tf.gather_nd()
1.tf.gather
tf.gather(params, indices, validate_indices=None, name=None, axis=0)
indices在axis这个轴上对params进行索引,拼接成一个新的张量。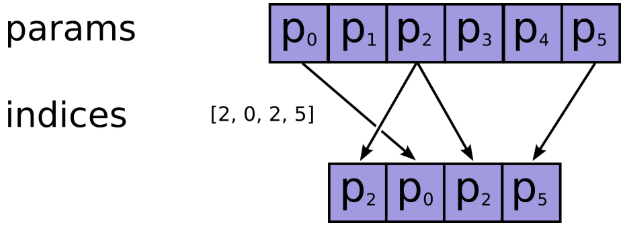
- params:需要被索引的张量
- indices:必须为整数类型,如int32,int64等,注意检查不要越界了,因为如果越界了,如果使用的
CPU,则会报错,如果在GPU上进行操作的,那么相应的输出值将会被置为0,而不会报错,因此认真检查是否越界。 - name:返回张量名称
import tensorflow as tf
temp4=tf.reshape(tf.range(0,20)+tf.constant(1,shape=[20]),[2,2,5])
temp4:
[[[ 1 2 3 4 5]
[ 6 7 8 9 10]] [[11 12 13 14 15]
[16 17 18 19 20]]]
temp5=tf.gather(temp4,[0,1],axis=0) #indices是向量
temp5:
[[[ 1 2 3 4 5]
[ 6 7 8 9 10]] [[11 12 13 14 15]
[16 17 18 19 20]]]
temp7=tf.gather(temp4,[1,4],axis=2)
# (2,2,5)[:2]+(2,)+(2,2,5)[3:]=(2,2,2)
temp7:
[[[ 2 5]
[ 7 10]] [[12 15]
[17 20]]]
temp6=tf.gather(temp4,1,axis=1) #indices是数值
# (2,2,5)[:1]+()+(2,2,5)[2:]=(2,5)
temp:
[[ 6 7 8 9 10]
[16 17 18 19 20]]
temp8=tf.gather(temp4,[[0,1],[3,4]],axis=2) #indices是多维的
# (2,2,5)[:2]+(2,2)+(2,2,5)[3:]=(2,2,2,2)
temp8:
[[[[ 1 2]
[ 4 5]] [[ 6 7]
[ 9 10]]] [[[11 12]
[14 15]] [[16 17]
[19 20]]]]
bert源码:
flat_input_ids = tf.reshape(input_ids, [-1]) #【batch_size*seq_length*input_num】
if use_one_hot_embeddings:
one_hot_input_ids = tf.one_hot(flat_input_ids, depth=vocab_size)
output = tf.matmul(one_hot_input_ids, embedding_table)
else:
output = tf.gather(embedding_table, flat_input_ids)
2.tf.gather_nd
tf.gather_nd(
params,
indices,
name=None,
batch_dims=0)
功能:类似于tf.gather,不过后者只能在一个维度上进行索引,而前者可以在多个维度上进行索引,
参数:
- params:待索引输入张量
- indices:索引,int32,int64,indices将切片定义为params的前N个维度,其中N = indices.shape [-1]
- 通常要求indices.shape[-1] <= params.rank(可以用np.ndim(params)查看)
- 如果等号成立是在索引具体元素
- 如果等号不成立是在沿params的indices.shape[-1]轴进行切片
- name=None:操作的名称(可选)
返回维度: indices.shape[:-1] + params.shape[indices.shape[-1]:],前面的indices.shape[:-1]代表索引后的指定形状
举例:
indices = [[0, 0], [1, 1]]
params = [['a', 'b'], ['c', 'd']]
# (2,2)[:-1]+(2,2)[(2,2)[-1]:]=(2,)
output = ['a', 'd']
表示将params对应第一行第一列的'a'和第二行第二列的'd'取出来 indices = [[1], [0]]
params = [['a', 'b'], ['c', 'd']]
# (2,1)[:-1]+(2,2)[(2,1)[-1]:]=(2,)+(2,)=(2,2)
output = [['c', 'd'], ['a', 'b']]
表示将params对应第二行和第一行取出来 '''
功能:T是一个二维tensor,我们想要根据另外一个二维tensor value的最后一维最大元素的下标选出tensor T中
最后一维最大的元素,组成一个新的一维的tensor,那么就可以首先选出最后一维度的下标[1,2,3],
然后将其扩展成[[0,1],[1,2],[2,3]],然后使用这个函数选择即可。
'''
import tensorflow as tf
sess = tf.InteractiveSession()
values = tf.constant([[0, 0, 0, 1],
[0, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 0]])
T = tf.constant([[0,1,2,3],
[4,5,6,7],
[8,9,10,11]]) max_indices = tf.argmax(values, axis=1) # 行
print('max_indices',max_indices.eval()) # [3 1 2]
# If T.get_shape()[0] is None, you can replace it with tf.shape(T)[0].
print(tf.stack((tf.range(T.get_shape()[0],dtype=max_indices.dtype),max_indices),axis=1).eval())
print(tf.range(T.get_shape()[0]).eval())
result = tf.gather_nd(T, tf.stack((tf.range(T.get_shape()[0],
dtype=max_indices.dtype),
max_indices),
axis=1))
print(result.eval())
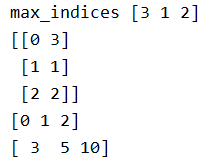
3.tf.batch_gather
作用:支持对张量的批量索引.注意因为是批处理,所以indices要有和params相同的第0个维度。
import tensorflow as tf
tensor_a = tf.Variable([[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]])
tensor_b = tf.Variable([[0],[1],[2]],dtype=tf.int32)
tensor_c = tf.Variable([[0],[0],[0]],dtype=tf.int32)
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
print('gather')
print(sess.run(tf.gather(tensor_a,tensor_b)))
print(sess.run(tf.gather(tensor_a,tensor_c)))
print('gather_nd')
print(sess.run(tf.gather_nd(tensor_a, tensor_b)))
print(sess.run(tf.gather_nd(tensor_a, tensor_c)))
print('batch_gather')
print(sess.run(tf.batch_gather(tensor_a, tensor_b)))
print(sess.run(tf.batch_gather(tensor_a, tensor_c)))

4.tf.where
tf.where(condition, x=None, y=None, name=None)
作用: 返回condition为True的元素坐标(x=y=None)
- condition:布尔型张量,True/False
- x:与y具有相同类型的张量,可以使用条件和y进行广播。
- y:与x具有相同类型的张量,可以在条件和x的条件下进行广播。
- name:操作名称(可选)
返回维度: (num_true, dim_size(condition)),其中dim_size为condition的维度。
(1)tf.where(condition)
- condition是bool型值,True/False
- 返回值,是condition中元素为True对应的索引
import tensorflow as tf
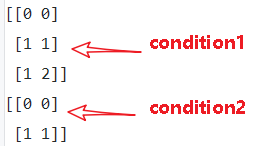
a = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6]]
b = [[1,0,3],[1,5,1]]
condition1 = [[True,False,False],
[False,True,True]]
condition2 = [[True,False,False],
[False,True,False]]
with tf.Session() as sess:
print(sess.run(tf.where(condition1)))
print(sess.run(tf.where(condition2)))
(2)tf.where(condition, x=None, y=None, name=None)
- condition, x, y 相同维度,condition是bool型值,True/False
- 返回值是对应元素,condition中元素为True的元素替换为x中的元素,为False的元素替换为y中对应元素
- x只负责对应替换True的元素,y只负责对应替换False的元素,x,y各有分工
- 由于是替换,返回值的维度,和condition,x , y都是相等的。
import tensorflow as tf
x = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6]]
y = [[7,8,9],[10,11,12]]
condition3 = [[True,False,False],
[False,True,True]]
condition4 = [[True,False,False],
[True,True,False]]
with tf.Session() as sess:
print(sess.run(tf.where(condition3,x,y)))
print(sess.run(tf.where(condition4,x,y)))

5.tf.slice()
tf.slice(inputs, begin, size, name)
作用:用来进行切片操作,实现在python中的a[:,2:3,5:6]类似的操作,从列表、数组、张量等对象中抽取一部分数据
- begin和size是两个多维列表,他们共同决定了要抽取的数据的开始和结束位置
- begin表示从inputs的哪几个维度上的哪个元素开始抽取
- size表示在inputs的各个维度上抽取的元素个数
- 若begin[]或size[]中出现-1,表示抽取对应维度上的所有元素
import tensorflow as tf
t = tf.constant([[[1, 1, 1], [2, 2, 2]],
[[3, 3, 3], [4, 4, 4]],
[[5, 5, 5], [6, 6, 6]]])
tf.slice(t, [1, 0, 0], [1, 1, 3]) # [[[3, 3, 3]]]
tf.slice(t, [1, 0, 0], [1, 2, 3]) # [[[3, 3, 3],
# [4, 4, 4]]]
tf.slice(t, [1, 0, 0], [2, 1, 3]) # [[[3, 3, 3]],
# [[5, 5, 5]]]
bert源码:
# 这里position embedding是可学习的参数,[max_position_embeddings, width]
# 但是通常实际输入序列没有达到max_position_embeddings
# 所以为了提高训练速度,使用tf.slice取出句子长度的embedding
# full_position_embeddings:[max_position_embeddings, width]
position_embeddings = tf.slice(full_position_embeddings, [0, 0],[seq_length, -1])
参考文献:
【1】tf.gather, tf.gather_nd和tf.slice_机器学习杂货铺1号店-CSDN博客
【2】tf.where/tf.gather/tf.gather_nd - 知乎
【3】tenflow 入门 tf.where()用法_ustbbsy的博客-CSDN博客
【4】tf.gather tf.gather_nd 和 tf.batch_gather 使用方法_张冰洋的天空-CSDN博客
tf.gather_nd()的更多相关文章
- tf.gather和tf.gather_nd、tf.cast、tf.greater
https://blog.csdn.net/Cyiano/article/details/76087747
- tf的一些基本用法
1.tf.where https://blog.csdn.net/ustbbsy/article/details/79564828 2.tf.less tf.less(x,y,name=None) ...
- TF常用知识
命名空间及变量共享 # coding=utf-8 import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt; ...
- 解释张量及TF的一些API
张量的定义 张量(Tensor)理论是数学的一个分支学科,在力学中有重要应用.张量这一术语起源于力学,它最初是用来表示弹性介质中各点应力状态的,后来张量理论发展成为力学和物理学的一个有力的数学工具.张 ...
- Mask_RCNN学习记录(matterport版本)
资源链接 Mask R-CNN论文 matterport版本的GitHub 基于Keras和Tensorflow GitHub上还有Facebook的官方实现版本:Detectron maskrcnn ...
- Stanford CS20学习笔记
Lecture Note 2 Tensorboard P3 Data Structures P4 Math Operations P6 Data Types P7 tf native &&am ...
- 第七节,TensorFlow编程基础案例-TensorBoard以及常用函数、共享变量、图操作(下)
这一节主要来介绍TesorFlow的可视化工具TensorBoard,以及TensorFlow基础类型定义.函数操作,后面又介绍到了共享变量和图操作. 一 TesnorBoard可视化操作 Tenso ...
- [转]tensorflow中的gather
原文链接 tensorflow中取下标的函数包括:tf.gather , tf.gather_nd 和 tf.batch_gather. 1.tf.gather(params,indices,vali ...
- DoubleDQN---tensorflow实现
完整代码:https://github.com/zle1992/Reinforcement_Learning_Game 开山之作: <Playing Atari with Deep Reinfo ...
随机推荐
- 误删除/boot ,如何修复
进入救援模式 1.chroot /mnt/sysimage 将路径修改为 /mnt/sysimage 2.mkdir /mnt/temp mount /dev/sr0 /mnt/temp 挂载光盘 ...
- Codeforces Round #549 (Div. 2) F 数形结合 + 凸包(新坑)
https://codeforces.com/contest/1143/problem/F 题意 有n条形如\(y=x^2+bx+c\)的抛物线,问有多少条抛物线上方没有其他抛物线的交点 题解 \(y ...
- 【洛谷】P4594 [COCI2011-2012#5] BLOKOVI
本来已经有一个专门记录洛谷题目的博客了,但这个题之毒瘤...... 为你专门写一篇总行了吧...... 传送门 先说一句,这个题每次摆放都靠到最右边不一定是最优的 因为它可以这个亚子 就是说上面那个块 ...
- Error running 'xxx': Command line is too long. Shorten command line for xxx
跑单元测试时,报错如下: Error running 'xxx': Command line is too long. Shorten command line for xxx 解决方案: 在项目所在 ...
- bcrypt 加密算法
MD5 的特性 MD5 是一种加密算法,在调用这个算法的时候,提供一个密码的明文, 调用的结果,得到一个 32 位长度的密文: MD5 算法的特性:相同的字符串,如果多次调用 md5 算法,得到的结果 ...
- base62与long的相互转换
public static class Converter { private static String keys = "0123456789abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvw ...
- HTTP之Web服务器是如何进行工作的!
Web服务器是如何进行工作的 ====================文章摘自<HTTP权威指南>====================== 1. 建立连接—接收一个客户端的连接,或者 ...
- Installing Google Chrome in Linux(RedHat Enterprise Linux 7)
# wget https://dl.google.com/linux/direct/google-chrome-stable_current_x86_64.rpm # yum -y install r ...
- C# Thread was being aborted
先重现问题 1.新建一个aspx页面项目,插入两个页面WebForm1.aspx,WebForm2.aspx, WebForm1代码修改如下 protected void Page_Load(obje ...
- dp - 最大子矩阵和 - HDU 1081 To The Max
To The Max Problem's Link: http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1081 Mean: 求N*N数字矩阵的最大子矩阵和. ana ...
