Markov Decision Process in Detail
From the last post about MDP, we know the environment consists of 5 basic elements:
S:State Space of environment;
A:Actions Space that the environment allows;
{Ps,s'}:Transition Matrix, the probabilities of how environment state transit from one to another when actions are taken. The number of matrices equals to the number of actions.
R: Reward, when the system transitions from state s to s' due to action a, how much reward can an agent receive from the environment. Sometimes, reward have different definition.
γ: How reward discounts by time.
How Different between MDP and MRP:
Keyword: Action
The five elements of MDP can be illustrated by the chart below, in which the green circles are states, orange circles are actions, and there are two rewards. In MRP and Markov Process, we directly know the transition matrix. However, in the transition path from one state to another is interupted by actions. And it's worth noting that when the environment is at a certain state, there is no probabilities for actions. The reason is quite understandable: we live in the some world(environment), but different people have different behaviors.

Agent and Policy
Agent is the person or robot who interacts with the environment in Reinforcement Learning. Like human being, everyone may have different behavior under the same condition. The probability distribution of behaviors under different states is Policy. There are so many probabilities in an environment, but for a specific agent (person), he or she may take only one or several possible actions under a certain state. Given states, the policy is defined by:
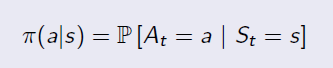
An example of policy is shown below:

From MRP to MDP: MRP+Policy
Transition Matrix: Without policies we do not exactly know the the probability from state s transitioning to s', because different agents may have different probabilitie to take actions. As long as we get π, we can calculate the state transition matrix. 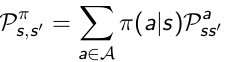
In the chart above, for example, if an agent has probabilitie 0.4 and 0.6 for action a0 and a1, the transition probability from s0 to s1 is: 0.4*0.5+0.6*1=0.8
Reward:
In MDP the reward function is related to actions, which average the uncertainties of the result from an action.
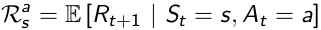
Once we've got the Policy π, we know the action distribution of a specific agent, so we can average the uncertaintie of actions, then measure how much immediate reward can receive from state s under policy π.

So now we go back from MDP to MRP, and the Markov Reward Process is defined by the tuple

Two Value Functions:
State Value Function:
State Value Function is the same as the value function in MRP. It is used to evaluate the goodness of being in a state s(by immedate and future reward), and the only difference is to average the uncertainty of actions under policy π. It is in the form of:
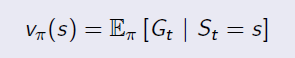
Action Value Function:
To average uncertainties of actions, it's neccesary to know the expected reward from possible actions. So we have Action Value Functionin MDP, which reveals whether an action is good or bad when an agent takes an particular action in state s.

If we calculate expectation of Action Value Functions under the same state s, we will end up with the State Value Function v:
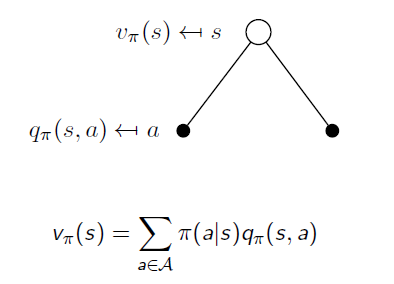
Similarly, when an action is taken, the system may end up with different states. When we remove the uncertainty of state transition, we go back from State Value Function to Action Value Function:
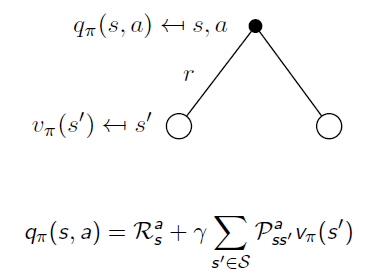
If we put them together:
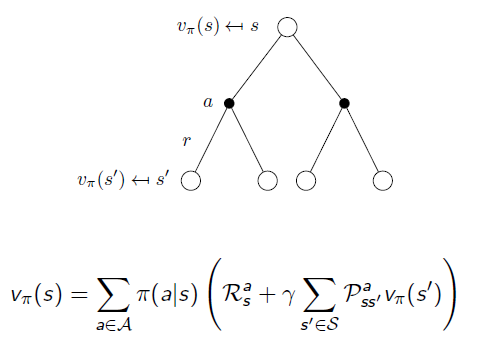
Another way:

Markov Decision Process in Detail的更多相关文章
- Step-by-step from Markov Process to Markov Decision Process
In this post, I will illustrate Markov Property, Markov Reward Process and finally Markov Decision P ...
- Ⅱ Finite Markov Decision Processes
Dictum: Is the true wisdom fortitude ambition. -- Napoleon 马尔可夫决策过程(Markov Decision Processes, MDPs ...
- Markov Decision Processes
为了实现某篇论文中的算法,得先学习下马尔可夫决策过程~ 1. https://leonardoaraujosantos.gitbooks.io/artificial-inteligence/conte ...
- Reinforcement Learning Index Page
Reinforcement Learning Posts Step-by-step from Markov Property to Markov Decision Process Markov Dec ...
- 论文笔记之:Learning to Track: Online Multi-Object Tracking by Decision Making
Learning to Track: Online Multi-Object Tracking by Decision Making ICCV 2015 本文主要是研究多目标跟踪,而 online ...
- 强化学习二:Markov Processes
一.前言 在第一章强化学习简介中,我们提到强化学习过程可以看做一系列的state.reward.action的组合.本章我们将要介绍马尔科夫决策过程(Markov Decision Processes ...
- (转) Deep Reinforcement Learning: Pong from Pixels
Andrej Karpathy blog About Hacker's guide to Neural Networks Deep Reinforcement Learning: Pong from ...
- 机器学习算法基础(Python和R语言实现)
https://www.analyticsvidhya.com/blog/2015/08/common-machine-learning-algorithms/?spm=5176.100239.blo ...
- How do I learn machine learning?
https://www.quora.com/How-do-I-learn-machine-learning-1?redirected_qid=6578644 How Can I Learn X? ...
随机推荐
- Java使用POI读取和写入Excel指南(转)
做项目时经常有通过程序读取Excel数据,或是创建新的Excel并写入数据的需求: 网上很多经验教程里使用的POI版本都比较老了,一些API在新版里已经废弃,这里基于最新的Apache POI 4.0 ...
- Sobel硬件实现的硬件代码分析(三)
#include "xaxivdma.h" #include "xaxivdma_i.h" #include "xhls_sobel.h" ...
- FFmpeg从入门到出家(FLV文件结构解析)
FLV(FLASH VIDEO),是一种常用的文件封装格式,目前国内外大部分视频分享网站都是采用的这种格式.其标准定义为<Adobe Flash Video File Format Specif ...
- #1062 - Duplicate entry '0' for key 'PRIMARY'—— mysql的小问题
问题:# 1062 -重复输入“0”. 原因:我估计可能是数据表中主键这一栏已经有一个为“0”了,一般出现这种问题是以int类型的字段在输入时没有输如数据,而int类型默认值为“0”,而你之前第一条数 ...
- linux 调整内核优化
所谓内核优化,主要是在 linux 中针对业务服务应用而进行的系统内核参数优化,优化并无特殊的 标准,下面以常见生产环境 linux 的内核优化为例讲解,仅供大家参考: 内核调优 #vi /etc/s ...
- Google Capture The Flag 2018 (Quals) - Reverse - Beginner's Quest - Gatekeeper
参考链接:https://ctftime.org/task/6264 题目 It's a media PC! All fully purchased through the online subscr ...
- AOP拦截日志类,抛异常:java.lang.IllegalStateException: It is illegal to call this method if the current request is not in asynchronous mode
AOP的日志拦截类中,抛出异常: java.lang.IllegalStateException: It is illegal to call this method if the current r ...
- Linux 查找指定内容在哪个文件中
在实际的工作中,忘记配置项放在哪个文件中时,可借助命令来查询. eg: 1.grep -r "查询内容" 文件目录 #这样查询出来的包括文件名+内容 grep -r -l ...
- sqlmap 基本使用步骤(二)
post------------------------------------------------------------------1.使用 -rpython sqlmap.py -r pos ...
- css3-css3属性选择器
在HTML中,通过各种各样的属性可以给元素增加很多附加的信息.例如,通过id属性可以将不同div元素进行区分. 在CSS2中引入了一些属性选择器,而CSS3在CSS2的基础上对属性选择器进行了扩展,新 ...
