Android笔记--LayoutInflator源码和使用分析
LayoutInflator源码分析
获取LayoutInflator对象
获取LayoutInflator的方式有两种:
- 使用LayoutInflator.from(Context context)可以获取到LayoutInflator对象。
- (LayoutInflater)context.getSystemService(Context.LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE)
第一种本质也是调用第二种方式。
从本质上看context无论是以何种形式传入,最终都是利用binder获取的远程Service的能力
进行XML文件的填装工作。
LayoutInflator方法
LyaoutInflator含有的方法如下:
其中核心功能地一个系列就是inflate方法和rInflate方法
inflate方法 | 作用是把XML文件以View形式实例化到内存中
rInflate方法 | 作用是递归调用把XML中相应的嵌套布局结构也实例化出来并添加到XML的根布局中
inflate方法
inflate系列方法最终调用的都是:
public View inflate(XmlPullParser parser, @Nullable ViewGroup root, boolean attachToRoot)
方法
但是实际上最常用的是:
public View inflate(@LayoutRes int resource, @Nullable ViewGroup root, boolean attachToRoot)
public View inflate(@LayoutRes int resource, @Nullable ViewGroup root)
因为XmlPullParser对象并不是普通的XML的来的。而是在编译器XML预编译出来的文件得到的。所以普通的XML在这里转换成
XmlPullParser对象并不允许。所以必须借助Resource得到布局id进行相关操作。
参数代表的含义:
- int resource | XML布局资源的id.(e.g. R.layout.main_activity)
- ViewGroup root | 父root对象,若attachTRoot==true, 则把resource代表的布局对象填充到root.
若attachToRoot == false,则resource代表的布局只是利用root的LayoutParams即布局参数,但是不往root里添加。 - attachToRoot | true 则返回父布局root, false 则返回XML对应得视图对象(源码中为temp对象)
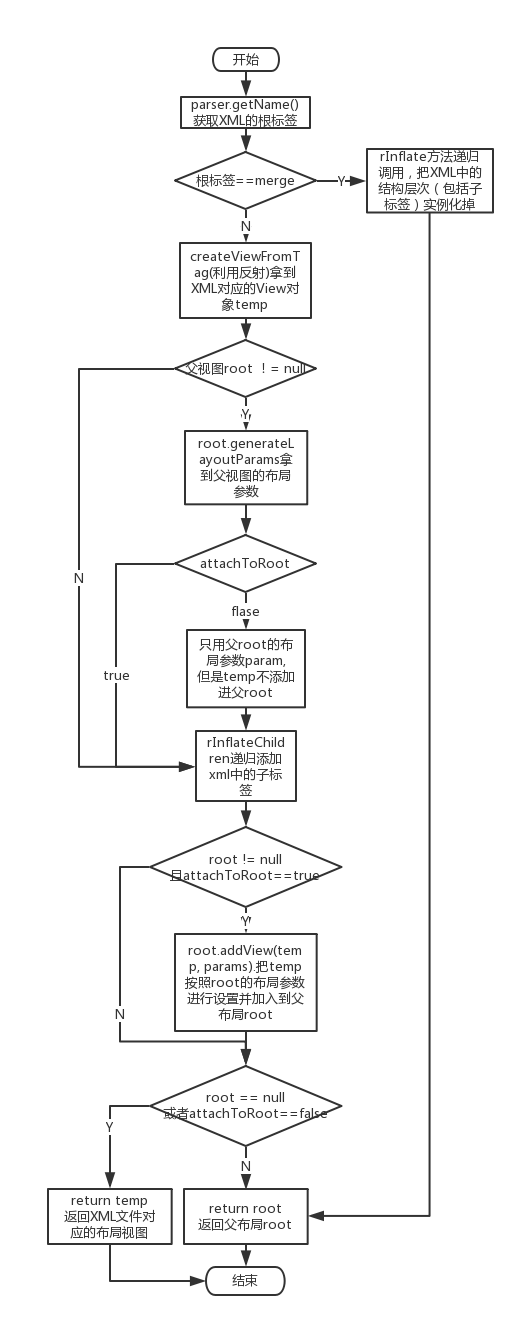
inflate方法的调用流程如下:
下面用代码做一些试验:
这个是activity_main.xml:
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:id="@+id/mainView"
tools:context="com.example.myapplication.MainActivity"
android:orientation="vertical">
</LinearLayout>
这个是一个textview 在layout文件夹命名为pink.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<TextView xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:background="@color/colorAccent"
android:text="red">
</TextView>
MainActivity.java
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private TextView view;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
ViewGroup parent = (ViewGroup) findViewById(R.id.mainView);
// result: layout_height=wrap_content layout_width=match_parent
view = (TextView) LayoutInflater.from(this).inflate(R.layout.pink, null);
parent.addView(view);
// result: layout_height=100 layout_width=100
view = (TextView) LayoutInflater.from(this).inflate(R.layout.pink, null);
parent.addView(view, 100, 100);
// result: layout_height=25dp layout_width=25dp
// view=textView due to attachRoot=false
view = (TextView) LayoutInflater.from(this).inflate(R.layout.pink, parent, false);
parent.addView(view);
// result: layout_height=25dp layout_width=25dp
// parent.addView not necessary as this is already done by attachRoot=true
// view=root due to parent supplied as hierarchy root and attachRoot=true
ViewGroup p = LayoutInflater.from(this).inflate(R.layout.pink, parent, true);
}
}
在开发者眼里这个inflate有时候显得很诡异。下面就意义分析一下上面的结果的原因:
inflate(R.layout.pink, null) 父布局addView(view)
// result: layout_height=wrap_content layout_width=match_parent
view = (TextView) LayoutInflater.from(this).inflate(R.layout.pink, null);
parent.addView(view);
这里的结果是宽match_parent 高wrap_content
刚开始肯定心里满是WTF,因为这里根本没有给pink布局文件指定一个父root.那pink在父布局中是怎么判定自己的布局参数的呢?
其实秘密就在addView方法中
/**
*
Adds a child view. If no layout parameters are already set on the child, the
* default parameters for this ViewGroup are set on the child.
*
*
Note: do not invoke this method from
* {@link #draw(android.graphics.Canvas)}, {@link #onDraw(android.graphics.Canvas)},
* {@link #dispatchDraw(android.graphics.Canvas)} or any related method.
*
* @param child the child view to add
*
* @see #generateDefaultLayoutParams()
*/
public void addView(View child) {
addView(child, -1);
}
/**
* Adds a child view. If no layout parameters are already set on the child, the
* default parameters for this ViewGroup are set on the child.
*
* <p><strong>Note:</strong> do not invoke this method from
* {@link #draw(android.graphics.Canvas)}, {@link #onDraw(android.graphics.Canvas)},
* {@link #dispatchDraw(android.graphics.Canvas)} or any related method.</p>
*
* @param child the child view to add
* @param index the position at which to add the child
*/
public void addView(View child, int index) {
if (child == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot add a null child view to a ViewGroup");
}
LayoutParams params = child.getLayoutParams();
if (params == null) {
params = generateDefaultLayoutParams();//这里是关键,不通的ViewGroup会重新此方法
if (params == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("generateDefaultLayoutParams() cannot return null");
}
}
addView(child, index, params);
}
@Override//此处我们用的LinearLayout 这里是他的重新实现
protected LayoutParams generateDefaultLayoutParams() {
if (mOrientation == HORIZONTAL) {
return new LayoutParams(LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
} else if (mOrientation == VERTICAL) {
return new LayoutParams(LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT, LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
}
return null;
}
通过源码可以看出addView对于要添加的View的默认布局参数是依据不同的ViewGroup来的。ViewGroup默认宽高都是wrap_content
。而LinearLayout对子View要求的默认布局参数是根据布局方向定的:
- 水平布局 | 宽高均为wrap_content
- 垂直布局 | 宽是match_parent 高是warp_content
所以就可以解释为什么在指定root为null的时候addView得到的是宽是match_parent 高是warp_content了。因为我么用了垂直布局
inflate(R.layout.pink, null) 父布局parent.addView(view, 100, 100)
这里依旧没有为pink指定其在父布局中的布局参数。但是父布局调用了parent.addView(view, 100, 100)。
/**
* Adds a child view with this ViewGroup's default layout parameters and the
* specified width and height.
*
* <p><strong>Note:</strong> do not invoke this method from
* {@link #draw(android.graphics.Canvas)}, {@link #onDraw(android.graphics.Canvas)},
* {@link #dispatchDraw(android.graphics.Canvas)} or any related method.</p>
*
* @param child the child view to add
*/
public void addView(View child, int width, int height) {
final LayoutParams params = generateDefaultLayoutParams();
params.width = width;
params.height = height;
addView(child, -1, params);
}
源码也很明确,虽然布局参数依旧是父布局默认的。但是为布局参数重新指定了宽高,覆盖了默认值。所以这样指定可以改掉
pink在父布局中的布局参数。
inflate(R.layout.pink, parent, false)
这里为pink指定了其在父布局中应当使用的布局参数是parent的布局参数。但是并不把pink布局加载到parent视图中。
返回的依旧是pink对应的布局。
这个过程其实就是上面的流程图中的过程。
这里不再分析。
inflate(R.layout.pink, parent, true)
这里同样是上述的流程图过程。pink的布局参数用parent的布局参数。并且把pink布局视图放到parent中。返回的是
parent。
这里需要注意,因为这里是传入的parent是mian_view对应的视图,所以返回的也是parent.但是如果这里传入的是
另外的ViewGroup,那么返回的就是那个ViewGroup了。
最具有迷惑性的属性是root 和attachToRoot
root相对来好解释一点:
root就仅仅是为xml文件提供一个布局参数LayoutParams。用于限定大小和位置。不论attachToRoot true或者false
这个布局参数都会实实在在的应用在xml对应的视图对象上。
attachToRoot | true xml布局对应的对象利用root的布局参数限定来填充到root对象中。返回的是root对象。
attachToRoot | false xml布局对应的对象利用root的布局参数但是返回的是xml对应对象的根布局对象。要想把返回的View
加到父布局中就要用其他的办法。
但是什么时候用true 什么时候用false呢?
用true的场景:
假如父布局是一个LinearLayout,在父布局上加一个button,那么直接用true即可
下面这两种方式是等价的
inflater.inflate(R.layout.custom_button, mLinearLayout, true);
inflater.inflate(R.layout.custom_button, mLinearLayout);
在root不空时,attachToRoot是true自定义View
自定义View初始化的时候,目的就是为了给自定义的View加一个自己的布局上去。
private void init() {
LayoutInflater inflater = LayoutInflater.from(getContext());
inflater.inflate(R.layout.view_with_merge_tag, this);
}
总结: 总结一下就是,在我们只是需要往root上加布局对象。而不需要的到返回的XML布局对象时。使用true即可
需要false的场景:
比如有个button的布局文件。想在加到父布局之前做一些定制。那么这是肯定需要先拿到符合父布局布局参数的button
的。做完定制以后再添加到父布局中
Button button = (Button) inflater.inflate(R.layout.custom_button, mLinearLayout, false);
。。。。。
mLinearLayout.addView(button);RecyclerView 子类中onCreateViewHolder方法中需要使用false
public ViewHolder onCreateViewHolder(ViewGroup parent, int viewType) {
LayoutInflater inflater = LayoutInflater.from(getActivity());
View view = inflater.inflate(android.R.layout.list_item_recyclerView, parent, false);
return new ViewHolder(view);
}
因为RecyclerView负责呈现和填充XML布局的时机
Fragment 中onCreateView方法要使用false
FragmentManager fragmentManager = getSupportFragmentManager();
Fragment fragment = fragmentManager.findFragmentById(R.id.root_viewGroup);if (fragment == null) {
fragment = new MainFragment();
fragmentManager.beginTransaction()
.add(R.id.root_viewGroup, fragment)
.commit();
}//这里的root_viewGroup就是fragment中onCreateView方法第二个参数的视图对象。
//而fragment_layout填充附加到parentViewGroup的过程是FragmentManager 来做的
//所以你一定不能为同一个parentViewGroup添加两次,所以下面要传false
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup parentViewGroup, Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_layout, parentViewGroup, false);
…
return view;
}
当然root参数也可以传null。但是可能会带来不符合预期的结果。因为root为null的情况要有ViewGroup及其子类自己决定。
而你在XML布局中指定的参数就会失效。所以为了保证XML中的布局参数就是我们想要XML展示的。那就需要传入root.
例外情况:AlertDialog。inflater.inflate(R.layout.custom_alert_dialog, null);这是合理的。
因为AlertDialog会为所有的布局都采取match_parent
总结
为了保证结果是符合预期的。需要尽量按照下面的方案来操作:
- 只要有父布局,就一定穿进去父布局当root.
- 避免给root传null因为不同的viewGroup实现的generateDefaultLayoutParams不同
- 只要我们不负责把xml附加到root上,attachToRoot 参数传false.
- 同一个XML不要为同一个ViewGroup传两次true,否则報异常
- 自定义View attachToRoot传true
参考:
https://www.bignerdranch.com/blog/understanding-androids-layoutinflater-inflate/
Android笔记--LayoutInflator源码和使用分析的更多相关文章
- SLAM学习笔记 - ORB_SLAM2源码运行及分析
参考资料: DBow2的理解 单目跑TUM数据集的运行和函数调用过程 跑数据集不需要ros和相机标定,进入ORB_SLAM目录,执行以下命令: ./Examples/Monocluar/mono_tu ...
- 从源码的角度分析ViewGruop的事件分发
从源码的角度分析ViewGruop的事件分发. 首先我们来探讨一下,什么是ViewGroup?它和普通的View有什么区别? 顾名思义,ViewGroup就是一组View的集合,它包含很多的子View ...
- Android 开源项目源码解析(第二期)
Android 开源项目源码解析(第二期) 阅读目录 android-Ultra-Pull-To-Refresh 源码解析 DynamicLoadApk 源码解析 NineOldAnimations ...
- 安卓图表引擎AChartEngine(二) - 示例源码概述和分析
首先看一下示例中类之间的关系: 1. ChartDemo这个类是整个应用程序的入口,运行之后的效果显示一个list. 2. IDemoChart接口,这个接口定义了三个方法, getName()返回值 ...
- android仿漫画源码、抽奖转盘、Google相册、动画源码等
Android精选源码 android实现仿今日头条的开源项目 波浪效果,实现流量的动态显示 美妆领域的app, 集成了摄像头取色, 朋友圈, 滤镜等 android仿漫画源码 android一个视差 ...
- android狼人杀源码,桌面源码,猎豹快切源码
Android精选源码 android实现狼人杀app源码 android实现精心打造的Android基础框架源码 android热门电影的客户端源码 android 实现桌面的Launcher源码 ...
- Android 视频 教程 源码 电子书 网址
资源名称 资源地址 下载量 好评率8天快速掌握Android视频教程67集(附源码)http://down.51cto.com/zt/2197 32157Android开发入门之实战技巧和源码 htt ...
- 第一部分:开发前的准备-第八章 Android SDK与源码下载
第8章 Android SDK与源码下载 如果你是新下载的SDK,请阅读一下步骤了解如何设置SDK.如果你已经下载使用过SDK,那么你应该使用AVD Manager,来更新即可. 下面是构建Andro ...
- Hadoop学习笔记(9) ——源码初窥
Hadoop学习笔记(9) ——源码初窥 之前我们把Hadoop算是入了门,下载的源码,写了HelloWorld,简要分析了其编程要点,然后也编了个较复杂的示例.接下来其实就有两条路可走了,一条是继续 ...
随机推荐
- 《Java多线程编程核心技术》读后感(十一)
方法join的使用 在很多情况下,主线程创建并启动子线程,如果子线程中要进行大量的耗时运算,主线程往往将早于子线程结束之前结束.这时,如果主线程想等待子线程执行完之后再结束,比如子线程处理一个数据,主 ...
- Jodd发送邮件
public static void main(String[] args) { Email email = Email.create().from("xxx") .to(&quo ...
- IE浏览器弹出窗口
//弹出一个对话框 参数的顺序: url, iWidth, iHeight, vArguments function openDialog() { var url, len = arguments.l ...
- 将Angular6自己定义的模块发布成npm包
创建自己的模块组件 1. ng new 一个工程 2. ng g m 创建模块 例如我这里的modules文件下创建header模块 3. ng g c modules/head 创建一个hear组件 ...
- 无监督学习:Linear Dimension Reduction(线性降维)
一 Unsupervised Learning 把Unsupervised Learning分为两大类: 化繁为简:有很多种input,进行抽象化处理,只有input没有output 无中生有:随机给 ...
- 关于$_SERVER['PHP_SELF']用法及其安全性---改良
网站来源:http://www.5idev.com/p-php_server_php_self.shtml PHP 使用 $_SERVER['PHP_SELF'] 获取当前页面地址及其安全性问题 PH ...
- GDB 远程调试Linux (CentOS)
1.引用: https://blogs.msdn.microsoft.com/vcblog/2016/03/30/visual-c-for-linux-development/ 注意安装gdbserv ...
- linux 安装mysql 5.7
1.下载安装包http://dev.mysql.com/downloads/mysql/#downloads推荐下载通用安装方法的TAR包(http://cdn.mysql.com//Download ...
- git配置命令
一.Git安装及密钥的生成 1.下载Git软件:http://msysgit.github.io/ 2.桌面右键 Git Bash Here 打开git命令行: 3.ssh-keygen -t rsa ...
- 小白入门AI教程:教你快速搭建大数据平台『Hadoop+Spark』
Apache Spark 简介 Apache Spark 是专为大规模数据处理而设计的快速通用的计算引擎.Spark是UC Berkeley AMP lab (加州大学伯克利分校的AMP实验室)所开源 ...
