SpringBoot入门之基于注解的Mybatis
今天学习下SpringBoot集成mybatis,集成mybatis一般有两种方式,一个是基于注解的一个是基于xml配置的。今天先了解下基于注解的mybatis集成。
一、引入依赖项
因为是mybatis嘛,肯定是要有mybatis相关的,同时用的是mysql,所以也需要引入mysql相关的。
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.mybatis.spring.boot/mybatis-spring-boot-starter -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.3.2</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/mysql/mysql-connector-java -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.11</version>
</dependency>
二、创建model
这里创建了一个User的model,这样方便与数据库的表对照,这里在mysql中创建了一个名为mybatis的数据库,里面创建了一个user的表.同时创建了枚举类UserSexEnum.
CREATE TABLE `user` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL,
`age` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`sex` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=9 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
package com.example.model;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class User implements Serializable{
@Override
public String toString() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return "User [id=" + Id + ", name=" + Name + ", age=" + Age + "]";
}
public int getId() {
return Id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
Id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return Name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
Name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return Age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
Age = age;
}
private int Id;
private String Name;
private int Age;
private UserSexEnum Sex;
public UserSexEnum getSex() {
return Sex;
}
public void setSex(UserSexEnum sex) {
Sex = sex;
}
}
package com.example.model;
public enum UserSexEnum {
MAN, WOMAN
}
三、创建Mapper
这里需要把model与操作数据库的sql对照起来,用什么对照呢?那就需要创建一个mapper.这里有增删改查。
package com.example.mapper;
import java.util.List; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Delete;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Insert;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Result;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Results;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Update; import com.example.model.*;; public interface UserMapper { @Select("SELECT * FROM user") @Results({ @Result(property = "Sex", column = "sex", javaType = UserSexEnum.class), @Result(property = "Name", column = "name") }) List<User> getAll(); @Select("SELECT * FROM user WHERE id = #{id}") @Results({ @Result(property = "Sex", column = "sex", javaType = UserSexEnum.class), @Result(property = "Name", column = "name") }) User getOne(int id); @Insert("INSERT INTO user(name,age,sex) VALUES(#{name}, #{age}, #{sex})") void insert(User user); @Update("UPDATE user SET name=#{userName},age=#{age} WHERE id =#{id}") void update(User user); @Delete("DELETE FROM user WHERE id =#{id}") void delete(int id);
}
四、配置扫描
上面配置了mapper,那怎么让系统知道mapper放在哪里呢?于是有了@MapperScan注解。
package com.example.demo; import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; @SpringBootApplication
@MapperScan("com.example.mapper")
public class DemoApplication { public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
五、创建Controller
这里创建了UserController,一个是显示所有用户,一个是新增一个用户之后再显示所有用户。
package com.example.demo; import java.util.List; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod; import com.example.mapper.UserMapper;
import com.example.model.User;
import com.example.model.UserSexEnum; @Controller
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController { @Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper; @RequestMapping(value = "/alluser.do",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String getallusers(Model model) {
List<User> users=userMapper.getAll();
model.addAttribute("users", users);
return "userlist";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/insert.do",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String adduser(Model model) {
User user=new User();
user.setName("cuiyw");
user.setAge(27);
user.setSex(UserSexEnum.MAN); userMapper.insert(user);
List<User> users=userMapper.getAll();
model.addAttribute("users", users);
return "userlist";
}
}
六、数据库配置
上面mapper也设置了,model也设置了,那要与数据库交互,肯定要配置数据库地址这些信息吧。这里在运行的时候还报了一个错误.nested exception is java.sql.SQLException: The server time zone value 'Öйú±ê׼ʱ¼ä' is unrecognized or represents more than one time zone. You must configure either the server or JDBC driver (via the serverTimezone configuration property) to use a more specifc time zone value if you want to utilize time zone support.在mysql中设置了下时区:set global time_zone='+8:00';
spring.mvc.view.prefix=/view/ spring.mvc.view.suffix=.jsp
mybatis.type-aliases-package=com.example.model spring.datasource.driverClassName = com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url = jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis
spring.datasource.username = root
spring.datasource.password = 123456
七、创建页面显示
这里还是按照上一博客用jsp显示数据。
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=utf-8"
pageEncoding="utf-8"%>
<%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<table>
<tr><th>名字</th><th>年龄</th><th>性别</th></tr>
<c:forEach items="${users}" var="item">
<tr><td>${item.name}</td><td>${item.age}</td><td>${item.sex}</td></tr>
</c:forEach>
</table>
</body>
</html>
八、测试
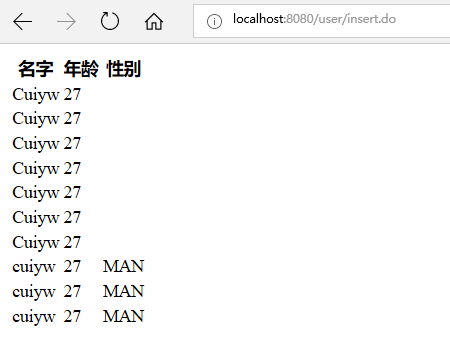
这里先在浏览器打开http://localhost:8080/user/alluser.do,可以看到用户列表,然后输入http://localhost:8080/user/insert.do,就会看到列表显示多了一行数据。
九、小结
使用基于注解的集成mybatis比较省事方便,但有利有弊,对于多表相连的可能就不太方便,使用基于xml配置的可能就更会好些。
SpringBoot入门之基于注解的Mybatis的更多相关文章
- SpringBoot入门之基于XML的Mybatis
上一博客介绍了下SpringBoot基于注解引入Mybatis,今天介绍基于XML引入Mybatis.还是在上一篇demo的基础上进行修改. 一.Maven引入 这个与上一篇的一样,需要引入mybat ...
- SpringBoot入门之基于Druid配置Mybatis多数据源
上一篇了解了Druid进行配置连接池的监控和慢sql处理,这篇了解下使用基于基于Druid配置Mybatis多数据源.SpringBoot默认配置数据库连接信息时只需设置url等属性信息就可以了,Sp ...
- SpringMVC入门(基于注解方式实现)
---------------------siwuxie095 SpringMVC 入门(基于注解方式实现) SpringMVC ...
- 基于注解的Mybatis mapper 接口注意事项
基于注解的Mybatis mapper 接口功能没有mapper xml配置文件丰富,并且动态sql语句的灵活性不能和xml配置相比. 这里仅仅说一下基于注解的动态sql注意事项: Mybatis提供 ...
- (一)SpringBoot入门【基于2.x版本】
SpringBoot入门[基于2.x版本] 一.SpringBoot简介 首先大家学习SpringBoot的话,我希望大家是有一定java基础的,如果是有Spring的基础的话,上手会更加得心应手,因 ...
- SpringBoot入门 (六) 数据库访问之Mybatis
本文记录学习在SpringBoot中使用Mybatis. 一 什么是Mybatis MyBatis 是一款优秀的持久层框架,它支持定制化 SQL.存储过程以及高级映射.MyBatis 避免了几乎所有的 ...
- Springboot入门及常用注解
1.微服务:一个项目 可以由多个 小型服务构成(微服务)2.spring boot可以快速开发 微服务模块 a.简化j2ee开发 b.整个spring技术栈的整合(整合springmvc spring ...
- SpringMVC的入门示例---基于注解的配置
注解版的配置,主要的修改就是将原来使用<bean>创建的业务控制器对象,修改为是扫描标签扫描到容器. 1.导入包 2.在 web.xml 配置核心控制器 <?xml version= ...
- SpringBoot入门笔记(四)、通常Mybatis项目目录结构
1.工程启动类(AppConfig.java) 2.实体类(domain) 3.数据访问层(dao) 4.数据服务层(service) 5.前端控制器(controller) 6.工具类(util) ...
随机推荐
- vs.code调试node.js的C++扩展
其实也很简单 点击“Add Configration..”后,会在launch.json增加一个节点,稍调整两个位置 以上完了后,就能在cpp源码里加上自己的断点,执行debug调试我们的C++源代码 ...
- 剪格子 dfs 蓝桥杯
问题描述 如下图所示,3 x 3 的格子中填写了一些整数. +--*--+--+ |10* 1|52| +--****--+ |20|30* 1| *******--+ | 1| 2| ...
- JavaWeb核心之Servlet
servlet规范:包含三个技术点 1)servlet技术 2)filter技术---过滤器 3)listener技术---监听器 Servlet快速入门 实现步骤: 1)创建类实现Servlet接口 ...
- iOS逆向工程之Cycript
1.连接设备 打开一个终端,输入指令: iproxy 重新打开一个新的终端,输入指令: ssh -p root@127.0.0.1 这时候会提示输入密码:默认密码为“alpine”.这样就可以连接到设 ...
- DRF 商城项目 - 日志处理
logging 模块 logging 模块是最基本的日志处理模块 缺陷 但是拥有一些很致命的缺陷 要求用户主动查询, 需要登录到服务器才可以查看日志文件 自带的报错外部通知也没办法判断同类取舍, 短 ...
- Linux源码编译安装程序
一.程序的组成部分 Linux下程序大都是由以下几部分组成: 二进制文件:也就是可以运行的程序文件 库文件:就是通常我们见到的lib目录下的文件 配置文件:这个不必多说,都知道 帮助文档:通常是我们在 ...
- Varnish实现Web站点加速
Varnish 是一款高性能的开源HTTP加速器,挪威最大的在线报纸 Verdens Gang使用3台Varnish代替了原来的12台Squid,性能比以前更好. Varnish 的作者Poul-He ...
- 8:String类
String类 String类的特点: 字符串对象一旦被初始化就不会被改变. 字符串是最常用的类型之一,所以为了使用方便java就给封装成了对象方便使用 public static void str ...
- 在IIS建立的ftp,可以成功连接登录,但是不显示目录
IIS建立FTP站点很简单,不作说明 Windows的防火墙也开通了FTP端口(默认21),Telnet也是通的,在本机可以打开,在局域网其它电脑或外网也可以连接,但就是不显示目录,如果用浏览器打开提 ...
- Python编程语言基础
今天给大家讲解python语言基础~~ 01.python核心数据类型 整型数 int:整数是不带有小数部分的数字 浮点型数 float:浮点数是带有小数部分的数字(小数部分可以是0) 复数 co ...
