对话框Dialog
QMainWindow
QMainWindow是 Qt 框架带来的一个预定义好的主窗口类。
主窗口,就是一个普通意义上的应用程序(不是指游戏之类的那种)最顶层的窗口。通常是由一个标题栏,一个菜单栏,若干工具栏和一个任务栏。在这些子组件之间则是我们的工作区。
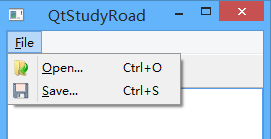
通过添加动作来添加菜单和工具栏等,比如添加一个打开菜单和工具
QAction *openaction;
openaction = new QAction(QIcon(":/img/open"),tr("&Open"),this);
openaction->setShortcut(QKeySequence::Open); //给菜单指定快捷键
openaction->setStatusTip(tr("open an existing file")); //提示 //加入菜单栏的File中
QMenu *file = menuBar()->addMenu(tr("&File"));
file->addAction(openaction); //加入工具栏
QToolBar *toolBar = addToolBar(tr("&File"));
toolBar->addAction(openaction);
QDialog
Qt 中使用QDialog类实现对话框
QDialog(及其子类,以及所有Qt::Dialog类型的类)的对于其 parent 指针都有额外的解释:如果 parent 为 NULL,则该对话框会作为一个顶层窗口,否则则作为其父组件的子对话框(此时,其默认出现的位置是 parent 的中心)。顶层窗口与非顶层窗口的区别在于,顶层窗口在任务栏会有自己的位置,而非顶层窗口则会共享其父组件的位置。
QDialog dialog; //顶层,在任务栏显示
QDialog dialog(this) //子窗口,在任务栏不显示
模态和非模态
对话框分为模态对话框和非模态对话框。所谓模态对话框,就是会阻塞同一应用程序中其它窗口的输入。模态对话框很常见,比如“打开文件”功能。你可以尝试一下记事本的打开文件,当打开文件对话框出现时,我们是不能对除此对话框之外的窗口部分进行操作的。与此相反的是非模态对话框,例如查找对话框,我们可以在显示着查找对话框的同时,继续对记事本的内容进行编辑。
Qt 支持模态对话框和非模态对话框。其中,Qt 有两种级别的模态对话框:应用程序级别的模态和窗口级别的模态,默认是应用程序级别的模态。应用程序级别的模态是指,当该种模态的对话框出现时,用户必须首先对对话框进行交互,直到关闭对话框,然后才能访问程序中其他的窗口。窗口级别的模态是指,该模态仅仅阻塞与对话框关联的窗口,但是依然允许用户与程序中其它窗口交互。
Qt 使用QDialog::exec()实现应用程序级别的模态对话框,使用QDialog::open()实现窗口级别的模态对话框,使用QDialog::show()实现非模态对话框。
模态:
void MainWindow::open()
{
QDialog dialog;
dialog.setWindowTitle(tr("Hello"));
dialog.exec();
}
非模态:注意必须用new创建否则一闪而过,这是因为,show()函数不会阻塞当前线程,对话框会显示出来,然后函数立即返回,代码继续执行。而用new是建立在堆上,执行完后不会消失。
不过,这样做有一个问题:如果我们的对话框不是在一个界面类中出现呢?由于QWidget的 parent 必须是QWidget指针,那就限制了我们不能将一个普通的 C++ 类指针传给 Qt 对话框。另外,如果对内存占用有严格限制的话,当我们将主窗口作为 parent 时,主窗口不关闭,对话框就不会被销毁,所以会一直占用内存。在这种情景下,我们可以设置 dialog 的WindowAttribute:
void MainWindow::open()
{
QDialog *dialog = new QDialog;
dialog->setAttribute(Qt::WA_DeleteOnClose);
dialog->setWindowTitle(tr("Hello, dialog!"));
dialog->show();
}
内置对话框
QColorDialog:选择颜色;QFileDialog:选择文件或者目录;QFontDialog:选择字体;QInputDialog:允许用户输入一个值,并将其值返回;QMessageBox:模态对话框,用于显示信息、询问问题等;QPageSetupDialog:为打印机提供纸张相关的选项;QPrintDialog:打印机配置;QPrintPreviewDialog:打印预览;QProgressDialog:显示操作过程。
QMessageBox
QMessageBox用于显示消息提示。我们一般会使用其提供的几个 static 函数:
显示关于对话框。这是一个最简单的对话框,其标题是 title,内容是 text,父窗口是 parent。对话框只有一个 OK 按钮
void about(QWidget * parent, const QString & title, const QString & text)
显示关于 Qt 对话框。该对话框用于显示有关 Qt 的信息
void aboutQt(QWidget * parent, const QString & title = QString())
显示严重错误对话框。这个对话框将显示一个红色的错误符号。我们可以通过 buttons 参数指明其显示的按钮。默认情况下只有一个 Ok 按钮,我们可以使用StandardButtons类型指定多种按钮
StandardButton critical(QWidget * parent, const QString & title, const QString & text, StandardButtons buttons = Ok, StandardButton defaultButton = NoButton)
QMessageBox::information()函数与QMessageBox::critical()类似,不同之处在于这个对话框提供一个普通信息图标
StandardButton information(QWidget * parent, const QString & title, const QString & text, StandardButtons buttons = Ok, StandardButton defaultButton = NoButton)
QMessageBox::question()函数与QMessageBox::critical()类似,不同之处在于这个对话框提供一个问号图标,并且其显示的按钮是“是”和“否”两个
StandardButton question(QWidget * parent, const QString & title, const QString & text, StandardButtons buttons = StandardButtons( Yes | No ), StandardButton defaultButton = NoButton)
QMessageBox::warning()函数与QMessageBox::critical()类似,不同之处在于这个对话框提供一个黄色叹号图标
StandardButton warning(QWidget * parent, const QString & title, const QString & text, StandardButtons buttons = Ok, StandardButton defaultButton = NoButton)
QFileDialog文件对话框
一个txt编辑保存的实例
主窗口继承mainwindow,#include <QtWidgets> 包含了QT的常用控件(比如QTextEdit,QAction)
mainwindow.h
#ifndef MAINWINDOW_H
#define MAINWINDOW_H #include <QMainWindow> class QTextEdit; class MainWindow : public QMainWindow
{
Q_OBJECT public:
explicit MainWindow(QWidget *parent = );
~MainWindow(); private slots:
void openFile();
void saveFile(); private:
QAction *openAction;
QAction *saveAction; QTextEdit *textEdit;
}; #endif // MAINWINDOW_H
main.cpp
#include <QApplication>
#include "mainwindow.h" int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
QApplication a(argc, argv); MainWindow w;
w.show(); return a.exec();
}
mainwindow.cpp
#include <QtGui>
#include <QtWidgets>
#include "mainwindow.h" MainWindow::MainWindow(QWidget *parent) :
QMainWindow(parent)
{
openAction = new QAction(QIcon(":/images/file-open"), tr("&Open..."), this);
openAction->setShortcuts(QKeySequence::Open);
openAction->setStatusTip(tr("Open an existing file"));
connect(openAction, &QAction::triggered, this, &MainWindow::openFile); saveAction = new QAction(QIcon(":/images/file-save"), tr("&Save..."), this);
saveAction->setShortcuts(QKeySequence::Save);
saveAction->setStatusTip(tr("Save a new file"));
connect(saveAction, &QAction::triggered, this, &MainWindow::saveFile); QMenu *file = menuBar()->addMenu(tr("&File"));
file->addAction(openAction);
file->addAction(saveAction); QToolBar *toolBar = addToolBar(tr("&File"));
toolBar->addAction(openAction);
toolBar->addAction(saveAction); textEdit = new QTextEdit(this);
setCentralWidget(textEdit);
} MainWindow::~MainWindow()
{
} void MainWindow::openFile()
{
QString path = QFileDialog::getOpenFileName(this, tr("Open File"), ".", tr("Text Files(*.txt)"));
if(!path.isEmpty()) {
QFile file(path);
if (!file.open(QIODevice::ReadOnly | QIODevice::Text)) {
QMessageBox::warning(this, tr("Read File"), tr("Cannot open file:\n%1").arg(path));
return;
}
QTextStream in(&file);
textEdit->setText(in.readAll());
file.close();
} else {
QMessageBox::warning(this, tr("Path"), tr("You did not select any file."));
}
} void MainWindow::saveFile()
{
QString path = QFileDialog::getSaveFileName(this, tr("Save File"), ".", tr("Text Files(*.txt)"));
if(!path.isEmpty()) {
QFile file(path);
if (!file.open(QIODevice::WriteOnly | QIODevice::Text)) {
QMessageBox::warning(this, tr("Write File"), tr("Cannot open file:\n%1").arg(path));
return;
}
QTextStream out(&file);
out << textEdit->toPlainText();
file.close();
} else {
QMessageBox::warning(this, tr("Path"), tr("You did not select any file."));
}
}
对话框Dialog的更多相关文章
- Android 对话框(Dialog)大全 建立你自己的对话框
Android 对话框(Dialog)大全 建立你自己的对话框 原文地址: http://www.cnblogs.com/salam/archive/2010/11/15/1877512.html A ...
- 转 Android 对话框(Dialog)大全 建立你自己的对话框
Activities提供了一种方便管理的创建.保存.回复的对话框机制,例如 onCreateDialog(int), onPrepareDialog(int, Dialog), showDialog( ...
- 95秀-自定义对话框 dialog 合集
普通的确认对话框 NormalDialog.java import android.app.Dialog; import android.content.Context; import android ...
- Android 常用对话框Dialog封装
Android 6种 常用对话框Dialog封装 包括: 消息对话框.警示(含确认.取消)对话框.单选对话框. 复选对话框.列表对话框.自定义视图(含确认.取消)对话框 分别如下图所示: ...
- Android项目实战(三十二):圆角对话框Dialog
前言: 项目中多处用到对话框,用系统对话框太难看,就自己写一个自定义对话框. 对话框包括:1.圆角 2.app图标 , 提示文本,关闭对话框的"确定"按钮 难点:1.对话框边框圆角 ...
- Android 对话框(Dialog)大全
转自: http://www.cnblogs.com/salam/archive/2010/11/15/1877512.html Activities提供了一种方便管理的创建.保存.回复的对话框机制, ...
- Android 对话框(Dialog)
Activities提供了一种方便管理的创建.保存.回复的对话框机制,例如 onCreateDialog(int), onPrepareDialog(int, Dialog), showDialog( ...
- Android 对话框(Dialog) 及 自己定义Dialog
Activities提供了一种方便管理的创建.保存.回复的对话框机制,比如 onCreateDialog(int), onPrepareDialog(int, Dialog), showDialog( ...
- (转载)Android项目实战(三十二):圆角对话框Dialog
Android项目实战(三十二):圆角对话框Dialog 前言: 项目中多处用到对话框,用系统对话框太难看,就自己写一个自定义对话框. 对话框包括:1.圆角 2.app图标 , 提示文本,关闭对话 ...
- android对话框(Dialog)的使用方法
Activities提供了一种方便管理的创建.保存.回复的对话框机制.比如 onCreateDialog(int), onPrepareDialog(int, Dialog), showDialog( ...
随机推荐
- andoroid项目使用Javah找不到class问题
比如目录结构是:Soffice\bin\classes\cn\com\isoffice\util\SofficeWebService.class 进入到bin/classes 下使用命令 javah ...
- 刀哥多线程串行队列gcd-04-dispatch_queue_serial
串行队列 特点 以先进先出的方式,顺序调度队列中的任务执行 无论队列中所指定的执行任务函数是同步还是异步,都会等待前一个任务执行完成后,再调度后面的任务 队列创建 dispatch_queue_t q ...
- SQLite判断某表是否存在
SQLite判断表是否存在:其实很简单,只要查看sqlite_master表中是否存在这条数据就可以知道了.SELECT count(*) FROM sqlite_master WHERE type= ...
- AsyncTask和Handler两种异步方式的实现和区别比较
1 AsyncTask实现的原理,和适用的优缺点 AsyncTask,是android提供的轻量级的异步类,可以直接继承AsyncTask,在类中实现异步操作,并提供接口反馈当前异步执行的程度(可以 ...
- android开发系列之多线程
今天在这篇博客里面,我只想谈谈自己对程序开发里面避无可避的一个问题-多线程的一些看法与思考. 其实说到多线程这个名称相信只要接触过软件这个行业的人都已经耳熟能详了,但是如果被问到到底什么才是多线程呢? ...
- 分布式服务框架HSF学习
HSF提供的是分布式服务开发框架,taobao内部使用较多,总体来说其提供的功能及一些实现基础:1.标准Service方式的RPC 1).Service定义:基于OSGI的Service定义方式 ...
- Paragon NTFS for Mac免费获取官方赠送正版.更新获取ntfs for mac 14方法
Paragon NTFS for Mac免费获取官方赠送正版,没有这个软件的朋友赶紧收下.获取地址http://www.paragon-drivers.com/cn/ntfs-mac-free/ntf ...
- iOS另类的内存管理
iOS的内存管理算是老生常谈的问题了,我们写iOS的时候无时无刻不在涉及到内存管理.从开始的MRR(manual retain-release)到后来ARC(Automatic Reference C ...
- chmod命令用法
指令名称 : chmod 使用权限 : 所有使用者 使用方式 : chmod [-cfvR] [--help] [--version] mode file... 说明 : Linux/Unix ...
- 单点登录 关于Cookie跨域的问题
public void ProcessRequest(HttpContext context) { HttpCookie cookie = new HttpCookie("name" ...
