6. Design Patterns with First-Class Functions
1. Refactoring Strategy
1.1 Classic Strategy
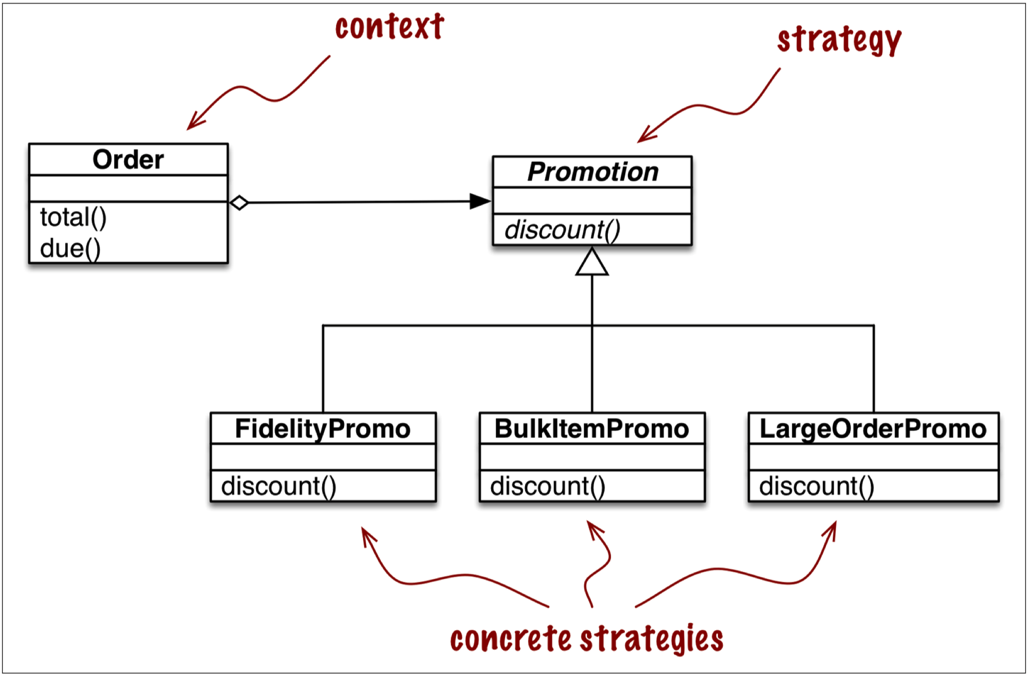
from abc import ABC, abstractmethod
from collections import namedtuple Customer = namedtuple('Customer', 'name fidelity') class LineItem:
def __init__(self, product, quantity, price):
self.product = product # 商品名
self.quantity = quantity # 数量
self.price = price # 单价 def total(self): # 总价
return self.price * self.quantity class Order:
def __init__(self, customer, cart, promotion=None):
self.customer = customer # 用户名
self.cart = list(cart) # 商品列表
self.promotion = promotion # obj
def total(self): # 总价
if not hasattr(self, '__total'):
self.__total = sum(item.total() for item in self.cart)
return self.__total
def due(self): # 折扣价
if self.promotion is None:
discount = 0
else:
discount = self.promotion.discount(self) # **********
return self.total() - discount
def __repr__(self): # 打印
fmt = '<Order total: {:.2f} due: {:.2f}>'
return fmt.format(self.total(), self.due()) class Promotion(ABC): # an abstract base class
@abstractmethod
def discount(self, order): # 返回折扣的总钱数
pass class FidelityPromo(Promotion):
"""5% discount for customers with 1000 or more fidelity points"""
def discount(self, order):
return order.total() * .05 if order.customer.fidelity >= 1000 else 0 class BulkItemPromo(Promotion):
"""10% discount for each LineItem with 20 or more units"""
def discount(self, order):
discount = 0
for item in order.cart:
if item.quantity >= 20:
discount += item.total() * .1
return discount class LargeOrderPromo(Promotion):
"""7% discount for orders with 10 or more distinct items"""
def discount(self, order):
distinct_items = {item.product for item in order.cart}
if len(distinct_items) >= 10:
return order.total() * .07
return 0 joe = Customer('John Doe', 1000)
cart = [LineItem('banana', 4, .5), LineItem('apple', 25, 1.5), LineItem('watermellon', 5, 5.0)]
print(Order(joe, cart, FidelityPromo())) # <Order total: 64.50 due: 61.27>
print(Order(joe, cart, BulkItemPromo())) # <Order total: 64.50 due: 60.75>
print(Order(joe, cart, LargeOrderPromo())) # <Order total: 64.50 due: 64.50>
1.2 Function-Oriented Strategy
- A flyweight is a shared object that can be used in multiple contexts simultaneously. (享元)
from collections import namedtuple
Customer = namedtuple('Customer', 'name fidelity')
class LineItem:
def __init__(self, product, quantity, price):
self.product = product # 商品名
self.quantity = quantity # 数量
self.price = price # 单价
def total(self): # 总价
return self.price * self.quantity
class Order:
def __init__(self, customer, cart, promotion=None):
self.customer = customer # 用户名
self.cart = list(cart) # 商品列表
self.promotion = promotion # obj
def total(self): # 总价
if not hasattr(self, '__total'):
self.__total = sum(item.total() for item in self.cart)
return self.__total
def due(self): # 折扣价
if self.promotion is None:
discount = 0
else:
discount = self.promotion(self) # **********
return self.total() - discount
def __repr__(self): # 打印
fmt = '<Order total: {:.2f} due: {:.2f}>'
return fmt.format(self.total(), self.due())
def fidelity_promo(order): # created just once
"""5% discount for customers with 1000 or more fidelity points"""
return order.total() * .05 if order.customer.fidelity >= 1000 else 0
def bulk_item_promo(order):
"""10% discount for each LineItem with 20 or more units"""
discount = 0
for item in order.cart:
if item.quantity >= 20:
discount += item.total() * .1
return discount
def large_order_promo(order):
"""7% discount for orders with 10 or more distinct items"""
distinct_items = {item.product for item in order.cart}
if len(distinct_items) >= 10:
return order.total() * .07
return 0
joe = Customer('John Doe', 1000)
cart = [LineItem('banana', 4, .5), LineItem('apple', 25, 1.5), LineItem('watermellon', 5, 5.0)]
print(Order(joe, cart, fidelity_promo)) # <Order total: 64.50 due: 61.27>
print(Order(joe, cart, bulk_item_promo)) # <Order total: 64.50 due: 60.75>
print(Order(joe, cart, large_order_promo)) # <Order total: 64.50 due: 64.50>
1.3 Choosing the Best Strategy
promos = [fidelity_promo, bulk_item_promo, large_order_promo]
# promos = [globals()[name] for name in globals() if name.endswith('_promo') and name != 'best_promo']
# import inspect
# promos = [func for name, func in inspect.getmembers(promotions, inspect.isfunction)] # promotions为自定模块
def best_promo(order):
"""Select best discount available"""
return max(promo(order) for promo in promos)
promos = []
def promotion(promo_func):
promos.append(promo_func)
return promo_func @promotion
def fidelity_promo(order): # created just once
"""5% discount for customers with 1000 or more fidelity points"""
return order.total() * .05 if order.customer.fidelity >= 1000 else 0 @promotion
def bulk_item_promo(order):
"""10% discount for each LineItem with 20 or more units"""
discount = 0
for item in order.cart:
if item.quantity >= 20:
discount += item.total() * .1
return discount @promotion
def large_order_promo(order):
"""7% discount for orders with 10 or more distinct items"""
distinct_items = {item.product for item in order.cart}
if len(distinct_items) >= 10:
return order.total() * .07
return 0
2. Command
6. Design Patterns with First-Class Functions的更多相关文章
- Learning JavaScript Design Patterns The Module Pattern
The Module Pattern Modules Modules are an integral piece of any robust application's architecture an ...
- Design Patterns Example Code (in C++)
Overview Design patterns are ways to reuse design solutions that other software developers have crea ...
- Massive Collection Of Design Patterns, Frameworks, Components, And Language Features For Delphi
Developer beNative over on GitHub has a project called Concepts which is a massive collection of Del ...
- Design Patterns Simplified - Part 3 (Simple Factory)【设计模式简述--第三部分(简单工厂)】
原文链接:http://www.c-sharpcorner.com/UploadFile/19b1bd/design-patterns-simplified-part3-factory/ Design ...
- Design Patterns Simplified - Part 2 (Singleton)【设计模式简述--第二部分(单例模式)】
原文链接: http://www.c-sharpcorner.com/UploadFile/19b1bd/design-patterns-simplified-part-2-singleton/ De ...
- Head First Design Patterns
From Head First Design Patterns. Design Principle: Idnetify the aspects of your application that var ...
- Apex Design Patterns
Apex allows you to build just about any custom solution on the Force.com platform. But what are the ...
- [Design Patterns] 4. Creation Pattern
设计模式是一套被反复使用.多数人知晓的.经过分类编目的.代码设计经验的总结,使用设计模式的目的是提高代码的可重用性,让代码更容易被他人理解,并保证代码可靠性.它是代码编制真正实现工程化. 四个关键元素 ...
- [Design Patterns] 3. Software Pattern Overview
When you're on the way which is unknown and dangerous, just follow your mind and steer the boat. 软件模 ...
- [Design Patterns] 1. Primary concept & term - UML
It's time to review design patterns, especially when I reach the turning-point of my career. That's ...
随机推荐
- Hadoop 部署之 Spark (六)
目录 一.Spark 是什么 二.Scala的安装(所有节点) 三.Spark 安装(所有节点) 1.下载安装 2.配置 Spark 环境变量 四.Spark 配置(namenode01) 1.配置 ...
- MySQL创建用户、授权、删除
1.在MySQL中创建新用户 使用具有shell访问权限的root用户登录MySQL服务器并创建名为“rahul”的新用户.下面的命令只允许从localhost系统访问用户rahul的MySQL服务器 ...
- PCM-FTL
1. 运行时第一行需要是write 错误位置 trace_stat->sectors += length;
- 鼠标拖拉div宽度
先看效果 先进入页面 当鼠标停留在中间div时,鼠标变成双箭头 点击拖拉 往右边拉 往最左边拉 代码 <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> & ...
- docker部署zabbix并设置自动发现规则
docker部署zabbix比源码安装简单一些,特此记录: 机器准备: zabbix-server: 192.168.0.150 homeserver zabbix-agent: 192.168. ...
- Docker 安装 Python
查找Docker Hub上的python镜像 docker search python 拉取官方的镜像,标签为3.5 docker pull python:3.5 使用python镜像 创建目录pyt ...
- PTA(Advanced Level)1037.Magic Coupon
The magic shop in Mars is offering some magic coupons. Each coupon has an integer N printed on it, m ...
- [百家号]铁流:华为Hi1620发布 自研内核还是ARM改?
华为Hi1620发布 自研内核还是ARM改? https://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1618735211251270521&wfr=spider&for=p ...
- windows 修改Administrator管理员账户名
用[Win+R]组合键命令打开[运行]界面,输入[gpedit.msc],按[回车键]或[鼠标左键]单击[确定]按钮: 在弹出的[本地组策略编辑器]对话框中,依次[鼠标左键]点击打开:[计算机 ...
- SQL SERVER 根据字段名称批量设置为主键
--设置主键 --alter table 你的表名 add constraint pk_s primary key (id) SELECT 'alter table ' + TABLE_NAME + ...
