Some 3D Graphics (rgl) for Classification with Splines and Logistic Regression (from The Elements of Statistical Learning)(转)
This semester I'm teaching from Hastie, Tibshirani, and Friedman's book, The Elements of Statistical Learning, 2nd Edition. The authors provide aMixture Simulation data set that has two continuous predictors and a binary outcome. This data is used to demonstrate classification procedures by plotting classification boundaries in the two predictors. For example, the figure below is a reproduction of Figure 2.5 in the book:
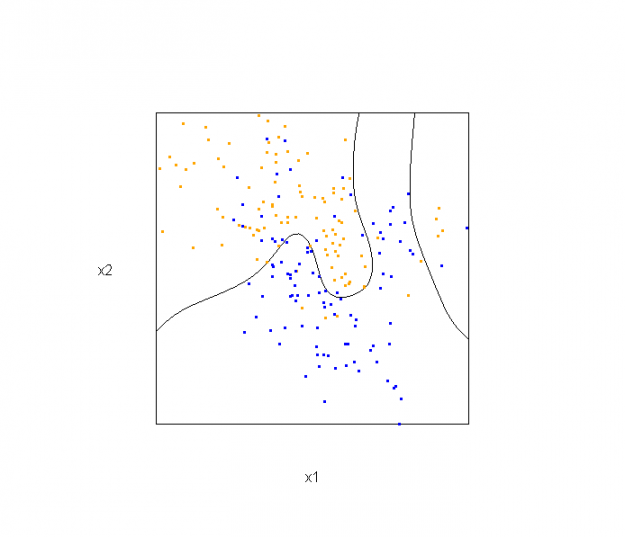
The solid line represents the Bayes decision boundary (i.e., {x: Pr("orange"|x) = 0.5}), which is computed from the model used to simulate these data. The Bayes decision boundary and other boundaries are determined by one or more surfaces (e.g., Pr("orange"|x)), which are generally omitted from the graphics. In class, we decided to use the R package rgl to create a 3D representation of this surface. Below is the code and graphic (well, a 2D projection) associated with the Bayes decision boundary:
library(rgl)
load(url("http://statweb.stanford.edu/~tibs/ElemStatLearn/datasets/ESL.mixture.rda"))
dat <- ESL.mixture ## create 3D graphic, rotate to view 2D x1/x2 projection
par3d(FOV=1,userMatrix=diag(4))
plot3d(dat$xnew[,1], dat$xnew[,2], dat$prob, type="n",
xlab="x1", ylab="x2", zlab="",
axes=FALSE, box=TRUE, aspect=1) ## plot points and bounding box
x1r <- range(dat$px1)
x2r <- range(dat$px2)
pts <- plot3d(dat$x[,1], dat$x[,2], 1,
type="p", radius=0.5, add=TRUE,
col=ifelse(dat$y, "orange", "blue"))
lns <- lines3d(x1r[c(1,2,2,1,1)], x2r[c(1,1,2,2,1)], 1) ## draw Bayes (True) decision boundary; provided by authors
dat$probm <- with(dat, matrix(prob, length(px1), length(px2)))
dat$cls <- with(dat, contourLines(px1, px2, probm, levels=0.5))
pls <- lapply(dat$cls, function(p) lines3d(p$x, p$y, z=1)) ## plot marginal (w.r.t mixture) probability surface and decision plane
sfc <- surface3d(dat$px1, dat$px2, dat$prob, alpha=1.0,
color="gray", specular="gray")
qds <- quads3d(x1r[c(1,2,2,1)], x2r[c(1,1,2,2)], 0.5, alpha=0.4,
color="gray", lit=FALSE)
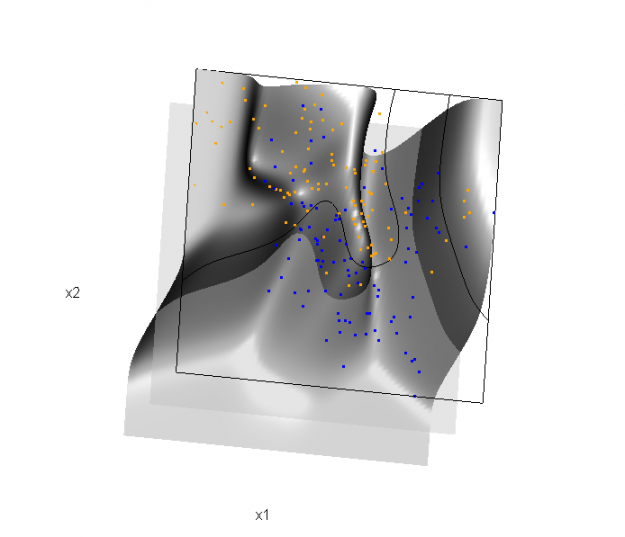
In the above graphic, the probability surface is represented in gray, and the Bayes decision boundary occurs where the plane f(x) = 0.5 (in light gray) intersects with the probability surface.
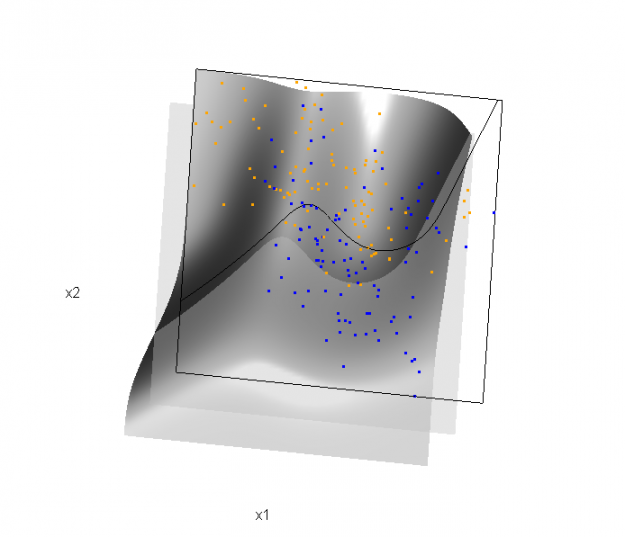
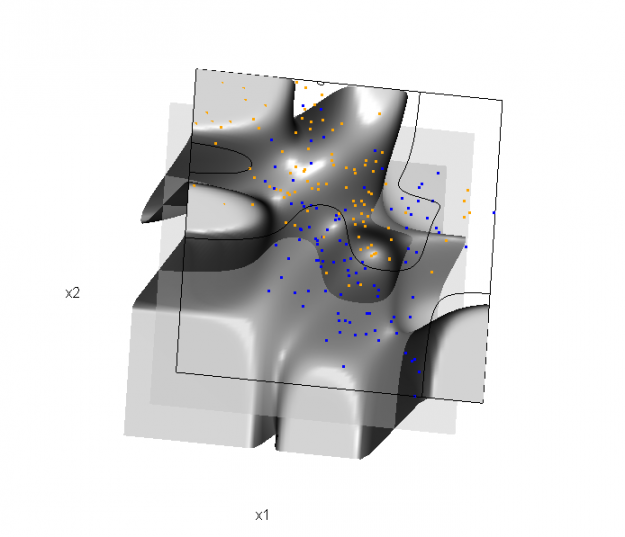
Of course, the classification task is to estimate a decision boundary given the data. Chapter 5 presents two multidimensional splines approaches, in conjunction with binary logistic regression, to estimate a decision boundary. The upper panel of Figure 5.11 in the book shows the decision boundary associated with additive natural cubic splines in x1 and x2 (4 df in each direction; 1+(4-1)+(4-1) = 7 parameters), and the lower panel shows the corresponding tensor product splines (4x4 = 16 parameters), which are much more flexible, of course. The code and graphics below reproduce the decision boundaries shown in Figure 5.11, and additionally illustrate the estimated probability surface (note: this code below should only be executed after the above code, since the 3D graphic is modified, rather than created anew):
Reproducing Figure 5.11 (top):
## clear the surface, decision plane, and decision boundary
par3d(userMatrix=diag(4)); pop3d(id=sfc); pop3d(id=qds)
for(pl in pls) pop3d(id=pl) ## fit additive natural cubic spline model
library(splines)
ddat <- data.frame(y=dat$y, x1=dat$x[,1], x2=dat$x[,2])
form.add <- y ~ ns(x1, df=3)+
ns(x2, df=3)
fit.add <- glm(form.add, data=ddat, family=binomial(link="logit")) ## compute probabilities, plot classification boundary
probs.add <- predict(fit.add, type="response",
newdata = data.frame(x1=dat$xnew[,1], x2=dat$xnew[,2]))
dat$probm.add <- with(dat, matrix(probs.add, length(px1), length(px2)))
dat$cls.add <- with(dat, contourLines(px1, px2, probm.add, levels=0.5))
pls <- lapply(dat$cls.add, function(p) lines3d(p$x, p$y, z=1)) ## plot probability surface and decision plane
sfc <- surface3d(dat$px1, dat$px2, probs.add, alpha=1.0,
color="gray", specular="gray")
qds <- quads3d(x1r[c(1,2,2,1)], x2r[c(1,1,2,2)], 0.5, alpha=0.4,
color="gray", lit=FALSE)
Reproducing Figure 5.11 (bottom)
## clear the surface, decision plane, and decision boundary
par3d(userMatrix=diag(4)); pop3d(id=sfc); pop3d(id=qds)
for(pl in pls) pop3d(id=pl) ## fit tensor product natural cubic spline model
form.tpr <- y ~ 0 + ns(x1, df=4, intercept=TRUE):
ns(x2, df=4, intercept=TRUE)
fit.tpr <- glm(form.tpr, data=ddat, family=binomial(link="logit")) ## compute probabilities, plot classification boundary
probs.tpr <- predict(fit.tpr, type="response",
newdata = data.frame(x1=dat$xnew[,1], x2=dat$xnew[,2]))
dat$probm.tpr <- with(dat, matrix(probs.tpr, length(px1), length(px2)))
dat$cls.tpr <- with(dat, contourLines(px1, px2, probm.tpr, levels=0.5))
pls <- lapply(dat$cls.tpr, function(p) lines3d(p$x, p$y, z=1)) ## plot probability surface and decision plane
sfc <- surface3d(dat$px1, dat$px2, probs.tpr, alpha=1.0,
color="gray", specular="gray")
qds <- quads3d(x1r[c(1,2,2,1)], x2r[c(1,1,2,2)], 0.5, alpha=0.4,
color="gray", lit=FALSE)
Although the graphics above are static, it is possible to embed an interactive 3D version within a web page (e.g., see the rgl vignette; best with Google Chrome), using the rgl function writeWebGL. I gave up on trying to embed such a graphic into this WordPress blog post, but I have created a separate page for the interactive 3D version of Figure 5.11b. Duncan Murdoch's work with this package is reall nice!
This entry was posted in Technical and tagged data, graphics, programming, R, statistics on February 1, 2015.
转自:http://biostatmatt.com/archives/2659
Some 3D Graphics (rgl) for Classification with Splines and Logistic Regression (from The Elements of Statistical Learning)(转)的更多相关文章
- More 3D Graphics (rgl) for Classification with Local Logistic Regression and Kernel Density Estimates (from The Elements of Statistical Learning)(转)
This post builds on a previous post, but can be read and understood independently. As part of my cou ...
- 机器学习理论基础学习3.3--- Linear classification 线性分类之logistic regression(基于经验风险最小化)
一.逻辑回归是什么? 1.逻辑回归 逻辑回归假设数据服从伯努利分布,通过极大化似然函数的方法,运用梯度下降来求解参数,来达到将数据二分类的目的. logistic回归也称为逻辑回归,与线性回归这样输出 ...
- 李宏毅机器学习笔记3:Classification、Logistic Regression
李宏毅老师的机器学习课程和吴恩达老师的机器学习课程都是都是ML和DL非常好的入门资料,在YouTube.网易云课堂.B站都能观看到相应的课程视频,接下来这一系列的博客我都将记录老师上课的笔记以及自己对 ...
- Logistic Regression Using Gradient Descent -- Binary Classification 代码实现
1. 原理 Cost function Theta 2. Python # -*- coding:utf8 -*- import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplo ...
- Classification week2: logistic regression classifier 笔记
华盛顿大学 machine learning: Classification 笔记. linear classifier 线性分类器 多项式: Logistic regression & 概率 ...
- Android Programming 3D Graphics with OpenGL ES (Including Nehe's Port)
https://www3.ntu.edu.sg/home/ehchua/programming/android/Android_3D.html
- Logistic Regression and Classification
分类(Classification)与回归都属于监督学习,两者的唯一区别在于,前者要预测的输出变量\(y\)只能取离散值,而后者的输出变量是连续的.这些离散的输出变量在分类问题中通常称之为标签(Lab ...
- Logistic Regression求解classification问题
classification问题和regression问题类似,区别在于y值是一个离散值,例如binary classification,y值只取0或1. 方法来自Andrew Ng的Machine ...
- 分类和逻辑回归(Classification and logistic regression)
分类问题和线性回归问题问题很像,只是在分类问题中,我们预测的y值包含在一个小的离散数据集里.首先,认识一下二元分类(binary classification),在二元分类中,y的取值只能是0和1.例 ...
随机推荐
- 高性能MySQL--索引学习笔记(原创)
看过一些人写的学习笔记,完全按书一字不漏照抄,内容很多,真不能叫笔记.遂自己整理了一份,取其精要. 更多笔记请访问@个人简书 [toc] 索引概述 索引即key 在存储引擎层实现,不同引擎工作方式不同 ...
- 如何在Windows系统下安装Linux虚拟机
先安装虚拟机这个软件,然后在虚拟机里装linux. 1,准备,下载VM虚拟机,链接: http://pan.baidu.com/s/1z79oU 密码: vbap.和linux镜像文件,可以下载ubu ...
- toastr.js插件用法
toastr.js插件用法 toastr.js是一个基于jQuery的非阻塞通知的JavaScript库.toastr.js可以设定四种通知模式:成功.出错.警告.提示.提示窗口的位置.动画效果等都可 ...
- Android系统--输入系统(五)输入系统框架
Android系统--输入系统(五)输入系统框架 1. Android设备使用场景: 假设一个Android平板,APP功能.系统功能(开机关机.调节音量).外接设备功能(键盘.触摸屏.USB外接键盘 ...
- druid 连接kafuk
java -Xmx256m -Duser.timezone=UTC -Dfile.encoding=UTF-8 -Ddruid.realtime.specFile=examples/indexing/ ...
- WebForm捆绑压缩js和css(WebForm Bundling and Minification)
.net framework 4以上,可以使用Microsoft.AspNet.Web.Optimization 新建4.0项目 Nuget搜索optimization,安装第一个包 加入Bundle ...
- MarkDown 学习笔记
MarkDown是一种适用于网络的书写语言,可以帮助你快速书写文档,不必再纠结文档排版的问题.并且它的语法简单,学习成本低,程序员必备技能...助你快速书写技术文档.文章. 用于书写 MarkDown ...
- CVSS3.0打分学习
打分计算器: Common Vulnerability Scoring System Version 3.0 Calculator: https://www.first.org/cvss/calcul ...
- Homebrew - macOS 不可或缺的套件管理器
一.Homebrew 是什么? Unix/Linux 安装软件的时候有个很常见.也很令人头疼的事情,那就是软件包依赖.值得高兴的是,当前主流的 Linux 两大发行版本都自带了解决方案,Red hat ...
- hdu3829最大独立集
The zoo have N cats and M dogs, today there are P children visiting the zoo, each child has a like-a ...
