自定义spark UDAF
Spark提供了两种自定义聚合函数的方法,分别如下:
Untyped User-Defined Aggregate Functions
有类型的自定义聚合函数,主要适用于 DataSet
Type-Safe User-Defined Aggregate Functions
无类型的自定义聚合函数,主要适用于 DataFrame
无类型的自定义聚合函数样例代码:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List; import org.apache.spark.sql.Dataset;
import org.apache.spark.sql.Row;
import org.apache.spark.sql.SparkSession;
import org.apache.spark.sql.expressions.MutableAggregationBuffer;
import org.apache.spark.sql.expressions.UserDefinedAggregateFunction;
import org.apache.spark.sql.types.DataType;
import org.apache.spark.sql.types.DataTypes;
import org.apache.spark.sql.types.StructField;
import org.apache.spark.sql.types.StructType; public static class MyAverage extends UserDefinedAggregateFunction { private StructType inputSchema;
private StructType bufferSchema; public MyAverage() {
List<StructField> inputFields = new ArrayList<>();
inputFields.add(DataTypes.createStructField("inputColumn", DataTypes.LongType, true));
inputSchema = DataTypes.createStructType(inputFields); List<StructField> bufferFields = new ArrayList<>();
bufferFields.add(DataTypes.createStructField("sum", DataTypes.LongType, true));
bufferFields.add(DataTypes.createStructField("count", DataTypes.LongType, true));
bufferSchema = DataTypes.createStructType(bufferFields);
}
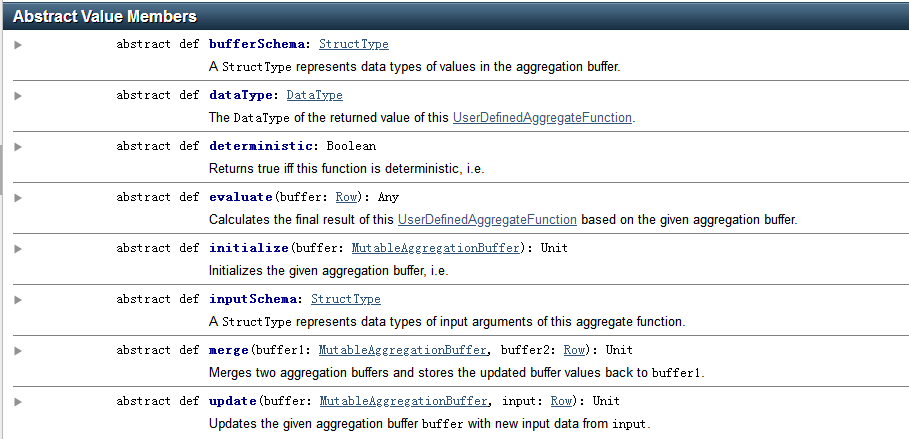
// Data types of input arguments of this aggregate function
public StructType inputSchema() {
return inputSchema;
}
// Data types of values in the aggregation buffer
public StructType bufferSchema() {
return bufferSchema;
}
// The data type of the returned value
public DataType dataType() {
return DataTypes.DoubleType;
}
// Whether this function always returns the same output on the identical 相同的 input
public boolean deterministic() {
return true;
}
// Initializes the given aggregation buffer. The buffer itself is a `Row` that in addition to
// standard methods like retrieving 获取 a value at an index (e.g., get(), getBoolean()), provides
// the opportunity 方式 to update its values. Note that arrays and maps inside the buffer are still
// immutable 不可变的.
public void initialize(MutableAggregationBuffer buffer) {
buffer.update(0, 0L);
buffer.update(1, 0L);
}
// Updates the given aggregation buffer `buffer` with new input data from `input`
public void update(MutableAggregationBuffer buffer, Row input) {
if (!input.isNullAt(0)) {
long updatedSum = buffer.getLong(0) + input.getLong(0);
long updatedCount = buffer.getLong(1) + 1;
buffer.update(0, updatedSum);
buffer.update(1, updatedCount);
}
}
// Merges two aggregation buffers and stores the updated buffer values back to `buffer1`
public void merge(MutableAggregationBuffer buffer1, Row buffer2) {
long mergedSum = buffer1.getLong(0) + buffer2.getLong(0);
long mergedCount = buffer1.getLong(1) + buffer2.getLong(1);
buffer1.update(0, mergedSum);
buffer1.update(1, mergedCount);
}
// Calculates the final result
public Double evaluate(Row buffer) {
return ((double) buffer.getLong(0)) / buffer.getLong(1);
}
} // Register the function to access it
spark.udf().register("myAverage", new MyAverage()); Dataset<Row> df = spark.read().json("examples/src/main/resources/employees.json");
df.createOrReplaceTempView("employees");
df.show();
// +-------+------+
// | name|salary|
// +-------+------+
// |Michael| 3000|
// | Andy| 4500|
// | Justin| 3500|
// | Berta| 4000|
// +-------+------+ Dataset<Row> result = spark.sql("SELECT myAverage(salary) as average_salary FROM employees");
result.show();
// +--------------+
// |average_salary|
// +--------------+
// | 3750.0|
// +--------------+
样例代码2:
import java.util.Arrays; import org.apache.spark.sql.Row;
import org.apache.spark.sql.expressions.MutableAggregationBuffer;
import org.apache.spark.sql.expressions.UserDefinedAggregateFunction;
import org.apache.spark.sql.types.DataType;
import org.apache.spark.sql.types.DataTypes;
import org.apache.spark.sql.types.StructType; /**
* 组内拼接去重函数(group_concat_distinct())
*/
public class GroupConcatDistinctUDAF extends UserDefinedAggregateFunction { private static final long serialVersionUID = -2510776241322950505L; // 指定输入数据的字段与类型
// 指定具体的输入数据的类型
// * 自段名称随意:Users can choose names to identify the input arguments - 这里可以是“name”,或者其他任意串
private StructType inputSchema = DataTypes.createStructType(Arrays.asList(
DataTypes.createStructField("cityInfo", DataTypes.StringType, true))); // 指定缓冲数据的字段与类型
// 在进行聚合操作的时候所要处理的数据的中间结果类型
private StructType bufferSchema = DataTypes.createStructType(Arrays.asList(
DataTypes.createStructField("bufferCityInfo", DataTypes.StringType, true))); // 指定返回类型
private DataType dataType = DataTypes.StringType; // 指定是否是确定性的
/*whether given the same input,
* always return the same output
* true: yes*/
private boolean deterministic = true; @Override
public StructType inputSchema() {
return inputSchema;
} @Override
public StructType bufferSchema() {
return bufferSchema;
} @Override
public DataType dataType() {
return dataType;
} @Override
public boolean deterministic() {
return deterministic;
} /**
* 初始化
* 可以认为是,你自己在内部指定一个初始的值
* Initializes the given aggregation buffer
*/
@Override
public void initialize(MutableAggregationBuffer buffer) {
buffer.update(0, "");
} /**
* 更新
* 可以认为是,一个一个地将组内的字段值传递进来
* 实现拼接的逻辑
*
* 在进行聚合的时候,每当有新的值进来,对分组后的聚合如何进行计算
* 本地的聚合操作,相当于Hadoop MapReduce模型中的Combiner
*/
@Override
public void update(MutableAggregationBuffer buffer, Row input) {
// 缓冲中的已经拼接过的城市信息串
String bufferCityInfo = buffer.getString(0);
// 刚刚传递进来的某个城市信息
String cityInfo = input.getString(0); // 在这里要实现去重的逻辑
// 判断:之前没有拼接过某个城市信息,那么这里才可以接下去拼接新的城市信息
if(!bufferCityInfo.contains(cityInfo)) {
if("".equals(bufferCityInfo)) {
bufferCityInfo += cityInfo;
} else {
// 比如1:北京
// 1:北京,2:上海
bufferCityInfo += "," + cityInfo;
} buffer.update(0, bufferCityInfo);
}
} /**
* 合并
* update操作,可能是针对一个分组内的部分数据,在某个节点上发生的
* 但是可能一个分组内的数据,会分布在多个节点上处理
* 此时就要用merge操作,将各个节点上分布式拼接好的串,合并起来
*/
@Override
public void merge(MutableAggregationBuffer buffer1, Row buffer2) {
String bufferCityInfo1 = buffer1.getString(0);
String bufferCityInfo2 = buffer2.getString(0); for(String cityInfo : bufferCityInfo2.split(",")) {
if(!bufferCityInfo1.contains(cityInfo)) {
if("".equals(bufferCityInfo1)) {
bufferCityInfo1 += cityInfo;
} else {
bufferCityInfo1 += "," + cityInfo;
}
}
} buffer1.update(0, bufferCityInfo1);
} @Override
public Object evaluate(Row row) {
return row.getString(0);
} }
有类型的自定义聚合函数,样例代码:
import java.io.Serializable; import org.apache.spark.sql.Dataset;
import org.apache.spark.sql.Encoder;
import org.apache.spark.sql.Encoders;
import org.apache.spark.sql.SparkSession;
import org.apache.spark.sql.TypedColumn;
import org.apache.spark.sql.expressions.Aggregator; public static class Employee implements Serializable {
private String name;
private long salary; // Constructors, getters, setters... } public static class Average implements Serializable {
private long sum;
private long count; // Constructors, getters, setters... } public static class MyAverage extends Aggregator<Employee, Average, Double> {
// A zero value for this aggregation. Should satisfy the property that any b + zero = b
public Average zero() {
return new Average(0L, 0L);
}
// Combine two values to produce a new value. For performance, the function may modify `buffer`
// and return it instead of constructing a new object
public Average reduce(Average buffer, Employee employee) {
long newSum = buffer.getSum() + employee.getSalary();
long newCount = buffer.getCount() + 1;
buffer.setSum(newSum);
buffer.setCount(newCount);
return buffer;
}
// Merge two intermediate values
public Average merge(Average b1, Average b2) {
long mergedSum = b1.getSum() + b2.getSum();
long mergedCount = b1.getCount() + b2.getCount();
b1.setSum(mergedSum);
b1.setCount(mergedCount);
return b1;
}
// Transform the output of the reduction
public Double finish(Average reduction) {
return ((double) reduction.getSum()) / reduction.getCount();
}
// Specifies the Encoder for the intermediate value type
public Encoder<Average> bufferEncoder() {
return Encoders.bean(Average.class);
}
// Specifies the Encoder for the final output value type
public Encoder<Double> outputEncoder() {
return Encoders.DOUBLE();
}
} Encoder<Employee> employeeEncoder = Encoders.bean(Employee.class);
String path = "examples/src/main/resources/employees.json";
Dataset<Employee> ds = spark.read().json(path).as(employeeEncoder);
ds.show();
// +-------+------+
// | name|salary|
// +-------+------+
// |Michael| 3000|
// | Andy| 4500|
// | Justin| 3500|
// | Berta| 4000|
// +-------+------+ MyAverage myAverage = new MyAverage();
// Convert the function to a `TypedColumn` and give it a name
TypedColumn<Employee, Double> averageSalary = myAverage.toColumn().name("average_salary");
Dataset<Double> result = ds.select(averageSalary);
result.show();
// +--------------+
// |average_salary|
// +--------------+
// | 3750.0|
// +--------------+
相关API
自定义spark UDAF的更多相关文章
- spark UDAF
感谢我的同事 李震给我讲解UDAF 网上找到的大部分都只有代码,但是缺少讲解,官网的的API有讲解,但是看不太明白.我还是自己记录一下吧,或许对其他人有帮助. 接下来以一个求几何平均数的例子来说明如何 ...
- 自定义Spark Partitioner提升es-hadoop Bulk效率
http://www.jianshu.com/p/cccc56e39429/comments/2022782 和 https://github.com/elastic/elasticsearch-ha ...
- Spark(十三)【SparkSQL自定义UDF/UDAF函数】
目录 一.UDF(一进一出) 二.UDAF(多近一出) spark2.X 实现方式 案例 ①继承UserDefinedAggregateFunction,实现其中的方法 ②创建函数对象,注册函数,在s ...
- Spark UDAF实现举例 -- average pooling
目录 1.UDAF定义 2.向量平均(average pooling) 2.1 average的并行化 2.2 代码实现 2.3 使用 参考 1.UDAF定义 spark中的UDF(UserDefin ...
- 自定义Spark Partitioner提升es-hadoop Bulk效率——续
对于es 2.4版本,要能定制spark partitioner需要如下方式启动spark shell: spark-2.0.0-bin-hadoop2.6/bin/spark-shell --jar ...
- [转]hive中自定义函数(UDAF)实现多行字符串拼接为一行
函数如何使用: hive> desc concat_test;OKa intb string hive> select * from concat_test;OK1 ...
- 自定义Hive UDAF 实现相邻去重
内置的两个聚合函数(UDAF) collect_list():多行字符串拼接为一行collect_set():多行字符串拼接为一行并去重多行字符串拼接为一行并相邻去重UDAF:Concat() con ...
- 原创:自定义spark GraphX中的collectNeighborIds方法
/** * 自定义收集VertexId的neighborIds * @author TongXueQiang */def collectNeighborIds[T,U](edgeDirection:E ...
- Spark SQL 用户自定义函数UDF、用户自定义聚合函数UDAF 教程(Java踩坑教学版)
在Spark中,也支持Hive中的自定义函数.自定义函数大致可以分为三种: UDF(User-Defined-Function),即最基本的自定义函数,类似to_char,to_date等 UDAF( ...
随机推荐
- [Linux] day01——运维
开发和运维,本质都是提供一种服务. ---------------------------------(最终用户)1 应用2 中间件 服务平台 存储 架构 3 操作系统 硬件驱动4 计算机 网络设备 ...
- Laplacian Mesh Editing 拉普拉斯形变(待回学校更新)
前言 因为实验需要用到拉普拉斯形变,但找了好久找到一个非常适合入门的资料.再此记录下我的学习过程,也算搬运翻译过来. Introduction / Basic Laplacian Mesh Repre ...
- 初学JQuery
JQuery是对JavaScript的封装,简化了JS代码,是主流框架的基础(VUE,EasyUI,Bootstrap) 它是2006年推出的 JQuery的优势:体积小,压缩后只有100KB左右强大 ...
- 图片IO域 旋转画面的组态 图片是4个静止的风扇 PLC的MW6为风扇指针..
图片IO域 旋转画面的组态 图片是4个静止的风扇 PLC的MW6为风扇指针.. Plc在循环中断组织块 OB35 中 将MW6 每100ms 加1 加到4 清0 图片[MW6] MW6 是图片指针 对 ...
- sklearn调用分类算法的评价指标
sklearn分类算法的评价指标调用#二分类问题的算法评价指标import numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport pandas as pdf ...
- NO29 用户提权sudo配置文件详解实践--志行为审计
用户提权sudo配置文件详解实践: 放到visudo里: 验证权限:
- GetHub上很实用的几个Demo
手机号匹配的正则表达式:https://github.com/VincentSit/ChinaMobilePhoneNumberRegex/blob/master/README-CN.md FEBS- ...
- vs2010编译C++ 栈的使用
// CTest.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点. // #include "stdafx.h" #include <iostream> #include &l ...
- 第3节 sqoop:3、sqoop的入门测试使用
3.5. Sqoop的数据导入 “导入工具”导入单个表从RDBMS到HDFS.表中的每一行被视为HDFS的记录.所有记录都存储为文本文件的文本数据(或者Avro.sequence文件等二进制数据) 列 ...
- BVS安全检测之检查Linux是否口令生存周期
口令生存周期的配置文件为 /etc/login.defs vim 打开该文件,命令模式下输入 /PASS_MAX_DAYS 找到该配置信息的位置 我的Linux操作系统默认显示的是99999,说明我当 ...
