IPC之PIPE
管道是一种只允许用在有亲属关系的进程间通信的方式,由函数pipe创建一个管道,read,write进行读写操作。
#include <unistd.h>
int pipe(int pipefd[]);
参数pipefd[2]数组返回打开的读写描述符,pipefd[0]为读,pipefd[1]为写。
第一个问题:文件描述符怎么会出现一个只能读,一个只能写呢?猜想是对一个文件打开了2次,一个以只读打开,一个以只写打开。使用fcntl来验证下:
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h> int fcntl(int fd, int cmd, ... /* arg */ );
F_GETFL (void)
Get the file access mode and the file status flags; arg is ignored.
cmd为F_GETFL时,最后一个参数arg被忽略。测试代码:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h> int main(void)
{
int flags;
int fd[]; if (pipe(fd) < )
{
perror("pipe error");
} flags = fcntl(fd[], F_GETFL,);
if ( flags < )
{
perror("fcntl");
close(fd[]);
close(fd[]);
}
switch (flags & O_ACCMODE)
{
case O_RDONLY:
printf("read only\n");
break; case O_WRONLY:
printf("write only\n");
break; case O_RDWR:
printf("read write\n");
break; default:
printf("unknown access mode\n");
} flags = fcntl(fd[], F_GETFL,);
if ( flags < )
{
perror("fcntl");
close(fd[]);
close(fd[]);
}
switch (flags & O_ACCMODE)
{
case O_RDONLY:
printf("read only\n");
break; case O_WRONLY:
printf("write only\n");
break; case O_RDWR:
printf("read write\n");
break; default:
printf("unknown access mode\n");
}
close(fd[]);
close(fd[]);
exit();
}
运行结果:
read only
write only
与猜想相符。
数据的流向:

从图中可以看出,进程可以以pipefd[1]写完,然后以pipefd[0]读,自己写自己读,这条数据流是通的。 验证:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h> #define MAXLINE 4096
int main(void)
{
int flags;
int fd[], n;
char buf[MAXLINE];
if (pipe(fd) < )
{
perror("pipe error");
} n = write(fd[], "hello world\n", MAXLINE);
if ( n < )
{
perror("write");
goto end;
}
n = read(fd[],buf, n);
if ( n < )
{
perror("read");
goto end;
}
printf("read:%s\n",buf); end:
close(fd[]);
close(fd[]);
exit();
}
输出:
read:hello world
既然是进程间通信,那么管道在同一个进程中读写基本是没什么意义的,管道常用的方式是,先创建一个管道,然后fork,父子进程就共享了这个管道了。数据流向如图:

这样,管道的写端有2个进程操作,读端有2个进程操作。但是这样一来就出现了一个问题,假设父进程读,那么这个数据是它自己写进去的呢?还是子进程写进去的?无法区分。通常一个进程关闭它的读,另一个进程关闭它的写,这样,数据流向就只有一个方向了,数据来自谁就显而易见了。如图:
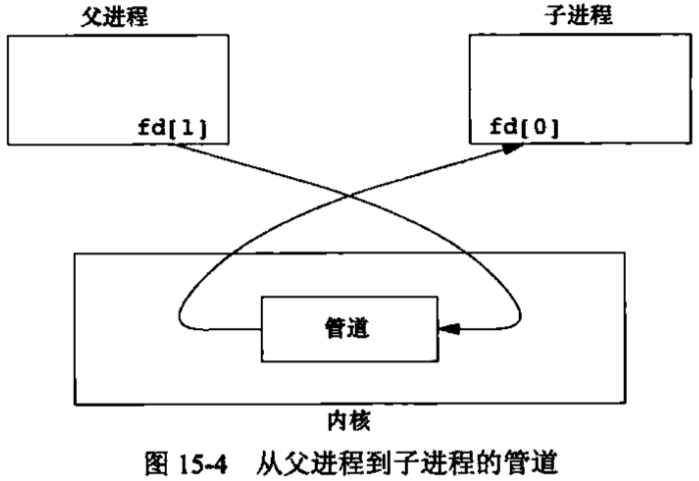
测试代码:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h> #define MAXLINE 4096 int main(void)
{
int n;
int fd[];
pid_t pid;
char line[MAXLINE]; if (pipe(fd) < )
perror("pipe error");
if ((pid = fork()) < )
{
perror("fork error");
}
else if (pid > ) /* parent */
{
close(fd[]);
write(fd[], "hello world\n", );
}
else /* child */
{
close(fd[]);
n = read(fd[], line, MAXLINE);
write(STDOUT_FILENO, line, n);
}
exit();
}
结果:
hello world
读一个空的管道或者写一个满的管道都将导致阻塞,不过可以通过fcntl的F_SETFL设置为O_NONBLOCK,从而不阻塞。
当管道一端被关闭后,有下列2条规则:
1.当读一个写端所有文件描述符引用都已被关闭的管道时,在所有数据被读完后,read将返回0。表示无数据可读。
2.当写一个读端所有文件描述符引用都已被关闭的管道时,将产生SIGPIPE信号,write返回-1。
混淆的东西,管道的容量和管道的缓冲区大小。
管道的容量:指管道满时装的字节数,自2.6.11内核后,容量为64k。管道满了就会导致写操作产生阻塞。
管道缓冲区大小:由PIPE_BUF指定,指的是保证管道写操作为原子操作的最大值,如果一次写入的内容超过这个值,那么这次的写操作就不是原子的。什么意思呢?就是指,可能存在多个进程写同一个管道,如果一次写入的字节数大于缓冲区大小,则可能会出现A进程写入的内容中插入了B进程写入的内容。
下面是出现这种情况的代码:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h> #define MAXLINE 4096+100 int main(void)
{
int n;
int fd[];
pid_t pid;
char line[MAXLINE]; if (pipe(fd) < )
{
perror("pipe error");
} if ((pid = fork()) < )
{
perror("fork error");
}
else if (pid > ) /* parent */
{
close(fd[]);
while ( )
{
n = read(fd[], line, MAXLINE);
write(STDOUT_FILENO, line, n);
write(STDOUT_FILENO, "\n\n\n", );
}
}
else /* child */
{
if ((pid = fork()) < )
{
perror("fork error");
}
else if (pid > )
{
close(fd[]); while ()
{
memset(line, 'a',MAXLINE);
write(fd[], line, MAXLINE);
}
}
else
{
close(fd[]); while ( )
{
memset(line, 'b',MAXLINE);
write(fd[], line, MAXLINE);
}
}
} exit();
}
IPC之PIPE的更多相关文章
- Linux IPC BSD Pipe
mkfifo() //创建有名管道(FIFO special file),创建完了就像普通文件一样open(),再读写,成功返回0,失败返回-1设errno.VS$man 3 mkfifo #incl ...
- Unix IPC之pipe
pipe创建函数: #include <unistd.h> /* Create a one-way communication channel (pipe). If successful, ...
- linux IPC的PIPE
一.PIPE(无名管道) 函数原型: #include <unistd.h> ]); 通常,进程会先调用pipe,接着调用fork,从而创建从父进程到子进程的IPC通道. 父进程和子进程之 ...
- CVE-2017-7494 Linux Samba named pipe file Open Vul Lead to DLL Execution
catalogue . 漏洞复现 . 漏洞代码原理分析 . 漏洞利用前提 . 临时缓解 && 修复手段 1. 漏洞复现 . SMB登录上去 . 枚举共享目录,得到共享目录/文件列表,匿 ...
- 【APUE】Chapter16 Network IPC: Sockets & makefile写法学习
16.1 Introduction Chapter15讲的是同一个machine之间不同进程的通信,这一章内容是不同machine之间通过network通信,切入点是socket. 16.2 Sock ...
- 高级IPC DBus
What is IPC IPC [Inter-Process Communication] 进程间通信,指至少两个进程或线程间传送数据或信号的一些技术或方法.在Linux/Unix中,提供了许多IPC ...
- (转)解决 ORA-12514: TNS: 监听程序当前无法识别连接描述符中请求的服务
下面操作默认在安装Oralce数据库的服务器上运行. 1)确保Oracle 基本服务都已启动 OracleDBConsoleorcl OracleOraDb11g_home1TNSListener O ...
- python高级之多进程
python高级之多进程 本节内容 多进程概念 Process类 进程间通讯 进程同步 进程池 1.多进程概念 multiprocessing is a package that supports s ...
- oracle 监听启动、停止、查看命令
1.su oracle 然后启动监听器 1.lsnrctl start 会看到启动成功的界面; 1.lsnrctl stop 停止监听器命令. 1.lsnrctl status 查看监听器命令. ...
随机推荐
- DIV嵌套垂直居中
第一记住一点:父级相对定位,子级绝对定位 下面演示CSS样式: .父级DIV{ margin:0px auto; position:relative; border:2px solid #ff0000 ...
- SVG操作插件:SVG.JS 个人提取部分实用中文文档
先贴出github地址:https://github.com/svgdotjs/svg.js(也就是原文档的说明和文件的下载地址) 创建SVG文档 var draw = SVG('drawing'). ...
- csharp: MVC Controls
http://mvccontrolstoolkit.codeplex.com/ MVC Controls Toolkit http://mvcjquerycontrols.codeplex.com/ ...
- 由简入繁实现Jquery树状结构
在项目中,我们经常会需要一些树状结构的样式来显示层级结构等,比如下图的样式,之前在学.net的时候可以直接拖个服务端控件过来直接使用非常方便.但是利用Jquery的一些插件,也是可以实现这些效果的,比 ...
- 常用SQL语句优化技巧
除了建立索引之外,保持良好的SQL语句编写习惯将会降低SQL性能问题发生. ①通过变量的方式来设置参数 好:stringsql = "select * from people p where ...
- 细说Mysql四种安装方法及自动化部署
一.简介 数据库(Database)是按照数据结构来组织.存储和管理数据的仓库, 每个数据库都有一个或多个不同的API用于创建,访问,管理,搜索和复制所保存的数据. 我们也可以将数据存储在文件中,但是 ...
- VM虚拟机忘记密码
关掉虚拟机. VM->Settings,选中Hard Disk,在右边出现了Utilities的一个下拉栏,OK,点击它选择Map,这时弹出一个"Map Virtual Disk&qu ...
- mvc项目架构分享系列之架构搭建之Repository和Service
项目架构搭建之Repository和Service的搭建 Contents 系列一[架构概览] 0.项目简介 1.项目解决方案分层方案 2.所用到的技术 3.项目引用关系 系列二[架构搭建初步] 4. ...
- andriod RadioButton
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <LinearLayout android:orientatio ...
- dict和set
#dict和set #dict #Python内置了字典:dict的支持,dict全称dictionary,在其他语言中也称为map #使用键-值(key-value)存储,具有极快的查找速度. #字 ...
