java数据结构----堆
1.堆:堆是一种树,由它实现的优先级队列的插入和删除的时间复杂度都是O(logn),用堆实现的优先级队列虽然和数组实现相比较删除慢了些,但插入的时间快的多了。当速度很重要且有很多插入操作时,可以选择堆来实现优先级队列。
2.java的堆和数据结构堆:java的堆是程序员用new能得到的计算机内存的可用部分。而数据结构的堆是一种特殊的二叉树。
3.堆是具有如下特点的二叉树:
3.1.它是完全二叉树,也就是说除了树的最后一层节点不需要是满的,其他的每一层从左到右都必须是满的。
3.1.1.完全二叉树图解: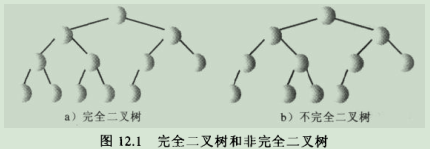
3.2.它常常用数组实现。
3.2.1.数组和堆的对应关系示意图: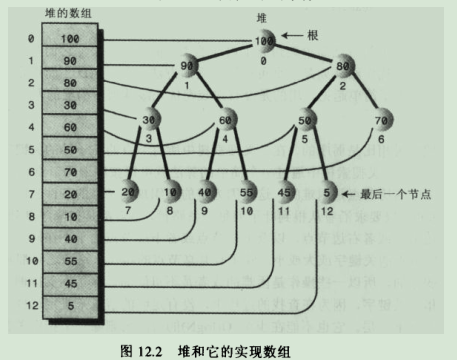
3.3.堆中每一个节点都满足堆的条件,也就是说每一个关键字的值都大于或等于这个节点的子节点的关键字值。
堆是完全二叉树的事实说明了表示堆的数组中没有空项,即从0-->n-1的每个数据单元都有数据项。
4.堆在存储器中的表示是数组,堆只是一个概念上的表示。
5.堆的弱序:堆和二叉搜索树相比是弱序的,在二叉搜索树中,当前节点的值总是比左子节点的值大,却比它的右子节点的值小,因此按序遍历相对容易。而堆的组织规则弱,它只要求从根到叶子节点的每一条路径,节点都是按降序排列的。同一节点的左右子节点都没有规律。因此,堆不支持按序遍历,也不能在堆上便利的查找指定关键字,因为在查找的过程中,没有足够的信息决定选择通过节点的两个那一个走向下一层。它也不能在少于O(logn)的时间内删除一个指定的节点,因为没有办法找到这个节点。因此,堆的这种近乎无序的规则似乎毫无用处,不过对于快速移除最大节点的操作,以及快速插入新节点的操作,这种顺序已经足够了。这些操作是使用堆作为优先级队列所需要的全部操作。
6.移除操作:移除是指删掉关键字值最大的节点,即根节点。移除思路如下:
6.1.移走根,
6.2.把左后一个节点移到根的位置,
6.3.一直向下筛选这个节点,知道它在一个大于它的节点之下,小于它的节点之上为止。
6.4.过程图解: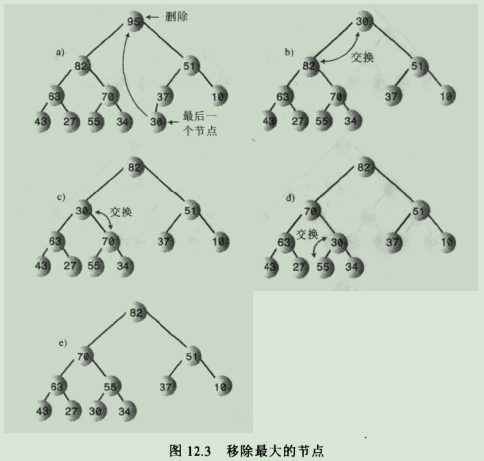
说明:在被筛选节点的每个暂时停留的位置,向下筛选的算法总是要检查那一个子节点更大,然后目标节点和较大的子节点交换位置,如果要把目标节点和较小的子节点交换,那么这个子节点就会变成大子节点的父节点,这就违背了堆的条件。
7.堆的插入:插入使用向上筛选,节点最后插入到数组最后第一个空着的单元中,数组容量大小增加1。
7.1.插入图解: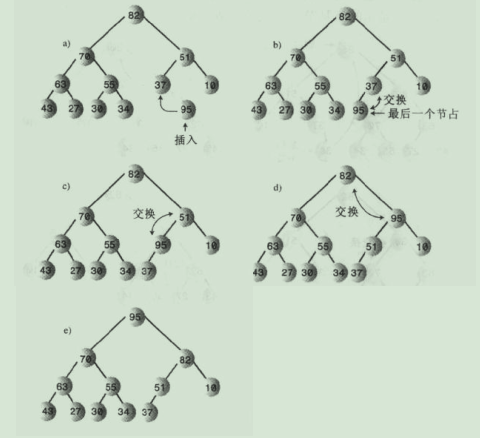
说明:向上筛选的算法比向下筛选的算法相对简单,因为它不需要比较两个子节点关键字值的大小,节点只有一个父节点。目标节点主要和它的父亲节点换位即可。
7.2.不是真的交换: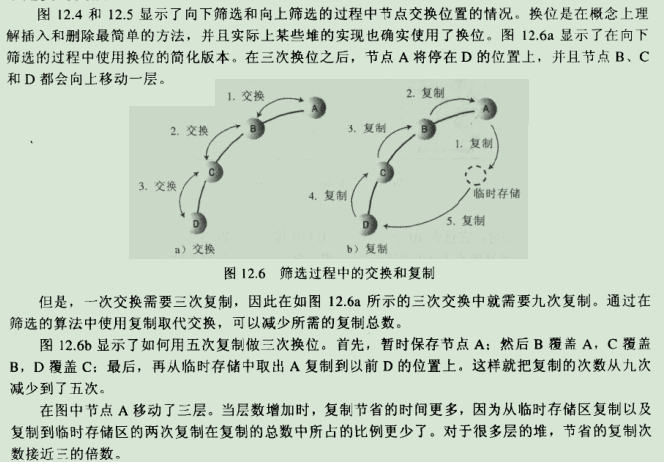
8.用数组表示一棵树时,如果数组中节点的索引位x,则
a.它的父节点的下标是:(x-1)/2;
b.它的左子节点的下标为2*x + 1;
c.它的右子节点的下标是2*x + 2;
9.堆的代码:
9.1.Node.java
package com.cn.heap;
/**
* 堆的节点类
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class Node {
private int iData;
public Node(int id){
iData = id;
}
public int getkey(){
return iData;
}
public void setkey(int id){
iData = id;
}
}
9.2.Heap.java
package com.cn.heap;
/**
* 堆的实现类
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class Heap {
private Node[] heapArray;
private int maxSize;
private int currentSize;
public Heap(int mx){
maxSize = mx;
heapArray = new Node[maxSize];
currentSize = 0;
}
public boolean isEmpty(){
return currentSize == 0 ;
}
public boolean insert(int key){
if (currentSize == maxSize)
return false;
Node thenode = new Node(key);
heapArray[currentSize] = thenode;
trickleUp(currentSize ++);
return true;
}
public void trickleUp(int index){
int parent = (index - 1) / 2;
Node bottom = heapArray[index];
while (index > 0 && heapArray[parent].getkey() < bottom.getkey()){
heapArray[index] = heapArray[parent];
index = parent;
parent = (parent - 1) / 2;
}
heapArray[index] = bottom;
}
public Node remove(){
Node root = heapArray[0];
heapArray[0] = heapArray[-- currentSize];
trickleDown(0);
return root;
}
public void trickleDown(int index){
int largeChild;
Node top = heapArray[index];
while (index < currentSize / 2){
int leftChild = 2 * index + 1;
int rightChild = 2 * index + 2;
if (rightChild < currentSize && heapArray[leftChild].getkey() < heapArray[rightChild].getkey())
largeChild = rightChild;
else
largeChild = leftChild;
if (top.getkey() >= heapArray[largeChild].getkey())
break;
heapArray[index] = heapArray[largeChild];
index = largeChild;
}
heapArray[index] = top;
}
public boolean change(int index,int newvalue){
if (index < 0 || index >=currentSize)
return false;
int oldvalue = heapArray[index].getkey();
heapArray[index].setkey(newvalue);
if (oldvalue < newvalue)
trickleUp(index);
else
trickleDown(index);
return true;
}
public void displayHeap(){
System.out.print("heapArray:");
for (int i = 0; i < currentSize; i++) {
if (heapArray[i] != null)
System.out.print(heapArray[i].getkey()+" ");
else
System.out.print("--");
}
System.out.println("");
int nBlanks = 32;
int itemsPerrow = 1;
int column = 0;
int j = 0;
String dots = "........................";
System.out.println(dots + dots);
while (currentSize > 0){
if (column == 0)
for (int i = 0; i < nBlanks; i++) {
System.out.print(" ");
}
System.out.print(heapArray[j].getkey());
if (++ j == currentSize)
break;
if (++ column == itemsPerrow){
nBlanks /= 2;
itemsPerrow *= 2;
column = 0;
System.out.println();
}
else
for (int i = 0; i < nBlanks * 2 - 2; i++)
System.out.print(' ');
}
System.out.println("\n"+dots + dots);
}
}
9.3.HTest.java
package com.cn.heap;
/**
* heap类的测试
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class HTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Heap h = new Heap(10);
h.insert(10);
h.insert(30);
h.insert(20);
h.insert(18);
h.insert(12);
h.displayHeap();
h.remove();
h.displayHeap();
}
}
10.堆的效率:上述操作的时间复杂度是:O(logn)。
11.堆排序实现思路:使用insert()向堆中插入所有无序的数据项,然后重复使用remove()方法,就可以按序移除所有数据项,它的效率和快速排序类似,都是O(NlogN),但快排稍微快些,因为堆插入时的向下筛选多出的比较所占用的时间。
11.1.Node.java
package com.cn.heap;
/**
* 堆的节点类
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class Node {
private int iData;
public Node(int id){
iData = id;
}
public int getkey(){
return iData;
}
public void setkey(int id){
iData = id;
}
}
11.2.Heap.java
package com.cn.heap;
/**
* 堆的实现类
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class Heap {
private Node[] heapArray;
private int maxSize;
private int currentSize;
public Heap(int mx){
maxSize = mx;
heapArray = new Node[maxSize];
currentSize = 0;
}
public boolean isEmpty(){
return currentSize == 0 ;
}
public boolean insert(int key){
if (currentSize == maxSize)
return false;
Node thenode = new Node(key);
heapArray[currentSize] = thenode;
trickleUp(currentSize ++);
return true;
}
public void trickleUp(int index){
int parent = (index - 1) / 2;
Node bottom = heapArray[index];
while (index > 0 && heapArray[parent].getkey() < bottom.getkey()){
heapArray[index] = heapArray[parent];
index = parent;
parent = (parent - 1) / 2;
}
heapArray[index] = bottom;
}
public Node remove(){
Node root = heapArray[0];
heapArray[0] = heapArray[-- currentSize];
trickleDown(0);
return root;
}
public void trickleDown(int index){
int largeChild;
Node top = heapArray[index];
while (index < currentSize / 2){
int leftChild = 2 * index + 1;
int rightChild = 2 * index + 2;
if (rightChild < currentSize && heapArray[leftChild].getkey() < heapArray[rightChild].getkey())
largeChild = rightChild;
else
largeChild = leftChild;
if (top.getkey() >= heapArray[largeChild].getkey())
break;
heapArray[index] = heapArray[largeChild];
index = largeChild;
}
heapArray[index] = top;
}
public boolean change(int index,int newvalue){
if (index < 0 || index >=currentSize)
return false;
int oldvalue = heapArray[index].getkey();
heapArray[index].setkey(newvalue);
if (oldvalue < newvalue)
trickleUp(index);
else
trickleDown(index);
return true;
}
public void displayHeap(){
System.out.print("heapArray:");
for (int i = 0; i < currentSize; i++) {
if (heapArray[i] != null)
System.out.print(heapArray[i].getkey()+" ");
else
System.out.print("--");
}
System.out.println("");
int nBlanks = 32;
int itemsPerrow = 1;
int column = 0;
int j = 0;
String dots = "........................";
System.out.println(dots + dots);
while (currentSize > 0){
if (column == 0)
for (int i = 0; i < nBlanks; i++) {
System.out.print(" ");
}
System.out.print(heapArray[j].getkey());
if (++ j == currentSize)
break;
if (++ column == itemsPerrow){
nBlanks /= 2;
itemsPerrow *= 2;
column = 0;
System.out.println();
}
else
for (int i = 0; i < nBlanks * 2 - 2; i++)
System.out.print(' ');
}
System.out.println("\n"+dots + dots);
}
public void displayArray(){
for (int i = 0; i < maxSize; i++)
System.out.print(heapArray[i].getkey()+" ");
System.out.println();
}
public void insertAt(int index,Node newnode){
heapArray[index] = newnode;
}
public void incrementSize(){
currentSize ++;
}
}
11.3.HeapSort.java
package com.cn.heap; import java.util.Scanner; /**
* 基于堆的排序----堆排序
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class HeapSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int size,j;
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter number of items: ");
size = in.nextInt();
Heap theheap = new Heap(size);
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
int random = (int)(Math.random()*100);
Node node = new Node(random);
theheap.insertAt(i, node);
theheap.incrementSize();
}
System.out.print("random: ");
theheap.displayArray();
for (int i = size / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i --) {
theheap.trickleDown(i);
}
System.out.print("heap: ");
theheap.displayArray();
theheap.displayHeap();
for (int i = size - 1; i >= 0; i --) {
Node node = theheap.remove();
theheap.insertAt(i,node);
}
System.out.print("sorted: ");
theheap.displayArray();
}
}
java数据结构----堆的更多相关文章
- Java数据结构和算法(五)二叉排序树(BST)
Java数据结构和算法(五)二叉排序树(BST) 数据结构与算法目录(https://www.cnblogs.com/binarylei/p/10115867.html) 二叉排序树(Binary S ...
- Java数据结构和算法(四)赫夫曼树
Java数据结构和算法(四)赫夫曼树 数据结构与算法目录(https://www.cnblogs.com/binarylei/p/10115867.html) 赫夫曼树又称为最优二叉树,赫夫曼树的一个 ...
- Java数据结构和算法(十四)——堆
在Java数据结构和算法(五)——队列中我们介绍了优先级队列,优先级队列是一种抽象数据类型(ADT),它提供了删除最大(或最小)关键字值的数据项的方法,插入数据项的方法,优先级队列可以用有序数组来实现 ...
- Java数据结构和算法 - 堆
堆的介绍 Q: 什么是堆? A: 这里的“堆”是指一种特殊的二叉树,不要和Java.C/C++等编程语言里的“堆”混淆,后者指的是程序员用new能得到的计算机内存的可用部分 A: 堆是有如下特点的二叉 ...
- 数据结构-堆 Java实现
数据结构-堆 Java实现. 实现堆自动增长 /** * 数据结构-堆. 自动增长 * */ public class Heap<T extends Comparable> { priva ...
- java数据结构和算法10(堆)
这篇我们说说堆这种数据结构,其实到这里就暂时把java的数据结构告一段落,感觉说的也差不多了,各种常见的数据结构都说到了,其实还有一种数据结构是“图”,然而暂时对图没啥兴趣,等有兴趣的再说:还有排序算 ...
- Java中堆内存和栈内存详解2
Java中堆内存和栈内存详解 Java把内存分成两种,一种叫做栈内存,一种叫做堆内存 在函数中定义的一些基本类型的变量和对象的引用变量都是在函数的栈内存中分配.当在一段代码块中定义一个变量时,ja ...
- Java中堆内存和栈内存详解
Java把内存分成两种,一种叫做栈内存,一种叫做堆内存 在函数中定义的一些基本类型的变量和对象的引用变量都是在函数的栈内存中分配.当在一段代码块中定义一个变量时,java就在栈中为这个变量分配内存空间 ...
- java中堆和堆栈的区别
java中堆和堆栈的区别(一) 1.栈(stack)与堆(heap)都是Java用来在Ram中存放数据的地方.与C++不同,Java自动管理栈和堆,程序员不能直接地设置栈或堆. 2. 栈的优势是,存取 ...
随机推荐
- linux host=${host:-"localhost"}使用方法
localhost=${host:-"localhost"} host 变量未设定或者为空,host取"-"后面的值;否则host=$host host=${h ...
- 关于Fragment的onActivityResult 不执行
1.getActivity().startActivityForResult(); 与 fragment.startActivityForActivity(): getActivity().star ...
- Disruptor学习杂记
慎入,有点乱,只是学习记录,disruptor_2.10.4 1.Disruptor对象有一个EventProcessorRepository对象 2.EventProcessorReposito ...
- 数据结构之 字符串---字符串匹配(kmp算法)
串结构练习——字符串匹配 Time Limit: 1000MS Memory limit: 65536K 题目描述 给定两个字符串string1和string2,判断string2是否为strin ...
- 深入理解c语言——‘\0’ ,‘0’, “0” ,0之间的区别
看来基础还是很重要的,基础不扎实就难以学好c语言,就别说写出高质量的c语言代码了.今天,我就被这个问题折磨的不行了,哈哈,不过现在终于明白了‘\0’ ,‘0’, “0” 之间的区别了.困惑和快乐与你分 ...
- hdu-5003 Osu!(水题)
题目链接: Osu! time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/65536 K (Java/Others) Prob ...
- 用python做自动化测试--Python实现远程性能监控
http://blog.csdn.net/powerccna/article/details/8044222 在性能测试中,监控被测试服务器的性能指标是个重要的工作,包括CPU/Memory/IO/N ...
- react之redux增加删除数字
比如在页面中添加和删除‘222’ action.js export const ADD= 'ADD'; export const RED='RED'; export const add=(str)=& ...
- android jni java类型与c语言类型互换
1.java String转换 C str char* Jstring2CStr(JNIEnv* env, jstring jstr) { char* rtn = NULL; jclass clsst ...
- 【旧文章搬运】关于windbg搜索符号文件的一点说明
原文发表于百度空间,2010-09-07========================================================================== 本来只是打 ...
