c++面向对象程序设计 谭浩强 第一章答案
c++面向对象程序设计 谭浩强 答案 第一章
目录:
第1章 C++ 的初步知识
1.请根据你的了解,叙述C++ 的特点。C++ 对C有哪些发展?
【解】 略。
2.一个C++的程序是由哪几部分构成的?其中的每一部分起什么作用?
【解】 略。
3.从拿到一个任务到得到最终结果,一般要经过几个步骤?
【解】 略。
4.请说明编辑、编译、连接的作用。在编译后得到的目标文件为什么不能直接运行?
【解】 编译是以源程序文件为单位进行的,而一个完整的程序可能包含若干个程序文件,在分别对它们编译之后,得到若干个目标文件(后缀一般为.obj),然后要将它们连接为一个整体。此外,还需要与编译系统提供的标准库相连接,才能生成一个可执行文件(后缀为.exe)。不能直接运行后缀为.obj的目标文件,只能运行后缀为.exe的可执行文件。
谭浩强 c++面向对象程序设计 课后答案
5.分析下面程序运行的结果。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
cout << "This" << "is";
cout << "a" << "C++";
cout << "program." << endl;
return ;
}
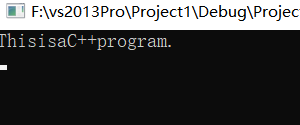
【解】 输出的结果为
ThisisaC++program.
谭浩强
6.分析下面程序运行的结果。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a, b, c;
a = ;
b = ;
c = a + b;
cout << "a+b=";
cout << c;
cout << endl;
return ;
}
【解】 前两个cout语句在输出数据后不换行,第3个cout语句输出一个换行,因此输出的结果为
a+b=33
7.分析下面程序运行的结果。请先阅读程序写出程序运行时应输出的结果,然后上机运行程序,验证自己分析的结果是否正确。以下各题同。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main( )
{
int a,b,c;
int f(int x,int y,int z);
cin>>a>>b>>c;
c=f(a,b,c);
cout<<c<<endl;
return ;
}
int f(int x,int y,int z)
{
int m;
if (x<y) m=x;
else m=y;
if (z<m) m=z;
return(m);
}
c++面向对象程序设计
【解】 程序的作用是:输入3个整数,然后输出其中值最小的数。在主函数中输入3个整数,然后调用f函数,在f函数中实现找最小的整数,用if语句比较两个数,将小者存放在变量m中,经过两个if语句的比较,m中存放的是3个整数中最小的数。运行情况如下:
1 5 3↙ (输入3个整数)
1 (输出其中最小的数)
8.在你所用的C++系统上,输入以下程序,进行编译,观察编译情况,如果有错误,请修改程序,再进行编译,直到没有错误,然后进行连接和运行,分析运行结果。
int main( );
{
int a,b;
c=a+b;
cout >>" a+b=" >> a+b;
}
【解】 上机编译出错,编译出错信息告知在第2行出错,经检查,发现第1行的末尾多了一个分号,编译系统无法理解第2行的花括号,导致报告第2行出错。将第1行的末尾的分号去掉,重新编译,编译出错信息告知在第5行和第6行出错。第5行出错原因是cout未经声明,因为cout不是C++语言提供的系统的关键字,而是输出流的对象,必须使用头文件iostream。第6行出错原因是main是int型函数,应返回一个整型值。将程序改为
#include <iostream>
int main( )
{
int a,b;
c=a+b;
cout >>" a+b=" >> a+b;
return 0;
}
重新编译。编译出错信息告知在第5行和第6行出错。第5行出错原因是变量c未定义,第6行出错原因是cout未经声明,说明#include <iostream>命令行未能起作用,原因是未指明命名空间。将程序改为
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main( )
{
int a,b,c;
c=a+b;
cout>>" a+b=" >>a+b;
return 0;
}
重新编译。编译出错信息告知在第7行出错,经检查,是“>>”用得不当,“>>”是提取运算符,应与cin联合使用,用来从输入流中提取数据,输出时应该用插入运算符“<<”。把两处“>>”都改为“<<”,再重新编译,发现没有error错误,但有两个警告(warning),原因是定义了a和b,但未对它们赋值。应增加赋值语句或输入语句,使a和b获得值,将程序改为
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main( )
{
int a,b,c;
cin>>a>>b;
c=a+b;
cout>>" a+b=" >>a+b;
return 0;
}
重新编译,没有编译错误,能通过编译和连接,可以正常运行,在Visual C++ 6.0环境下运行时屏幕显示如下:
5 9↙
a+b=14Press any key to continue
显然这样的输出不理想,“Press any key to continue”是Visual C++系统在输出了运行结果后自动显示的一个信息,告诉用户“如果想继续工作,请按任何一个键”。当用户按任何一个键后,显示运行结果的窗口消失,屏幕显示回到Visual C++的主窗口,显示出源程序和编译信息。
为了解决以上输出不理想的情况,可以在最后一个输出语句中增加输出一个换行符。最后的程序如下:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main( )
{
int a,b,c;
cin>>a>>b;
c=a+b;
cout<<"a+b="<<a+b<<endl;
return 0;
}
运行时屏幕显示如下:
5 9↙
a+b=14
Press any key to continue
这就完成了程序的调试。
这里对本题的调试过程作了比较详细的分析,以便使读者对如何调试程序有比较具体而清晰的了解。需要说明:
(1)编译系统给出的编译出错信息,只是提示性的,引导用户去检查错误,用户必须根据程序的上下文和编译出错信息,全面考虑,找出真正出错之处。例如编译出错信息通知第2行出错,其实可能是第1行出错。
(2)有时,有的错误开始时未被检查出来并告知用户(例如未定义变量c),由于其他错误未解决,掩盖了这个错误。当解决了其他错误后,这个错误会被检查出来。有时在调试过程中会不断检查出新的错误,这是不奇怪的。一一处理,问题会迎刃而解。
(3)为了说明调试过程,这里全部依靠计算机系统来检查错误,其实有些明显的错误,完全可以由人工查出,这样可以提高调试效率。由人工在纸面或屏幕上检查错误,称为静态查错,用计算机编译系统检查错误,称为动态查错。建议尽量先用静态查错的方法排除错误,只有人工检查不出来的错误才让计算机检查。
9.输入以下程序,进行编译,观察编译情况,如果有错误,请修改程序,再进行编译,直到没有错误,然后进行连接和运行,分析运行结果。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main( )
{
int a,b;
c=add(a,b)
cout<<"a+b="<<c<<endl;
return 0;
}
int add(int x,int y);
{
z=x+y;
retrun(z);
}
【解】 发现7个错误:
(1)对add函数未声明就调用,应在main函数中对add函数进行声明。
(2)定义add函数时,函数首行末尾不应有分号。
(3)变量c未经定义。
(4)add函数中的变量z未经定义。
(5)第6行末尾少了一个分号。
(6)add函数中的retrun拼写错误,应为return。编译系统把retrun作为未声明的标识符而报错,因为retrun(z)会被认为是函数调用的形式。
(7)变量a和b未被赋值。
改正后的程序如下:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main( )
{int add(int x,int y);
int a,b,c;
cin >> a >> b;
c=add(a,b);
cout <<" a+b=" << c <<endl;
return 0;
}
int add(int x,int y)
{int z;
z=x+y;
return(z);
}
运行情况如下:
5 8↙
13
10.输入以下程序,编译并运行,分析运行结果。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main( )
{ void sort(int x,int y,int z);
int x,y,z;
cin >> x >> y >> z;
sort(x,y,z);
return 0;
}
void sort(int x, int y, int z)
{
int temp;
if (x>y) {temp=x;x=y;y=temp;} //{ }内3个语句的作用是将x和y的值互换
if (z<x) cout << z << ',' << x << ',' << y << endl;
else if (z<y) cout << x <<',' << z << ',' << y << endl;
else cout << x << ',' << y << ',' << z << endl;
}
请分析此程序的作用。sort函数中的if语句是一个嵌套的if语句。
运行时先后输入以下几组数据,观察并分析运行结果。
① 3 6 10↙
② 6 3 10↙
③ 10 6 3↙
④ 10,6,3↙
【解】 程序的作用是对输入的3个整数按由小到大的顺序进行排序。sort函数中的第1个if语句的作用是先将x和y排序,使x小于或等于y。第2个if语句是一个嵌套的if语句,先比较z和x,如果z<x,显然由小到大的顺序应当是z,x,y,按此顺序输出;如果z不小于x,而小于y,显然由小到大的顺序应当是x,z,y,按此顺序输出;如果z既不小于x,又不小于y,显然由小到大的顺序应当是x,y,z,按此顺序输出。
按题目要求分别输入以下几组数据,运行结果如下:
① 3 6 10↙
3,6,10
② 6 3 10↙
3,6,10
③ 10 6 3↙
3,6,10
④ 10,6,3↙
-858993460,-858993460,10
以上是在Visual C++ 6.0环境下运行的情况,前3次运行正常,表明当输入不同的数据时,程序能实现由小到大的排序功能。第4次运行的结果显然不正常,这是由于输入数据时出了问题,本来要求在输入数据时,数据之间以空格或换行相隔,而现在却以逗号相隔,只有第一个整数能正常赋给变量x,第二和第三个数据均无法正常赋给变量y和z,y和z的值来自输入流中相应字节的内容。
11.求2个或3个正整数中的最大数,用带有默认参数的函数实现。
【解】 可以编写出以下程序:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main( )
{int max(int a,int b,int c=0);
int a,b,c;
cin >> a >> b >> c;
cout << " max(a,b,c)= " << max(a,b,c) << endl;
cout << " max(a,b)= " <<max(a,b) << endl;
return 0;
}
int max(int a,int b,int c)
{if(b>a) a=b;
if(c>a) a=c;
return a;
}
运行情况如下:
13 5 76↙
max(a,b,c)=76 (从3个数中找最大者)
max(a,b)=13 (从前2个数中找最大者)
如果想从3个数中找大者,可以在调用时写成“max(a,b,c)”形式,如果只想从2个数中找大者,则在调用时写成“max(a,b)”形式,此时c自动取默认值0,由于0比任何正整数都小,因此从14,5,0中选最大者和从14,5中选大者的结果是一样的。
12.输入两个整数,将它们按由大到小的顺序输出。要求使用变量的引用。
【解】 可以编写出以下程序:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main( )
{ void change(int &,int &);
int a,b;
cin>>a>>b;
if(a<b) change(a,b); //如果a<b,使a和b的值互换
cout<<"max="<<a<<" min="<<b<<endl;
return 0;
}
void change(int &r1,int &r2) //函数的作用是使r1与r2互换
{ int temp;
temp=r1;
r1=r2;
r2=temp;
}
运行情况如下:
12 67↙
max=67 min=12
13.对3个变量按由小到大顺序排序,要求使用变量的引用。
【解】 可以编写出以下程序:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main( )
{void sort(int &,int &,int &);
int a,b,c,a1,b1,c1;
cout<<" Please enter 3 integers:";
cin>>a>>b>>c;
a1=a;b1=b;c1=c;
sort(a1,b1,c1);
cout<<a<<" "<<b<<" "<<c<<" in sorted order is ";
cout<<a1<<" "<<b1<<" "<<c1<<endl;
return 0;
}
void sort(int &i,int &j,int &k)
{ void change(int &,int &);
if (i>j) change(i, j);
if (i>k) change(i, k);
if (j>k) change(j, k);
}
void change(int &x,int &y)
{ int temp;
temp=x;
x=y;
y=temp;
}
运行情况如下:
Please enter 3 integers:23 67 -55↙
23 67 –55 in sorted order is –55 23 67
这个程序很容易理解,不易出错。由于在调用sort函数时虚实结合使形参i,j,k成为实参a1,b1,c1的引用(别名),因此通过调用函数sort(a1,b1,c1)既实现了对i,j,k排序,也就同时实现了对a1,b1,c1排序。同样,执行change(i,j)函数,可以实现对实参i和j的互换。
14.编一程序,将两个字符串连接起来,结果取代第一个字符串。要求用string方法。
【解】 可以编写出以下程序:
#include <iostream>
#include <string> //程序中若使用字符串变量,必须包含头文件string
using namespace std;
int main( )
{ string s1= " week ",s2= " end ";
cout << " s1= " << s1 << endl;
cout << "s2=" << s2 << endl;
s1=s1+s2;
cout<<" The new string is: "<<s1<<endl;
return 0;
}
运行情况如下:
s1=week
s2=end
The new string is: weekend
15.输入一个字符串,把其中的字符按逆序输出。如输入LIGHT,输出THGIL。要求用string方法。
【解】 可以编写出以下程序:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main( )
{ string str; //定义字符串变量str
int i,n;
char temp; //定义字符变量temp
cout<<" please input a string: ";
cin>>str; //输入一个字符串赋给字符串变量str
n=str.size( ); //测量str的长度n
for(i=0;i<n/2;i++) //使str中的字符对称互换
{temp=str[i];str[i]=str[n-i-1];str[n-i-1]=temp;}
cout << str << endl;
return 0;
}
运行情况如下:
please input a string:
LIGHT↙
THGIL
注意:输入的字符串中不能含有空格。
16.有5个字符串,要求将它们按由小到大的顺序排列,用string方法。
【解】 可以编写出以下程序:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main( )
{ int i;
string str[5]={" BASIC"," C"," FORTRAN"," C++","PASCAL"};
void sort(string [ ]);
sort(str); //对字符串排序
cout<<" the sorted strings : "<<endl;
for(i=0;i<5;i++)
cout<<str[i]<<" "; //按已排好的顺序输出字符串
cout<<endl;
return 0;
}
void sort(string s[ ])
{int i, j;
string t;
for (j=0; j<5; j++)
for(i=0; i<5-j; i++)
if (s[i]>s[i+1])
{t=s[i];s[i]=s[i+1];s[i+1]=t;}
}
运行结果如下:
the sorted strings :
BASIC C C++ FORTRAN PASCAL
17.编一个程序,用同一个函数名对n个数据进行从小到大排序,数据类型可以是整型、单精度型、双精度型。用重载函数实现。
【解】 可以编写出以下两个程序:
(1)建立3个函数,分别用于处理整型、单精度型、双精度型数据的排序,在3个函数中都采用选择法排序方法。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main( )
{
long a[5]={10100,-123567, 1198783,-165654, 3456};
int b[5]={1,9,0,23,-45};
float c[5]={2.4, 7.6, 5.5, 6.6, -2.3 };
void sort(long [ ]);
void sort(int [ ]);
void sort(float [ ]);
sort(a);
sort(b);
sort(c);
return 0;
}
void sort(long a[ ])
{int i, j;
long t;
for (j=0; j<5; j++)
for(i=0;i<5-j;i++)
if (a[i]>a[i+1])
{t=a[i];a[i]=a[i+1];a[i+1]=t;}
cout<<" the sorted numbers : "<<endl;
for(i=0;i<5;i++)
cout<<a[i]<< " ";
cout<<endl<<endl;
}
void sort(int a[ ])
{int i, j, t;
for (j=0; j<5; j++)
for(i=0;i<5-j;i++)
if (a[i]>a[i+1])
{t=a[i];a[i]=a[i+1];a[i+1]=t;}
cout<<" the sorted numbers : "<<endl;
for(i=0;i<5;i++)
cout<<a[i]<< " ";
cout<<endl<<endl;
}
void sort(float a[ ])
{int i, j;
float t;
for (j=0;j<5;j++)
for(i=0;i<5-j;i++)
if (a[i]>a[i+1])
{t=a[i];a[i]=a[i+1];a[i+1]=t;}
cout<<" the sorted numbers : "<<endl;
for(i=0;i<5;i++)
cout<<a[i]<< " ";
cout<<endl<<endl;
}
运行结果如下:
the sorted numbers :
-123567 -165654 10100 3456 1198783 (长整型数据排序)
the sorted numbers : (整型数据排序)
-45 0 1 9 23
the sorted numbers :
-2.3 2.4 5.5 6.6 7.6 (单精度型数据排序)
(2)在第1种方法中,3个函数的函数体基本上是相同的,都是采用选择法排序,在下面的程序中,3个函数的函数体不全相同,前两个函数采用选择法排序,最后一个函数采用起泡法排序。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main( )
{ long a[5]= {10100,-123567, 1198783,-165654, 3456};
int b[5]={1,9,0,23,-45};
float c[5]={2.4, 7.6, 5.5, 6.6, -2.3 };
void sort(int [ ]);
void sort(float [ ]);
void sort(long [ ]);
sort(a); //对长整型数据排序
sort(b); //对整型数据排序
sort(c); //对单精度型数据排序
return 0;
}
void sort(long a[ ]) //对长整型数据用选择法排序的函数
{int i,j,min;
long t;
for(i=0;i<5;i++)
{min=i;
for (j=i+1;j<5;j++)
if(a[min]>a[j]) min=j;
{t=a[i]; a[i]=a[min]; a[min]=t; }
cout<<" the sorted numbers : "<<endl;
for(i=0;i<5;i++)
cout<<a[i]<< " ";
cout<<endl<<endl;
}
void sort(int a[ ]) //对整型数据用选择法排序的函数
{int i, j, t;
for (j=0; j<5; j++)
for(i=0;i<5-j;i++)
if (a[i]>a[i+1])
{t=a[i];a[i]=a[i+1];a[i+1]=t;}
cout<<" the sorted numbers : "<<endl;
for(i=0;i<5;i++)
cout<<a[i]<< " ";
cout<<endl<<endl;
}
void sort(float a[ ]) //对单精度型数据用起泡法排序的函数
{int i, j;
float t;
for (j=0;j<5;j++)
for(i=0;i<5-j;i++)
if (a[i]>a[i+1])
{t=a[i];a[i]=a[i+1];a[i+1]=t;}
cout<<" the sorted numbers : "<<endl;
for(i=0;i<5;i++)
cout<<a[i]<< " ";
cout<<endl<<endl;
}
运行结果如下:
the sorted numbers :
-123567 -165654 10100 3456 1198783 (长整型数据排序结果)
the sorted numbers : (整型数据排序结果)
-45 0 1 9 23
the sorted numbers :
-2.3 2.4 5.5 6.6 7.6 (单精度型数据排序结果)
对比两种方法,可以看到,并不要求重载函数的函数体相同,在本例中,采用不同的排序方法,结果是相同的。从理论上说,重载的函数可以用来实现完全不同的功能,但是应该注意:同一个函数名最好用来实现相近的功能,而不要用来实现完全不相干的功能,以方便用户理解和使用。
18.对第17题改用函数模板实现。并与17题程序进行对比分析。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
template <typename T >
void sort(T a[ ]) //函数模板,采用选择法排序
{int i, j, min;
T t;
for(i=0;i<5;i++)
{min=i;
for (j=i+1; j<5; j++)
if(a[min]>a[j]) min=j;
t=a[i]; a[i]=a[min]; a[min]=t;
}
cout<<" the sorted numbers : "<<endl;
for(i=0;i<5;i++)
cout<<a[i]<< " ";
cout<<endl<<endl;
}
int main( )
{ long a[5]={10100,-123567, 1198783,-165654, 3456};
int b[5]={1,9,0,23,-45};
float c[5]={2.4, 7.6, 5.5, 6.6, -2.3 };
sort(a);
sort(b);
sort(c);
return 0;
}
运行结果如下:
the sorted numbers :
-123567 -165654 10100 3456 1198783 (长整型数据排序)
the sorted numbers : (整型数据排序)
-45 0 1 9 23
the sorted numbers :
-2.3 2.4 5.5 6.6 7.6 (单精度型数据排序)
对比第17题和18题,可以看到,如果重载函数的函数体基本相同的话,用函数模板显然更方便,可以压缩程序篇幅,使用方便。
c++面向对象程序设计 谭浩强 第一章答案的更多相关文章
- c++面向对象程序设计 谭浩强 第二章答案
类体内定义成员函数 #include <iostream> using namespace std; class Time { public: void set_time(); void ...
- c++面向对象程序设计 谭浩强 第三章答案
2: #include <iostream> using namespace std; class Date {public: Date(int,int,int); Date(int,in ...
- c++面向对象程序设计 谭浩强 第五章答案
1: #include <iostream> using namespace std; class Student {public: void get_value() {cin>&g ...
- C语言程序设计·谭浩强(第四版)第二章课后习题的答案,算法——程序的灵魂
C语言程序小练习 1.用C语言设计程序算出1-1/2+1/3-14+1/5...+1/99-1/100的值 #include<stdio.h> int main() { ; double ...
- 关于指针的笔记【1】【C语言程序设计-谭浩强】
指针是什么? 一个 变量的地址称为该变量的"指针"[将地址形象化的称为“指针”].(指针是什么百度百科) 注意区分储存单元的地址和内容这两个概念的区别. 直接访问:直接按变量名进行 ...
- c++面向对象程序设计 课后题 答案 谭浩强 第四章
c++面向对象程序设计课后题答案 谭浩强 第四章 1: #include <iostream> using namespace std; class Complex {public: Co ...
- C程序设计(谭浩强)第五版课后题答案 第一章
大家好,这篇文章分享了C程序设计(谭浩强)第五版课后题答案,所有程序已经测试能够正常运行,如果小伙伴发现有错误的的地方,欢迎留言告诉我,我会及时改正!感谢大家的观看!!! 1.什么是程序?什么是程序设 ...
- 再论谭浩强《C语言程序设计》
一些同学学不好C语言,把罪责归于“因为教材是谭浩强写的”实在是很滑稽. 谭浩强老先生 1934 年生,现在已经 80 岁了.他 1958 年从清华大学自动控制系毕业,那年 24 岁.要知道 C 语言那 ...
- 挂羊头卖狗肉蓄意欺骗读者——谭浩强《C程序设计(第四版)》中所谓的“按照C99”(二)
挂羊头卖狗肉蓄意欺骗读者——谭浩强<C程序设计(第四版)>中所谓的“按照C99”(二) 在<谭C>p4:“本书的叙述以C99标准为依据”,下面从C89到C99的主要变化方面来看 ...
随机推荐
- 利用javascript(自定义事件)记录尺寸可变元素的尺寸变化过程
1.效果图 2.源码 <%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %&g ...
- python 模块导入详解
本文不讨论 Python 的导入机制(底层实现细节),仅讨论模块与包,以及导入语句相关的概念.通常,导入模块都是使用如下语句: import ... import ... as ... from .. ...
- css处理图片下方留白问题
引用图片的时候,图片和下方内容会有一点小空白,大概如下图紫色横条: 不是说有margin还是padding,是因为ing是行级元素,浏览器就会默认留白了,这时候处理方法很简单,给img加上样式disp ...
- postgreSQL格式化时间的函数详解
数据类型格式化函数: PostgreSQL格式化函数提供一套有效的工具用于把各种数据类型(日期/时间.integer.floating point和numeric)转换成格式化的字符串以及反过来 ...
- 杭电1003 Max Sum 【连续子序列求最大和】
题目链接: http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1003 题目意思: 即给出一串数据,求连续的子序列的最大和 解题思路: 因为我们很容易想到用一个max ...
- (转)基于MVC4+EasyUI的Web开发框架经验总结(5)--使用HTML编辑控件CKEditor和CKFinder
http://www.cnblogs.com/wuhuacong/p/3780356.html Web开发上有很多HTML的编辑控件,如CKEditor.kindeditor等等,很多都做的很好,本文 ...
- Js中的4个事件
除了加载文档的事件onload和鼠标相关的一些事件如onclick,onmouseover等.js还有一些相对不常用的事件,这些事件也有各自的应用场景,本文就介绍 onkeydown,oncontex ...
- spring cloud(四) feign
spring cloud 使用feign进行服务间调用 1. 新建boot工程 pom引入依赖 <dependency> <groupId>org.springframewor ...
- java 常用API
package com.orcal.demc01; public class Regex { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto ...
- sklearn学习2-----LogisticsRegression
1.官网地址: http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.linear_model.LogisticRegression.htm ...
