spark streaming 3: Receiver 到 submitJobSet
/**
* :: DeveloperApi ::
* Abstract class of a receiver that can be run on worker nodes to receive external data. A
* custom receiver can be defined by defining the functions `onStart()` and `onStop()`. `onStart()`
* should define the setup steps necessary to start receiving data,
* and `onStop()` should define the cleanup steps necessary to stop receiving data.
* Exceptions while receiving can be handled either by restarting the receiver with `restart(...)`
* or stopped completely by `stop(...)` or
*
* A custom receiver in Scala would look like this.
*
* {{{
* class MyReceiver(storageLevel: StorageLevel) extends NetworkReceiver[String](storageLevel) {
* def onStart() {
* // Setup stuff (start threads, open sockets, etc.) to start receiving data.
* // Must start new thread to receive data, as onStart() must be non-blocking.
*
* // Call store(...) in those threads to store received data into Spark's memory.
*
* // Call stop(...), restart(...) or reportError(...) on any thread based on how
* // different errors needs to be handled.
*
* // See corresponding method documentation for more details
* }
*
* def onStop() {
* // Cleanup stuff (stop threads, close sockets, etc.) to stop receiving data.
* }
* }
* }}}
*/
@DeveloperApi
abstract class Receiver[T](val storageLevel: StorageLevel) extends Serializable {
/**
* This method is called by the system when the receiver is started. This function
* must initialize all resources (threads, buffers, etc.) necessary for receiving data.
* This function must be non-blocking, so receiving the data must occur on a different
* thread. Received data can be stored with Spark by calling `store(data)`.
*
* If there are errors in threads started here, then following options can be done
* (i) `reportError(...)` can be called to report the error to the driver.
* The receiving of data will continue uninterrupted.
* (ii) `stop(...)` can be called to stop receiving data. This will call `onStop()` to
* clear up all resources allocated (threads, buffers, etc.) during `onStart()`.
* (iii) `restart(...)` can be called to restart the receiver. This will call `onStop()`
* immediately, and then `onStart()` after a delay.
*/
def onStart()
/**
* Store an ArrayBuffer of received data as a data block into Spark's memory.
* The metadata will be associated with this block of data
* for being used in the corresponding InputDStream.
*/
def store(dataBuffer: ArrayBuffer[T], metadata: Any) {
executor.pushArrayBuffer(dataBuffer, Some(metadata), None)
}
/**
* Abstract class that is responsible for supervising a Receiver in the worker.
* It provides all the necessary interfaces for handling the data received by the receiver.
*/
private[streaming] abstract class ReceiverSupervisor(
receiver: Receiver[_],
conf: SparkConf
) extends Logging {
/**
* Concrete implementation of [[org.apache.spark.streaming.receiver.ReceiverSupervisor]]
* which provides all the necessary functionality for handling the data received by
* the receiver. Specifically, it creates a [[org.apache.spark.streaming.receiver.BlockGenerator]]
* object that is used to divide the received data stream into blocks of data.
*/
private[streaming] class ReceiverSupervisorImpl(
receiver: Receiver[_],
env: SparkEnv
) extends ReceiverSupervisor(receiver, env.conf) with Logging {
private val blockManager = env.blockManager
private val storageLevel = receiver.storageLevel
/** Remote Akka actor for the ReceiverTracker */
private val trackerActor = {
val ip = env.conf.get("spark.driver.host", "localhost")
val port = env.conf.getInt("spark.driver.port", 7077)
val url = "akka.tcp://%s@%s:%s/user/ReceiverTracker".format(
SparkEnv.driverActorSystemName, ip, port)
env.actorSystem.actorSelection(url)
}
/** Timeout for Akka actor messages */
private val askTimeout = AkkaUtils.askTimeout(env.conf)
/** Akka actor for receiving messages from the ReceiverTracker in the driver */
private val actor = env.actorSystem.actorOf(
Props(new Actor {
override def preStart() {
logInfo("Registered receiver " + streamId)
val msg = RegisterReceiver(
streamId, receiver.getClass.getSimpleName, Utils.localHostName(), self)
val future = trackerActor.ask(msg)(askTimeout)
Await.result(future, askTimeout)
}
override def receive() = {
case StopReceiver =>
logInfo("Received stop signal")
stop("Stopped by driver", None)
}
def ref = self
}), "Receiver-" + streamId + "-" + System.currentTimeMillis())
/** Unique block ids if one wants to add blocks directly */
private val newBlockId = new AtomicLong(System.currentTimeMillis())
/** Divides received data records into data blocks for pushing in BlockManager. */
private val blockGenerator = new BlockGenerator(new BlockGeneratorListener {
def onError(message: String, throwable: Throwable) {
reportError(message, throwable)
}
def onPushBlock(blockId: StreamBlockId, arrayBuffer: ArrayBuffer[_]) {
pushArrayBuffer(arrayBuffer, None, Some(blockId))
}
}, streamId, env.conf)
/**
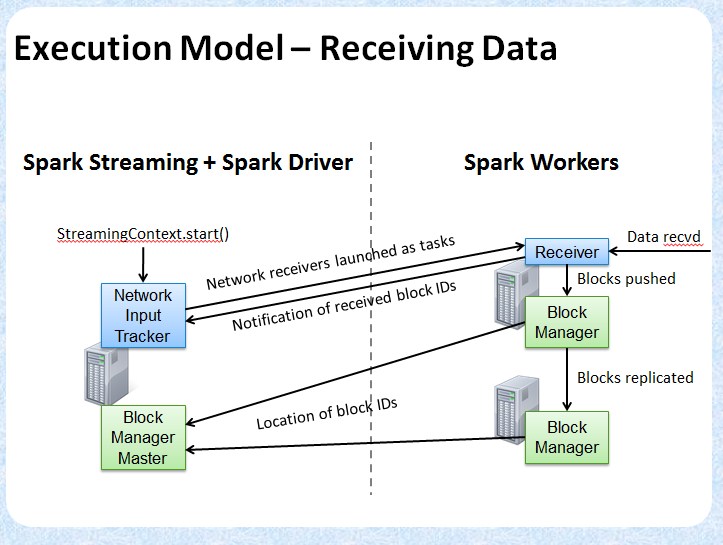
* This class manages the execution of the receivers of NetworkInputDStreams. Instance of
* this class must be created after all input streams have been added and StreamingContext.start()
* has been called because it needs the final set of input streams at the time of instantiation.
*/
private[streaming]
class ReceiverTracker(ssc: StreamingContext) extends Logging {
val receiverInputStreams = ssc.graph.getReceiverInputStreams()
val receiverInputStreamMap = Map(receiverInputStreams.map(x => (x.id, x)): _*)
val receiverExecutor = new ReceiverLauncher()
val receiverInfo = new HashMap[Int, ReceiverInfo] with SynchronizedMap[Int, ReceiverInfo]
val receivedBlockInfo = new HashMap[Int, SynchronizedQueue[ReceivedBlockInfo]]
with SynchronizedMap[Int, SynchronizedQueue[ReceivedBlockInfo]]
val timeout = AkkaUtils.askTimeout(ssc.conf)
val listenerBus = ssc.scheduler.listenerBus
// actor is created when generator starts.
// This not being null means the tracker has been started and not stopped
var actor: ActorRef = null
var currentTime: Time = null
/** Add new blocks for the given stream */
def addBlocks(receivedBlockInfo: ReceivedBlockInfo) {
getReceivedBlockInfoQueue(receivedBlockInfo.streamId) += receivedBlockInfo
logDebug("Stream " + receivedBlockInfo.streamId + " received new blocks: " +
receivedBlockInfo.blockId)
}
/**
* Get the receivers from the ReceiverInputDStreams, distributes them to the
* worker nodes as a parallel collection, and runs them.
*/
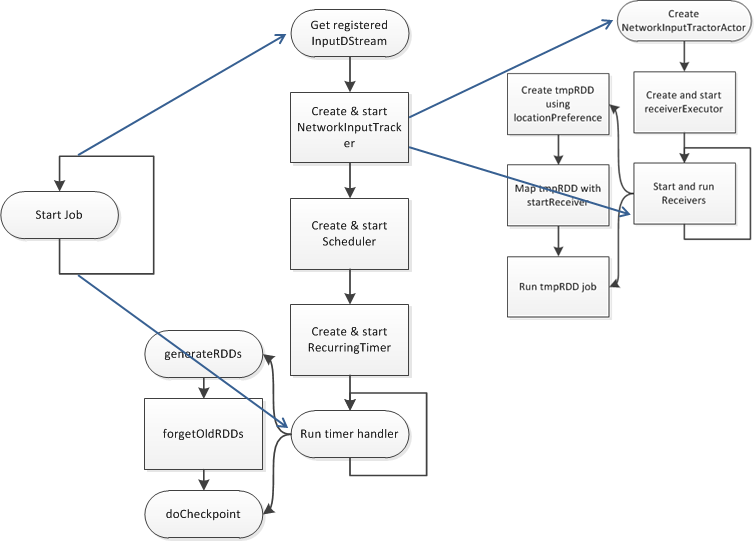
private def startReceivers() {
/** Event classes for JobGenerator */
private[scheduler] sealed trait JobGeneratorEvent
private[scheduler] case class GenerateJobs(time: Time) extends JobGeneratorEvent
private[scheduler] case class ClearMetadata(time: Time) extends JobGeneratorEvent
private[scheduler] case class DoCheckpoint(time: Time) extends JobGeneratorEvent
private[scheduler] case class ClearCheckpointData(time: Time) extends JobGeneratorEvent
/**
* This class generates jobs from DStreams as well as drives checkpointing and cleaning
* up DStream metadata.
*/
private[streaming]
class JobGenerator(jobScheduler: JobScheduler) extends Logging {
private val ssc = jobScheduler.ssc
private val conf = ssc.conf
private val graph = ssc.graph
val clock = {
val clockClass = ssc.sc.conf.get(
"spark.streaming.clock", "org.apache.spark.streaming.util.SystemClock")
Class.forName(clockClass).newInstance().asInstanceOf[Clock]
}
private val timer = new RecurringTimer(clock, ssc.graph.batchDuration.milliseconds,
longTime => eventActor ! GenerateJobs(new Time(longTime)), "JobGenerator")
/** Generate jobs and perform checkpoint for the given `time`. */
private def generateJobs(time: Time) {
SparkEnv.set(ssc.env)
Try(graph.generateJobs(time)) match {
case Success(jobs) =>
val receivedBlockInfo = graph.getReceiverInputStreams.map { stream =>
val streamId = stream.id
val receivedBlockInfo = stream.getReceivedBlockInfo(time)
(streamId, receivedBlockInfo)
}.toMap
jobScheduler.submitJobSet(JobSet(time, jobs, receivedBlockInfo))
case Failure(e) =>
jobScheduler.reportError("Error generating jobs for time " + time, e)
}
eventActor ! DoCheckpoint(time)
}
def generateJobs(time: Time): Seq[Job] = {
logDebug("Generating jobs for time " + time)
val jobs = this.synchronized {
outputStreams.flatMap(outputStream => outputStream.generateJob(time))
}
logDebug("Generated " + jobs.length + " jobs for time " + time)
jobs
}
/**
* Class representing a Spark computation. It may contain multiple Spark jobs.
*/
private[streaming]
class Job(val time: Time, func: () => _) {
var id: String = _
var result: Try[_] = null
def run() {
result = Try(func())
}
def setId(number: Int) {
id = "streaming job " + time + "." + number
}
override def toString = id
}
/** Class representing a set of Jobs
* belong to the same batch.
*/
private[streaming]
case class JobSet(
time: Time,
jobs: Seq[Job],
receivedBlockInfo: Map[Int, Array[ReceivedBlockInfo]] = Map.empty
) {
private val incompleteJobs = new HashSet[Job]()
private val submissionTime = System.currentTimeMillis() // when this jobset was submitted
private var processingStartTime = -1L // when the first job of this jobset started processing
private var processingEndTime = -1L // when the last job of this jobset finished processing
jobs.zipWithIndex.foreach { case (job, i) => job.setId(i) }
incompleteJobs ++= jobs
/**
* :: DeveloperApi ::
* Class having information on completed batches.
* @param batchTime Time of the batch
* @param submissionTime Clock time of when jobs of this batch was submitted to
* the streaming scheduler queue
* @param processingStartTime Clock time of when the first job of this batch started processing
* @param processingEndTime Clock time of when the last job of this batch finished processing
*/
@DeveloperApi
case class BatchInfo(
batchTime: Time,
receivedBlockInfo: Map[Int, Array[ReceivedBlockInfo]],
submissionTime: Long,
processingStartTime: Option[Long],
processingEndTime: Option[Long]
) {
spark streaming 3: Receiver 到 submitJobSet的更多相关文章
- spark Streaming的Receiver和Direct的优化对比
Direct 1.简化并行读取:如果要读取多个partition,不需要创建多个输入DStream然后对它们进行union操作.Spark会创建跟Kafka partition一样多的RDD part ...
- Spark Streaming自定义Receiver
一 背景 Spark社区为Spark Streaming提供了很多数据源接口,但是有些比较偏的数据源没有覆盖,由于公司技术栈选择,用了阿里云的MQ服务ONS,要做实时需求,要自己编写Receiver ...
- 9. Spark Streaming技术内幕 : Receiver在Driver的精妙实现全生命周期彻底研究和思考
原创文章,转载请注明:转载自 听风居士博客(http://www.cnblogs.com/zhouyf/) Spark streaming 程序需要不断接收新数据,然后进行业务逻辑 ...
- Spark Streaming Backpressure分析
1.为什么引入Backpressure 默认情况下,Spark Streaming通过Receiver以生产者生产数据的速率接收数据,计算过程中会出现batch processing time > ...
- Spark Streaming性能优化: 如何在生产环境下应对流数据峰值巨变
1.为什么引入Backpressure 默认情况下,Spark Streaming通过Receiver以生产者生产数据的速率接收数据,计算过程中会出现batch processing time > ...
- 【Streaming】30分钟概览Spark Streaming 实时计算
本文主要介绍四个问题: 什么是Spark Streaming实时计算? Spark实时计算原理流程是什么? Spark 2.X下一代实时计算框架Structured Streaming Spark S ...
- 第12课:Spark Streaming源码解读之Executor容错安全性
一.Spark Streaming 数据安全性的考虑: Spark Streaming不断的接收数据,并且不断的产生Job,不断的提交Job给集群运行.所以这就涉及到一个非常重要的问题数据安全性. S ...
- 4. Spark Streaming解析
4.1 初始化StreamingContext import org.apache.spark._ import org.apache.spark.streaming._ val conf = new ...
- Spark Streaming高吞吐、高可靠的一些优化
分享一些Spark Streaming在使用中关于高吞吐和高可靠的优化. 目录 1. 高吞吐的优化方式 1.1 更改序列化的方式 1.2 修改Receiver接受到的数据的存储级别 1.3 广播配置变 ...
随机推荐
- Docker简易使用手册
1. Docker介绍 Docker中文社区文档 Docker 是一个开源的软件部署解决方案. Docker 包括三个基本概念: 镜像(Image) Docker的镜像概念类似于虚拟机里的镜像,是一个 ...
- css3实现div自动左右动
<!DOCTYPE html> <meta charset="UTF-8"/> <html> <head> <style> ...
- Ubuntu18.10中pip install mysqlclient 出现EnvironmentError: mysql_config not found错误
Complete output from command python setup.py egg_info: sh: 1: mysql_config: not found Traceback (mos ...
- namenode datanode理解
HDFS是以NameNode和DataNode管理者和工作者模式运行的. NameNode管理着整个HDFS文件系统的元数据.从架构设计上看,元数据大致分成两个层次:Name ...
- Runtime.getRuntime.exec()执行linux脚本导致程序卡死问题
rumtime程序执行中出现卡住,执行成果达不到预期的标准.查看输出流以及错误流程是否内存占满了.开两个线程来运行输出流程和错误流程. rumtime运行windows脚本执行是要添加执行环境 cmd ...
- 自学Python5.6-面向对象三大基本特征_多态
自学Python之路-Python基础+模块+面向对象自学Python之路-Python网络编程自学Python之路-Python并发编程+数据库+前端自学Python之路-django 自学Pyth ...
- particlesjs
今天发现一个粒子动画的插件下个笔记做个备用: <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta ...
- 标准C语言(8)
指针变量用来记录地址数据,指针变量的用途就是找到另外一个变量,没有记录有效地址的指针不能用来找到其它变量,声明指针变量时必须在变量名称前写*.如果一个指针变量记录了另外一个变量的地址就可以认为它们之间 ...
- 牛客练习赛46 B 华华送奕奕小礼物 (预处理前缀和,二分)
链接:https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/894/B?&headNav=acm 来源:牛客网 华华送奕奕小礼物 时间限制:C/C++ 1秒,其他语言2秒 空 ...
- 清北学堂dp图论营游记day2
上午讲数位dp和背包问题. 先讲背包: 完全背包:换了个顺序: 多重背包: 多重背包优化: 这样把每个物品分成这些组,那么把他们转变成不同的物品,就变成了01背包问题: 滑动窗口取最值问题.单调队列优 ...
