NetScaler VLAN’s Demystified
NetScaler VLAN’s Demystified
https://www.citrix.com/blogs/2014/12/29/netscaler-vlans-demystified/
The Citrix NetScaler appliance is an amazingly flexible application delivery controller (ADC). It’s capable of performing both simple and very complex tasks, positioning it solidly for the eighth consecutive year in the Gartner Leaders Quadrant for ADC’s: http://www.citrix.com/news/announcements/oct-2014/citrix-positioned-for-the-eighth-consecutive-year-in-the-leaders.html
Unlike many networking devices the NetScaler uses ‘floating’ IP addresses, which means that any NetScaler-owned IP address can egress any NetScaler interface with the generic default ‘vanilla’ configuration in place.
This may actually be the desired configuration, but if there is a need to ensure that ingress and egress traffic flows out one particular interface on the NetScaler, this can simply be configured by using layer three (L3) VLAN’s to bind IP subnets to specific interfaces. With L3 VLAN’s configured, all traffic destined for a particular network/subnet will be forced out the desired interface.
Note: VLAN’s are actually layer two constructs, but the term L3 VLAN is used to describe the VLAN-to-IP subnet binding occurring.
How Does This All Work?
By default all interfaces are members of Native VLAN 1. That being said, specific to RX and TX, there are a few different rules to understand.
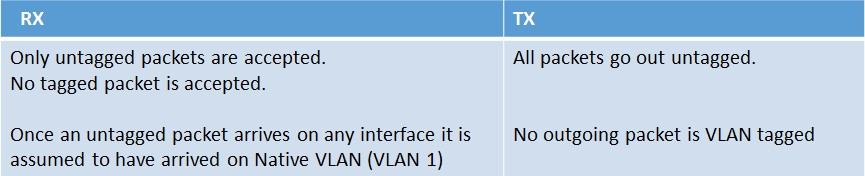
Below shows the structure of a VLAN packet:

Port-Based VLAN’s
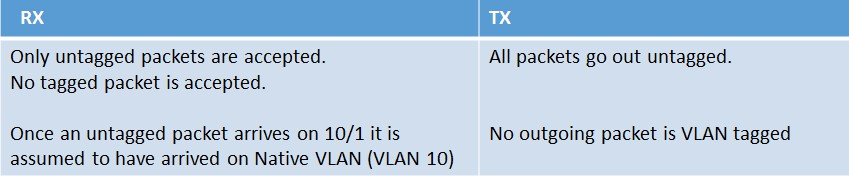
Let’s add a new VLAN to the NetScaler (VLAN 10). This new VLAN is created with the following command: ‘add vlan 10’
Then let’s bind interface 10/1 to the newly created VLAN 10 natively. This is accomplished with the following command: ‘bind vlan 10 -ifnum 10/1’
When bound natively, interface 10/1 is removed automatically from VLAN 1, the current native VLAN. It is then added to VLAN 10. When this configuration is implemented the following rules will then apply:
Tagged VLAN’s
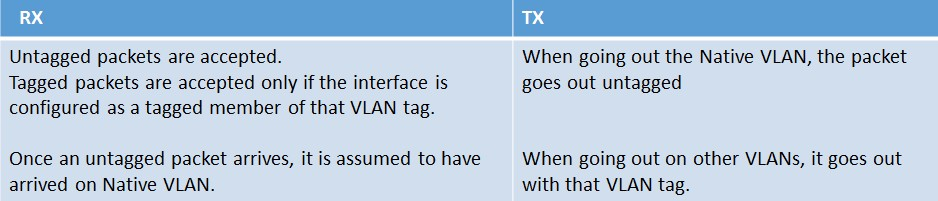
Let’s add a tagged VLAN to the NetScaler (VLAN 30). This new VLAN is created with the following command: ‘add vlan 30’
Then let’s bind interface 10/2 to the newly created VLAN 30 as a tagged member. This is accomplished with the following command: ‘bind vlan 30 -ifnum 10/2 –tagged’
When VLAN 30 is bound as a tagged member of interface 10/2, it is kept in VLAN 1 as a native member, but also added to VLAN 30 as a tagged member. When this configuration is implemented the following rules will then apply.

Summary
- An interface can have only one (hence also referred to as ‘port based’) Native VLAN.
- Untagged packets arriving on an interface are assumed to have arrived on that Native VLAN.
- An interface can be part of any number of tagged VLANs.
- When an interface is bound to a VLAN Natively, its Native VLAN changes from the current one to new one.
- When an interface is bound to a particular VLAN as a tagged member, it’s just added to the new VLAN as a tagged member.
An overview of the rules are as follows:
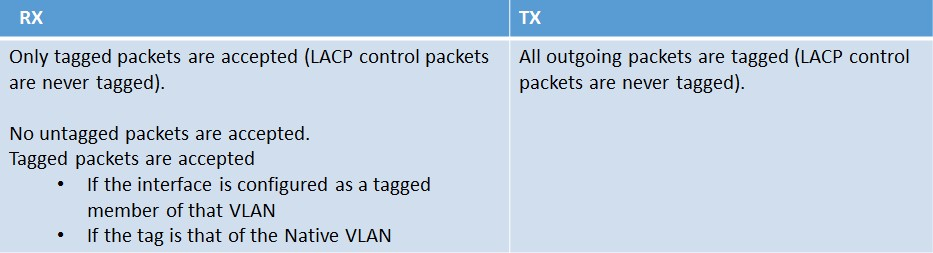
The Interface TAGALL Configuration
The TAGALL configuration on the NetScaler is specific only to the interface. The following rules apply when leveraging the TAGALL feature:
Link Aggregation (LA)
Let’s create a new link aggregation channel. This new LA channel is created with the following command: ‘add channel LA/1’
Then let’s bind interfaces 10/1 and 10/2 to the newly created channel with the following command: ‘bind channel LA/1 -ifnum 10/1 10/2’
Then following rules will apply for the default LA channel:

Link Aggregation (LA) and VLANs
Let’s create a new link aggregation channel (LA/2). This new LA channel is created with the following command: ‘add channel LA/2’
Then let’s bind interfaces 10/1 and 10/2 to the newly created channel with the following command: bind channel LA/2 -ifnum 10/1 10/2’ (as referenced previously the VLAN bindings of 10/1 and 10/2 are lost once they are part of an LA channel – unless specifically configured as such as we’ll see in the following example).
We can bind the new LA channel to a new VLAN with the following commands: ‘add vlan 2’ and then ‘bind vlan 2 –ifnum LA/2’
NOTES:
- If we unbind interfaces 10/1 and 10/2 (for example) from an LA channel (e.g. ‘unbind channel LA/1 -ifnum 10/1 10/2’) and then remove the channel with the following command: ‘rm channel LA/1’, then interfaces 10/1 and 10/2 will be moved to VLAN 1 as Native members again.
- The NetScaler does not have the concept of “trunk ports”, which by default will accept all VLAN IDs and only accept tagged traffic. Further restrictions on which VLANs to accept can be controlled by configuring an ‘allowed list’ of VLAN IDs on a particular interface.
Additional References:
How to Associate an IP Subnet with a NetScaler Interface by Using VLANs:http://support.citrix.com/article/CTX136926
How to Restrict the Management Access to a NetScaler Appliance from a Specific Interface: http://support.citrix.com/article/CTX126038
NetScaler VLAN’s Demystified的更多相关文章
- NetScaler SNIPs Bound To An Interface Without A VLAN
NetScaler SNIPs Bound To An Interface Without A VLAN https://www.citrix.com/blogs/2014/04/09/work-yo ...
- hd loadBalanceServer F5 BIG-IP / Citrix NetScaler / Radware / Array / HAProxy /
s 五.Citrix NetScaler 和 CDN 案例 问题描述: Citrix 10.5.66.9软件版本下,存在计时器bug,此bug会造成CDN长连接回源超过设备默认的180S,会发fin包 ...
- Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) in NetScaler Appliance
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) in NetScaler Appliance 来源 https://support.citrix.com/article/CTX112341 ...
- NetScaler + Wireshark = A Perfect Combination!
NetScaler + Wireshark = A Perfect Combination! https://www.citrix.com/blogs/2014/05/03/netscaler-wir ...
- NetScaler Best Practice With VMAC In A High Availability Configuration
NetScaler Best Practice With VMAC In A High Availability Configuration https://www.citrix.com/blogs/ ...
- SNMP OID Reference - NetScaler 10
SNMP OID Reference - NetScaler 10 https://docs.citrix.com/content/dam/docs/en-us/netscaler/10/downlo ...
- NetScaler Active-Active模式
NetScaler Active-Active模式 NetScaler Active-Active模式 (此文档基于版本:NS9.3: Build 55.6 nc) By ShingTan Activ ...
- Citrix NetScaler HA(高可用性)解析
Citrix NetScaler HA(高可用性)解析 来源 https://www.iyunv.com/thread-172259-1-1.html 1.1 NetScaler高可用概述 我 ...
- Configure a VLAN on top of a team with NetworkManager (nmcli) in RHEL7
SOLUTION VERIFIED September 13 2016 KB1248793 Environment Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 NetworkManager ...
随机推荐
- 成都Uber优步司机奖励政策(2月20日)
滴快车单单2.5倍,注册地址:http://www.udache.com/ 如何注册Uber司机(全国版最新最详细注册流程)/月入2万/不用抢单:http://www.cnblogs.com/mfry ...
- [ES]Elasticsearch在windows下的安装
1.环境 win7 64位 2.下载包环境 https://www.elastic.co/cn/downloads/elasticsearch 选择对应安装包 3.安装过程 解压安装包,例如我的,解压 ...
- 1057: [ZJOI2007]棋盘制作
1057: [ZJOI2007]棋盘制作 https://www.lydsy.com/JudgeOnline/problem.php?id=1057 分析: 首先对于(i+j)&1的位置0-& ...
- Selenium(Python) ddt数据驱动
首先, 添加ddt模块: import unittestfrom time import sleep from ddt import ddt, data, unpack# 导入ddt模块from se ...
- Selenium(Python)调用pywin32上传图片
import unittestfrom time import sleep import osfrom selenium import webdriverimport win32apiimport w ...
- APP功能性测试-1
疑难点 根据软件说明()或用户需求()验证App的各个功能实现 根据需求,提炼App的用户使用场景,验证功能 根据测试指标,验证功能 根据被测试功能点的特性采用特定的方法进行测试(场景,边界值,,,) ...
- Linux命令应用大词典-第37章 Linux系统故障排错
37.1 mkbootdisk:创建用于运行系统的独立启动软盘 37.2 chroot:切换根目录环境 37.3 badblocks:搜索设备的坏块 37.4 mkinitrd:创建要载入ramdis ...
- 372. Delete Node in a Linked List【LintCode java】
Description Implement an algorithm to delete a node in the middle of a singly linked list, given onl ...
- Python数据分析基础——Numpy tutorial
参考link https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy-dev/user/quickstart.html 基础 Numpy主要用于处理多维数组,数组中元素通常是数字,索引值为 ...
- 最短路径算法(II)
什么??你问我为什么不在一篇文章写完所有方法?? Hmm…其实我是想的,但是博皮的加载速度再带上文章超长图片超多的话… 可能这辈子都打不开了吧… 上接https://www.cnblogs.com/U ...
