python 特征选择 绘图 + mine
demo代码:
# _*_coding:UTF-8_*_
import numpy as np
import sys
import pandas as pd
from pandas import Series,DataFrame
import numpy as np
import sys
from sklearn import preprocessing
from sklearn.ensemble import ExtraTreesClassifier
import os
from minepy import MINE def iterbrowse(path):
for home, dirs, files in os.walk(path):
for filename in files:
yield os.path.join(home, filename) def get_data(filename):
white_verify = []
with open(filename) as f:
lines = f.readlines()
data = {}
for line in lines:
a = line.split("\t")
if len(a) != 78:
print(line)
raise Exception("fuck")
white_verify.append([float(n) for n in a[3:]])
return white_verify if __name__ == '__main__':
# pdb.set_trace()
neg_file = "cc_data/black_all.txt"
pos_file = "cc_data/white_all.txt"
X = []
y = []
if os.path.isfile(pos_file):
if pos_file.endswith('.txt'):
pos_set = np.genfromtxt(pos_file)
elif pos_file.endswith('.npy'):
pos_set = np.load(pos_file)
X.extend(pos_set)
y += [0] * len(pos_set)
if os.path.isfile(neg_file):
if neg_file.endswith('.txt'):
neg_set = np.genfromtxt(neg_file)
elif neg_file.endswith('.npy'):
neg_set = np.load(neg_file) '''
X.extend(list(neg_set) * 5)
y += [1] * (5 * len(neg_set))
'''
X.extend(neg_set)
y += [1] * len(neg_set) print("len of X:", len(X))
print("X sample:", X[:3])
print("len of y:", len(y))
print("y sample:", y[:3])
X = [x[3:] for x in X]
print("filtered X sample:", X[:3]) cols = [str(i + 6) for i in range(len(X[0]))]
clf = ExtraTreesClassifier()
clf.fit(X, y)
print (clf.feature_importances_)
print "Features sorted by their score:"
print sorted(zip(clf.feature_importances_, cols), reverse=True) black_verify = []
for f in iterbrowse("todo/top"):
print(f)
black_verify += get_data(f)
# ValueError: operands could not be broadcast together with shapes (1,74) (75,) (1,74)
print(black_verify)
black_verify_labels = [3] * len(black_verify) white_verify = get_data("todo/white_verify.txt")
print(white_verify)
white_verify_labels = [2] * len(white_verify) unknown_verify = get_data("todo/pek_feature74.txt")
print(unknown_verify) # extend data
X = np.concatenate((X, black_verify))
y += black_verify_labels
X = np.concatenate((X, white_verify))
y += white_verify_labels #################################### plot ####################################
data_train = pd.DataFrame(X)
# cols = [str(i) for i in range(6, 81)]
data_train.columns = cols # add label column
# data_train = data_train.assign(label=pd.Series(y))
data_train["label"] = pd.Series(y) print(data_train.info())
print(data_train.columns) import matplotlib.pyplot as plt for col in cols:
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(20, 16), dpi=8)
fig.set(alpha=0.2)
plt.figure()
data_train[data_train.label == 0.0][col].plot()
data_train[data_train.label == 1.0][col].plot()
data_train[data_train.label == 2.0][col].plot()
data_train[data_train.label == 3.0][col].plot()
plt.xlabel(u"sample data id")
plt.ylabel(u"value")
plt.title(col)
plt.legend((u'white', u'black', u"white-todo", u"black-todo"), loc='best')
plt.show() print "calculate MINE mic value:"
for col in cols:
print col,
mine = MINE(alpha=0.6, c=15,
est="mic_approx") # http://minepy.readthedocs.io/en/latest/python.html#second-example
mine.compute_score(data_train[col], y)
print "MIC=", mine.mic() sys.exit(-1)
extend data 表示待预测的数据
关于mic:
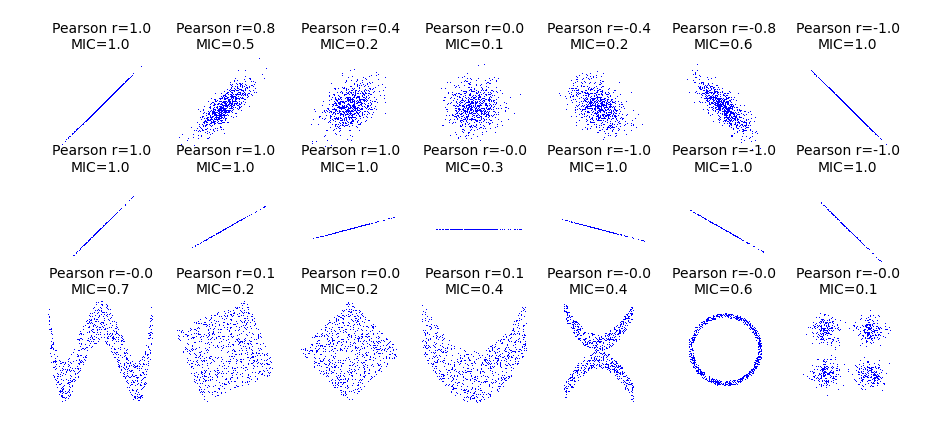
from __future__ import division
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from minepy import MINE rs = np.random.RandomState(seed=0) def mysubplot(x, y, numRows, numCols, plotNum,
xlim=(-4, 4), ylim=(-4, 4)): r = np.around(np.corrcoef(x, y)[0, 1], 1)
mine = MINE(alpha=0.6, c=15, est="mic_approx")
mine.compute_score(x, y)
mic = np.around(mine.mic(), 1)
ax = plt.subplot(numRows, numCols, plotNum,
xlim=xlim, ylim=ylim)
ax.set_title('Pearson r=%.1f\nMIC=%.1f' % (r, mic),fontsize=10)
ax.set_frame_on(False)
ax.axes.get_xaxis().set_visible(False)
ax.axes.get_yaxis().set_visible(False)
ax.plot(x, y, ',')
ax.set_xticks([])
ax.set_yticks([])
return ax def rotation(xy, t):
return np.dot(xy, [[np.cos(t), -np.sin(t)], [np.sin(t), np.cos(t)]]) def mvnormal(n=1000):
cors = [1.0, 0.8, 0.4, 0.0, -0.4, -0.8, -1.0]
for i, cor in enumerate(cors):
cov = [[1, cor],[cor, 1]]
xy = rs.multivariate_normal([0, 0], cov, n)
mysubplot(xy[:, 0], xy[:, 1], 3, 7, i+1) def rotnormal(n=1000):
ts = [0, np.pi/12, np.pi/6, np.pi/4, np.pi/2-np.pi/6,
np.pi/2-np.pi/12, np.pi/2]
cov = [[1, 1],[1, 1]]
xy = rs.multivariate_normal([0, 0], cov, n)
for i, t in enumerate(ts):
xy_r = rotation(xy, t)
mysubplot(xy_r[:, 0], xy_r[:, 1], 3, 7, i+8) def others(n=1000):
x = rs.uniform(-1, 1, n)
y = 4*(x**2-0.5)**2 + rs.uniform(-1, 1, n)/3
mysubplot(x, y, 3, 7, 15, (-1, 1), (-1/3, 1+1/3)) y = rs.uniform(-1, 1, n)
xy = np.concatenate((x.reshape(-1, 1), y.reshape(-1, 1)), axis=1)
xy = rotation(xy, -np.pi/8)
lim = np.sqrt(2+np.sqrt(2)) / np.sqrt(2)
mysubplot(xy[:, 0], xy[:, 1], 3, 7, 16, (-lim, lim), (-lim, lim)) xy = rotation(xy, -np.pi/8)
lim = np.sqrt(2)
mysubplot(xy[:, 0], xy[:, 1], 3, 7, 17, (-lim, lim), (-lim, lim)) y = 2*x**2 + rs.uniform(-1, 1, n)
mysubplot(x, y, 3, 7, 18, (-1, 1), (-1, 3)) y = (x**2 + rs.uniform(0, 0.5, n)) * \
np.array([-1, 1])[rs.random_integers(0, 1, size=n)]
mysubplot(x, y, 3, 7, 19, (-1.5, 1.5), (-1.5, 1.5)) y = np.cos(x * np.pi) + rs.uniform(0, 1/8, n)
x = np.sin(x * np.pi) + rs.uniform(0, 1/8, n)
mysubplot(x, y, 3, 7, 20, (-1.5, 1.5), (-1.5, 1.5)) xy1 = np.random.multivariate_normal([3, 3], [[1, 0], [0, 1]], int(n/4))
xy2 = np.random.multivariate_normal([-3, 3], [[1, 0], [0, 1]], int(n/4))
xy3 = np.random.multivariate_normal([-3, -3], [[1, 0], [0, 1]], int(n/4))
xy4 = np.random.multivariate_normal([3, -3], [[1, 0], [0, 1]], int(n/4))
xy = np.concatenate((xy1, xy2, xy3, xy4), axis=0)
mysubplot(xy[:, 0], xy[:, 1], 3, 7, 21, (-7, 7), (-7, 7)) plt.figure(facecolor='white')
mvnormal(n=800)
rotnormal(n=200)
others(n=800)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
python 特征选择 绘图 + mine的更多相关文章
- python常用绘图软件包记录
在没有使用python之前,觉得matlab的绘图功能还算可以~但现在发现python的绘图包真的好强大,绘制出的图像非常专业漂亮,但具体使用还有待学习,这里记录学习过程中遇到的python绘图包,以 ...
- Python之绘图和可视化
Python之绘图和可视化 1. 启用matplotlib 最常用的Pylab模式的IPython(IPython --pylab) 2. matplotlib的图像都位于Figure对象中. 可以使 ...
- 10分钟轻松学会python turtle绘图
 1. 画布(canvas) 1.1 相关函数: 2. 画笔 2.1 画笔的状态 2.2 画笔的属性 2.3 绘图命令 3. 命令详解 4. 绘图举例 4.1 太阳花 4.2 绘制小蟒蛇 4.3 绘 ...
- python matplotlib 绘图基础
在利用Python做数据分析时,探索数据以及结果展现上图表的应用是不可或缺的. 在Python中通常情况下都是用matplotlib模块进行图表制作. 先理下,matplotlib的结构原理: mat ...
- 10分钟轻松学会 Python turtle 绘图
python2.6版本中后引入的一个简单的绘图工具,叫做海龟绘图(Turtle Graphics),turtle库是python的内部库,使用导入即可 import turtle 先说明一下turtl ...
- Python函数绘图
最近看数学,发现有时候画个图还真管用,对理解和展示效果都不错.尤其是三维空间和一些复杂函数,相当直观,也有助于解题.本来想用mathlab,下载安装都太费事,杀鸡不用牛刀,Python基本就能实现.下 ...
- 【Matplotlib】利用Python进行绘图
[Matplotlib] 教程:https://morvanzhou.github.io/tutorials/data-manipulation/plt/ 官方文档:https://matplotli ...
- python海龟绘图
最近学了python,看了几本书之后,才明白python的强大,python是一种解释型的语言,即每写一行程序就执行一行. 而且在科学计算方面,处理的能力特别的方便. 比如python中的字典dict ...
- 【震惊】手把手教你用python做绘图工具(一)
在这篇博客里将为你介绍如何通过numpy和cv2进行结和去创建画布,包括空白画布.白色画布和彩色画布.创建画布是制作绘图工具的前提,有了画布我们就可以在画布上尽情的挥洒自己的艺术细胞. 还在为如何去绘 ...
随机推荐
- httpd在嵌入式中应用
在启动脚本合适位置添加: httpd -h /usr/app/www/ 即开始httpd服务,并定位到/usr/app/www/ 注:busybox已支持httpd命令,所以直接用即可. busybo ...
- KSTORE日常工作遇到问题总结
1.csv导入kstore命令语句 oimpexp -F "E:/127.csv" -S KSTORE -T "T_BUSDATA" -d 1 -z -B 7 ...
- linux下LAMP环境搭建
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ linux下LAMP环境搭建 ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ ...
- Selenium+Python :WebDriver设计模式( Page Object )
Page Object 设计原理 Page Object设计模式是Selenium自动化测试项目的最佳设计模式之一,强调测试.逻辑.数据和驱动相互分离. Page Object模式是Selenium中 ...
- hiho一下 第二周&第四周:从Trie树到Trie图
hihocoder #1014 题目地址:http://hihocoder.com/problemset/problem/1014 hihocoder #1036 题目地址: http://hihoc ...
- element开源框架
vue-element-admin:https://gitee.com/accest/bod-element https://gitee.com/liuyuantao/vue-element-ad ...
- scp命令需要指定端口时要紧跟在scp后
问题来源:我本地是Ubuntu操作系统,有时需要更新一些文件到服务器.但是,为了安全起见我们都是将服务器的sshd端口修改的,通常不使用默认的22号端口. 如果我们使用scp命令时:scp upl ...
- 关于iOS的手势UIGestureRecognizer问题
typedef NS_ENUM(NSInteger, UIGestureRecognizerState) { UIGestureRecognizerStatePossible, // 尚未识别是何种手 ...
- 如何更改CSDN博客高亮代码皮肤的样式,使博客看起来更有范(推荐)
由于本人写博客的时候,也没有配置博客的相关属性,因此贴出来的代码块都是CSDN默认的,因此代码背景色都是白色的,如下所示: 但是本人在浏览他人博客的时候,发现有些博客的代码块看起来比较有范,整个代码库 ...
- 学习Filter
http://www.cnblogs.com/jbelial/archive/2012/07/09/2582638.html Filter 介绍: 它主要用于对用户请求进行预处理,也可以对HttpSe ...
