201871010107-公海瑜《面向对象程序设计(java)》第6-7周学习总结
201871010107-公海瑜《面向对象程序设计(java)》第6-7周学习总结
| 项目 | 内容 |
| 《面向对象程序设计(java)》 | https://home.cnblogs.com/u/nwnu-daizh/ |
| 这个作业的要求在哪里 | https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p/11605051.html |
| 作业学习目标 |
|
第一部分:总结第五章理论知识
1.继承:用已有类来构造新类的一种机制。当定义了一个新类继承了一个类时,这个新类就继承了这个类的方法和域。
2.继承的特点:具有层次结构、子类继承了父类的方法和域。
3.继承的优点:(1)代码可重用性(2)可以轻松定义子类(3)父类的域和方法可用于子类(4)设计应用程序变得更加简单
4.子类比超类拥有的功能更加丰富。
5.通过扩展超类来定义子类时,仅需要指出子类与超类的不同之处。
6.super是一个指示编译器调用超类方法的特有关键字。
7.super的用途:(1)调用超类的方法(2)调用超类的构造器
8.超类中的方法可在子类中进行方法重写。
9.可将子类对象赋给超类变量。
10.方法的名称和参数列表称为方法的签名。
11.不允许继承的类称为final类,在类的定义中用final修饰符加以说明。
12.把超类对象赋给子类对象变量,就必须进行强制类型转换。
子类 对象=(子类)(超类对象变量)
13.为了提高程序的清晰度,包含一个或多个抽象方法的类本身必须被声明为抽象类。除了抽象方法之外,抽象类还可以包含具体数据和具体方法。
14.抽象方法充当着占位的角色,他们的具体实现在子类中。
15.抽象类不能被实例化,即不能创建对象,只能产生子类。可以创建抽象类的对象变量。
第二部分:实验部分
1、实验目的与要求
(1) 理解继承的定义;
(2) 掌握子类的定义要求
(3) 掌握多态性的概念及用法;
(4) 掌握抽象类的定义及用途。
2、实验内容和步骤
实验1:导入第5章示例程序,测试并进行代码注释。
测试程序1:
Ÿ 在elipse IDE中编辑、调试、运行程序5-1 —5-3(教材152页-153页) ;
Ÿ 掌握子类的定义及用法;
Ÿ 结合程序运行结果,理解并总结OO风格程序构造特点,理解Employee和Manager类的关系子类的用途,并在代码中添加注释;
Ÿ 删除程序中Manager类、ManagerTest类,背录删除类的程序代码,在代码录入中理解父类与子类的关系和使用特点。
实验5-1代码如下:
ManagerTest:
package inheritance; /**
* This program demonstrates inheritance.
* @version 1.21 2004-02-21
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class ManagerTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// construct a Manager object
var boss = new Manager("Carl Cracker", , , , ); //构建管理者对象
boss.setBonus(); var staff = new Employee[]; //用管理者和雇员对象填充工作人员数组 // fill the staff array with Manager and Employee objects staff[] = boss;
staff[] = new Employee("Harry Hacker", , , , );
staff[] = new Employee("Tommy Tester", , , , ); // print out information about all Employee objects
for (Employee e : staff)
System.out.println("name=" + e.getName() + ",salary=" + e.getSalary());
}
}
运行结果如下:
实验5-2代码如下:
Employee:
package inheritance; import java.time.*; public class Employee
{
private String name;
private double salary;
private LocalDate hireDay; public Employee(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day)
{
this.name = name; //将局部变量的值传递给成员变量
this.salary = salary;
hireDay = LocalDate.of(year, month, day);
} //一个构造器,构造器与类同名 public String getName()
{
return name;
} public double getSalary()
{
return salary;
} public LocalDate getHireDay()
{
return hireDay;
} public void raiseSalary(double byPercent)
{
double raise = salary * byPercent / ;
salary += raise;
}
}
运行结果如图:
实验5-3代码如下:
Manager:
package inheritance; public class Manager extends Employee
{
private double bonus; /**
* @param name the employee's name
* @param salary the salary
* @param year the hire year
* @param month the hire month
* @param day the hire day
*/
public Manager(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day)
{
super(name, salary, year, month, day); //调用超类构造器
bonus = ;
} public double getSalary()
{
double baseSalary = super.getSalary(); //调用父类的方法
return baseSalary + bonus;
} public void setBonus(double b) //更改器
{
bonus = b;
}
}
运行结果如图:
测试程序2:
Ÿ 编辑、编译、调试运行教材PersonTest程序(教材163页-165页);
Ÿ 掌握超类的定义及其使用要求;
Ÿ 掌握利用超类扩展子类的要求;
Ÿ 在程序中相关代码处添加新知识的注释;
Ÿ 删除程序中Person类、PersonTest类,背录删除类的程序代码,在代码录入中理解抽象类与子类的关系和使用特点。
实验5-4代码如下:
PersonTest:
package abstractClasses; /**
* This program demonstrates abstract classes.
* @version 1.01 2004-02-21
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class PersonTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
var people = new Person[]; // fill the people array with Student and Employee objects
people[] = new Employee("Harry Hacker", , , , );
people[] = new Student("Maria Morris", "computer science"); // print out names and descriptions of all Person objects
for (Person p : people)
System.out.println(p.getName() + ", " + p.getDescription());
}
}
运行结果如下:

实验5-5代码如下:
Person:
package abstractClasses; public abstract class Person //定义抽象类型Person
{
public abstract String getDescription(); //定义抽象描述
private String name; public Person(String name)
{
this.name = name;
} public String getName()
{
return name;
}
}
运行结果如下:

实验5-6代码如下:
Employee:
package abstractClasses; import java.time.*; public class Employee extends Person //子类Employee继承父类Person
{
private double salary;
private LocalDate hireDay; public Employee(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day)
{
super(name); //继承父类的方法
this.salary = salary;
hireDay = LocalDate.of(year, month, day); //hireDay使用LocalDate的方法
} public double getSalary()
{
return salary;
} public LocalDate getHireDay()
{
return hireDay;
} public String getDescription()
{
return String.format("an employee with a salary of $%.2f", salary);
} public void raiseSalary(double byPercent)
{
double raise = salary * byPercent / ;
salary += raise;
}
}
运行结果如下:

实验5-7代码如下:
Student:
package abstractClasses; public class Student extends Person //子类Student继承父类Person
{
private String major; /**
* @param name the student's name
* @param major the student's major
*/
public Student(String name, String major)
{
// 将name传递给父类构造函数
super(name);
this.major = major;
} public String getDescription()
{
return "a student majoring in " + major;
}
}
运行结果如下:

测试程序3:
Ÿ 编辑、编译、调试运行教材程序5-8、5-9、5-10,结合程序运行结果理解程序(教材174页-177页);
Ÿ 掌握Object类的定义及用法;
Ÿ 在程序中相关代码处添加新知识的注释。
实验5-8代码如下:
Equalas Test:
package equals; /**
* This program demonstrates the equals method.
* @version 1.12 2012-01-26
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class EqualsTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
var alice1 = new Employee("Alice Adams", , , , );
var alice2 = alice1;
var alice3 = new Employee("Alice Adams", , , , );
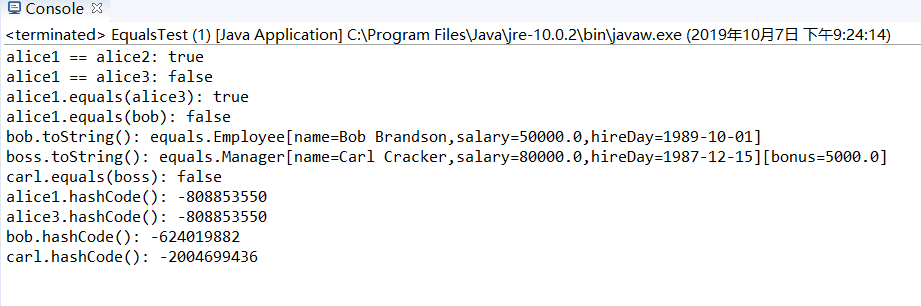
var bob = new Employee("Bob Brandson", , , , ); System.out.println("alice1 == alice2: " + (alice1 == alice2)); System.out.println("alice1 == alice3: " + (alice1 == alice3)); System.out.println("alice1.equals(alice3): " + alice1.equals(alice3)); System.out.println("alice1.equals(bob): " + alice1.equals(bob)); System.out.println("bob.toString(): " + bob); var carl = new Manager("Carl Cracker", , , , );
var boss = new Manager("Carl Cracker", , , , );
boss.setBonus();
System.out.println("boss.toString(): " + boss);
System.out.println("carl.equals(boss): " + carl.equals(boss));
System.out.println("alice1.hashCode(): " + alice1.hashCode());
System.out.println("alice3.hashCode(): " + alice3.hashCode());
System.out.println("bob.hashCode(): " + bob.hashCode());
System.out.println("carl.hashCode(): " + carl.hashCode());
}
}
运行结果如下:
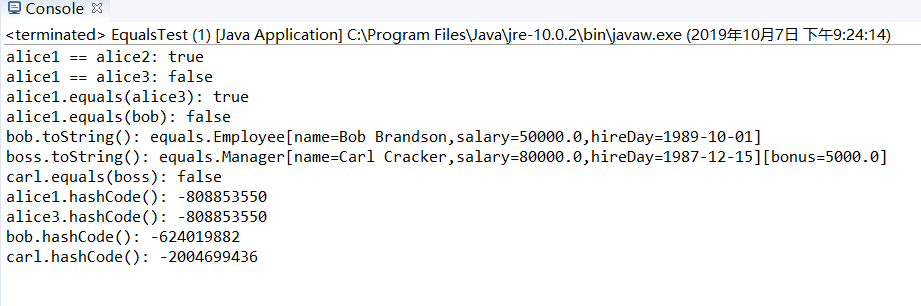
实验5-9代码如下:
Employee:
package equals; import java.time.*;
import java.util.Objects; public class Employee
{
private String name;
private double salary;
private LocalDate hireDay; public Employee(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day)
{
this.name = name;
this.salary = salary;
hireDay = LocalDate.of(year, month, day);
} public String getName()
{
return name;
} public double getSalary()
{
return salary;
} public LocalDate getHireDay()
{
return hireDay;
} public void raiseSalary(double byPercent)
{
double raise = salary * byPercent / ;
salary += raise;
} public boolean equals(Object otherObject)
{
// 快速测试,看看这些对象是否相同
if (this == otherObject) return true; // 如果显式参数为空,则必须返回false
if (otherObject == null) return false; // 如果显式参数为空,则必须返回false
if (getClass() != otherObject.getClass()) return false; // 现在我们知道otherObject是一个非空雇员
var other = (Employee) otherObject; // 测试字段是否具有相同的值
return Objects.equals(name, other.name)
&& salary == other.salary && Objects.equals(hireDay, other.hireDay);
} public int hashCode()
{
return Objects.hash(name, salary, hireDay);
} public String toString()
{
return getClass().getName() + "[name=" + name + ",salary=" + salary + ",hireDay="
+ hireDay + "]";
}
}
运行结果如下:

实验5-10代码如下:
Manager:
package equals; public class Manager extends Employee
{
private double bonus; public Manager(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day)
{
super(name, salary, year, month, day);
bonus = ;
} public double getSalary()
{
double baseSalary = super.getSalary();
return baseSalary + bonus;
} public void setBonus(double bonus)
{
this.bonus = bonus;
} public boolean equals(Object otherObject)
{
if (!super.equals(otherObject)) return false;
var other = (Manager) otherObject;
// super.equals checked that this and other belong to the same class
return bonus == other.bonus;
} public int hashCode()
{
return java.util.Objects.hash(super.hashCode(), bonus);
} public String toString()
{
return super.toString() + "[bonus=" + bonus + "]";
}
}
运行结果如下:
实验2:编程练习
Ÿ定义抽象类Shape:
属性:不可变常量double PI,值为3.14;
方法:public double getPerimeter();public double getArea())。
Ÿ 让Rectangle与Circle继承自Shape类。
Ÿ 编写double sumAllArea方法输出形状数组中的面积和和double sumAllPerimeter方法输出形状数组中的周长和。
Ÿ main方法中
1)输入整型值n,然后建立n个不同的形状。如果输入rect,则再输入长和宽。如果输入cir,则再输入半径。
2) 然后输出所有的形状的周长之和,面积之和。并将所有的形状信息以样例的格式输出。
3) 最后输出每个形状的类型与父类型,使用类似shape.getClass()(获得类型),shape.getClass().getSuperclass()(获得父类型);
思考sumAllArea和sumAllPerimeter方法放在哪个类中更合适?
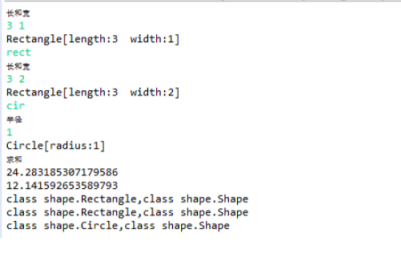
输入样例:
3
rect
1 1
rect
2 2
cir
1
输出样例:
18.28
8.14
[Rectangle [width=1, length=1], Rectangle [width=2, length=2], Circle [radius=1]]
class Rectangle,class Shape
class Rectangle,class Shape
程序代码如下:
shape:
package shape;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("个数");
int a = in.nextInt();
System.out.println("种类");
String rect="rect";
String cir="cir";
Shape[] num=new Shape[a];
for(int i=;i<a;i++){
String input=in.next();
if(input.equals(rect)) {
System.out.println("长和宽");
int length = in.nextInt();
int width = in.nextInt();
num[i]=new Rectangle(width,length);
System.out.println("Rectangle["+"length:"+length+" width:"+width+"]");
}
if(input.equals(cir)) {
System.out.println("半径");
int radius = in.nextInt();
num[i]=new Circle(radius);
System.out.println("Circle["+"radius:"+radius+"]");
}
}
Test c=new Test();
System.out.println("求和");
System.out.println(c.sumAllPerimeter(num));
System.out.println(c.sumAllArea(num));
for(Shape s:num) {
System.out.println(s.getClass()+","+s.getClass().getSuperclass());
}
}
public double sumAllArea(Shape score[])
{
double sum=;
for(int i=;i<score.length;i++)
sum+= score[i].getArea();
return sum;
}
public double sumAllPerimeter(Shape score[])
{
double sum=;
for(int i=;i<score.length;i++)
sum+= score[i].getPerimeter();
return sum;
}
}
Test:
package shape;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("个数");
int a = in.nextInt();
System.out.println("种类");
String rect="rect";
String cir="cir";
Shape[] num=new Shape[a];
for(int i=;i<a;i++){
String input=in.next();
if(input.equals(rect)) {
System.out.println("长和宽");
int length = in.nextInt();
int width = in.nextInt();
num[i]=new Rectangle(width,length);
System.out.println("Rectangle["+"length:"+length+" width:"+width+"]");
}
if(input.equals(cir)) {
System.out.println("半径");
int radius = in.nextInt();
num[i]=new Circle(radius);
System.out.println("Circle["+"radius:"+radius+"]");
}
}
Test c=new Test();
System.out.println("求和");
System.out.println(c.sumAllPerimeter(num));
System.out.println(c.sumAllArea(num));
for(Shape s:num) {
System.out.println(s.getClass()+","+s.getClass().getSuperclass());
}
}
public double sumAllArea(Shape score[])
{
double sum=;
for(int i=;i<score.length;i++)
sum+= score[i].getArea();
return sum;
}
public double sumAllPerimeter(Shape score[])
{
double sum=;
for(int i=;i<score.length;i++)
sum+= score[i].getPerimeter();
return sum;
}
}
运行结果如图:
3. 实验总结
通过这一周的学习以及自己在后期的自学过程当中,我深入了解了什么叫做继承,以及在继承中所包含的类型有哪些。继承是用已有类来构建新类的一种机制,当定义了一个新类继承了一个类时,这个新类继承一个类时,这个新类就继承了这个类的方法和域。而且继承是具有层次的,其代码也是可重用的,可以轻松定义子类。首先在学习过程当中我们学习了类,超类和子类的定义,让我明白了父类和子类时相对的。还学习了泛型数组列表与对象包装器与自动装箱,在后面还介绍了反射的概念,它是在程序运行期间发现更多的类及其属性的能力。并体会颇多,在今后的日子里我会好好深入学习Java知识。
201871010107-公海瑜《面向对象程序设计(java)》第6-7周学习总结的更多相关文章
- 201571030332 扎西平措 《面向对象程序设计Java》第八周学习总结
<面向对象程序设计Java>第八周学习总结 项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https: ...
- 201771010118马昕璐《面向对象程序设计java》第八周学习总结
第一部分:理论知识学习部分 1.接口 在Java程序设计语言中,接口不是类,而是对类的一组需求描述,由常量和一组抽象方法组成.Java为了克服单继承的缺点,Java使用了接口,一个类可以实现一个或多个 ...
- 201771010134杨其菊《面向对象程序设计java》第十周学习总结
第8章泛型程序设计学习总结 第一部分:理论知识 主要内容: 什么是泛型程序设计 泛型类的声明及实例化的方法 泛型方法的定义 ...
- 201771010134杨其菊《面向对象程序设计java》第八周学习总结
第八周学习总结 第一部分:理论知识 一.接口.lambda和内部类: Comparator与comparable接口: 1.comparable接口的方法是compareTo,只有一个参数:comp ...
- 201771010134杨其菊《面向对象程序设计java》第七周学习总结
第七周学习总结 第一部分:理论知识 1.继承是面向对象程序设计(Object Oriented Programming-OOP)中软件重用的关键技术.继承机制使用已经定义的类作为基础建立新的类定义,新 ...
- 201771010118 马昕璐《面向对象程序设计java》第十周学习总结
第一部分:理论知识学习部分 泛型:也称参数化类型(parameterized type)就是在定义类.接口和方法时,通过类型参数 指示将要处理的对象类型. 泛型程序设计(Generic program ...
- 201871010126 王亚涛《面向对象程序设计 JAVA》 第十三周学习总结
内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p/ ...
- 马凯军201771010116《面向对象程序设计Java》第八周学习总结
一,理论知识学习部分 6.1.1 接口概念 两种含义:一,Java接口,Java语言中存在的结构,有特定的语法和结构:二,一个类所具有的方法的特征集合,是一种逻辑上的抽象.前者叫做“Java接口”,后 ...
- 周强201771010141《面向对象程序设计Java》第八周学习总结
一.理论知识学习部分 Java为了克服单继承的缺点,Java使用了接口,一个类可以实现一个或多个接口. 接口体中包含常量定义和方法定义,接口中只进行方法的声明,不提供方法的实现. 类似建立类的继承关系 ...
- 201777010217-金云馨《面向对象程序设计Java》第八周学习总结
项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p ...
随机推荐
- 解决angular单页面页面底部跳转到新页面滚动条不在顶部的问题
以上jquery,下面js this.router.events.subscribe((event) => { document.body.scrollTop=0; }); 另一种写法 impo ...
- DRF--介绍和安装
前后端不分离 在前后端不分离的应用模式中,前端页面看到的效果都是由后端控制,由后端渲染页面或重定向,也就是后端需要控制前端的展示,前端与后端的耦合度很高.这种应用模式比较适合纯网页应用,但是当后端对接 ...
- 正睿暑期培训day1考试
链接 A 理解一下题意,然后玩几组样例就能发现,实际上就是\(k\)个\(i\)等价于\(1\)个\(i-1\).所以就类似于\(k\)进制进行进位,如果最后\(0\)位上不是\(0\),那么就存在划 ...
- polyfll方案优化
polyfill 在es6风靡的时候,babel给了我们一个有力的转换方案,可以在低版本浏览器上写一些新语法而不用考虑兼容问题 polyfill的诞生 语法和API区分 语法是用来产生特殊效果的一些符 ...
- hw笔试题-01
#include <stdlib.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> int str_split(char *inp ...
- Docker入门之安装与使用
1. 安装(windows) win7.win8以及win10家庭版 等需要利用 docker toolbox 来安装,国内可以使用阿里云的镜像来下载,下载地址:http://mirrors.aliy ...
- 【Java语言特性学习之四】常用集合
java中常见的数据结构
- 【linux】查看GPU使用率
nvidia-smi -l 1 每秒刷新一次
- 使用selenium爬虫抓取数据
写在前面 本来这篇文章该几个月前写的,后来忙着忙着就给忘记了.ps:事多有时候反倒会耽误事.几个月前,记得群里一朋友说想用selenium去爬数据,关于爬数据,一般是模拟访问某些固定网站,将自己关注的 ...
- POJ 1094 (传递闭包 + 拓扑排序)
题目链接: POJ 1094 题目大意:有 1 ~ N 个大写字母,且从 A 开始依次 N 个.再给你 M 个小于的关系,比如 A < B ,让你判断三种可能: 1.在第 i 个关系罗列之后,是 ...
