数论 Day 13
数论_CRT(中国剩余定理)& Lucas (卢卡斯定理)
前言
又是一脸懵逼的一天。
正文
按照道理来说,我们应该先做一个介绍。
中国剩余定理
中国剩余定理,Chinese Remainder Theorem,又称孙子定理,给出了一元线性同余方程组的有解判定条件,并用构造法给出了通解的具体形式。

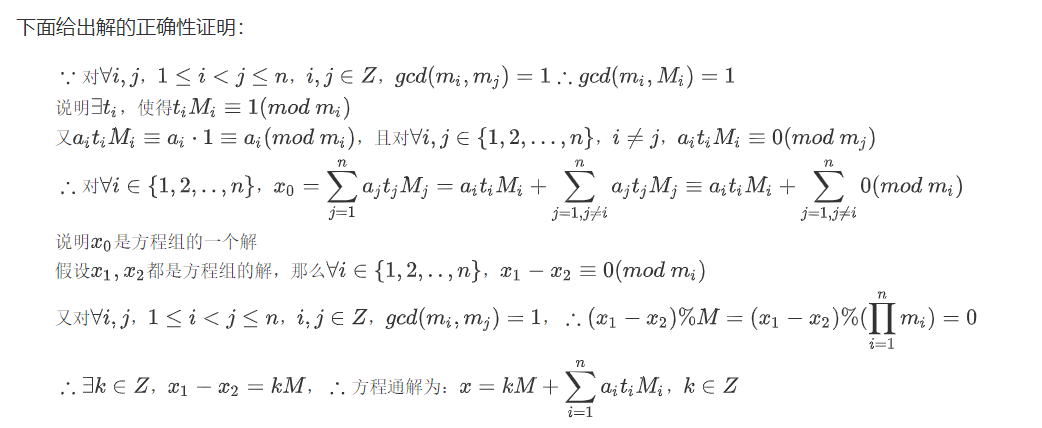
扩展中国剩余定理
在一般情况下,要求任两个数互质这个条件太苛刻了,CRT派不上用场,我们需要一个更具普遍性的结论,这就是EX-CRT。虽然是称为EX-CRT,但这个定理并没有直接用到CRT的结论。

typedef long long ll;
;
// m为模数组,a为余数数组,0~n-1
ll m[maxn], a[maxn];
ll exgcd(ll a, ll b, ll &x, ll &y) {
) {
x = ; y = ;
return a;
}
ll ans = exgcd(b, a % b, y, x);
y -= a / b * x;
return ans;
}
ll excrt() {
ll lcm = m[], last_a = a[];
; i < n; i++) {
ll lcm_a = ((a[i] - last_a) % m[i] + m[i]) % m[i];
ll k = lcm, x, y;
ll gcd = exgcd(lcm, m[i], x, y);
ll mod = m[i] / gcd;
x = (x * lcm_a / gcd % mod + mod) % mod;
lcm = lcm / gcd * m[i], last_a = (last_a + k * x) % lcm;
}
return (last_a % lcm + lcm) % lcm;
}
卢卡斯定理
卢卡斯定理是关于组合数和同余的定理,它表明当p为素数时:

因为当m>n时,二项式系数为0,那么二项式系数即组合数能被p整除等价于在p进制下,存在某一位m的数值大于对应的n的数值。
基于母函数可以简单证明这个定理。

可以用除法和取模方便的在循环中求出各个系数,代码如下:
typedef long long ll;
;
;
void init() {
F[] = ;
; i < maxn; i++)
F[i] = i * F[i - ] % mod;
}
ll qpow(ll a, ll b) {
ll ans = ;
while(b) {
) ans = ans * a % mod;
b >>= ; a = a * a % mod;
}
return ans;
}
ll lucas(ll N, ll M) {
ll ans = ;
while(N & M) {
ll n = N % mod, m = M % mod;
;
ans = ans * F[a] % mod * qpow(F[m] * F[n - m] % mod, mod - ) % mod;
N /= p; M /= p;
}
return ans;
}
扩展卢卡斯定理
卢卡斯定理同样不能处理模数不是素数的情况,这时便需要扩展卢卡斯定理。我们一步步分析如何求解模数不是素数的组合数问题。
完整代码如下:
typedef long long ll;
;
ll n, m, p;
ll qpow(ll a, ll b, ll mod) {
ll ans = ;
while(b) {
) ans = ans * a % mod;
b >>= ; a = a * a % mod;
}
return ans;
}
ll fac(ll n, ll p, ll pk) {
;
ll ans = ;
; i < pk; i++)
if (i % p) ans = ans * i % pk;
ans = qpow(ans, n / pk, pk);
int npk = n % pk;
; i <= npk; i++)
if (i % p) ans = ans * i % pk;
return ans * fac(n / p, p, pk) % pk;
}
ll exgcd(ll a, ll b, ll &x, ll &y) {
) {
x = ; y = ;
return a;
}
ll ans = exgcd(b, a % b, y, x);
y -= a / b * x;
return ans;
}
ll inv(ll a, ll p) {
, p);
}
ll C(ll n, ll m, ll p, ll pk) {
;
ll fn = fac(n, p, pk),
fm = fac(m, p, pk),
fn_m = fac(n - m, p, pk),
cnt = ;
for (ll i = n; i; i /= p)
cnt += i / p;
for (ll i = m; i; i /= p)
cnt -= i / p;
for (ll i = n - m; i; i /= p)
cnt -= i / p;
return fn * inv(fm * fn_m % pk, pk) % pk * qpow(p, cnt, pk) % pk;
}
ll a[N], mod[N]; // a[]是通过卢卡斯分解出来的组合数值,m[]是对应的模数
int cnt; // 质因数的种数
ll CRT() {
ll M = , ans = ;
; i < cnt; i++)
M *= mod[i];
; i < cnt; i++)
ans = (ans + a[i] * (M / mod[i]) % M * inv(M / mod[i], mod[i]) % M) % M;
return ans;
}
ll exlucas(ll n, ll m, ll p) {
ll sqrtp = sqrt(p + 0.5);
; p > && i <= sqrtp; i++) {
ll pk = ;
)
p /= i, pk *= i;
)
a[cnt] = C(n, m, i, pk), mod[cnt++] = pk;
}
)
a[cnt] = C(n, m, p, p), mod[cnt++] = p;
return CRT();
}
题目
其实这篇博客到这里几乎就可以没了,因为我。。。爆0了
难啊。。。
A题
Some people believe that there are three cycles in a person's life that start the day he or she is born. These three cycles are the physical, emotional, and intellectual cycles, and they have periods of lengths 23, 28, and 33 days, respectively. There is one peak in each period of a cycle. At the peak of a cycle, a person performs at his or her best in the corresponding field (physical, emotional or mental). For example, if it is the mental curve, thought processes will be sharper and concentration will be easier. Since the three cycles have different periods, the peaks of the three cycles generally occur at different times. We would like to determine when a triple peak occurs (the peaks of all three cycles occur in the same day) for any person. For each cycle, you will be given the number of days from the beginning of the current year at which one of its peaks (not necessarily the first) occurs. You will also be given a date expressed as the number of days from the beginning of the current year. You task is to determine the number of days from the given date to the next triple peak. The given date is not counted. For example, if the given date is 10 and the next triple peak occurs on day 12, the answer is 2, not 3. If a triple peak occurs on the given date, you should give the number of days to the next occurrence of a triple peak. This problem contains multiple test cases! The first line of a multiple input is an integer N, then a blank line followed by N input blocks. Each input block is in the format indicated in the problem description. There is a blank line between input blocks. The output format consists of N output blocks. There is a blank line between output blocks. Input You will be given a number of cases. The input for each case consists of one line of four integers p, e, i, and d. The values p, e, and i are the number of days from the beginning of the current year at which the physical, emotional, and intellectual cycles peak, respectively. The value d is the given date and may be smaller than any of p, e, or i. All values are non-negative and at most 365, and you may assume that a triple peak will occur within 21252 days of the given date. The end of input is indicated by a line in which p = e = i = d = -1. Output For each test case, print the case number followed by a message indicating the number of days to the next triple peak, in the form: Case 1: the next triple peak occurs in 1234 days. Use the plural form ``days'' even if the answer is 1. Sample Input 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 100 5 20 34 325 4 5 6 7 283 102 23 320 203 301 203 40 -1 -1 -1 -1 Sample Output Case 1: the next triple peak occurs in 21252 days. Case 2: the next triple peak occurs in 21152 days. Case 3: the next triple peak occurs in 19575 days. Case 4: the next triple peak occurs in 16994 days. Case 5: the next triple peak occurs in 8910 days. Case 6: the next triple peak occurs in 10789 days.
Biorhythms HDU-1370
题意
一个人有三个值(不知道是啥),然后每个值每到一个周期就会到达顶峰,求从d天开始,他三个值都到达顶峰是第几天。
思路
然而,三个周期都是质数,显然用的是中国剩余定理(CRT)
抽象一点来说,就是给你三个同余方程。
代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
ll exgcd(ll a, ll b, ll &x, ll &y)
{
if(!b)
{
x = ;
y = * ;
return a;
}
ll d = exgcd(b, a % b, x, y);
ll t = x;
x = y;
y = t - a / b * y;
return d;
}
ll inv(ll a,ll n)
{
ll y, d, x, fre, pf, qw;
/*cnt't*/
fre = pf = qw = ;
fre++, pf++, qw++;
/*can't*/
d = exgcd(a,n,x,y);
? (x + n) % n:-;
}
ll CN(ll leo, ll *a, ll *m)
{
ll M = , ret = ;
; i < leo; i ++)
M *= m[i];
; i < leo; i ++)
{
ll w = M / m[i];
ret = (ret + w * inv(w, m[i]) * a[i]) % M;
}
return (ret + M) % M;
}
int main()
{
ll t = , d;
ll a[],m[];
m[] = ;
m[] = ;
m[] = ;
/*GN*/
ll tea;
scanf("%lld", &tea);
while(true)
{
scanf(], &a[], &a[], &d);
] == - && a[] == - && a[] == - && d == -)
break;
ll ans = CN(, a, m);
if(ans <= d)
ans += ;
ans -= d;
printf("Case %lld: the next triple peak occurs in %lld days.\n", t, ans);
t++;
}
;
}
B题
F(x) is a polynomial in x with integer coefficients, here F(x) = (1+x)^a1 + (1+x)^a2 + ... + (1+x)^am. Given a1, a2, ... , am, find number of odd coefficients of F(x). Input The first line contains a single positive integer T( T <= 10000 ), indicates the number of test cases. For each test case: First line contains an integer N(1 <= N <= 15). Second line contains N integers a1, a2, ..., am ( 0 <= ai <= 2^45 ) Output For each test case: output the case number as shown and an the odd coefficients of F(x). Sample Input 4 1 1 1 3 2 1 3 3 1 2 3 Sample Output Case #1: 2 Case #2: 4 Case #3: 2 Case #4: 2 Hint Case #3: (1+x) + (1+x)^3 = 2 + 4x + 3x^2 + x^3. it contains 2 odd coefficients. Case #4: (1+x) + (1+x)^2 + (1+x)^3 = 3 + 6x + 4x^2 + x^3. it contains 2 odd coefficients.
Big Coefficients HDU-3929
题意
略
思路
显然是用卢卡斯,但我不知道为哈
未完待续
数论 Day 13的更多相关文章
- 洛谷P1621 集合 [2017年6月计划 数论13]
P1621 集合 题目描述 现在给你一些连续的整数,它们是从A到B的整数.一开始每个整数都属于各自的集合,然后你需要进行一下的操作: 每次选择两个属于不同集合的整数,如果这两个整数拥有大于等于P的公共 ...
- Educational Codeforces Round 13 D:Iterated Linear Function(数论)
http://codeforces.com/contest/678/problem/D D. Iterated Linear Function Consider a linear function f ...
- CodeForces 300C --数论
A - A Time Limit:2000MS Memory Limit:262144KB 64bit IO Format:%I64d & %I64u Submit Statu ...
- [Swust OJ 1125]--又见GCD(数论,素数表存贮因子)
题目链接:http://acm.swust.edu.cn/problem/1125/ Time limit(ms): 1000 Memory limit(kb): 65535 Descriptio ...
- ARZhu的数论初步
数论 2017年3月4日02:11:35 gcd 1. 原理: gcd( a, b ) = gcd( b, a - b ) -> gcd( a, b ) = gcd( b, b % a ) 2. ...
- HDU 1013.Digital Roots【模拟或数论】【8月16】
Digital Roots Problem Description The digital root of a positive integer is found by summing the dig ...
- 2017年浙江理工大学程序设计竞赛校赛 题解&源码(A.水, D. 简单贪心 ,E.数论,I 暴力)
Problem A: 回文 Time Limit: 1 Sec Memory Limit: 128 MB Submit: 1719 Solved: 528 Description 小王想知道一个字 ...
- [自用]数论和组合计数类数学相关(定理&证明&板子)
0 写在前面 本文受 NaVi_Awson 的启发,甚至一些地方直接引用,在此说明. 1 数论 1.0 gcd 1.0.0 gcd $gcd(a,b) = gcd(b,a\;mod\;b)$ 证明:设 ...
- 数论ex
数论ex 数学学得太差了补补知识点or复习 Miller-Rabin 和 Pollard Rho Miller-Rabin 前置知识: 费马小定理 \[ a^{p-1}\equiv 1\pmod p, ...
随机推荐
- 11、增强型for循环对二维数组的输出(test8.java)
由于笔者原因,这部分知识,尚不能整理出代码,笔者会好好学习增强型for循环中迭代起的相关知识,在笔者有能力,书写好这段代码后,将对本篇文章,进行二次修改,也同时欢迎大家与笔者交流,共同学习,共同进步. ...
- NS3中一些难以理解的常数
摘要:在NS3的学习中,PHY MAC中总有一些常数,需要理解才能修改.如帧间间隔等.那么,本文做个简单分析,帮助大家理解.针对802.11标准中MAC协议. void WifiMac::Conf ...
- 状压DP概念 及例题(洛谷 P1896 互不侵犯)
状压DP 就是状态压缩DP.所谓状态压缩,就是将一些复杂的状态压缩起来,一般来说是压缩为一个二进制数,用01来表示某一元素的状态. 比如一排灯泡(5个) 我们可以用一串二进制01串来表示他们的状态 1 ...
- 3.php基础(控制语句,函数,数组遍历)
if条件判断语句 结构一:只判断true,不管false 结构二:既判断true,也判断false(二选一) 结构三:多条件判断 switch多分支结构 Switch语法结构说明: l Switch的 ...
- 苹果电脑基本设置+Linux 命令+Android 实战集锦
本文微信公众号「AndroidTraveler」首发. 背景 大多数应届毕业生在大学期间使用的比较多的是 windows 电脑,因此初入职场如果拿到一台苹果电脑,可能一时间不能够很快的上手.基于此,这 ...
- 常见ASP脚本攻击及防范技巧
由于ASP的方便易用,越来越多的网站后台程序都使用ASP脚本语言.但是, 由于ASP本身存在一些安全漏洞,稍不小心就会给黑客提供可乘之机.事实上,安全不仅是网管的事,编程人员也必须在某些安全细节上注意 ...
- ThreadLocal中优雅的数据结构如何体现农夫山泉的广告语
本篇文章主要讲解 ThreadLocal 的用法和内部的数据结构及实现.有时候我们写代码的时候,不太注重类之间的职责划分,经常造出一些上帝类,也就是什么功能都往这个类里放.虽然能实现功能但是并不优雅且 ...
- Go语言-基本的http请求操作
Go发起GET请求 基本的GET请求 //基本的GET请求 package main import ( "fmt" "io/ioutil" "net/ ...
- jmeter之beanshell使用
beanshell官网:http://www.BeanShell.org/ 一.beanshell介绍 是一种完全符合Java语法规范的轻量级的脚本语言: 相当于一个小巧免费嵌入式的Java源代码解释 ...
- 吉特日化MES-电子批记录普通样本
在实施吉特日化配料系统的时候,客户希望一键式生成生产过程电子批记录,由于功能的缺失以及部分设备的数据暂时还无法完全采集到,先做一个普通样本的电子批记录格式打印. 电子批记录包含如下几个部分: 1. ...
