Multi-Dimensional Recurrent Neural Networks
Multi-Dimensional Recurrent Neural Networks
The basic idea of MDRNNs is to replace the single recurrent connection found in standard RNNs with as many recurrent connections as there are dimensions in the data. During the forward pass, at each point in the data sequence, the hidden layer of the network receives both an external input and its own activations from one step back along all dimensions.
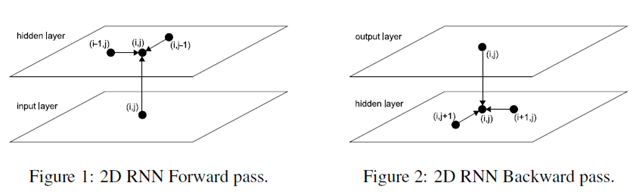
Clearly, the data must be processed in such a way that when the network reaches a poin in an n-dimensional sequence, it has already passed through all the points from which it will rechive its previous activations.
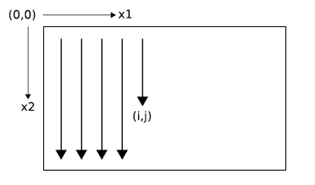
2D sequence ordering. The MDRNN forword pass starts at the origin and follows the direction of the arrows. The point(I,j) is never reached before both (i-1,j) and (i,j-1)
The forward pass of an MDRNN can then be carried out by feeding forward the input and the n previous hidden layer activations at each point in the ordered input sequence, and storing the resulting hidden layer activations at each point in the ordered input sequence, and storing the resulting hidden layer activations. Care must be taken at the sequence boundaries not to feed forward activations from points outside the sequence.
Note that each 'point' in the input sequence will in general be a multivalued vector. For example, in a two dimensional color image, the inputs could be single pixels represented by RGB triples, or blocks of pixels, or the outputs of a preprocessing method such as a discrete cosine transform.
The error gradient of an MDRNN(that is, the derivative of some objective function with respect to the network weights) can be calculated with an n-dimensional extension of the backpropagation through time(BPTT) algorithm. As with one dimensional BPTT, the sequence is processed in the reverse order of the forward pass. At each timestep, the hidden layer receives both the output error derivatives and its own n 'future' derivatives. Figure 2 illustrates the BPTT backword pass for two dimensions. Again, care must be taken at the sequence boundaries.
At a point in an n-dimensional sequence, define and respectively as the activations of the input unit and the hidden unit. Define as the weight of the connection going from unit j to unit k. Then for an n-dimensional MDRNN whose hidden layer consists of summation units with the tanh activation function, the forward pass for a sequence with dimensions can be sumarised as follows:

Defining and respectively as the derivatives of the objective function with respect to the activations of the output unit and the hidden unit at point x, the backward pass is:
Since the forward and backward pass require one pass each through the data sequence, the overall complexity of MDRNN training is linear in the number of data points and the unmber of network weights.

Multi-directional MDRNNs
For one dimensional RNNs, the problem of multi-directional context was solved in 1997 by the introduction of bidirectional recurrent neural networks (BRNNs). BRNNs contain two separate hidden layers that process the input sequence in the forward and reverse directions. The two hidden layers are connected to a single output layer, thereby providing the network with access to both past and future context.
BRNNs can be extended to n-dimensional data by using separate hidden layers, each of which processes the sequence using the ordering defined above, but with a different choice of axes.
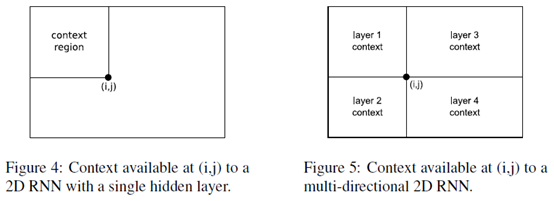
More specifically, the axes are chosen so that their origins lie on the the vertices of the sequence. The 2 dimensional case is illustrated in Figure 6.

As before, the hidden layers are connected to a single output layer, which now has access to all surrounding context.
If the size of the hidden layers is held constan, multi-direcitonal MDRNNs scales as O() for n-dimensional data. In practive however, we have found that using small layers gives better results than 1 large layer with the same overall number of weights, presumably because the data processing is shared between the hidden layers. This also holds in one dimension, as previous experiments have demonstrated. In any case the complexity of the algorithm remains linear in the number of data points and the number of parameters, and the number of parameters is independent of the data dimensionality.
For a multi-directional MDRNN, the forward and backward passes through an n-dimensional sequence can be summarized as follows:


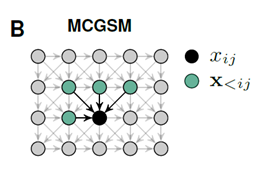
MCGSM
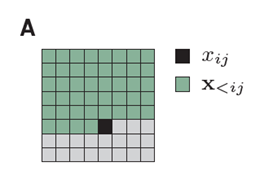
We factorize the distribution of images such that the prediction of a pixel(black) may depend on any pixel in the upper-left green region.
A graphical model representation of an MCGSM with a causal neighborhood limited to a small region.
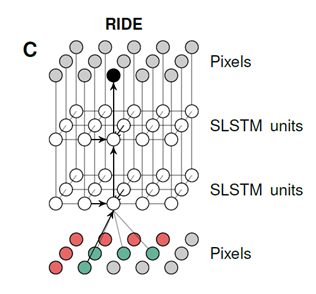
A visualization of our recurrent iamge model with two layers of spatial LSTMs. The pixels of the image are represented twice and some arrows are omitted for clarity. Through feedforward connections, the prediction of a pixel depends directly on its neighborhood(gre-e),but through recurrent connections it hs access to the information in a much larger region(r-ed).
Multi-Dimensional Recurrent Neural Networks的更多相关文章
- The Unreasonable Effectiveness of Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN)
http://karpathy.github.io/2015/05/21/rnn-effectiveness/ There’s something magical about Recurrent Ne ...
- 循环神经网络(RNN, Recurrent Neural Networks)介绍(转载)
循环神经网络(RNN, Recurrent Neural Networks)介绍 这篇文章很多内容是参考:http://www.wildml.com/2015/09/recurrent-neur ...
- Attention and Augmented Recurrent Neural Networks
Attention and Augmented Recurrent Neural Networks CHRIS OLAHGoogle Brain SHAN CARTERGoogle Brain Sep ...
- cs231n spring 2017 lecture10 Recurrent Neural Networks 听课笔记
(没太听明白,下次重新听一遍) 1. Recurrent Neural Networks
- 第十四章——循环神经网络(Recurrent Neural Networks)(第一部分)
由于本章过长,分为两个部分,这是第一部分. 这几年提到RNN,一般指Recurrent Neural Networks,至于翻译成循环神经网络还是递归神经网络都可以.wiki上面把Recurrent ...
- 第十四章——循环神经网络(Recurrent Neural Networks)(第二部分)
本章共两部分,这是第二部分: 第十四章--循环神经网络(Recurrent Neural Networks)(第一部分) 第十四章--循环神经网络(Recurrent Neural Networks) ...
- Pixel Recurrent Neural Networks翻译
Pixel Recurrent Neural Networks 目前主要在用的文档存放: https://www.yuque.com/lart/papers/prnn github存档: https: ...
- 循环神经网络(Recurrent Neural Networks, RNN)介绍
目录 1 什么是RNNs 2 RNNs能干什么 2.1 语言模型与文本生成Language Modeling and Generating Text 2.2 机器翻译Machine Translati ...
- 《转》循环神经网络(RNN, Recurrent Neural Networks)学习笔记:基础理论
转自 http://blog.csdn.net/xingzhedai/article/details/53144126 更多参考:http://blog.csdn.net/mafeiyu80/arti ...
随机推荐
- BZOJ 3712: [PA2014]Fiolki 倍增+想法
3712: [PA2014]Fiolki Time Limit: 30 Sec Memory Limit: 128 MBSubmit: 437 Solved: 115[Submit][Status ...
- UVA 11572 Unique snowflakes (滑窗)
用set,保存当前区间出现过的数字,如果下一个数字没有出现过,加入,否则删掉左端点,直到没有重复为止 #include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std ...
- Write Once, Run Anywhere:这不是Java,这是C#
注意,本文目的并非挑起语言之争.虽然有为C#平反之意,但主要还是介绍Mono并进行简单的测试. UPDATED: 25th August 2012 更新了「Compile Once, Run Anyw ...
- oracle中print_table存储过程实例介绍
oracle中pro_print_table存储过程实例介绍 存储过程(Stored Procedure),就是一组用于完成特定数据库功能的SQL语句集,该SQL语句集经过编译后存储在数据库系统中.这 ...
- Maven各种常用架包配置文件,保存一份
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/20 ...
- UICollectionView实现无限轮播
#import "KGNewsController.h"#import "KGNewsCell.h"#import "KGNews.h"#i ...
- Linux下如何通过命令检查网卡是否插上网线
How To:Linux下如何通过命令检查网卡是否插上网线 主要工具为ethtool来检查,主要关注的字段为"Link detected",注意如下的输出,其中em4实际物理上 ...
- redis学习笔记(3)
redis学习笔记第三部分 --redis持久化介绍,事务,主从复制 三,redis的持久化 RDB(Redis DataBase)AOF(Append Only File) RDB:在指定的时间间隔 ...
- Voyager下的Settings方法
设置网站标题,logo,描述: 自定义setting字段,添加group为文章,key为title的字段: 添加成功: 前端页面写法: <img src="{{ Voyager::im ...
- Linux:FTP服务匿名用户,本地用户,虚拟用户配置
匿名用户 FTP协议占用两个端口号: 21端口:命令控制,用于接收客户端执行的FTP命令. 20端口:数据传输,用于上传.下载文件数据. 实验:匿名访问,服务器192.168.10.10 客户 ...
