高呢.兼容性如何 三栏自适应布局,左右两侧300px,中间宽度自适应 (1) 给出5种方案 方案一: float (左右浮动,中间不用给宽,设置 ...
- IDEA找回Run Dashboard
特别提示:本人博客部分有参考网络其他博客,但均是本人亲手编写过并验证通过.如发现博客有错误,请及时提出以免误导其他人,谢谢!欢迎转载,但记得标明文章出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/ ...
- Servlet——理解会话Session
1.什么是会话(Session) 超文本传输协议(HTTP)被设计成一种无状态的协议. 所谓无状态协议就是指在服务器端的请求彼此相互之间是不认识彼此的,哪怕是来自同一个客户端的请求,相互之间也是不认识 ...
- linux系统空间不足,lsof看到异常的delete状态的文件。
#20191101更新---这篇文章适用于产生僵尸文件的进程是可kill的状态参考,就是这个进程死亡不影响业务,那么另外一种情况,也是我现在管理的项目中生产环境中出现过的情况,产生僵尸文件的进程是we ...
