caffe中ConvolutionLayer的前向和反向传播解析及源码阅读
一、前向传播
在caffe中,卷积层做卷积的过程被转化成了由卷积核的参数组成的权重矩阵weights(简记为W)和feature map中的元素组成的输入矩阵(简记为Cin)的矩阵乘积W * Cin。在进行乘积之前,需要对卷积核的参数和feature map作处理,以得到W和Cin。
下面用一个例子来说名上述两个过程。假设某一卷积层输入为c X h X w = 3 X 8 X 8的feature map,卷积核大小h1 X w1 = 2 X 2,个数c1 = 4,stride = 1,pad_h = pad_w = 0。
对feature map作处理,得到Cin的过程如下图(图中描述的是输入一个样本时的处理过程,在caffe中对一个batch_size的样本,也是在一个循环中一个一个地计算对输入的卷积)。

从图中可以看出,多层的feature map被转化成了一个矩阵,在caffe中,这个矩阵是以行优先的存储顺序存储在一个数组中。输出feature map的高、宽分别为
ho = (h + 2 * pad_h - h1)/stride + 1
wo = (w + 2 * pad_w - w1)/stride + 1
col_buff(即Cin)的维度为高 × 宽 = (c × h1 × w1) × (ho × wo)
对卷积核的参数作处理,得到W的过程如下图
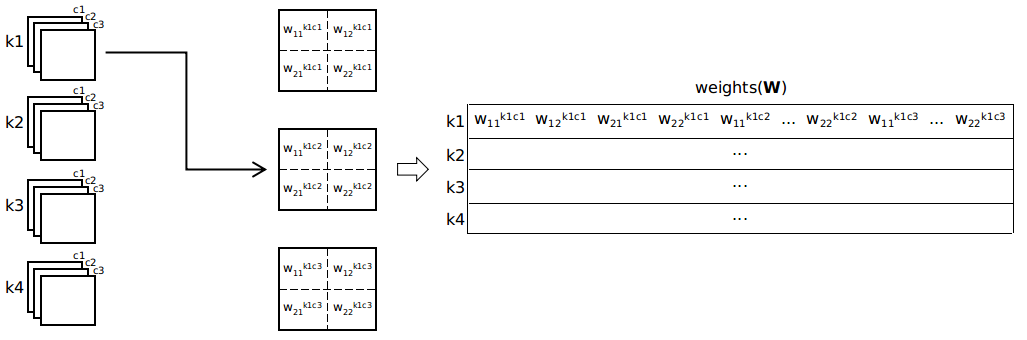
权重矩阵的维度为高 × 宽 = (c1) × (c × h1 × w1)。caffe中的数据存储采用Blob结构,其存储的优先顺序为样本数(num) × 通道数(c) × 高(h) × 宽(w),w优先级最低,即在w维度上相邻元素之间的地址差是最小的。所以卷积核的参数按照blob的存储结构恰好就是一个权重矩阵W,不需要作任何处理。
下面以caffe自带的例子LeNet为例,结合源代码,来分析代码的实现过程(代码注释中参数的值是batch_size=64,网络正向传播到conv2层时的值)
网络结构如下
name: "LeNet"
layer {
name: "mnist"
type: "Data"
top: "data"
top: "label"
include {
phase: TRAIN
}
transform_param {
scale: 0.00390625
}
data_param {
source: "examples/mnist/mnist_train_lmdb"
batch_size: 64
backend: LMDB
}
}
layer {
name: "mnist"
type: "Data"
top: "data"
top: "label"
include {
phase: TEST
}
transform_param {
scale: 0.00390625
}
data_param {
source: "examples/mnist/mnist_test_lmdb"
batch_size: 100
backend: LMDB
}
}
layer {
name: "conv1"
type: "Convolution"
bottom: "data"
top: "conv1"
param {
lr_mult: 1
}
param {
lr_mult: 2
}
convolution_param {
num_output: 20
kernel_size: 5
stride: 1
weight_filler {
type: "xavier"
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
}
}
}
layer {
name: "pool1"
type: "Pooling"
bottom: "conv1"
top: "pool1"
pooling_param {
pool: MAX
kernel_size: 2
stride: 2
}
}
layer {
name: "conv2"
type: "Convolution"
bottom: "pool1"
top: "conv2"
param {
lr_mult: 1
}
param {
lr_mult: 2
}
convolution_param {
num_output: 50
kernel_size: 5
stride: 1
weight_filler {
type: "xavier"
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
}
}
}
layer {
name: "pool2"
type: "Pooling"
bottom: "conv2"
top: "pool2"
pooling_param {
pool: MAX
kernel_size: 2
stride: 2
}
}
layer {
name: "ip1"
type: "InnerProduct"
bottom: "pool2"
top: "ip1"
param {
lr_mult: 1
}
param {
lr_mult: 2
}
inner_product_param {
num_output: 500
weight_filler {
type: "xavier"
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
}
}
}
layer {
name: "relu1"
type: "ReLU"
bottom: "ip1"
top: "ip1"
}
layer {
name: "ip2"
type: "InnerProduct"
bottom: "ip1"
top: "ip2"
param {
lr_mult: 1
}
param {
lr_mult: 2
}
inner_product_param {
num_output: 10
weight_filler {
type: "xavier"
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
}
}
}
layer {
name: "accuracy"
type: "Accuracy"
bottom: "ip2"
bottom: "label"
top: "accuracy"
include {
phase: TEST
}
}
layer {
name: "loss"
type: "SoftmaxWithLoss"
bottom: "ip2"
bottom: "label"
top: "loss"
}
conv_layer.cpp
template <typename Dtype>
void ConvolutionLayer<Dtype>::Forward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) {
const Dtype* weight = this->blobs_[]->cpu_data();
for (int i = ; i < bottom.size(); ++i) {
// bottom_data is the pointer of input feature map.
// top_data is the pointer of matrix Cout.
const Dtype* bottom_data = bottom[i]->cpu_data();
Dtype* top_data = top[i]->mutable_cpu_data();
// Every time just forward one single sample.
for (int n = ; n < this->num_; ++n) {
// Compute Cout = W X Cin.
this->forward_cpu_gemm(bottom_data + n * this->bottom_dim_, weight,
top_data + n * this->top_dim_);
if (this->bias_term_) {
const Dtype* bias = this->blobs_[]->cpu_data();
// Compute Cout = Cout + b X I.
this->forward_cpu_bias(top_data + n * this->top_dim_, bias);
}
}
}
}
依次进入
this->forward_cpu_gemm(bottom_data + n * this->bottom_dim_, weight, top_data + n * this->top_dim_)
this->forward_cpu_bias(top_data + n * this->top_dim_, bias)
base_conv_layer.cpp
template <typename Dtype>
void BaseConvolutionLayer<Dtype>::forward_cpu_gemm(const Dtype* input,
const Dtype* weights, Dtype* output, bool skip_im2col) {
const Dtype* col_buff = input;
if (!is_1x1_) {
if (!skip_im2col) {
// Generating Cin by one single input feature map.
conv_im2col_cpu(input, col_buffer_.mutable_cpu_data());
}
// col_buff is the pointer of matrix Cin.
col_buff = col_buffer_.cpu_data();
}
// The following takes caffe's example mnist as example to explain the value of every parameter.
// The value of these parameters are as follows when the solver forwarding into the conv2 layer.
// group_ = 1(usually is 1)
// conv_out_channels_ = c1 = 50
// conv_out_spatial_dim_ = ho * wo = 8 * 8 = 64
// kernel_dim_ = c(the number of channels of bottom) * h1 * w1 = 20 * 5 * 5 = 500
// weight_offset_ = conv_out_channels_ * kernel_dim_ / group_ = 50 * 500 / 1 = 25000
// col_offset_ = kernel_dim_ * conv_out_spatial_dim_ / group_ = 500 * 64 / 1 = 32000
// output_offset_ = conv_out_channels_ * conv_out_spatial_dim_ / group_ = 50 * 64 / 1 = 3200
// This function computes Cout = W X Cin.
for (int g = ; g < group_; ++g) {
caffe_cpu_gemm<Dtype>(CblasNoTrans, CblasNoTrans, conv_out_channels_ /
group_, conv_out_spatial_dim_, kernel_dim_,
(Dtype)., weights + weight_offset_ * g, col_buff + col_offset_ * g,
(Dtype)., output + output_offset_ * g);
}
} template <typename Dtype>
void BaseConvolutionLayer<Dtype>::forward_cpu_bias(Dtype* output,
const Dtype* bias) {
// The following takes caffe's example mnist as example to explain the value of every parameter.
// The value of these parameters are as follows when the solver forwarding into the conv2 layer.
// num_output_ = c1 = 50
// out_spatial_dim_ = ho * wo = 8 * 8 = 64
// bias_multiplier_ is the Blob of I(dimension h * w = 1 * out_spatial_dim_ = 1 * 64).
// This function computes Cout = Cout + b X I.
caffe_cpu_gemm<Dtype>(CblasNoTrans, CblasNoTrans, num_output_,
out_spatial_dim_, , (Dtype)., bias, bias_multiplier_.cpu_data(),
(Dtype)., output);
}
函数caffe_cpu_gemm
math_functions.cpp
template<>
void caffe_cpu_gemm<float>(const CBLAS_TRANSPOSE TransA,
const CBLAS_TRANSPOSE TransB, const int M, const int N, const int K,
const float alpha, const float* A, const float* B, const float beta,
float* C) {
int lda = (TransA == CblasNoTrans) ? K : M;
int ldb = (TransB == CblasNoTrans) ? N : K;
cblas_sgemm(CblasRowMajor, TransA, TransB, M, N, K, alpha, A, lda, B,
ldb, beta, C, N);
}
参数说明参考该博客。
进入conv_im2col_cpu(input, col_buffer_.mutable_cpu_data())
base_conv_layer.hpp
// wrap im2col/col2im so we don't have to remember the (long) argument lists
inline void conv_im2col_cpu(const Dtype* data, Dtype* col_buff) {
if (!force_nd_im2col_ && num_spatial_axes_ == ) {
// Generating Cin by one single input feature map.
im2col_cpu(data, conv_in_channels_,
conv_input_shape_.cpu_data()[], conv_input_shape_.cpu_data()[],
kernel_shape_.cpu_data()[], kernel_shape_.cpu_data()[],
pad_.cpu_data()[], pad_.cpu_data()[],
stride_.cpu_data()[], stride_.cpu_data()[],
dilation_.cpu_data()[], dilation_.cpu_data()[], col_buff);
} else {
im2col_nd_cpu(data, num_spatial_axes_, conv_input_shape_.cpu_data(),
col_buffer_shape_.data(), kernel_shape_.cpu_data(),
pad_.cpu_data(), stride_.cpu_data(), dilation_.cpu_data(), col_buff);
}
}
最后进入im2col_cpu
im2col.cpp
// Function uses casting from int to unsigned to compare if value of
// parameter a is greater or equal to zero and lower than value of
// parameter b. The b parameter is of type signed and is always positive,
// therefore its value is always lower than 0x800... where casting
// negative value of a parameter converts it to value higher than 0x800...
// The casting allows to use one condition instead of two.
inline bool is_a_ge_zero_and_a_lt_b(int a, int b) {
return static_cast<unsigned>(a) < static_cast<unsigned>(b);
} template <typename Dtype>
void im2col_cpu(const Dtype* data_im, const int channels,
const int height, const int width, const int kernel_h, const int kernel_w,
const int pad_h, const int pad_w,
const int stride_h, const int stride_w,
const int dilation_h, const int dilation_w,
Dtype* data_col) {
const int output_h = (height + * pad_h -
(dilation_h * (kernel_h - ) + )) / stride_h + ;
const int output_w = (width + * pad_w -
(dilation_w * (kernel_w - ) + )) / stride_w + ;
const int channel_size = height * width;
for (int channel = channels; channel--; data_im += channel_size) {
for (int kernel_row = ; kernel_row < kernel_h; kernel_row++) {
for (int kernel_col = ; kernel_col < kernel_w; kernel_col++) {
int input_row = -pad_h + kernel_row * dilation_h;
for (int output_rows = output_h; output_rows; output_rows--) {
if (!is_a_ge_zero_and_a_lt_b(input_row, height)) {
for (int output_cols = output_w; output_cols; output_cols--) {
// Pad up and below with 0 (the size of the two sides is identical).
*(data_col++) = ;
}
} else {
int input_col = -pad_w + kernel_col * dilation_w;
for (int output_col = output_w; output_col; output_col--) {
if (is_a_ge_zero_and_a_lt_b(input_col, width)) {
// Select all the elements corresponding to the same order in every
// convolutional window and arrange them in a row successively.
*(data_col++) = data_im[input_row * width + input_col];
} else {
// Pad left and right with 0 (the size of the two sides is identical).
*(data_col++) = ;
}
input_col += stride_w;
}
}
input_row += stride_h;
}
}
}
}
}
二、反向传播
经过上面对前向传播的描述,可以将该过程简单地描述为权重矩阵(W)和输入矩阵(Cin)相乘最终得到输出矩阵(Cout)的过程,即W × Cin = Cout。反向传播的大体过程如下图(可以参考我写的前一章节)
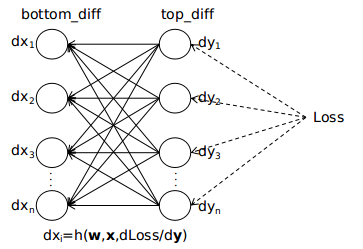
现在使用前向传播图示部分所使用的各种参数值为例,接着分析对应的反向传播的过程。
Loss对Cout的导数top_diff记为Tf

Tf另记为

反向传播的实质是在已知Tf的条件下求Loss对Cin的导数bottom_diff,我记为Bf,以及Loss对权重矩阵W的导数Wf.

Bf另记为
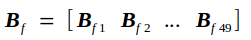
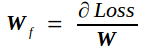
W另记为
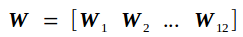
输入矩阵Cin另记为
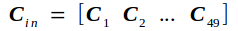
前向传播的过程如下图所示

根据链式求导法则,易知

同理,有
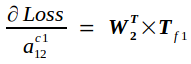
以此类推,有
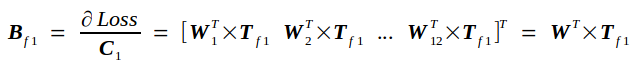
从而,有
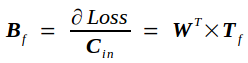
同理可推出Loss对权重矩阵的导数

若卷积核中带有偏置项,则前向传播的过程变为
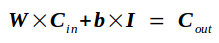
其中b的维度为(高 × 宽 = 4 × 1),I是一个维度为(高 × 宽 = 1 × 49)的元素全为1的矩阵
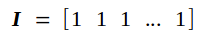
通过上述分析可知,此时Bf和Wf都没变,Loss对偏置项的导数为
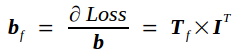
下面仍然以caffe自带的例子LeNet为例,结合源代码,来分析代码的实现过程(代码注释中参数的值是batch_size=64,网络反向传播到conv2层时的值)
conv_layer.cpp
template <typename Dtype>
void ConvolutionLayer<Dtype>::Backward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top,
const vector<bool>& propagate_down, const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom) {
// weight is the pointer of weight matrix W.
// weight_diff is the pointer of matrix Wf
// which is gradient with respect to weight.
const Dtype* weight = this->blobs_[]->cpu_data();
Dtype* weight_diff = this->blobs_[]->mutable_cpu_diff();
for (int i = ; i < top.size(); ++i) {
// top_diff point to data that is the derivative of Loss respect to the output
// of the forward process of this layer (Cout), namely Tf.
// bottom_data is Cin.
// bottom_diff point to data that is the derivative of Loss respect to the input
// of the forward process of this layer (Cin), namely Bf.
const Dtype* top_diff = top[i]->cpu_diff();
const Dtype* bottom_data = bottom[i]->cpu_data();
Dtype* bottom_diff = bottom[i]->mutable_cpu_diff();
// Bias gradient, if necessary.
if (this->bias_term_ && this->param_propagate_down_[]) {
// bias_diff is the pointer of matrix bf
// which is gradient with respect to bias.
Dtype* bias_diff = this->blobs_[]->mutable_cpu_diff();
// Every time just backward one single sample, and then accumulate them.
for (int n = ; n < this->num_; ++n) {
// Compute bf and accumulate them (accumulate bf of a batch samples).
this->backward_cpu_bias(bias_diff, top_diff + n * this->top_dim_);
}
}
if (this->param_propagate_down_[] || propagate_down[i]) {
for (int n = ; n < this->num_; ++n) {
if (this->param_propagate_down_[]) {
// Compute Wf and accumulate them (accumulate Wf of a batch samples).
this->weight_cpu_gemm(bottom_data + n * this->bottom_dim_,
top_diff + n * this->top_dim_, weight_diff);
}
if (propagate_down[i]) {
// Compute Bf.
this->backward_cpu_gemm(top_diff + n * this->top_dim_, weight,
bottom_diff + n * this->bottom_dim_);
}
}
}
}
}
依次进入
this->backward_cpu_bias(bias_diff, top_diff + n * this->top_dim_)
this->weight_cpu_gemm(bottom_data + n * this->bottom_dim_, top_diff + n * this->top_dim_, weight_diff)
this->backward_cpu_gemm(top_diff + n * this->top_dim_, weight, bottom_diff + n * this->bottom_dim_)
template <typename Dtype>
void BaseConvolutionLayer<Dtype>::backward_cpu_bias(Dtype* bias,
const Dtype* input) {
// The following takes caffe's example mnist as example to explain the value of every parameter.
// The value of these parameters are as follows when the solver backwarding into the conv2 layer.
// num_output_ = c1 = 50
// out_spatial_dim_ = ho * wo = 8 * 8 = 64
// bias_multiplier_ is the Blob of I(dimension h * w = 1 * out_spatial_dim_ = 1 * 64).
// This function computes bf = bf + Tf X I^T.
caffe_cpu_gemv<Dtype>(CblasNoTrans, num_output_, out_spatial_dim_, .,
input, bias_multiplier_.cpu_data(), ., bias);
} template <typename Dtype>
void BaseConvolutionLayer<Dtype>::weight_cpu_gemm(const Dtype* input,
const Dtype* output, Dtype* weights) {
const Dtype* col_buff = input;
if (!is_1x1_) {
// Generate Cin from input feature map.
conv_im2col_cpu(input, col_buffer_.mutable_cpu_data());
// col_buff is the pointer of matrix Cin.
col_buff = col_buffer_.cpu_data();
}
for (int g = ; g < group_; ++g) {
// The following takes caffe's example mnist as example to explain the value of every parameter.
// The value of these parameters are as follows when the solver backwarding into the conv2 layer.
// group_ = 1(usually is 1)
// conv_out_channels_ = c1 = 50
// kernel_dim_ = c(the number of channels of bottom) * h1 * w1 = 20 * 5 * 5 = 500
// conv_out_spatial_dim_ = ho * wo = 8 * 8 = 64
// output_offset_ = conv_out_channels_ * conv_out_spatial_dim_ / group_ = 50 * 64 / 1 = 3200
// col_offset_ = kernel_dim_ * conv_out_spatial_dim_ / group_ = 500 * 64 / 1 = 32000
// weight_offset_ = conv_out_channels_ * kernel_dim_ / group_ = 50 * 500 / 1 = 25000
// This function computes Wf = Wf + Tf X Cin^T.
caffe_cpu_gemm<Dtype>(CblasNoTrans, CblasTrans, conv_out_channels_ / group_,
kernel_dim_, conv_out_spatial_dim_,
(Dtype)., output + output_offset_ * g, col_buff + col_offset_ * g,
(Dtype)., weights + weight_offset_ * g);
}
} template <typename Dtype>
void BaseConvolutionLayer<Dtype>::backward_cpu_gemm(const Dtype* output,
const Dtype* weights, Dtype* input) {
// col_buff is the pointer of matrix Bf.
Dtype* col_buff = col_buffer_.mutable_cpu_data();
if (is_1x1_) {
col_buff = input;
}
for (int g = ; g < group_; ++g) {
// The following takes caffe's example mnist as example to explain the value of every parameter.
// The value of these parameters are as follows when the solver backwarding into the conv2 layer.
// group_ = 1(usually is 1)
// kernel_dim_ = c(the number of channels of bottom) * h1 * w1 = 20 * 5 * 5 = 500
// conv_out_spatial_dim_ = ho * wo = 8 * 8 = 64
// conv_out_channels_ = c1 = 50
// weight_offset_ = conv_out_channels_ * kernel_dim_ / group_ = 50 * 500 / 1 = 25000
// output_offset_ = conv_out_channels_ * conv_out_spatial_dim_ / group_ = 50 * 64 / 1 = 3200
// col_offset_ = kernel_dim_ * conv_out_spatial_dim_ / group_ = 500 * 64 / 1 = 32000
// This function computes Bf = W^T X Tf.
caffe_cpu_gemm<Dtype>(CblasTrans, CblasNoTrans, kernel_dim_,
conv_out_spatial_dim_, conv_out_channels_ / group_,
(Dtype)., weights + weight_offset_ * g, output + output_offset_ * g,
(Dtype)., col_buff + col_offset_ * g);
}
if (!is_1x1_) {
// This function is the reverse of conv_im2col_cpu. It transforms Bf into the form
// which is the same as the input feature map.
conv_col2im_cpu(col_buff, input);
}
}
函数caffe_cpu_gemv
math_functions.cpp
template <>
void caffe_cpu_gemv<float>(const CBLAS_TRANSPOSE TransA, const int M,
const int N, const float alpha, const float* A, const float* x,
const float beta, float* y) {
cblas_sgemv(CblasRowMajor, TransA, M, N, alpha, A, N, x, , beta, y, );
}
参数说明参考该博客。
接着,进入conv_col2im_cpu(col_buff, input)
base_conv_layer.hpp
inline void conv_col2im_cpu(const Dtype* col_buff, Dtype* data) {
if (!force_nd_im2col_ && num_spatial_axes_ == ) {
// This function is the reverse of conv_im2col_cpu. It transforms Bf into the form
// which is the same as the input feature map.
col2im_cpu(col_buff, conv_in_channels_,
conv_input_shape_.cpu_data()[], conv_input_shape_.cpu_data()[],
kernel_shape_.cpu_data()[], kernel_shape_.cpu_data()[],
pad_.cpu_data()[], pad_.cpu_data()[],
stride_.cpu_data()[], stride_.cpu_data()[],
dilation_.cpu_data()[], dilation_.cpu_data()[], data);
} else {
col2im_nd_cpu(col_buff, num_spatial_axes_, conv_input_shape_.cpu_data(),
col_buffer_shape_.data(), kernel_shape_.cpu_data(),
pad_.cpu_data(), stride_.cpu_data(), dilation_.cpu_data(), data);
}
}
最后进入col2im_cpu
im2col.cpp
template <typename Dtype>
void col2im_cpu(const Dtype* data_col, const int channels,
const int height, const int width, const int kernel_h, const int kernel_w,
const int pad_h, const int pad_w,
const int stride_h, const int stride_w,
const int dilation_h, const int dilation_w,
Dtype* data_im) {
caffe_set(height * width * channels, Dtype(), data_im);
const int output_h = (height + * pad_h -
(dilation_h * (kernel_h - ) + )) / stride_h + ;
const int output_w = (width + * pad_w -
(dilation_w * (kernel_w - ) + )) / stride_w + ;
const int channel_size = height * width;
for (int channel = channels; channel--; data_im += channel_size) {
for (int kernel_row = ; kernel_row < kernel_h; kernel_row++) {
for (int kernel_col = ; kernel_col < kernel_w; kernel_col++) {
int input_row = -pad_h + kernel_row * dilation_h;
for (int output_rows = output_h; output_rows; output_rows--) {
if (!is_a_ge_zero_and_a_lt_b(input_row, height)) {
// Skip these addresses, because they are corresponding to padding zone(up and below).
data_col += output_w;
} else {
int input_col = -pad_w + kernel_col * dilation_w;
for (int output_col = output_w; output_col; output_col--) {
if (is_a_ge_zero_and_a_lt_b(input_col, width)) {
// This expression is the reverse of the corresponding one in im2col_cpu.
data_im[input_row * width + input_col] += *data_col;
}
// Skip these addresses, because they are corresponding to padding zone(left and right).
data_col++;
input_col += stride_w;
}
}
input_row += stride_h;
}
}
}
}
}
caffe中ConvolutionLayer的前向和反向传播解析及源码阅读的更多相关文章
- flask_sqlalchemy中db.session是如何保持请求间独立的--源码阅读笔记
本文主要是为了验证两个问题: flask处理请求时通过新建线程.进程.协程的区别(顺带一提) flask_sqlalchemy是如何使用db.session使多个请求中保函的改变同一个表的sql操作不 ...
- caffe中batch norm源码阅读
1. batch norm 输入batch norm层的数据为[N, C, H, W], 该层计算得到均值为C个,方差为C个,输出数据为[N, C, H, W]. <1> 形象点说,均值的 ...
- 《神经网络的梯度推导与代码验证》之CNN前向和反向传播过程的代码验证
在<神经网络的梯度推导与代码验证>之CNN的前向传播和反向梯度推导 中,我们学习了CNN的前向传播和反向梯度求导,但知识仍停留在纸面.本篇章将基于深度学习框架tensorflow验证我们所 ...
- 《神经网络的梯度推导与代码验证》之vanilla RNN前向和反向传播的代码验证
在<神经网络的梯度推导与代码验证>之vanilla RNN的前向传播和反向梯度推导中,我们学习了vanilla RNN的前向传播和反向梯度求导,但知识仍停留在纸面.本篇章将基于深度学习框架 ...
- caffe源码阅读(2)-Layer
神经网络是由层组成的,深度神经网络就是层数多了.layer对应神经网络的层.数据以Blob的形式,在不同的layer之间流动.caffe定义的神经网络已protobuf形式定义.例如: layer { ...
- Caffe源码阅读(1) 全连接层
Caffe源码阅读(1) 全连接层 发表于 2014-09-15 | 今天看全连接层的实现.主要看的是https://github.com/BVLC/caffe/blob/master/src ...
- caffe-windows中classification.cpp的源码阅读
caffe-windows中classification.cpp的源码阅读 命令格式: usage: classification string(模型描述文件net.prototxt) string( ...
- 源码阅读笔记 - 1 MSVC2015中的std::sort
大约寒假开始的时候我就已经把std::sort的源码阅读完毕并理解其中的做法了,到了寒假结尾,姑且把它写出来 这是我的第一篇源码阅读笔记,以后会发更多的,包括算法和库实现,源码会按照我自己的代码风格格 ...
- go 中 select 源码阅读
深入了解下 go 中的 select 前言 1.栗子一 2.栗子二 3.栗子三 看下源码实现 1.不存在 case 2.select 中仅存在一个 case 3.select 中存在两个 case,其 ...
随机推荐
- fopen文件目录问题
程序当前目录下.如果是在 VC 里面运行的, 这个目录是工程的目录. 如果是双击 exe 运行的, 这个目录就是 exe 所在的目录.
- JavaScript学习三
2019-05-30 20:38:50 逻辑运算符 && || ! !如果对非布尔值取反,则将会把数值变成布尔值,然后再取反 隐式类型转化 为任意的数据类型做两次非运算,既可将其转换成 ...
- Struts和Spring MVC的比较(非原创)
文章大纲 一.Spring MVC项目例子二.Struts项目例子三.Struts和Spring MVC对比四.参考文章 一.Spring MVC项目例子 https://www.jianshu. ...
- 3Ddungeon-------三维搜索-----偷个懒 把 亡命逃窜 的代码修改了一下 拿来用了
题 很简单 就是给一个 三维的迷宫然后 开你起始地点 S 问你能不能到达 出口 E 能的话 需要多长时间 ? #include<stdio.h> #include<string ...
- POJ 1236 Tarjan算法
这道题认真想了想.. [ 题目大意:有N个学校,从每个学校都能从一个单向网络到另外一个学校,两个问题 1:初始至少需要向多少个学校发放软件,使得网络内所有的学校最终都能得到软件. 2:至少需要添加几条 ...
- B - String Task
Problem description Petya started to attend programming lessons. On the first lesson his task was to ...
- css3动画之1--animation小例子
1.首先看效果 2.代码及分析 <style type="text/css"> #div1 { margin:100px; position: absolute; te ...
- 复习java基础第三天(集合:Collection、Set、HashSet、LinkedHashSet、TreeSet)
一.Collection常用的方法: Java 集合可分为 Set.List 和 Map 三种体系: Set:无序.不可重复的集合. List:有序,可重复的集合. Map:具有映射关系的集合. Co ...
- 07--c++类的构造函数详解
c++类的构造函数详解 c++构造函数的知识在各种c++教材上已有介绍,不过初学者往往不太注意观察和总结其中各种构造函数的特点和用法,故在此我根据自己的c++编程经验总结了一下c++中各种构造函数的特 ...
- scala类型系统:24) 理解 higher-kinded-type
首先我们从最基本的泛型来看: 现在我们对上面泛型中的类型参数再进一步,也是个泛型会如何呢? 可以看到,java中不支持类型参数也是泛型类型的情况,而scala支持.这是一个很重要的区别,scala在类 ...
