Asp.net Core 系列之--1.事件驱动初探:简单事件总线实现(SimpleEventBus)
ChuanGoing 2019-08-06
前言
开篇之前,简单说明下随笔原因。在园子里游荡了好久,期间也起过要写一些关于.NET的随笔,因各种原因未能付诸实现。
前段时间拜读daxnet的系列文章,感受颇深,犹豫好久,终于决定开始记录本人的学习点滴。
系列说明
本系列目的是构建一套基于领域驱动设计(DDD)的基础架构,渐进式实现CQRS/消息事件驱动型业务基础框架,中间会夹杂着其他的中间件的学习介绍,仅供学习交流用(.NET CORE/Standard 2.0)。
因为接触领域驱动设计时间不长,现实上述目标可能会比较曲折,有不规范的地方望读者指正。
构建开始前,简单介绍下本篇的学习曲线:
1.引入Ioc/DI
2.简单型事件驱动总线(EventBus)实现(事件定义/订阅及派发,事件处理器等)
注:篇尾我会附上Github源码地址(开发工具是VS2017/19,.NET CORE 2.2)
Ioc/DI
Asp.net Core 自带的Ioc容器用起来不大方便,本系列引入Autofac作为Ioc/DI容器,先简单介绍下几个常规用法
首先创建一个Asp.net core web api应用程序,新建一个.Net Standard项目Base.Ioc用于管理Ioc/DI操作,并添加下图的Nuget依赖
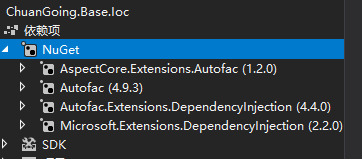
添加扩展类AutofacExtensions,添加如下方法(这里引入了AspectCore动态代理后续实现Aop会用到)
public static IServiceProvider UseAutofac<TModule>(this IServiceCollection services)
where TModule : Module, new()
{
ContainerBuilder builder = new ContainerBuilder();
builder.Populate(services); builder.RegisterModule<TModule>();
//引入AspectCore.Extensions.Autofac
builder.RegisterDynamicProxy();
IContainer container = builder.Build();
return new AutofacServiceProvider(container);
}
在Startup.cs文件的ConfigureServices中替换Asp.net Core自带Ioc容器:
// This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to add services to the container.
public IServiceProvider ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddMvc().SetCompatibilityVersion(CompatibilityVersion.Version_2_2); //替换Ioc容器,并扩展Autofac模块注册
return services.UseAutofac<WebModule>();
}
上面替换Ioc容器的时候,引入了Autofac的模块自动注入功能
public class WebModule : Module
{
protected override void Load(ContainerBuilder builder)
{
//builder.RegisterType<AutoFacManager>();
//builder.RegisterType<Worker>().As<IPerson>();
//扫描程序集自动注册
builder.RegisterAssembly(ThisAssembly);
}
}
在Base.Ioc项目中添加AutofacInjectionExtensions.cs文件
/// <summary>
/// Autofac自动注入
/// </summary>
/// <param name="builder"></param>
/// <param name="assembly"></param>
public static void RegisterAssembly(this ContainerBuilder builder, Assembly assembly)
{
foreach (var type in assembly.ExportedTypes)
{
if (type.IsPublic && !type.IsAbstract && type.IsClass)
{
var interfaces = type.GetInterfaces();
IList<Type> transientList = new List<Type>();
IList<Type> scopeList = new List<Type>();
IList<Type> singletonList = new List<Type>();
foreach (var intrType in interfaces)
{
if (intrType.IsGenericType)
{
if (intrType.IsAssignableTo<IDependencyInstance>())
{
transientList.Add(intrType);
}
else if (intrType.IsAssignableTo<IScopeInstance>())
{
scopeList.Add(intrType);
}
else if (intrType.IsAssignableTo<ISingletonInstance>())
{
singletonList.Add(intrType);
}
}
else
{
if (intrType.IsAssignableTo<IDependencyInstance>())
{
transientList.Add(intrType);
}
else if (intrType.IsAssignableTo<IScopeInstance>())
{
scopeList.Add(intrType);
}
else if (intrType.IsAssignableTo<ISingletonInstance>())
{
singletonList.Add(intrType);
}
}
} if (type.IsGenericType)
{
if (transientList.Count > )
{
builder.RegisterGeneric(type).As(transientList.ToArray()).InstancePerDependency();
}
if (scopeList.Count > )
{
builder.RegisterGeneric(type).As(scopeList.ToArray()).InstancePerLifetimeScope();
}
if (singletonList.Count > )
{
builder.RegisterGeneric(type).As(singletonList.ToArray()).SingleInstance();
} //泛型
if (type.IsAssignableTo<IDependencyInstance>())
{
builder.RegisterGeneric(type).AsSelf().InstancePerDependency();
}
else if (type.IsAssignableTo<IScopeInstance>())
{
builder.RegisterGeneric(type).AsSelf().InstancePerLifetimeScope();
}
else if (type.IsAssignableTo<ISingletonInstance>())
{
builder.RegisterGeneric(type).AsSelf().SingleInstance();
}
}
else
{
if (transientList.Count > )
{
builder.RegisterType(type).As(transientList.ToArray()).InstancePerDependency();
}
if (scopeList.Count > )
{
builder.RegisterType(type).As(scopeList.ToArray()).InstancePerLifetimeScope();
}
if (singletonList.Count > )
{
builder.RegisterType(type).As(singletonList.ToArray()).SingleInstance();
}
//
if (type.IsAssignableTo<IDependencyInstance>())
{
builder.RegisterType(type).AsSelf().InstancePerDependency();
}
else if (type.IsAssignableTo<IScopeInstance>())
{
builder.RegisterType(type).AsSelf().InstancePerLifetimeScope();
}
else if (type.IsAssignableTo<ISingletonInstance>())
{
builder.RegisterType(type).AsSelf().SingleInstance();
}
}
}
}
}
上面一段代码用到了IDependencyInstance/IScopeInstance/ISingletonInstance三个接口,分别用于瞬时/Scope/单例的服务标识。
大概说明下这段代码的作用:通过扫描传入的程序集获取外部可见的Public类型的Type(这里我们指的是类),扫描该类的所有继承了服务标识接口,并注册为对应的服务
至此,Ioc容器已替换为Autofac
EventBus
事件总线实现发布/订阅功能,首先定义IEvent/IEventHandler,IEventHandler 定义了事件处理方法
public interface IEvent
{
Guid Id { get; }
/// <summary>
/// 时间戳
/// </summary>
long Timestamp { get; }
}
public interface IEventHandler
{
/// <summary>
/// 处理事件
/// </summary>
/// <param name="event"></param>
/// <param name="cancellationToken"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
Task<bool> HandleAsync(IEvent @event, CancellationToken cancellationToken = default(CancellationToken));
/// <summary>
/// 可否处理
/// </summary>
/// <param name="event"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
bool CanHandle(IEvent @event);
}
接着定义发布/订阅及事件总线接口
public interface IEventPublisher
{
/// <summary>
/// 发布事件
/// </summary>
/// <typeparam name="TEvent"></typeparam>
/// <param name="event"></param>
/// <param name="cancellationToken"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
Task PublishAsync<TEvent>(TEvent @event, CancellationToken cancellationToken = default(CancellationToken))
where TEvent : IEvent;
}
public interface IEventSubscriber
{
/// <summary>
/// 事件订阅
/// </summary>
void Subscribe();
}
public interface IEventBus : IEventSubscriber, IEventPublisher
{
}
EventBus实现发布/订阅器,并在事件发布的同时通知相应的事件处理器进行相关处理。
这里引入了"消息队列"的概念(当然目前我们只是用来模拟消息队列,后续会引入RabbitMQ来实现)
相关代码如下:
internal sealed class EventQueue
{
public event EventHandler<EventProcessedEventArgs> EventPushed; public EventQueue()
{ } public void Push(IEvent @event)
{
OnMessagePushed(new EventProcessedEventArgs(@event));
} private void OnMessagePushed(EventProcessedEventArgs e)
{
this.EventPushed?.Invoke(this, e);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 消息事件参数
/// </summary>
public class EventProcessedEventArgs : EventArgs
{
public IEvent Event { get; } public EventProcessedEventArgs(IEvent @event)
{
Event = @event;
}
}
public class EventBus : IEventBus
{
private readonly EventQueue eventQueue = new EventQueue();
private readonly IEnumerable<IEventHandler> eventHandlers; public EventBus(IEnumerable<IEventHandler> eventHandlers)
{
this.eventHandlers = eventHandlers;
} /// <summary>
/// 发布事件到队列时触发处理事件
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sendere"></param>
/// <param name="e"></param>
private void EventQueue_EventPushed(object sendere, EventProcessedEventArgs e)
{
(from eh in this.eventHandlers
where
eh.CanHandle(e.Event)
select eh).ToList().ForEach(async eh => await eh.HandleAsync(e.Event));
} public Task PublishAsync<TEvent>(TEvent @event, CancellationToken cancellationToken = default(CancellationToken))
where TEvent : IEvent
=> Task.Factory.StartNew(() => eventQueue.Push(@event)); /// <summary>
/// 事件订阅(订阅队列上的事件)
/// </summary>
public void Subscribe()
{
eventQueue.EventPushed += EventQueue_EventPushed;
}
上面的代码中EventQueue的Push方法被调用时,会触发EventPushed事件,在EventBus中,我们注册了EventQueue的EventPushed事件,即最终会触发EventBus的EventQueue_EventPushed事件,进而通过事件处理器来处理(这块详细说明,请阅读DaxNet-事件驱动型架构实现一)
到此,消息总线机制处理完成,接下来我们创建一个Web API应用程序来演示消息发布/订阅及处理
上面我们定义了IEvent/IEventHandler,这里我们先在WebAPI 项目中来实现
public class CustomerCreatedEvent : IEvent
{
public CustomerCreatedEvent(string customerName)
{
this.Id = Guid.NewGuid();
this.Timestamp = DateTimeOffset.Now.ToUnixTimeMilliseconds();
this.CustomerName = customerName;
} public Guid Id { get; } public long Timestamp { get; } public string CustomerName { get; }
}
public class CustomerCreatedEventHandler : IEventHandler<CustomerCreatedEvent>
{
public bool CanHandle(IEvent @event)
=> @event.GetType().Equals(typeof(CustomerCreatedEvent)); public Task<bool> HandleAsync(CustomerCreatedEvent @event, CancellationToken cancellationToken = default(CancellationToken))
{
return Task.FromResult(true);
} public Task<bool> HandleAsync(IEvent @event, CancellationToken cancellationToken = default(CancellationToken))
=> CanHandle(@event) ? HandleAsync((CustomerCreatedEvent)@event, cancellationToken) : Task.FromResult(false);
}
值得说明下的是,在实现IEventHandler的时候,利用了泛型接口IEventHandler<T>来建立IEventHandler对于IEvent的依赖,因为事件处理器最终处理的必然是某个事件。
OK,现在新建一个Controller
[Route("api/[controller]")]
public class CustomersController : Controller
{private readonly IEventBus _eventBus;
public CustomersController(IEventBus eventBus)
{
_eventBus = eventBus;
}
// 创建新的客户信息
[HttpPost]
public async Task<IActionResult> Create([FromBody] CustomerDto model)
{
var name = model.Name;
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(name))
{
return BadRequest();
}
//这里其他业务处理...
await _eventBus.PublishAsync(new CustomerCreatedEvent(name));
} }
上面的CustomersController构造函数中由Ioc注入了eventBus,需要注意的是,引用eventBus前,需要在Startup.cs中注册对应的服务,我们这里用到的是Autofac的模块化注册。
利用Web API下的WebModule.cs引用SimpleEventBus中的EventBusModule
public class WebModule : Module
{
protected override void Load(ContainerBuilder builder)
{
//扫描程序集自动注册
builder.RegisterAssembly(ThisAssembly);
//注册模块化EventBusModule
builder.RegisterModule<EventBusModule>();
}
}
public class EventBusModule : Module
{
protected override void Load(ContainerBuilder builder)
{
//扫描程序集自动注册
builder.RegisterAssembly(ThisAssembly);
}
}
关于扫描程序集自动注册,上面Ioc段落有详细说明,这里就不再啰嗦。
到此为止,编码工作告一段落,运行Web API,利用Postman或PowerShell 自带的命令 Invoke-WebRequest模拟http请求,结果如下图:
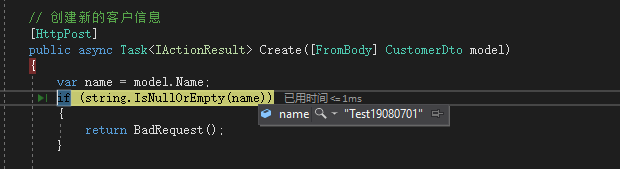
请求进来,数据加载到Dto中

EventBus的事件发布时调用EventQueue的Push函数,同时会触发EventPushed事件,通过对应的时间处理器处理事件
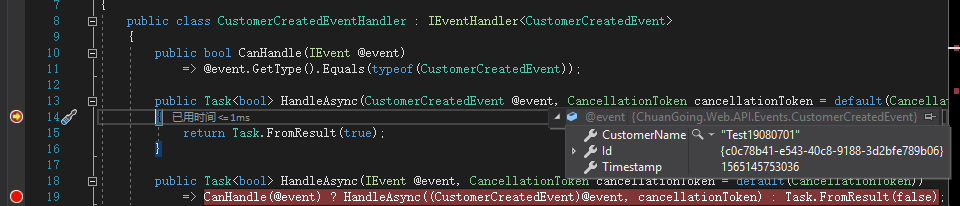
最终,消息在事件处理器中进行相关处理
回顾
回顾一下,本篇开头介绍了Autofac替换Asp.Net Core自带Ioc容器,Autofac的模块注册/泛型/服务注册等;然后介绍了事件总线的工作流程:事件发布到总线中,通过消息队列触发注册到总线中的事件处理器处理事件消息;最后,我们利用Web API 展示了程序的运行过程。
因为篇幅有限,代码中关于Storage的部分,涉及到了仓储的概念,我想到时放到领域设计部分一起介绍。
源码
本篇涉及的源码在Github的https://github.com/ChuanGoing/Start.git 的SimpleEventBus分支可以找到。
Asp.net Core 系列之--1.事件驱动初探:简单事件总线实现(SimpleEventBus)的更多相关文章
- Asp.net Core 系列之--2.ORM初探:Dapper实现MySql数据库各类操作
ChuanGoing 2019-09-10 距离上一篇近一个月时间,断断续续才把本篇码完,后面将加快进度,争取年度内把本系列基本介绍完成,同时督促本人持续学习. 本篇学习曲线: 1.初识Dapper ...
- Asp.net Core 系列之--4.事务、日志及错误处理
ChuanGoing 2019-11-17 这篇原本时想把事务处理.日志处理.错误处理.授权于鉴权一并介绍完的,授权和鉴权我想结合自定义权限来介绍,全部放到这里篇幅可能太长,因此权限部分将会在下篇来介 ...
- Asp.net Core 系列之--3.领域、仓储、服务简单实现
ChuanGoing 2019-11-11 距离上篇近两个月时间,一方面时因为其他事情耽搁,另一方面也是之前准备不足,关于领域驱动有几个地方没有想通透,也就没有继续码字.目前网络包括园子里大多领域驱 ...
- 重温.NET下Assembly的加载过程 ASP.NET Core Web API下事件驱动型架构的实现(三):基于RabbitMQ的事件总线
重温.NET下Assembly的加载过程 最近在工作中牵涉到了.NET下的一个古老的问题:Assembly的加载过程.虽然网上有很多文章介绍这部分内容,很多文章也是很久以前就已经出现了,但阅读之后 ...
- Asp.net Core 系列之--5.认证、授权与自定义权限的实现
ChuanGoing 2019-11-24 asp.net core系列已经来到了第五篇,通过之前的基础介绍,我们了解了事件订阅/发布的eventbus整个流程,初探dapper ORM实现,并且简单 ...
- 1.1专题介绍「深入浅出ASP.NET Core系列」
大家好,我是IT人张飞洪,专注于.NET平台十年有余. 工作之余喜欢阅读和写作,学习的内容包括数据结构/算法.网络技术.Linux系统原理.数据库技术原理,设计模式.前沿架构.微服务.容器技术等等…… ...
- asp.net core系列 30 EF管理数据库架构--必备知识 迁移
一.管理数据库架构概述 EF Core 提供两种主要方法来保持 EF Core 模型和数据库架构同步.一是以 EF Core 模型为基准,二是以数据库为基准. (1)如果希望以 EF Core 模型为 ...
- asp.net core系列 40 Web 应用MVC 介绍与详细示例
一. MVC介绍 MVC架构模式有助于实现关注点分离.视图和控制器均依赖于模型. 但是,模型既不依赖于视图,也不依赖于控制器. 这是分离的一个关键优势. 这种分离允许模型独立于可视化展示进行构建和测试 ...
- asp.net core系列 39 Web 应用Razor 介绍与详细示例
一. Razor介绍 在使用ASP.NET Core Web开发时, ASP.NET Core MVC 提供了一个新特性Razor. 这样开发Web包括了MVC框架和Razor框架.对于Razor来说 ...
随机推荐
- 手把手教你安装Eclipse最新版本的详细教程 - 大佬的鸡肋,菜鸟的盛宴(非常详细,非常实用)
简介 首先声明此篇文章主要是针对测试菜鸟或者刚刚入门的小伙们或者童鞋们,大佬就没有必要往下看了. 写这篇文章的由来是因为后边要用这个工具,但是由于某些原因有部分小伙伴和童鞋们可能不会安装此工具,为了方 ...
- .netCore+Vue 搭建的简捷开发框架 (5)
文章目录:.netCore+Vue 搭建的简捷开发框架--目录 上两节的内容介绍了一些关于.netCore 相关的一些基础知识.介绍这些的目的,最主要的还是为了我们的架构搭建服务. 上一节中,我们介绍 ...
- Fiddler的安装
相关下载软件(链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1HFdFNph6FGHOFtZq09ldpg 提取码:3u3l ) fiddler是基于.net环境的,所以需要先安装.net 安 ...
- web安全之点击劫持
点击劫持(ClickJacking)是一种视觉上的欺骗手段.大概有两种方式, 一是攻击者使用一个透明的iframe,覆盖在一个网页上,然后诱使用户在该页面上进行操作,此时用户将在不知情的情况下点击透明 ...
- 一次看懂 Https 证书认证
TLS 传输层安全性协定 TLS(Transport Layer Security),及其前身安全套接层 SSL(Secure Sockets Layer)是一种安全协议,目的是为网际网路通信,提供安 ...
- redis应用场景总结redis平时我们用到的地方蛮多的,下面就了解的应用场景做个总结:
redis常见应用场景 1.热点数据的缓存 由于redis访问速度块.支持的数据类型比较丰富,所以redis很适合用来存储热点数据,另外结合expire,我们可以设置过期时间然后再进行缓存更新操作,这 ...
- linux上安装newman
1. newman的安装依赖nodejs,首先安装node/npm 进入到 /usr/local目录[root@ipha-dev71- local]# cd /usr/local [root@ipha ...
- textView 实现完成收键盘操作
-(BOOL)textView:(UITextView *)textView shouldChangeTextInRange:(NSRange)range replacementText:(NSStr ...
- Java中的锁[原理、锁优化、CAS、AQS]
1.为什么要用锁? 锁-是为了解决并发操作引起的脏读.数据不一致的问题. 2.锁实现的基本原理 2.1.volatile Java编程语言允许线程访问共享变量, 为了确保共享变量能被准确和一致地更新, ...
- 4. SOFAJRaft源码分析— RheaKV初始化做了什么?
前言 由于RheaKV要讲起来篇幅比较长,所以这里分成几个章节来讲,这一章讲一讲RheaKV初始化做了什么? 我们先来给个例子,我们从例子来讲: public static void main(fin ...
