行为识别TSM训练ucf101数据集
序言
最近有个行为检测的需求,打算用行为识别做,纯小白入这个方向,啃了两周的TSM原理和源码,训练好自己的数据集后,发现好像没法应用到自己的需求场景??玛德!算了,还是要记录一下。原理就没别要讲了,网上很多,感兴趣的可以自己去搜。
一、数据准备
首先把代码git下来temporal-shift-module,然后作者提供了一个mobilenetv2版本的手势识别在线demo,使用了tvm推理,在Jeston Nano能够达到实时,看着还不错的样子,赶紧试一下,可是我没有nano怎么办?没关系,修改一下。
该demo放在online_demo目录中的main.py文件,可是没有nano,又不想安装tvm怎么办?问题不大,修改一下,用pytorch推理!把改下的模型下载下来,README.md中有提供下载链接,推荐使用迅雷下载。在noline_demo下新建一个demo.py文件,将tvm的那部分推理换成pytorch的推理即可,基于main.py修改后的代码如下:
import torch
from online_demo.mobilenet_v2_tsm import MobileNetV2
import cv2
import numpy as np
import torchvision
from PIL import Image
import time
SOFTMAX_THRES = 1
HISTORY_LOGIT = True
REFINE_OUTPUT = True
shift_buffer = [torch.zeros([1, 3, 56, 56]),
torch.zeros([1, 4, 28, 28]),
torch.zeros([1, 4, 28, 28]),
torch.zeros([1, 8, 14, 14]),
torch.zeros([1, 8, 14, 14]),
torch.zeros([1, 8, 14, 14]),
torch.zeros([1, 12, 14, 14]),
torch.zeros([1, 12, 14, 14]),
torch.zeros([1, 20, 7, 7]),
torch.zeros([1, 20, 7, 7])]
class GroupScale(object):
""" Rescales the input PIL.Image to the given 'size'.
'size' will be the size of the smaller edge.
For example, if height > width, then image will be
rescaled to (size * height / width, size)
size: size of the smaller edge
interpolation: Default: PIL.Image.BILINEAR
"""
def __init__(self, size, interpolation=Image.BILINEAR):
self.worker = torchvision.transforms.Scale(size, interpolation)
def __call__(self, img_group):
return [self.worker(img) for img in img_group]
class GroupCenterCrop(object):
def __init__(self, size):
self.worker = torchvision.transforms.CenterCrop(size)
def __call__(self, img_group):
return [self.worker(img) for img in img_group]
class Stack(object):
def __init__(self, roll=False):
self.roll = roll
def __call__(self, img_group):
if img_group[0].mode == 'L':
return np.concatenate([np.expand_dims(x, 2) for x in img_group], axis=2)
elif img_group[0].mode == 'RGB':
if self.roll:
return np.concatenate([np.array(x)[:, :, ::-1] for x in img_group], axis=2)
else:
return np.concatenate(img_group, axis=2)
class ToTorchFormatTensor(object):
""" Converts a PIL.Image (RGB) or numpy.ndarray (H x W x C) in the range [0, 255]
to a torch.FloatTensor of shape (C x H x W) in the range [0.0, 1.0] """
def __init__(self, div=True):
self.div = div
def __call__(self, pic):
if isinstance(pic, np.ndarray):
# handle numpy array
img = torch.from_numpy(pic).permute(2, 0, 1).contiguous()
else:
# handle PIL Image
img = torch.ByteTensor(torch.ByteStorage.from_buffer(pic.tobytes()))
img = img.view(pic.size[1], pic.size[0], len(pic.mode))
# put it from HWC to CHW format
# yikes, this transpose takes 80% of the loading time/CPU
img = img.transpose(0, 1).transpose(0, 2).contiguous()
return img.float().div(255) if self.div else img.float()
class GroupNormalize(object):
def __init__(self, mean, std):
self.mean = mean
self.std = std
def __call__(self, tensor):
rep_mean = self.mean * (tensor.size()[0] // len(self.mean))
rep_std = self.std * (tensor.size()[0] // len(self.std))
# TODO: make efficient
for t, m, s in zip(tensor, rep_mean, rep_std):
t.sub_(m).div_(s)
return tensor
def get_transform():
cropping = torchvision.transforms.Compose([
GroupScale(256),
GroupCenterCrop(224),
])
transform = torchvision.transforms.Compose([
cropping,
Stack(roll=False),
ToTorchFormatTensor(div=True),
GroupNormalize([0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
])
return transform
def transform(frame: np.ndarray):
# 480, 640, 3, 0 ~ 255
frame = cv2.resize(frame, (224, 224)) # (224, 224, 3) 0 ~ 255
frame = frame / 255.0 # (224, 224, 3) 0 ~ 1.0
frame = np.transpose(frame, axes=[2, 0, 1]) # (3, 224, 224) 0 ~ 1.0
frame = np.expand_dims(frame, axis=0) # (1, 3, 480, 640) 0 ~ 1.0
return frame
def process_output(idx_, history):
# idx_: the output of current frame
# history: a list containing the history of predictions
if not REFINE_OUTPUT:
return idx_, history
max_hist_len = 20 # max history buffer
# mask out illegal action
# 等于这些类时默认为2
if idx_ in [7, 8, 21, 22, 3]:
idx_ = history[-1]
# use only single no action class
# 做其他事情默认也为2
if idx_ == 0:
idx_ = 2
# history smoothing
if idx_ != history[-1]:
if not (history[-1] == history[-2]): # and history[-2] == history[-3]):
idx_ = history[-1]
history.append(idx_)
history = history[-max_hist_len:]
return history[-1], history # 返回本帧结果和历史结果
catigories = [
"Doing other things", # 0
"Drumming Fingers", # 1
"No gesture", # 2
"Pulling Hand In", # 3
"Pulling Two Fingers In", # 4
"Pushing Hand Away", # 5
"Pushing Two Fingers Away", # 6
"Rolling Hand Backward", # 7
"Rolling Hand Forward", # 8
"Shaking Hand", # 9
"Sliding Two Fingers Down", # 10
"Sliding Two Fingers Left", # 11
"Sliding Two Fingers Right", # 12
"Sliding Two Fingers Up", # 13
"Stop Sign", # 14
"Swiping Down", # 15
"Swiping Left", # 16
"Swiping Right", # 17
"Swiping Up", # 18
"Thumb Down", # 19
"Thumb Up", # 20
"Turning Hand Clockwise", # 21
"Turning Hand Counterclockwise", # 22
"Zooming In With Full Hand", # 23
"Zooming In With Two Fingers", # 24
"Zooming Out With Full Hand", # 25
"Zooming Out With Two Fingers" # 26
]
# catigories = [
# "做其他事情", # 0
# "Drumming Fingers", # 1
# "没有手势", # 2
# "Pulling Hand In", # 3
# "把两根手指往里拉", # 4
# "手推掉", # 5
# "推开两根手指", # 6
# "向后滚动手", # 7
# "向前滚动手", # 8
# "颤抖的手", # 9
# "向下滑动两根手指", # 10
# "向左滑动两根手指", # 11
# "向右滑动两根手指", # 12
# "向上滑动两根手指", # 13
# "停止手势", # 14
# "刷下来", # 15
# "向左刷", # 16
# "向右刷", # 17
# "向上刷", # 18
# "拇指向下", # 19
# "拇指向上", # 20
# "顺时针", # 21
# "逆时针", # 22
# "全手放大", # 23
# "两根手指放大", # 24
# "全手缩小", # 25
# "Z两根手指缩小" # 26
# ]
n_still_frame = 0
WINDOW_NAME = 'Video Gesture Recognition'
def main():
torch_module = MobileNetV2(n_class=27)
torch_module.load_state_dict(torch.load(r"H:\github\TSM\online_demo\mobilenetv2_jester_online.pth.tar")) # 加载模型,路径自己修改
torch_module.eval()
print("Open camera...")
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0) # 打开摄像头
print(cap)
# set a lower resolution for speed up 为加速设置一个较低的分辨率
cap.set(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH, 320)
cap.set(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT, 240)
# env variables 窗口变量
full_screen = False
cv2.namedWindow(WINDOW_NAME, cv2.WINDOW_NORMAL)
cv2.resizeWindow(WINDOW_NAME, 640, 480)
cv2.moveWindow(WINDOW_NAME, 0, 0)
cv2.setWindowTitle(WINDOW_NAME, WINDOW_NAME)
t = None
index = 0
print("Build transformer...")
transform = get_transform() # 预处理
print("Build Executor...")
idx = 0
history = [2]
history_logit = []
history_timing = []
i_frame = -1
print("Ready!")
while True: # 读取摄像头
i_frame += 1
_, img = cap.read() # (480, 640, 3) 0 ~ 255
if i_frame % 2 == 0: # skip every other frame to obtain a suitable frame rate , 隔帧抽取
t1 = time.time()
img_tran = transform([Image.fromarray(img).convert('RGB')]) # 图片预处理
input_var = torch.autograd.Variable(img_tran.view(1, 3, img_tran.size(1), img_tran.size(2))) # 张量转换
with torch.no_grad():
feat, *buffer = torch_module(input_var, *shift_buffer)
if SOFTMAX_THRES > 0:
feat_np = feat.numpy().reshape(-1)
feat_np -= feat_np.max()
softmax = np.exp(feat_np) / np.sum(np.exp(feat_np))
print(max(softmax))
if max(softmax) > SOFTMAX_THRES:
idx_ = np.argmax(feat.numpy(), axis=1)[0]
else:
idx_ = idx
print(idx_)
else:
idx_ = np.argmax(feat.numpy(), axis=1)[0] # 得到结果值
if HISTORY_LOGIT: # 平均
history_logit.append(feat.numpy())
history_logit = history_logit[-12:]
avg_logit = sum(history_logit)
idx_ = np.argmax(avg_logit, axis=1)[0]
idx, history = process_output(idx_, history) # 本帧结果、历史帧结果(最大保留20帧)
t2 = time.time()
print(f"{index} {catigories[idx]}")
current_time = t2 - t1 # 推理时间
# 识别效果展示部分
img = cv2.resize(img, (640, 480))
img = img[:, ::-1]
height, width, _ = img.shape
label = np.zeros([height // 10, width, 3]).astype('uint8') + 255
cv2.putText(label, 'Prediction: ' + catigories[idx],
(0, int(height / 16)),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,
0.7, (0, 0, 0), 2)
cv2.putText(label, '{:.1f} Vid/s'.format(1 / current_time),
(width - 170, int(height / 16)),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,
0.7, (0, 0, 0), 2)
img = np.concatenate((img, label), axis=0)
cv2.imshow(WINDOW_NAME, img)
key = cv2.waitKey(1)
if key & 0xFF == ord('q') or key == 27: # exit
break
elif key == ord('F') or key == ord('f'): # full screen
print('Changing full screen option!')
full_screen = not full_screen
if full_screen:
print('Setting FS!!!')
cv2.setWindowProperty(WINDOW_NAME, cv2.WND_PROP_FULLSCREEN,
cv2.WINDOW_FULLSCREEN)
else:
cv2.setWindowProperty(WINDOW_NAME, cv2.WND_PROP_FULLSCREEN,
cv2.WINDOW_NORMAL)
if t is None:
t = time.time()
else:
nt = time.time()
index += 1
t = nt
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
main()
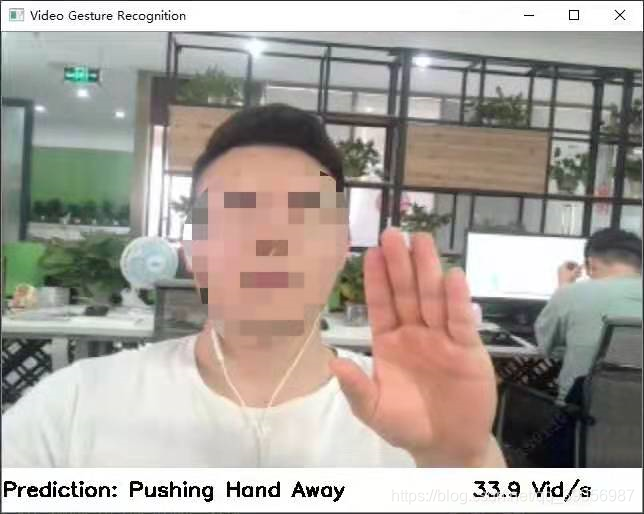
个人隐私打个码,不得不吐槽的是,效果真的不太行。。。。我想说的是这个demo也太辣鸡了吧,虽然不知道作者是咋训练的,亦或是因为我pytorch推理的原因哪里没设置好,如果有按照教程用tvm推理测试的带佬,效果可以评论区告知一下。好了,不纠结这个了,进入正题!
二、数据准备
我的数据是按照ucf101的格式准备的,如果手头上没有数据的同学,建议从ucf101中抽出10个类简单训练一下,没必要用全部的101个类,因为一会抽帧抽出来的图片实在是太多了!!全部的话得有150万+。
很头大的是,程序里面没有提供ucf101格式的数据准备脚本!!可是我踏马没有接触过行为识别啊,完全不知道数据该怎么准备!!靠!硬着头皮翻了很多不同模型的行为识别模型的代码,慢慢的整理,终于整出来了,妈卖批。首先看下ucf101下下来后的文件结构: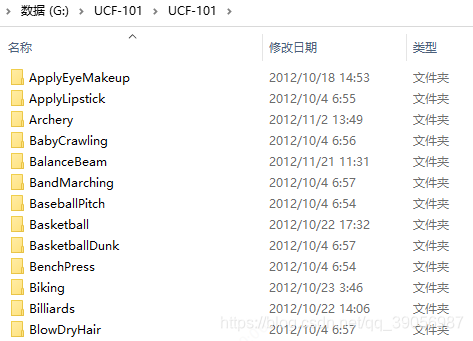
其实就是101的文件夹,每个文件夹里面有每个动作的短视频。类似于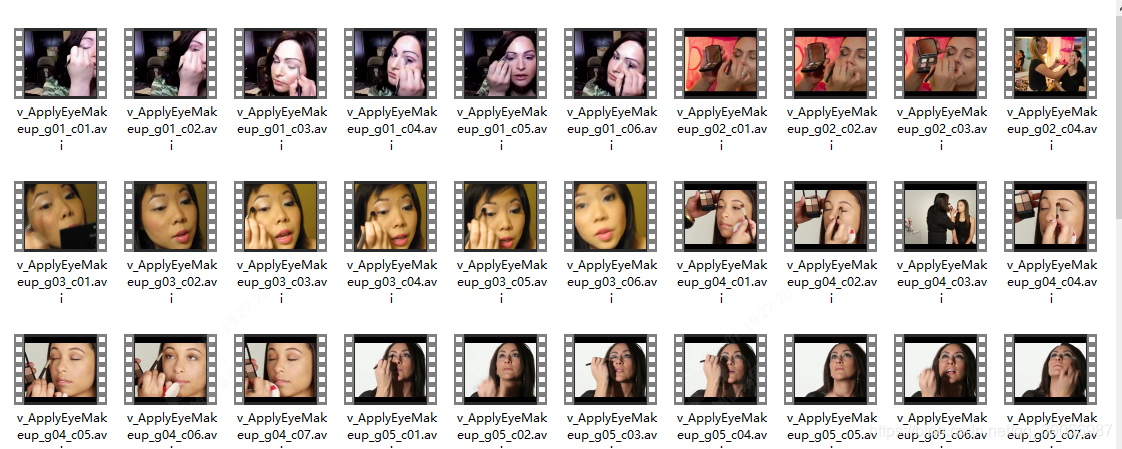
这是数据文件,还需要标签文件,官方划分训练集和测试集的txt文件: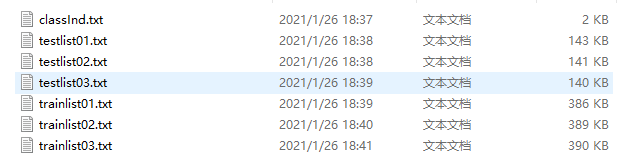
因为这里只提取了10个类,提取了前十个类的视频文件,并且修改label里面的标签,将后91个类别的标签信息去掉。在tools文件夹中新建一个文件夹,取名vid2img_ucf101.py,代码如下(需要安装ffmpeg,因为要用它来抽帧,这个自行百度就好,比较简单):
from __future__ import print_function, division
import os
import sys
import subprocess
def class_process(dir_path, dst_dir_path, class_name):
class_path = os.path.join(dir_path, class_name)
if not os.path.isdir(class_path):
return
dst_class_path = os.path.join(dst_dir_path, class_name)
if not os.path.exists(dst_class_path):
os.mkdir(dst_class_path)
for file_name in os.listdir(class_path):
if '.avi' not in file_name:
continue
name, ext = os.path.splitext(file_name)
dst_directory_path = os.path.join(dst_class_path, name)
video_file_path = os.path.join(class_path, file_name)
try:
if os.path.exists(dst_directory_path):
if not os.path.exists(os.path.join(dst_directory_path, 'image_00001.jpg')):
subprocess.call('rm -r \"{}\"'.format(dst_directory_path), shell=True)
print('remove {}'.format(dst_directory_path))
os.mkdir(dst_directory_path)
else:
continue
else:
os.mkdir(dst_directory_path)
except:
print(dst_directory_path)
continue
cmd = 'ffmpeg -i \"{}\" -vf scale=-1:480 \"{}/image_%05d.jpg\"'.format(video_file_path, dst_directory_path)
print(cmd)
subprocess.call(cmd, shell=True)
print('\n')
if __name__=="__main__":
dir_path = sys.argv[1] # 视频文件总路径
dst_dir_path = sys.argv[2] # 抽帧后图片存放路径
for class_name in os.listdir(dir_path):
class_process(dir_path, dst_dir_path, class_name)
运行命令,如果没有报错的话,要等比较久:
python tools/vid2img_ucf101.py 视频路径 抽帧后图片存放路径
抽完后,再继续新建一个gen_label_ucf101.py文件,内容如下,一些路径自己修改,需要注意的是数据生成是在windows上,所以在linux的话.split(’\’)可能要修改一下:
import os
import glob
import fnmatch
import random
root = r"/ssd1/cai/TSM-action/UCF101/jpg/" # 抽帧后的图片存放目录文件夹,用于写到txt文件中在构建数据集的时候读取
def parse_ucf_splits():
class_ind = [x.strip().split() for x in open(r'G:\UCF101\label/classInd.txt')] # 类别txt
class_mapping = {x[1]:int(x[0])-1 for x in class_ind}
def line2rec(line):
items = line.strip().split('/')
label = class_mapping[items[0]]
vid = items[1].split('.')[0]
return vid, label
splits = []
for i in range(1, 4):
train_list = [line2rec(x) for x in open(r'G:\UCF101\label/trainlist{:02d}.txt'.format(i))] # 训练集txt
test_list = [line2rec(x) for x in open(r'G:\UCF101\label/testlist{:02d}.txt'.format(i))] # 测试集txt
splits.append((train_list, test_list))
return splits
split_parsers = dict()
split_parsers['ucf101'] = parse_ucf_splits()
def parse_split_file(dataset):
sp = split_parsers[dataset]
return tuple(sp)
def parse_directory(path, rgb_prefix='image_', flow_x_prefix='flow_x_', flow_y_prefix='flow_y_'):
"""
Parse directories holding extracted frames from standard benchmarks
"""
print('parse frames under folder {}'.format(path))
frame_folders = []
frame = glob.glob(os.path.join(path, '*'))
for frame_name in frame:
frame_path = glob.glob(os.path.join(frame_name, '*'))
frame_folders.extend(frame_path)
def count_files(directory, prefix_list):
lst = os.listdir(directory)
cnt_list = [len(fnmatch.filter(lst, x+'*')) for x in prefix_list]
return cnt_list
# check RGB
rgb_counts = {}
flow_counts = {}
dir_dict = {}
for i,f in enumerate(frame_folders):
all_cnt = count_files(f, (rgb_prefix, flow_x_prefix, flow_y_prefix))
k = f.split('\\')[-1]
rgb_counts[k] = all_cnt[0]
dir_dict[k] = f
x_cnt = all_cnt[1]
y_cnt = all_cnt[2]
if x_cnt != y_cnt:
raise ValueError('x and y direction have different number of flow images. video: '+f)
flow_counts[k] = x_cnt
if i % 200 == 0:
print('{} videos parsed'.format(i))
print('frame folder analysis done')
return dir_dict, rgb_counts, flow_counts
def build_split_list(split_tuple, frame_info, split_idx, shuffle=False):
split = split_tuple[split_idx]
def build_set_list(set_list):
rgb_list, flow_list = list(), list()
for item in set_list:
frame_dir = frame_info[0][item[0]]
frame_dir = root + frame_dir.split('\\')[-2] +'/'+ frame_dir.split('\\')[-1]
rgb_cnt = frame_info[1][item[0]]
flow_cnt = frame_info[2][item[0]]
rgb_list.append('{} {} {}\n'.format(frame_dir, rgb_cnt, item[1]))
flow_list.append('{} {} {}\n'.format(frame_dir, flow_cnt, item[1]))
if shuffle:
random.shuffle(rgb_list)
random.shuffle(flow_list)
return rgb_list, flow_list
train_rgb_list, train_flow_list = build_set_list(split[0])
test_rgb_list, test_flow_list = build_set_list(split[1])
return (train_rgb_list, test_rgb_list), (train_flow_list, test_flow_list)
spl = parse_split_file('ucf101')
f_info = parse_directory(r"G:\UCF101\jpg") # 存放抽帧后的图片
out_path = r"G:\UCF101\label" # 标签路径
dataset = "ucf101"
for i in range(max(3,len(spl))):
lists = build_split_list(spl,f_info,i)
open(os.path.join(out_path, '{}_rgb_train_split_{}.txt'.format(dataset, i + 1)), 'w').writelines(lists[0][0])
open(os.path.join(out_path, '{}_rgb_val_split_{}.txt'.format(dataset, i + 1)), 'w').writelines(lists[0][1])
# open(os.path.join(out_path, '{}_flow_train_split_{}.txt'.format(dataset, i + 1)), 'w').writelines(lists[1][0])
# open(os.path.join(out_path, '{}_flow_val_split_{}.txt'.format(dataset, i + 1)), 'w').writelines(lists[1][1])
最后得到六个txt文件如下,这里只用到了split_1.txt的即可,其他的可以删掉: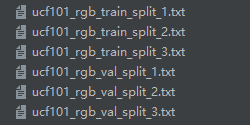
每个文件的格式如下,图片路径、帧数、类别: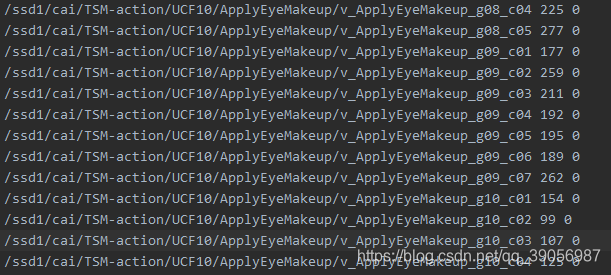
三、配置修改
修改以下配置,在ops/dataset_config.py中修改为自己文件的路径: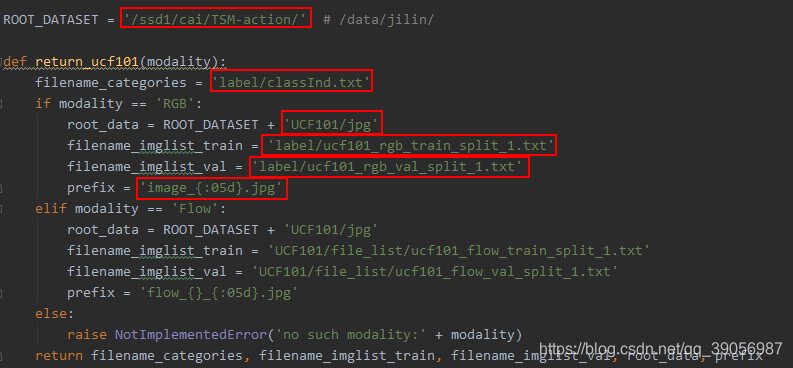
其中ROOT_DATASET为图片的总路径,与train_split_1.txt衔接的完整的图片路径,需要自己修改。
配置完成后下载相应的预训练权重,运行训练命令:
python main.py ucf101 RGB --arch resnet --num_segment 8 --gd 20 --lr 0.001 --lr_steps 10 20 --epochs 25 --batch-size 16 -j 16 --dropout 0.8 --consensus_type=avg --eval-freq=1 --shift --shift_div=8 --shift_place=blockres --tune_from=pretrained/TSM_kinetics_RGB_resnet50_shift8_blockres_avg_segment8_e50.pth
python main.py ucf101 RGB --arch mobilenetv2 --num_segment 8 --gd 20 --lr 0.001 --lr_steps 10 20 --epochs 25 --batch-size 16 -j 16 --dropout 0.8 --consensus_type=avg --eval-freq=1 --shift --shift_div=8 --shift_place=blockres --tune_from=pretrained/TSM_kinetics_RGB_mobilenetv2_shift8_blockres_avg_segment8_e100_dense.pth
看到如下界面的话,训练开始;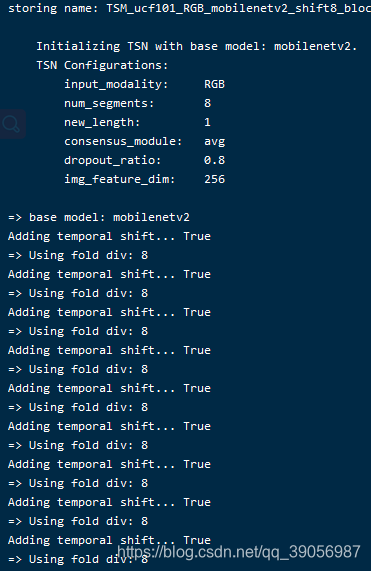
不过这里可能会遇到个问题,如果使用mobilenetv2的预训练权重加载不上,在main文件中,将这部分替换一下,大概在97行左右:
if args.tune_from:
print(("=> fine-tuning from '{}'".format(args.tune_from)))
sd = torch.load(args.tune_from)
sd = sd['state_dict']
if args.arch == "mobilenetv2":
model_dict = model.module.state_dict()
else:
model_dict = model.state_dict()
replace_dict = []
for k, v in sd.items():
if k not in model_dict and k.replace('.net', '') in model_dict:
print('=> Load after remove .net: ', k)
replace_dict.append((k, k.replace('.net', '')))
for k, v in model_dict.items():
if k not in sd and k.replace('.net', '') in sd:
print('=> Load after adding .net: ', k)
replace_dict.append((k.replace('.net', ''), k))
for k, k_new in replace_dict:
sd[k_new] = sd.pop(k)
keys1 = set(list(sd.keys()))
keys2 = set(list(model_dict.keys()))
set_diff = (keys1 - keys2) | (keys2 - keys1)
print('#### Notice: keys that failed to load: {}'.format(set_diff))
if args.dataset not in args.tune_from: # new dataset
print('=> New dataset, do not load fc weights')
if args.arch == "mobilenetv2":
sd = {k: v for k, v in sd.items() if k in model.state_dict().keys() and model.state_dict().keys()[k].numel() == v.numel}
else:
sd = {k: v for k, v in sd.items() if 'fc' not in k}
if args.modality == 'Flow' and 'Flow' not in args.tune_from:
sd = {k: v for k, v in sd.items() if 'conv1.weight' not in k}
model_dict.update(sd)
if args.arch == "mobilenetv2":
model.module.load_state_dict(model_dict)
else:
model.load_state_dict(model_dict)
if args.temporal_pool and not args.resume:
make_temporal_pool(model.module.base_model, args.num_segments)
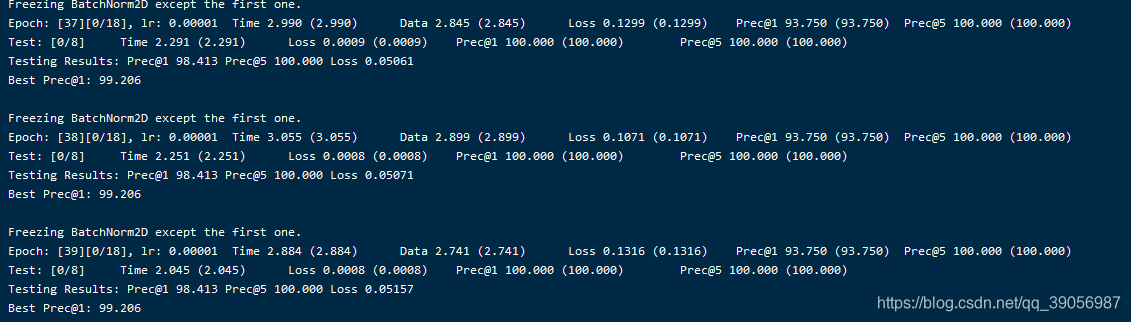
最后训练完了,精度还不错,百分之99点多,可是要怎么输入视频测试呢??这就是这个程序里面最操蛋的地方!!连个纯视频输入的demo都没有,又要自己写,不得不说这个代码看了我两周,写的太乱了,看的我脑阔疼,要放假了,下回再说。
行为识别TSM训练ucf101数据集的更多相关文章
- 实践详细篇-Windows下使用VS2015编译的Caffe训练mnist数据集
上一篇记录的是学习caffe前的环境准备以及如何创建好自己需要的caffe版本.这一篇记录的是如何使用编译好的caffe做训练mnist数据集,步骤编号延用上一篇 <实践详细篇-Windows下 ...
- matlab练习程序(神经网络识别mnist手写数据集)
记得上次练习了神经网络分类,不过当时应该有些地方写的还是不对. 这次用神经网络识别mnist手写数据集,主要参考了深度学习工具包的一些代码. mnist数据集训练数据一共有28*28*60000个像素 ...
- YOLOV4在linux下训练自己数据集(亲测成功)
最近推出了yolo-v4我也准备试着跑跑实验看看效果,看看大神的最新操作 这里不做打标签工作和配置cuda工作,需要的可以分别百度搜索 VOC格式数据集制作,cuda和cudnn配置 我们直接利用 ...
- Fast RCNN 训练自己数据集 (1编译配置)
FastRCNN 训练自己数据集 (1编译配置) 转载请注明出处,楼燚(yì)航的blog,http://www.cnblogs.com/louyihang-loves-baiyan/ https:/ ...
- 使用caffe训练mnist数据集 - caffe教程实战(一)
个人认为学习一个陌生的框架,最好从例子开始,所以我们也从一个例子开始. 学习本教程之前,你需要首先对卷积神经网络算法原理有些了解,而且安装好了caffe 卷积神经网络原理参考:http://cs231 ...
- 使用py-faster-rcnn训练VOC2007数据集时遇到问题
使用py-faster-rcnn训练VOC2007数据集时遇到如下问题: 1. KeyError: 'chair' File "/home/sai/py-faster-rcnn/tools/ ...
- 【转】CNN+BLSTM+CTC的验证码识别从训练到部署
[转]CNN+BLSTM+CTC的验证码识别从训练到部署 转载地址:https://www.jianshu.com/p/80ef04b16efc 项目地址:https://github.com/ker ...
- Scaled-YOLOv4 快速开始,训练自定义数据集
代码: https://github.com/ikuokuo/start-scaled-yolov4 Scaled-YOLOv4 代码: https://github.com/WongKinYiu/S ...
- yolov2训练ICDAR2011数据集
首先下载数据集train-textloc.zip 其groundtruth文件如下所示: 158,128,412,182,"Footpath" 442,128,501,170,&q ...
- 机器学习初探(手写数字识别)matlab读取数据集
手写数字识别是机器学习里面的一个经典问题,今天就这一段时间学习的机器学习,花一个下午茶的时间,试试机器学习. 首先数据库是在MNIST(http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist ...
随机推荐
- 微服务实战系列(七)-网关springcloud gateway-copy
1. 场景描述 springcloud刚推出的时候用的是netflix全家桶,路由用的zuul,但是据说zull1.0在大数据量访问的时候存在较大性能问题,2.0就没集成到springcloud中了, ...
- Linux性能优化-网络性能优化思路
目录 确定优化目标 网络性能工具 网络性能优化 应用程序 套接字 传输层 网络层 链路层 确定优化目标优化前,首先要确定观察到的网络性能指标,要达到多少才合适?虽然网络性能优化的整体目标,是降低网络延 ...
- Nodify学习 四:预先连接
前置 预先连接 可以从连接器创建预先连接,并可以放置在ItemContainer或Connector上(如果AllowOnlyConnectors为false). 预先连接的Content可以使用Co ...
- Q:bash: fork: 无法分配内存,ssh无法连接新会话
老版本系统的内核pid参数比较小(默认设置的是32768) 原因分析,– 内存不足或进程数超出限制– 系统内部的总进程数达到pid_max的上限,创建新进程看到以上提示 查看最大进程数 sysctl ...
- Recent 做题记录(重写)
重构. 2023.9 CF922D 考虑交换法即可.Livshits-Kladov 定理. CF1528C 第一棵树上是一条链:第二棵树上使用数据结构维护贪心(小的区间比大的更优:树上具有包含/无交性 ...
- NOIP 游记
前情提要:color \(100\to 0\),arena \(92/100\to 36\). 最后一场模拟赛喜提 0+0+100+0,挺乐的. Day 0 晚上九点睡,然而还是很早就醒了,但是时间体 ...
- JUC并发—13.Future模式和异步编程简介
大纲 1.Runnable接口与Callable接口 (1)Runnable接口实现异步任务 (2)Callable接口实现异步任务 2.Future模式 (1)Future模式的概念 (2)Futu ...
- 2024.11.14随笔&联考总结
前言 今天联考直接炸纲了.但是不得不说:HEZ 的题要比 BSZX 好多了. 联考 今天联考题说实话难度应该比较适合我.第一题是推结论的题,我赛时 20min 想出正解,但是有两个细节没有考虑清楚,导 ...
- 补充:基于项目的协同过滤推荐算法(Item-Based Collaborative Filtering Recommendation Algorithms)
前言 继续上篇博客,继续读论文. 想看上篇论文的同学可以点击这里 相关工作 In this section we briefly present some of the research litera ...
- 分享4款.NET开源、免费、实用的商城系统
前言 今天大姚给大家分享4款.NET开源.免费.实用的商城系统,希望可以帮助到有商城系统开发需求的同学. nopCommerce nopCommerce是一个.NET开源功能丰富.免费.灵活且可定制的 ...
