Notes : <Hands-on ML with Sklearn & TF> Chapter 1
<Hands-on ML with Sklearn & TF> Chapter 1
- what is ml
- from experience E with respect to some task T and some performance measure P, if its performance on T, as measured by P, improves with experience E.
- what problems to solve
- exist solution but a lot of hand-tuning/rules
- no good solutions using a traditional approach
- fluctuating environment
- get insight about conplex problem and large data
- type
- whether or not trained with human supervision(supervised, unsupervised, semisupervised, reinforcement)
- whether or not learn incrementally on the fly(online, batch)
- whether or not work by simply comparing new data point vs know data point,or instance detect pattern in training data and build a prediction model(instace-based, model-based)
- (un)supervision learning
- supervision : include the desired solution called labels
- classification,K-Nearest Neighbors, Linear Regression, Logistic Regression, SVM, Decision Trees, Random Forests, Neural network
- unsupervision : without labels
- Clustering : k-means, HCA, ecpectation maximization
- Viualization and dimensionality reducation : PCA, kernal PCA, LLE, t-SNE
- Association rule learning : Apriori, Eclat
- semisupervision
- unsupervision --> supervision
- reinforcement : an agent in context
- observe the environment
- select and perform action
- get rewards in return
- supervision : include the desired solution called labels
- batch/online learning
- batch : offline, to known new data need to train a new version from scratch one the full dataset
- online : incremental learning : challenge is bad data
- instance-based/model-based
- instance-based : the system learns the examples by heart, then the generalizes to the new cases using a similarity measure
- model-based : studied the data; select a model; train it on the training data; applied the model to make predictions on new cases
- Challenge
- insufficient quantity of training data
- nonrepresentative training data
- poor-quality data
- irrelevant features : feature selection; feature extraction; creating new feature by gathering new data
- overfitting : regularization -> hyperparameter
- underfitting : powerful model; better feature; reduce construct
- Testing and Validating
- 80% of data for training 20% for testing
- validating : best model and hyperparameter for training set unliking perform as well on new data
- train multiple models with various hyperparameters using training data
- to get generatlization error , select the model and hyperparamaters that perform best on the validation set
- cross-validating : the training set is split into complementary subsets, ans each model is trained against a different conbination of thse subsets and validated against the remain parts.
Example 1-1:
import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import sklearn.linear_model #load the data
oecd_bli = pd.read_csv("datasets/lifesat/oecd_bli_2015.csv",thousands=',')
gdp_per_capita = pd.read_csv("datasets/lifesat/gdp_per_capita.csv",thousands=',',delimiter='\t',encoding='latin1',na_values='n/a') #prepare the data
def prepare_country_stats(oecd_bli, gdp_per_capita):
#get the pandas dataframe of GDP per capita and Life satisfaction
oecd_bli = oecd_bli[oecd_bli["INEQUALITY"]=="TOT"]
oecd_bli = oecd_bli.pivot(index="Country", columns="Indicator", values="Value")
gdp_per_capita.rename(columns={"": "GDP per capita"}, inplace=True)
gdp_per_capita.set_index("Country", inplace=True)
full_country_stats = pd.merge(left=oecd_bli, right=gdp_per_capita, left_index=True, right_index=True)
return full_country_stats[["GDP per capita", 'Life satisfaction']] country_stats = prepare_country_stats(oecd_bli, gdp_per_capita)
#regularization remove_indices = [0, 1, 6, 8, 33, 34, 35]
country_stats.to_csv('country_stats.csv',encoding='utf-8')
X = np.c_[country_stats["GDP per capita"]]
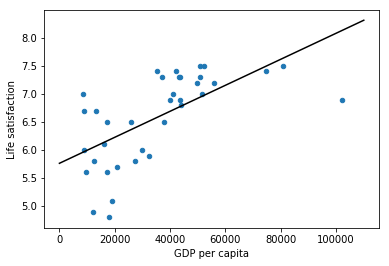
Y = np.c_[country_stats["Life satisfaction"]] #Visualize the data
country_stats.plot(kind='scatter',x='GDP per capita',y='Life satisfaction') #Select a linear model
lin_reg_model = sklearn.linear_model.LinearRegression() #Train the model
lin_reg_model.fit(X, Y) #plot Regression model
t0, t1 = lin_reg_model.intercept_[0], lin_reg_model.coef_[0][0]
X = np.linspace(0, 110000, 1000)
plt.plot(X, t0 + t1 * X, "k")
plt.show() #Make a prediction for Cyprus
X_new=[[22587]]
print(lin_reg_model.predict(X_new))
课后练习挺好的
Notes : <Hands-on ML with Sklearn & TF> Chapter 1的更多相关文章
- Notes : <Hands-on ML with Sklearn & TF> Chapter 5
.caret, .dropup > .btn > .caret { border-top-color: #000 !important; } .label { border: 1px so ...
- Notes : <Hands-on ML with Sklearn & TF> Chapter 7
.caret, .dropup > .btn > .caret { border-top-color: #000 !important; } .label { border: 1px so ...
- Notes : <Hands-on ML with Sklearn & TF> Chapter 6
.caret, .dropup > .btn > .caret { border-top-color: #000 !important; } .label { border: 1px so ...
- Notes : <Hands-on ML with Sklearn & TF> Chapter 4
.caret, .dropup > .btn > .caret { border-top-color: #000 !important; } .label { border: 1px so ...
- Notes : <Hands-on ML with Sklearn & TF> Chapter 3
Chapter 3-Classification .caret, .dropup > .btn > .caret { border-top-color: #000 !important; ...
- Book : <Hands-on ML with Sklearn & TF> pdf/epub
非常好的书,最近发现了pdf版本,链接:http://www.finelybook.com/hands-on-machine-learning-with-scikit-learn-and-tensor ...
- H5 Notes:PostMessage Cross-Origin Communication
Javascript中要实现跨域通信,主要有window.name,jsonp,document.domain,cors等方法.不过在H5中有一种新的方法postMessage可以安全实现跨域通信,并 ...
- H5 Notes:Navigator Geolocation
H5的地理位置API可以帮助我们来获取用户的地理位置,经纬度.海拔等,因此我们可以利用该API做天气应用.地图服务等. Geolocation对象是我们获取地理位置用到的对象. 首先判断浏览器是否支持 ...
- notes:spm多重比较校正
SPM做完统计后,statistical table中的FDRc实际上是在该p-uncorrected下,可以令FDR-correcred p<=0.05的最小cluster中的voxel数目: ...
随机推荐
- Android 开发 AlarmManager 定时器
介绍 AlarmManager是Android中常用的一种系统级别的提示服务,在特定的时刻为我们广播一个指定的Intent.简单的说就是我们设定一个时间,然后在该时间到来时,AlarmManager为 ...
- 实战ELK(5) Logstash 入门
Logstash 是一个开源的数据收集引擎,它具有备实时数据传输能力.它可以统一过滤来自不同源的数据,并按照开发者的制定的规范输出到目的地. 一.原理 Logstash 通过管道进行运作,管道有两个必 ...
- python:win下将py文件打包成exe
[环境]windows,正常运行的python文件 1.安装pyinstaller ,cmd下执行以下命令,需看到安装成功界面 pip install pyinstaller 2.cmd中进入要打包的 ...
- 学习:D3
http://www.ourd3js.com/wordpress/?p=196 http://www.ourd3js.com/demo/rm/R-9.2/force.html 力导向图(那个可以拖拽的 ...
- Elasticsearch 整合spring(不是sprig boot)
公司做统计任务,有使用Es做聚合操作,使用的是自己封装的版本,这边整合下原生spring,做下学习记录,随便看一下,发现差不多都是spring boot的案例...我该怎么办,...发现整合的过程其实 ...
- 自动滚动标签marquee
<marquee>标签,它是成对出现的标签,首标签<marquee>和尾标签</marquee>之间的内容就是滚动内容.<marquee>标签的属性主要 ...
- 443. String Compression
原题: 443. String Compression 解题: 看到题目就想到用map计数,然后将计数的位数计算处理,这里的解法并不满足题目的额外O(1)的要求,并且只是返回了结果array的长度,并 ...
- 关于HashMap和HashTable.md
目录 先来些简单的问题 你用过HashMap吗?" "什么是HashMap?你为什么用到它?" "你知道HashMap的工作原理吗?" "你 ...
- ansible自动化运维详细教程及playbook详解
前言 当下有许多的运维自动化工具( 配置管理 ),例如:Ansible.SaltStack.Puppet.Fabric 等. Ansible 一种集成 IT 系统的配置管理.应用部署.执行特定任务的开 ...
- tesseract编译错误:fatal error: allheaders.h: No such file or directory
错误描述: globaloc.cpp::: fatal error: allheaders.h: No such file or directory #include "allheaders ...
