ASP.NET Core - 从Program和Startup开始
Program
我们先看一下1.x和2.x的程序入口项的一个差异
1.x
public class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
var host = new WebHostBuilder()
.UseKestrel()
.UseContentRoot(Directory.GetCurrentDirectory())
.UseIISIntegration()
.UseStartup<Startup>()
.Build(); host.Run();
}
}
2.x
public class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
BuildWebHost(args).Run();
} public static IWebHost BuildWebHost(string[] args) =>
WebHost.CreateDefaultBuilder(args)
.UseStartup<Startup>()
.Build();
}
2.x对默认配置进行了简化,把一些基本配置移动了 CreateDefaultBuilder 方法中
public static IWebHostBuilder CreateDefaultBuilder(string[] args)
{
IWebHostBuilder hostBuilder = new WebHostBuilder()
.UseKestrel((Action<WebHostBuilderContext, KestrelServerOptions>) ((builderContext, options) => options.Configure((IConfiguration) builderContext.Configuration.GetSection("Kestrel"))))
.UseContentRoot(Directory.GetCurrentDirectory())
.ConfigureAppConfiguration((Action<WebHostBuilderContext, IConfigurationBuilder>) ((hostingContext, config) =>
{
IHostingEnvironment hostingEnvironment = hostingContext.HostingEnvironment;
config.AddJsonFile("appsettings.json", true, true)
.AddJsonFile("appsettings." + hostingEnvironment.EnvironmentName + ".json", true, true);
if (hostingEnvironment.IsDevelopment())
{
Assembly assembly = Assembly.Load(new AssemblyName(hostingEnvironment.ApplicationName));
if (assembly != (Assembly) null)
config.AddUserSecrets(assembly, true);
}
config.AddEnvironmentVariables();
if (args == null)
return;
config.AddCommandLine(args);
}))
.ConfigureLogging((Action<WebHostBuilderContext, ILoggingBuilder>) ((hostingContext, logging) =>
{
logging.AddConfiguration((IConfiguration) hostingContext.Configuration.GetSection("Logging"));
logging.AddConsole();
logging.AddDebug();
}))
.ConfigureServices((Action<WebHostBuilderContext, IServiceCollection>) ((hostingContext, services) =>
{
services.PostConfigure<HostFilteringOptions>((Action<HostFilteringOptions>) (options =>
{
if (options.AllowedHosts != null && options.AllowedHosts.Count != )
return;
string str = hostingContext.Configuration["AllowedHosts"];
string[] strArray1;
if (str == null)
strArray1 = (string[]) null;
else
strArray1 = str.Split(new char[]{ ';' }, StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries);
string[] strArray2 = strArray1;
HostFilteringOptions filteringOptions = options;
string[] strArray3;
if (strArray2 == null || strArray2.Length == )
strArray3 = new string[]{ "*" };
else
strArray3 = strArray2;
filteringOptions.AllowedHosts = (IList<string>) strArray3;
}));
services.AddSingleton<IOptionsChangeTokenSource<HostFilteringOptions>>((IOptionsChangeTokenSource<HostFilteringOptions>) new ConfigurationChangeTokenSource<HostFilteringOptions>(hostingContext.Configuration));
services.AddTransient<IStartupFilter, HostFilteringStartupFilter>();
}))
.UseIISIntegration()
.UseDefaultServiceProvider((Action<WebHostBuilderContext, ServiceProviderOptions>) ((context, options) => options.ValidateScopes = context.HostingEnvironment.IsDevelopment()));
if (args != null)
hostBuilder.UseConfiguration((IConfiguration) new ConfigurationBuilder().AddCommandLine(args).Build());
return hostBuilder;
}
这里我们可以看到在CreateDefaultBuilder生成器中,定义了默认使用的Web服务器(UseKestrel,使用的是KestrelServer)和一些基础的配置,包括文件路径、应用配置(按appsettings.json,appsettings.{Environment}.json次序加载)、环境变量、日志,IIS集成等,如果需要的话,还可以指定其他类型的Server(IIS HTTP Server,HTTP.sys Server)和自定义Server(继承IServer)。
返回到Program中,在获取到了WebHostBuilder之后紧接着就指定了启动类UseStartup<Startup>(),Build方法是WebHostBuilder最终的目的(在这个方法里面构建了管道),将构造一个WebHost返回,这里引出了我们在ASP.NET Core - 开篇所说的重要对象:WebHost,并且运行它的Run方法用于启动应用并开始监听所有到来的HTTP请求。
Startup
Startup方法用来指定应用程序的启动类,这里主要有两个作用:
- 配置应用需要的服务(服务注册,ConfigureServices方法)。
- 创建应用的请求处理处理管道(Configure方法)。
public class Startup
{
private readonly IHostingEnvironment _env;
private readonly IConfiguration _config;
private readonly ILoggerFactory _loggerFactory; public Startup(IHostingEnvironment env, IConfiguration config,
ILoggerFactory loggerFactory)
{
_env = env;
_config = config;
_loggerFactory = loggerFactory;
} // 注入服务到容器中
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
var logger = _loggerFactory.CreateLogger<Startup>(); if (_env.IsDevelopment())
{
// Development service configuration
logger.LogInformation("Development environment");
}
else
{
// Non-development service configuration
logger.LogInformation($"Environment: {_env.EnvironmentName}");
} ...
} // 配置Http请求处理管道
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app)
{
...
}
}
Startup 类的 执行顺序:构造 -> ConfigureServices -> Configure
1)Startup Constructor(构造函数)
上面的构造函数引出了我们开篇说的三个重要对象:IHostingEnvironment ,IConfiguration ,ILoggerFactory ,这里先讲构造函数的作用,这些对象后面会分篇讲。显而易见,这里主要是通过依赖注入实例化了该类中需要用到的对象(根据自己的业务),比较简单。
2) ConfigureServices
首先这个方法是可选的,它的参数是IServiceCollection,这也是我们开篇说的重要对象,而且是非常重要的对象,这是一个原生的Ioc容器,所有需要用到的服务都可以注册到里面,一般是通过约定风格services.Addxxx, 这样就可以让这些服务在应用和Configure方法使用(用来构建管道)。
3)Configure
用于构建管道处理Http请求,管道中的每个中间件(Middleware)组件负责请求处理和选择是否将请求传递到管道中的下一个组件,在这里我们可以添加自己想要的中间件来处理每一个Http请求,一般是使用上面的ConfigureServices方法中注册好的服务,一般的用法是 app.Usexxx,这个Usexxx方法是基于IApplicationBuilder的扩展。
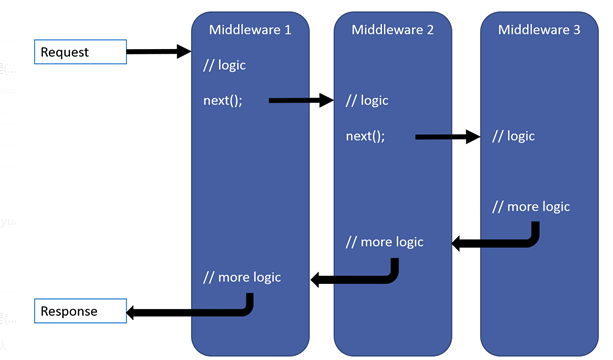
需要注意的有三个地方:
- 应尽早在管道中调用异常处理委托,这样就能捕获在后续管道发生的异常,所以能看到微软的经典写法是先把异常处理的中间件写在最前面,这样方可捕获稍后调用中发生的任何异常。
- 当某个中间件不将请求传递给下一个中间件时,这被称为“请求管道短路”。 我们通常都会需要短路,这样可以避免资源浪费,类似与当抛出异常时我们将不会再往下请求,因为这完全没有必要:)
- 如果你想某些模块不需要授权就能访问,应把这些模块放在认证模块前面,所以我们一般会把访问静态文件的中间件放在认证模块的前面。
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app)
{
if (env.IsDevelopment())
{// Use the Developer Exception Page to report app runtime errors.
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
}
else
{// Enable the Exception Handler Middleware to catch exceptions
// thrown in the following middlewares.
app.UseExceptionHandler("/Error");
}
// Return static files and end the pipeline.
app.UseStaticFiles(); // Use Cookie Policy Middleware to conform to EU General Data
// Protection Regulation (GDPR) regulations.
app.UseCookiePolicy(); // Authenticate before the user accesses secure resources.
app.UseAuthentication(); // If the app uses session state, call Session Middleware after Cookie
// Policy Middleware and before MVC Middleware.
app.UseSession(); // Add MVC to the request pipeline.
app.UseMvc();
}
如果你不想使用Startup类的话,可以使用以下方式配置自己的服务注册和管道构建,虽然这种方式有点odd :)
public class Program
{
public static IHostingEnvironment HostingEnvironment { get; set; }
public static IConfiguration Configuration { get; set; } public static void Main(string[] args)
{
CreateWebHostBuilder(args).Build().Run();
} public static IWebHostBuilder CreateWebHostBuilder(string[] args) =>
WebHost.CreateDefaultBuilder(args)
.ConfigureAppConfiguration((hostingContext, config) =>
{
})
.ConfigureServices(services =>
{
...
})
.Configure(app =>
{
var loggerFactory = app.ApplicationServices
.GetRequiredService<ILoggerFactory>();
var logger = loggerFactory.CreateLogger<Program>();
var env = app.ApplicationServices.GetRequiredServices<IHostingEnvironment>();
var config = app.ApplicationServices.GetRequiredServices<IConfiguration>(); logger.LogInformation("Logged in Configure"); if (env.IsDevelopment())
{
...
}
else
{
...
} var configValue = config["subsection:suboption1"]; ...
});
}
这里需要注意的是,Startup只是一个概念,类的名字是可以任意的,只需要在启动项UseStartup中指定你这个启动类即可。
总结
正如ASP.NET Core - 开篇所说的,一个ASP.NET Core应用其实就是一个控制台应用程序,它在应用启动时构建一个 Web 服务器,并且通过指定的Startup类来构建应用服务和请求管道,进而监听和处理所有的Http请求。
ASP.NET Core - 从Program和Startup开始的更多相关文章
- 如何在 asp.net core 3.x 的 startup.cs 文件中获取注入的服务
一.前言 从 18 年开始接触 .NET Core 开始,在私底下.工作中也开始慢慢从传统的 mvc 前后端一把梭,开始转向 web api + vue,之前自己有个半成品的 asp.net core ...
- asp.net core 系列 2 启动Startup类介绍
一.Startup类 ASP.NET Core 应用是一个控制台应用,它在其 Program.Main 方法中创建 Web 服务器.其中Main方法是应用的托管入口点,Main 方法调用 WebHos ...
- asp.netcore 3.1 program、Startup 类详解
Program类 public class Program { /// <summary> /// 应用程序入口 /// 1.asp.netcore 本质上是控制台程序 /// </ ...
- ASP.NET Core Web API中Startup的使用技巧
Startup类和服务配置 STARTUP CLASS AND THE SERVICE CONFIGURATION 在 Startup 类中,有两个方法:ConfigureServices 是用于 ...
- ASP.NET Core[源码分析篇] - Startup
应用启动的重要类 - Startup 在ASP.NET Core - 从Program和Startup开始这篇文章里面,我们知道了Startup这个类的重要性,它主要负责了: 配置应用需要的服务(服务 ...
- ASP.NET Core 运行原理剖析2:Startup 和 Middleware(中间件)
ASP.NET Core 运行原理剖析2:Startup 和 Middleware(中间件) Startup Class 1.Startup Constructor(构造函数) 2.Configure ...
- ASP.NET Core 运行原理剖析1:初始化WebApp模版并运行
ASP.NET Core 运行原理剖析1:初始化WebApp模版并运行 核心框架 ASP.NET Core APP 创建与运行 总结 之前两篇文章简析.NET Core 以及与 .NET Framew ...
- ASP.NET Core 运行原理剖析
1. ASP.NET Core 运行原理剖析 1.1. 概述 1.2. 文件配置 1.2.1. Starup文件配置 Configure ConfigureServices 1.2.2. appset ...
- ASP.NET Core 实战:构建带有版本控制的 API 接口
一.前言 在上一篇的文章中,主要是搭建了我们的开发环境,同时创建了我们的项目模板框架.在整个前后端分离的项目中,后端的 API 接口至关重要,它是前端与后端之间进行沟通的媒介,如何构建一个 “好用” ...
随机推荐
- ratelimit.go
// The ratelimit package provides an efficient token bucket implementation , false } tb.avai ...
- mime.go
package manager import ( "mime" "path" ) //初始化数据 func init() { if mi ...
- im2col:将卷积运算转为矩阵相乘
目录 im2col实现 优缺点分析 参考 博客:blog.shinelee.me | 博客园 | CSDN im2col实现 如何将卷积运算转为矩阵相乘?直接看下面这张图,以下图片来自论文High P ...
- FreemarkerJavaDemo【Android将表单数据生成Word文档的方案之一(基于freemarker2.3.28,只能java生成)】
版权声明:本文为HaiyuKing原创文章,转载请注明出处! 前言 这个方案只能在java中运行,无法在Android项目中运行.所以此方案是:APP将表单数据发送给后台,后台通过freemarker ...
- mySql入门-(一)
学了很多乱七杂八的东西,但是依然停留在前端,在工作中一直和后端交流,但是不太了解数据库是怎么回事,为了加强学习,准备学习一些关于数据库相关的东西. 说起数据库可能会有很多很多,SQLServer.Or ...
- go语言调度器源代码情景分析之六:go汇编语言
go语言runtime(包括调度器)源代码中有部分代码是用汇编语言编写的,不过这些汇编代码并非针对特定体系结构的汇编代码,而是go语言引入的一种伪汇编,它同样也需要经过汇编器转换成机器指令才能被CPU ...
- 【JVM虚拟机】(5)---深入理解JVM-Class中常量池
深入理解Class---常量池 一.概念 1.jvm生命周期 启动:当启动一个java程序时,一个jvm实例就诞生了,任何一个拥有main方法的class都可以作为jvm实例运行的起点. 运行:mai ...
- 六大设计原则(一)SRP单一职责原则
单一职责原则SRP(Single reponsibility principle) BO(Business Object):业务对象 Biz(Business Logic):业务逻辑 SRP最简单的例 ...
- 结合JDK源码看设计模式——原型模式
定义: 指原型实例指定创建对象的种类,并且通过拷贝这些原型创建新的对象.不需要知道任何创建的细节,不调用构造函数适用场景: 类初始化的时候消耗较多资源 new产生的对象需要非常繁琐的过程 构造函数比较 ...
- NFS挂载异常 mount.nfs: Input/output error
[root@localhost ~]# vi /etc/exports #增加/nfs 192.168.10.132(rw,no_root_squash,no_all_squash,async) [r ...
