spring源码 ConfigurableListableBeanFactory根接口
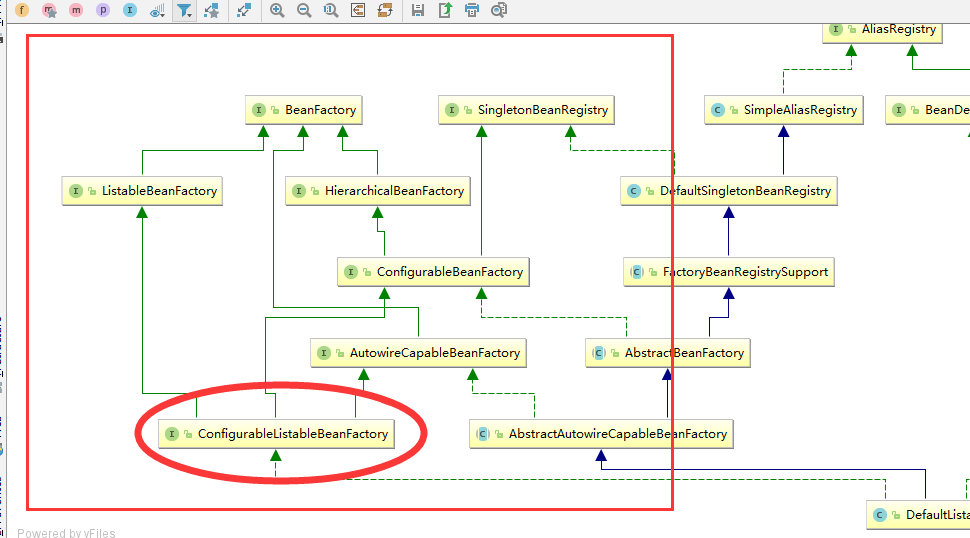
用机器翻译+原作者的翻译:https://blog.csdn.net/u011179993/article/details/51636742
/*
* Copyright 2002-2015 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/ package org.springframework.beans.factory.config; import java.util.Iterator; import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.ListableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.NoSuchBeanDefinitionException; /**
* Configuration interface to be implemented by most listable bean factories.
* In addition to {@link ConfigurableBeanFactory}, it provides facilities to
* analyze and modify bean definitions, and to pre-instantiate singletons.
*
* <p>This subinterface of {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory}
* is not meant to be used in normal application code: Stick to
* {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory} or
* {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.ListableBeanFactory} for typical
* use cases. This interface is just meant to allow for framework-internal
* plug'n'play even when needing access to bean factory configuration methods.
*
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 03.11.2003
* @see org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#getBeanFactory()
*/
public interface ConfigurableListableBeanFactory
extends ListableBeanFactory, AutowireCapableBeanFactory, ConfigurableBeanFactory { /**
* Ignore the given dependency type for autowiring:
* for example, String. Default is none.
* @param type the dependency type to ignore
设置忽略的依赖类型关系,注册找到特殊的依赖
*/
void ignoreDependencyType(Class<?> type); /**
* Ignore the given dependency interface for autowiring.
* <p>This will typically be used by application contexts to register
* dependencies that are resolved in other ways, like BeanFactory through
* BeanFactoryAware or ApplicationContext through ApplicationContextAware.
* <p>By default, only the BeanFactoryAware interface is ignored.
* For further types to ignore, invoke this method for each type.
* @param ifc the dependency interface to ignore
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactoryAware
* @see org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware
设置忽略依赖接口关系
*/
void ignoreDependencyInterface(Class<?> ifc); /**
* Register a special dependency type with corresponding autowired value.
* <p>This is intended for factory/context references that are supposed
* to be autowirable but are not defined as beans in the factory:
* e.g. a dependency of type ApplicationContext resolved to the
* ApplicationContext instance that the bean is living in.
* <p>Note: There are no such default types registered in a plain BeanFactory,
* not even for the BeanFactory interface itself.
* @param dependencyType the dependency type to register. This will typically
* be a base interface such as BeanFactory, with extensions of it resolved
* as well if declared as an autowiring dependency (e.g. ListableBeanFactory),
* as long as the given value actually implements the extended interface.
* @param autowiredValue the corresponding autowired value. This may also be an
* implementation of the {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.ObjectFactory}
* interface, which allows for lazy resolution of the actual target value.
*/
void registerResolvableDependency(Class<?> dependencyType, Object autowiredValue); /**
* Determine whether the specified bean qualifies as an autowire candidate,
* to be injected into other beans which declare a dependency of matching type.
* <p>This method checks ancestor factories as well.
* @param beanName the name of the bean to check
* @param descriptor the descriptor of the dependency to resolve
* @return whether the bean should be considered as autowire candidate
* @throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException if there is no bean with the given name
*/
boolean isAutowireCandidate(String beanName, DependencyDescriptor descriptor)
throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException; /**
* Return the registered BeanDefinition for the specified bean, allowing access
* to its property values and constructor argument value (which can be
* modified during bean factory post-processing).
* <p>A returned BeanDefinition object should not be a copy but the original
* definition object as registered in the factory. This means that it should
* be castable to a more specific implementation type, if necessary.
* <p><b>NOTE:</b> This method does <i>not</i> consider ancestor factories.
* It is only meant for accessing local bean definitions of this factory.
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return the registered BeanDefinition
* @throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException if there is no bean with the given name
* defined in this factory
获取bean的定义(可以访问属性值和构造方法的参数值)
*/
BeanDefinition getBeanDefinition(String beanName) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException; /**
* Return a unified view over all bean names managed by this factory.
* <p>Includes bean definition names as well as names of manually registered
* singleton instances, with bean definition names consistently coming first,
* analogous to how type/annotation specific retrieval of bean names works.
* @return the composite iterator for the bean names view
* @since 4.1.2
* @see #containsBeanDefinition
* @see #registerSingleton
* @see #getBeanNamesForType
* @see #getBeanNamesForAnnotation
迭代BeanName
*/
Iterator<String> getBeanNamesIterator(); /**
* Clear the merged bean definition cache, removing entries for beans
* which are not considered eligible for full metadata caching yet.
* <p>Typically triggered after changes to the original bean definitions,
* e.g. after applying a {@link BeanFactoryPostProcessor}. Note that metadata
* for beans which have already been created at this point will be kept around.
* @since 4.2
* @see #getBeanDefinition
* @see #getMergedBeanDefinition
清除元数据缓存
*/
void clearMetadataCache(); /**
* Freeze all bean definitions, signalling that the registered bean definitions
* will not be modified or post-processed any further.
* <p>This allows the factory to aggressively cache bean definition metadata.
锁定配置信息,在调用refresh时会用到
*/
void freezeConfiguration(); /**
* Return whether this factory's bean definitions are frozen,
* i.e. are not supposed to be modified or post-processed any further.
* @return {@code true} if the factory's configuration is considered frozen
*/
boolean isConfigurationFrozen(); /**
* Ensure that all non-lazy-init singletons are instantiated, also considering
* {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBean FactoryBeans}.
* Typically invoked at the end of factory setup, if desired.
* @throws BeansException if one of the singleton beans could not be created.
* Note: This may have left the factory with some beans already initialized!
* Call {@link #destroySingletons()} for full cleanup in this case.
* @see #destroySingletons()
预加载不是懒加载的单例,用于解决循环依赖的问题
*/
void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException; }
spring源码 ConfigurableListableBeanFactory根接口的更多相关文章
- spring源码 BeanFactory根接口
/* * Copyright 2002-2016 the original author or authors. * * Licensed under the Apache License, Vers ...
- Spring源码解析 - BeanFactory接口体系解读
不知道为什么看着Spring的源码,感触最深的是Spring对概念的抽象,所以我就先学接口了. BeanFactory是Spring IOC实现的基础,这边定义了一系列的接口,我们通过这些接口的学习, ...
- spring源码分析——BeanPostProcessor接口
BeanPostProcessor是处理bean的后置接口,beanDefinitionMaps中的BeanDefinition实例化完成后,完成populateBean,属性设置,完成 初始化后,这 ...
- spring源码:Aware接口(li)
一.spring容器中的aware接口介绍 Spring中提供了各种Aware接口,比较常见的如BeanFactoryAware,BeanNameAware,ApplicationContextAwa ...
- spring源码:Aware接口
一.spring容器中的aware接口介绍 Spring中提供了各种Aware接口,比较常见的如BeanFactoryAware,BeanNameAware,ApplicationContextAwa ...
- Spring源码解析 - AbstractBeanFactory 实现接口与父类分析
我们先来看类图吧: 除了BeanFactory这一支的接口,AbstractBeanFactory主要实现了AliasRegistry和SingletonBeanRegistry接口. 这边主要提供了 ...
- Spring源码分析——资源访问利器Resource之接口和抽象类分析
从今天开始,一步步走上源码分析的路.刚开始肯定要从简单着手.我们先从Java发展史上最强大的框架——Spring...旗下的资源抽象接口Resource开始吧. 我看了好多分析Spring源码的,每每 ...
- spring源码分析系列 (1) spring拓展接口BeanFactoryPostProcessor、BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
更多文章点击--spring源码分析系列 主要分析内容: 一.BeanFactoryPostProcessor.BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor简述与demo示例 ...
- spring源码分析系列 (2) spring拓展接口BeanPostProcessor
Spring更多分析--spring源码分析系列 主要分析内容: 一.BeanPostProcessor简述与demo示例 二.BeanPostProcessor源码分析:注册时机和触发点 (源码基于 ...
随机推荐
- ORACLE 用32進制表示月中的一天
WHEN 'YMD' THEN v_year := to_char(SYSDATE, 'Y'); v_month := FN_CONVERT_DECIM ...
- 使用anaconda 3安装tensorflow 1.15.0 (win10环境)
0.写在前面 之前其实安装过一次tensorflow,但是由于电脑中毒,重装了系统,把所有的环境全部删除了.之前在博客里转发了一篇别人在win10安装tensorflow的教程,但是版本比较旧了, ...
- 库克承认iPhone销售不佳是因定价太高,但降价能救苹果吗?
iPhone定价愈来愈高,已经是不争的事实.但iPhone价格的飙升,其实并不是"正常"的.早在乔布斯时代,iPhone的价格维持在5000元左右.虽然看起来价格略高,但也在很多人 ...
- tomcat安装apr报错解决
参考http://www.cnblogs.com/nuccch/p/7598361.html 1.no c complie 安装gcc解决 2.rm: cannot remove `libtoolT' ...
- codeforces 962 F Simple Cycles Edges
求简单环,即求点=边数的点双分量,加上判断点和边的模板即可 (简单环模板,区分与点双缩点) ; ], edgecnt, dfn[maxm], low[maxm], bcc_cnt, bccnum[ma ...
- IOS 常用View属性设置
设置按钮属性 1.设置按钮背景颜色 backgroundColor @property (weak, nonatomic) IBOutlet UIButton *deleteButton; self. ...
- 对于文章的字母、单词、短语,(无用词表)的检索Java代码实现
日期:2019.5.9 博客期:073 星期四 今天软件工程课上,又做了测试,老师说我们的速度太慢了,实际上我也觉得自己很慢.老师说了这是我们的上一届的大二上半学期学习中的速度,所以呢?意思就是说我们 ...
- eclipse中从数据库生成hibernate实体类
为什么写这篇BLOG,是因为经常有同事或网友问起我hiberante实体类的生成问题.所以下次再有人问我可以省一堆的话了,其实这个真的是很简单. 现在hibernate在项目中的应用是越 ...
- 使用自己定义的DIV的滚动条
基本思路: 让DIV浮动起来,利用postion:fixed/absolute,设定height:100% var $card=$("#cardDetail"); $ca ...
- [STL]string类型的getline函数
3.cin.getline() 实际是cin.getline(接收字符串到m,接收个数n,结束字符).接收一个字符串,可以接收空格等,最后一个字符为‘\0’.结束符可以通过设置第三个参数自己设置,默认 ...
