Linux/UNIX编程:使用C语言实现简单的 ls 命令
刚好把 Linux/UNIX 编程中的文件和IO部分学完了,就想编写个 ls 命令练习一下,本以为很简单,调用个 stat 就完事了,没想到前前后后弄了七八个小时,90%的时间都用在格式化(像 ls -l 中的对齐)输出了,反反复复改了好几遍。
一共实现了常用的四个选项:-a -h -l -d。可以从命令行参数中同时接受多个目录和文件,然后分开输出。
演示:
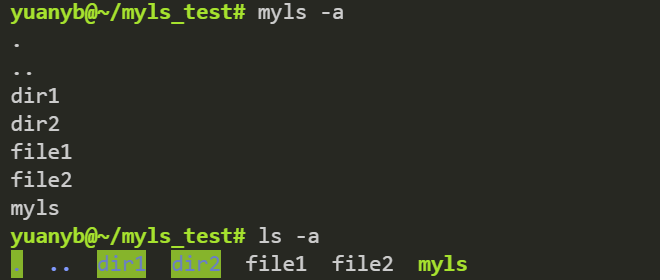
-a 命令:
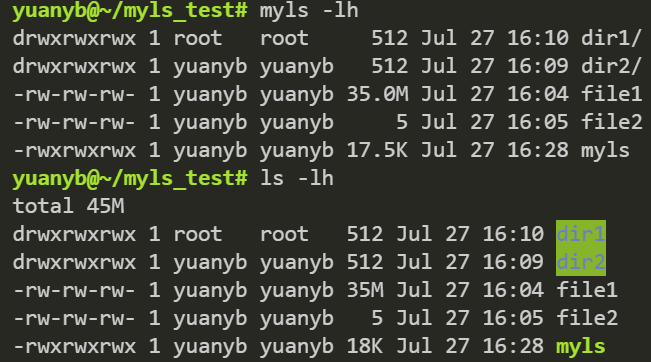
-l 和 -h 命令:
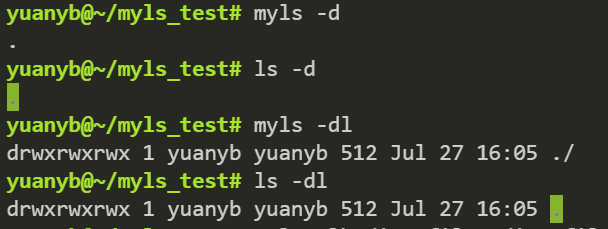
-d 命令:
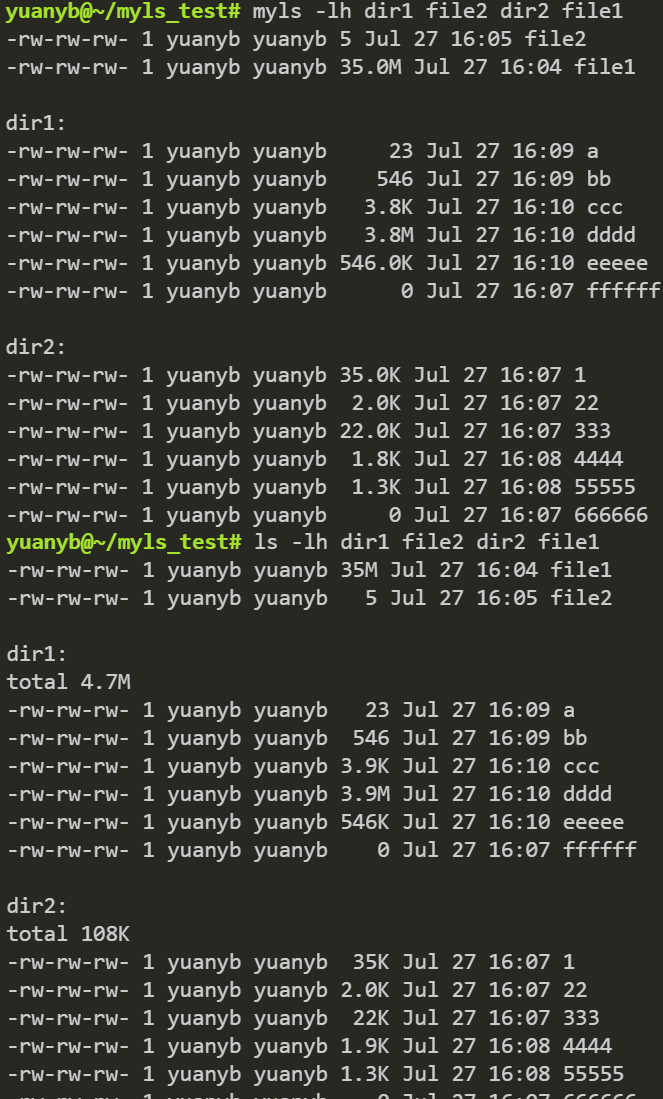
参数同时接受多个文件和目录名:
思路:
先使用 getopt 解析选项
然后判断参数有没有目录或文件(通过 operand 标志变量),没有的话仅输出进程当前目录
有的话将参数中的文件和目录分开(files 和 dirs数组),然后输出信息
因为要格式化输出,所以得将目录中所有项目读取完成后并转换成字符串形式(get_stat_str)才能获得长度最长的某个信息(如,文件名,尺寸),而目录中的文件数目又事先不可知,所以用链表结构(stat_str)将所有目录中所有文件的信息存储下来。
代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <dirent.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <limits.h>
#include <pwd.h>
#include <grp.h>
#define err_exit(func) {perror(func); exit(EXIT_FAILURE);} //打印出错函数,并结束程序
#define max(a, b) ((a) > (b) ? (a) : (b)) typedef struct stat_str{ //字符串形式的stat信息
char fname[NAME_MAX]; //大概长度,不严谨
char user[20];
char group[20];
char size[16];
char time[13];
char mode[11];
char nlink[5];
struct stat_str *next; //链表结构,因为需要预先获得目录里的所有项(为了控制格式化),但数目不确定,所以用链表保存
} st_str; int nlink_maxlen = 0, user_maxlen = 0, group_maxlen = 0, size_maxlen = 0; //字符串形式的最大长度,为了格式化构造字符串
int ARG_L = 0, ARG_A = 0, ARG_H = 0, ARG_D = 0; //参数是否定义 //解析选项
void analyse_opt(int argc, char* argv[]);
//将文件大小(字节数)转换成易读(human readable)的形式
void human_readable(off_t bytes, char *szbuf);
//构造文件的详细信息
void build_line(const st_str *stat_strbuf, char* fmtstrbuf);
//打印目录信息
void print_dir_info(const char *dir);
//获得文件信息的str形式
void get_stat_str(const struct stat* stbuf, const char* fname, st_str *strbuf); int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
struct stat stbuf;
st_str st_strbuf;
int no_operand = 1; //是否没有操作数
analyse_opt(argc, argv); //解析选项 //分别获得目录和其他文件,为了格式化输出
char *files[argc-1], *dirs[argc-1];
int nf = 0, nd = 0;
for(int i = 1; i < argc; i++){
if(argv[i][0] == '-') //跳过选项
continue;
else
no_operand = 0;
if(-1 == lstat(argv[i], &stbuf))
err_exit("lstat");
if(S_ISDIR(stbuf.st_mode))
dirs[nd++] = argv[i];
else
files[nf++] = argv[i];
} if(no_operand){
//命令行没有输入路径
print_dir_info(".");
} else {
//先列出文件的信息
for(int i = 0; i < nf; i++){
char fmtstrbuf[256];
if(-1 == lstat(files[i], &stbuf))
err_exit("lstat");
get_stat_str(&stbuf, files[i], &st_strbuf);
if(ARG_L){
build_line(&st_strbuf, fmtstrbuf);
puts(fmtstrbuf);
} else {
puts(files[i]);
}
}
//再列出目录的信息
for(int i = 0; i < nd; i++){
if(nf > 0)
printf("\n%s:\n", dirs[i]);
print_dir_info(dirs[i]);
}
}
return 0;
} void analyse_opt(int argc, char* argv[]){
int opt;
while((opt = getopt(argc, argv, "lahd")) != -1){
switch (opt) {
case 'l':
ARG_L = 1;
break;
case 'a':
ARG_A = 1;
break;
case 'h':
ARG_H = 1;
break;
case 'd':
ARG_D = 1;
break;
}
}
} void human_readable(off_t nbytes, char *szbuf){
if(nbytes < 1024)
sprintf(szbuf, "%ld\0", nbytes);
else if(nbytes < 1024 * 1024)
sprintf(szbuf, "%.1lfK\0", (double)nbytes / 1024);
else if(nbytes < 1024 * 1024 * 1024)
sprintf(szbuf, "%.1lfM\0", (double)nbytes / 1024 / 1024);
else
sprintf(szbuf, "%.1lfG\0", (double)nbytes / 1024 / 1024 / 1024);
} void get_stat_str(const struct stat* stbuf, const char* fname, st_str *strbuf){
//mode
sprintf(strbuf->mode, "%c%c%c%c%c%c%c%c%c%c",
S_ISREG(stbuf->st_mode) ? '-' : (
S_ISDIR(stbuf->st_mode) ? 'd' : (
S_ISBLK(stbuf->st_mode) ? 'b' : (
S_ISCHR(stbuf->st_mode) ? 'c' : 'l'
)
)
),
(S_IRUSR & stbuf->st_mode ) ? 'r' : '-',
(S_IWUSR & stbuf->st_mode ) ? 'w' : '-',
(S_IXUSR & stbuf->st_mode ) ? 'x' : '-',
(S_IRGRP & stbuf->st_mode ) ? 'r' : '-',
(S_IWGRP & stbuf->st_mode ) ? 'w' : '-',
(S_IXGRP & stbuf->st_mode ) ? 'x' : '-',
(S_IROTH & stbuf->st_mode ) ? 'r' : '-',
(S_IWOTH & stbuf->st_mode ) ? 'w' : '-',
(S_IXOTH & stbuf->st_mode ) ? 'x' : '-' );
//nlink
sprintf(strbuf->nlink, "%ld\0", stbuf->st_nlink);
nlink_maxlen = max(nlink_maxlen, strlen(strbuf->nlink));
//user, group
sprintf(strbuf->user, "%s\0", getpwuid(stbuf->st_uid)->pw_name);
sprintf(strbuf->group, "%s\0", getgrgid(stbuf->st_gid)->gr_name);
user_maxlen = max(user_maxlen, strlen(strbuf->user));
group_maxlen = max(group_maxlen, strlen(strbuf->group));
//size
if(ARG_H){
char szbuf[16];
human_readable(stbuf->st_size, szbuf);
sprintf(strbuf->size, "%s\0", szbuf);
} else {
sprintf(strbuf->size, "%ld\0", stbuf->st_size);
}
size_maxlen = max(size_maxlen, strlen(strbuf->size));
//time
strftime(strbuf->time, 13, "%b %d %H:%M\0", localtime(&(stbuf->st_mtime)));
//fname
sprintf(strbuf->fname, "%s\0", fname); } void build_line(const st_str *stat_strbuf, char* fmtstrbuf){
char fmt[32];
sprintf(fmt, "%%s %%%ds %%-%ds %%-%ds %%%ds %%s %%s\0", nlink_maxlen, user_maxlen, group_maxlen, size_maxlen);
// puts(fmt);
if((stat_strbuf->mode)[0] == 'd')
strcat(stat_strbuf->fname, "/");
sprintf(fmtstrbuf, fmt, stat_strbuf->mode, stat_strbuf->nlink, stat_strbuf->user,
stat_strbuf->group, stat_strbuf->size, stat_strbuf->time, stat_strbuf->fname);
} void print_dir_info(const char *dir){
if(ARG_D){
//显式目录本身的信息
st_str stat_strbuf;
struct stat stbuf;
char fmtstrbuf[256];
if(-1 == lstat(dir, &stbuf))
err_exit("lstat");
get_stat_str(&stbuf, dir, &stat_strbuf);
if(ARG_L){
build_line(&stat_strbuf, fmtstrbuf);
puts(fmtstrbuf);
} else {
puts(stat_strbuf.fname);
}
} else {
group_maxlen = nlink_maxlen = user_maxlen = size_maxlen = 0;
//列出目录所有项
struct DIR *pdir = opendir(dir);
if(pdir == NULL)
err_exit("opendir");
struct dirent *pdirent;
struct stat stbuf;
st_str * head_st_str = (st_str*)(malloc(sizeof(st_str))), *p = head_st_str; //链表头(字符串形式的stat)
//循环都目录
errno = 0;
while((pdirent = readdir(pdir)) != NULL){
if((pdirent->d_name)[0] != '.' || ARG_A) {
//是否显示隐藏文件
if(ARG_L) {
char path[256];
strcpy(path, dir); //!!!!! 找了一个多小时才找出来这个错误
strcat(path, "/"); //!!!!! d_name仅是个文件名而已
strcat(path, pdirent->d_name); //!!!!! 需要加上完整路径
if(-1 == lstat(path, &stbuf)){
err_exit("lstat");
}
p->next = (st_str*)(malloc(sizeof(st_str)));
p = p->next;
p->next = NULL;
get_stat_str(&stbuf, pdirent->d_name, p);
} else {
puts(pdirent->d_name);
}
}
}
if(errno != 0)
err_exit("readdir"); //输出信息链表的格式化内容
p = head_st_str->next;
while(ARG_L && p){
char fmtstrbuf[256];
build_line(p, fmtstrbuf);
puts(fmtstrbuf);
p = p->next;
}
if(-1 == closedir(pdir))
err_exit("closedir");
st_str *q = head_st_str->next; //释放链表
while(q){
free(head_st_str);
head_st_str = q;
q = q->next;
}
free(head_st_str);
}
}
Linux/UNIX编程:使用C语言实现简单的 ls 命令的更多相关文章
- 学习linux/unix编程方法的建议(转)
假设你是计算机科班出身,计算机系的基本课程如数据结构.操作系统.体系结构.编译原理.计算机网络你全修过 我想大概可以分为4个阶段,水平从低到高从安装使用=>linux常用命令=>linux ...
- 学习linux/unix编程方法的建议,学习Linux的四个步骤(转)
解答:学习Linux的四个步骤假设你是计算机科班出身,计算机系的基本课程如数据结构.操作系统.体系结构.编译原理.计算机网络你全修过我想大概可以分为4个阶段,水平从低到高从安装使用=>linux ...
- Linux/UNIX编程如何保证文件落盘
本文转载自Linux/UNIX编程如何保证文件落盘 导语 我们编写程序write数据到文件中时,其实数据不会立马写入磁盘,而是会经过层层缓存.每层缓存都有自己的刷新时机,每层缓存都刷新后才会写入磁盘. ...
- Linux用户应知应会的7个‘ls’命令的独特技巧
在前面我们系列报道的两篇文章中,我们已经涵盖了关于‘ls’命令的绝大多数内容.本文时‘ls命令’系列的最后一部分.如果你还没有读过该系列的其它两篇文章,你可以访问下面的链接. Linux中的15个基本 ...
- Linux/UNIX编程:实现简单 tee 命令
思路很简单,从标准输入文件描述符读入数据,然后同时向标准输出和参数指定的文件写出数据:如果加了 -a 选项,则以追加的方式向文件写出数据.还没了解 getopt() 函数就没判断参数是否合法. #in ...
- Linux/Unix编程中的线程安全问题【转】
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/zhengzhoudaxue2/article/details/6432984 在目前的计算机科学中,线程是操作系统调度的最小单元,进程是资源分配的最小 ...
- linux socket 编程(C语言)
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/piaojun_pj/article/details/5920888 最近看了一些网络编程的书籍,一直以来总感觉网络编程神秘莫测,其实网络编程入门还是很 ...
- linux socket 编程(C语言)[转]
最近看了一些网络编程的书籍,一直以来总感觉网络编程神秘莫测,其实网络编程入门还是很容易学的,下面这些代码是我在linux下编写的,已经运行过了,编译之后就可以运行了.有不足之处希望大家多多指出,共同学 ...
- Linux网络编程:客户端/服务器的简单实现
一. Socket的基本知识 1. socket功能 Socket层次 Socket实质上提供了进程通信的端点,进程通信之前,双方必须首先各自创建一个端点,否则是没有办法建立联系并相互通信的. 每一个 ...
随机推荐
- win2003浏览器提示是否需要将当前访问的网站添加到自己信任的站点中去
Win2003的操作系统,的确比其它操作系统在安全上增加了不少,这是为用户所考虑的.当然,既然提供了安全性,尤其是在上网的时候,可以禁止某些活动脚本的显示,这样,就可以多方面的避免在使用Win2003 ...
- GO方法与接口
Go语言没有沿袭传统面向对象编程中的诸多概念,比如继承.虚函数.构造函数和析构函数.隐藏的this指针等. 方法 Go 语言中同时有函数和方法.方法就是一个包含了接受者(receiver)的函数,re ...
- 创建一个简单的Django项目
1.首先,启动pycharm,点击File->New Project,如下图所示. 2.在New Project对话框中,选择Django,在Location中设置项目路径以及项目名称,在App ...
- never下的easysql
什么是EasySql 在我们早期写的代码中,想实现组装灵活的sql语句与参数,我们可以去翻阅早期自己写的代码 var @sb = new StringBuilder(); sb.Append(&quo ...
- Scala 学习之路(十一)—— 模式匹配
一.模式匹配 Scala支持模式匹配机制,可以代替swith语句.执行类型检查.以及支持析构表达式等. 1.1 更好的swith Scala不支持swith,可以使用模式匹配match...case语 ...
- python基础--定义装饰器(内置装饰器)
装饰器的定义: 装饰器本质上就是一个python函数,它可以让其它函数在不需要做任何代码改动的前提下增加额外的功能,装饰器的返回值也是一个函数对象.它经常用于有切面需求的场景中,比如-- >插入 ...
- 【半小时大话.net依赖注入】(一)理论基础+实战控制台程序实现AutoFac注入
系列目录 第一章|理论基础+实战控制台程序实现AutoFac注入 第二章|AutoFac的常见使用套路 第三章|实战Asp.Net Framework Web程序实现AutoFac注入 第四章|实战A ...
- C++ luogu1352没有上司的舞会 from_树形DP
luogu1352没有上司的舞会 分析(树形DP模板题): 没学树形DP的,看一下. 把该题抽象到一颗树中,设i的下属就是他的儿子,则有两种情况: 如果i参加,他的儿子就不能参加. 如果i不参加,他的 ...
- 高并发架构系列:Redis缓存和MySQL数据一致性方案详解
一.需求起因 在高并发的业务场景下,数据库大多数情况都是用户并发访问最薄弱的环节.所以,就需要使用redis做一个缓冲操作,让请求先访问到redis,而不是直接访问MySQL等数据库. 这个业务场景, ...
- 西门子S7-1200与 G120系列变频器USS通信
西门子S7-1200 紧凑型PLC在当前的市场中有着广泛的应用,作为经常与SINAMICS G120系列变频器共同使用的PLC,其USS通信协议的使用一直在市场上有着非常广泛的应用.本文将主要介绍如何 ...
