HPL Study 2
1.并行编程
(1)并行程序的逻辑:
1)将当前问题划分为多个子任务
2)考虑任务间所需要的通信通道
3)将任务聚合成复合任务
4)将复合任务分配到核上
(2)共享内存编程:
路障 ----> 条件变量,互斥量+忙等待(浪费cpu周期,重置),信号量(多个路障产生竞争条件)
临界区(更新共享资源的代码段)------>忙等待(标识变量),互斥量,信号量(信号量没有个体拥有权),读写锁
共享内存带来的问题:缓存一致性,线程的安全性,多个线程尝试更新一个共享变量的时候会产生问题(竞争条件)
线程是否越多越好:否,由于线程的切换和可能导致的二义性。
线程和进程:线程是轻量级的进程,由进程派生,共享进程的大部分资源,但拥有独立的程序计数器和函数调用栈
局部性原理
空间局部性
时间局部性
串行部分决定了加速比的上限
2.矩阵
(1)矩阵的加减乘除
矩阵加减
template <class T>
T** add_sub(int n1,int m1,int n2,int m2,T **a,T *bb,int flag){
T c[n1+10][m1+10];
if(n1!=n2||m1!=m2){
cout<<"No Solution";
return 0;
}
for(int i=1;i<=n1;i++)
for(int t=1;t<=m1;t++)
c[i][t]=a[i][t]+b[i][t]*flag;
}矩阵乘法
template <class T>
T** mul(int n1,int m1,int n2,int m2,T **a,T **b){
if(m1!=n2){
cout<<"No Solution";
return 0;
}
T c[n1+10][m2+10];
for(int i=1;i<=n1;i++)
for(int t=1;t<=m2;t++)
c[i][t]=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n1;i++)
for(int t=1;t<=m1;t++){
for(int j=1;j<=m2;j++){
c[i][j]+=a[i][t]*b[t][j];
}
}
}矩阵除法
template <class T>
T** div(int n1,int m1,int n2,int m2,T **a,T **b){
T e[n1+10][n2+10];
for(int i=1;i<=n2;i++){
for(int t=1;t<=n2;t++){
if(i==t) e[i][t]=1;
else e[i][t]=0;
}
}
//Gauss-Jordan消元法求矩阵的逆
for(int i=1;i<=n2;i++){
int max=i;
for(int t=i+1;t<=n2;t++)
if(fabs(a[t][i])>fabs(a[max][i])) max=t;
if(fabs(a[max][i])<1e-10){
cout<<"No Solution";
return 0;
}
if(i!=max){
swap(a[i],a[max]);
swap(e[i],e[max]);
}
for(int t=1;t<=n2;t++){
if(t!=i){
double flag=a[i][i]/a[t][i];
for(int j=1;j<=n2;j++){
a[t][j]=flag*a[t][j]-a[i][j];
e[t][j]=flag*e[t][j]-e[i][j];
}
}
}
}
for(int i=1;i<=n2;i++){
printf("%.2lf\n",a[i][n2+1]/a[i][i]);
}
return mul(n1,m1,n2,m2,a,e);
}(2)矩阵乘法优化
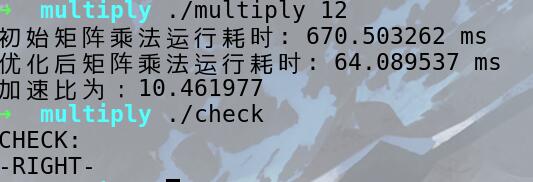
优化方法
矩阵分块(减少cache的缺失由于缓存容量的有限性)
矩阵的转置(空间局部性原理)
指令集向量化:avx256
多线程:pthread
核心代码
`for(int i=1;i<N;i++)
for(int t=1+i;t<N;t++)
swap(b[i][t],b[t][i]);
N--;
thread_count=strtol(argv[1],NULL,10);thread_count=10;
flag=(N+thread_count-1)/thread_count;
pthread_t *threads;
threads=(pthread_t*)malloc(thread_count * sizeof(pthread_t));
for(int i=0;i<thread_count;i++){
int* id = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int));
*id = i;
pthread_create(&threads[i],NULL,matrixMul,(void* )id);
}
for(int i=0;i<thread_count;i++)
pthread_join(threads[i],NULL);
free(threads);`
`void *matrixMul(void *rank){
__m256d a1,b1;
__m256d z= _mm256_setzero_pd();
int my_rank=*((int*)rank);
int T=128;
for(int l=1+flag*my_rank;l<=min(N,flag*(my_rank+1));l+=T)
for(int r=1;r<=N;r+=T)
for(int k=1;k<=N;k+=T)
for(int i=l;i<=min(l+T-1,flag*(my_rank+1));i++){
for(int j=r;j<=min(r+T-1,N);j++){
for(int t=k;t<=min(k+T-1,N/4*4);t+=4){
a1=_mm256_loadu_pd(&a[i][t]);
b1=_mm256_loadu_pd(&b[j][t]);
a1=_mm256_mul_pd(a1,b1);
c[i][j]+=a1[3]+a1[2]+a1[1]+a1[0];
}
}
}
for(int i=1+flag*my_rank;i<=min(N,flag*(my_rank+1));i++)
for(int j=1;j<=N;j++){
for(int t=N/4*4+1;t<=N;t++){
c[i][j]+=a[i][t]*b[j][t];
}
}
}`3.HPL测试
查看本机cpu为 12th Gen Intel Core tm i5-12500H 支持的指令集拓展为sse4.1,sse4.2,avx2
AVX2的处理器的单指令的长度是256bit,每颗intelCPU包含2个FMA,一个FMA一个时钟周期可以进行2次乘或者加的运算,那么这个处理器在1个核心1个时钟周期可以执行256bit2FMA2M/A/64=16次浮点运算,也称为16FLOPs,就是Floating Point Operations Per Second
查看虚拟机cpu参数主频为3.1GH 8核
本机Gfloat = 8核 * 3.1(GHz) *16=396.8
初始实际峰值
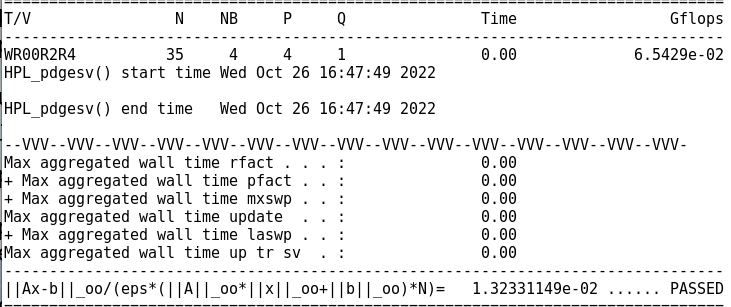
调试后实际峰值
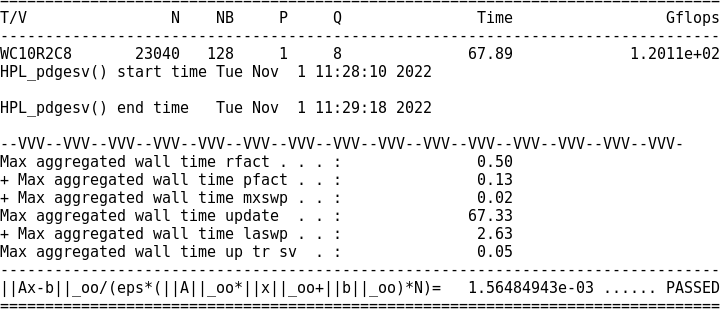
调试前比值0.0001769
调试后比值0.3026966(和理想差得有点多QAQ)
4.shell
对后台CPU使用率的的监控
#!/bin/bash
flag=0
file=/home/consonm/cpuMonitor.txt
echo -e '\t\t\t\tcpu Monitor' >$file
top -b -n 1 | awk 'NR==7,NR==10{print $0}NR==6{print $0}' >> $file
for ((i=4;i<=6;i++))
do
no=`expr $i - 3`
echo "---------------------------------------------------------------------------" >> $file
echo "NO:$no process the first three threads" >> $file
awk -v t=$i 'NR==t{printf $1}' $file | xargs top -H -n 1 -b -p| awk 'NR==7,NR==10{print $0}NR==6{print $0}'>>$file
done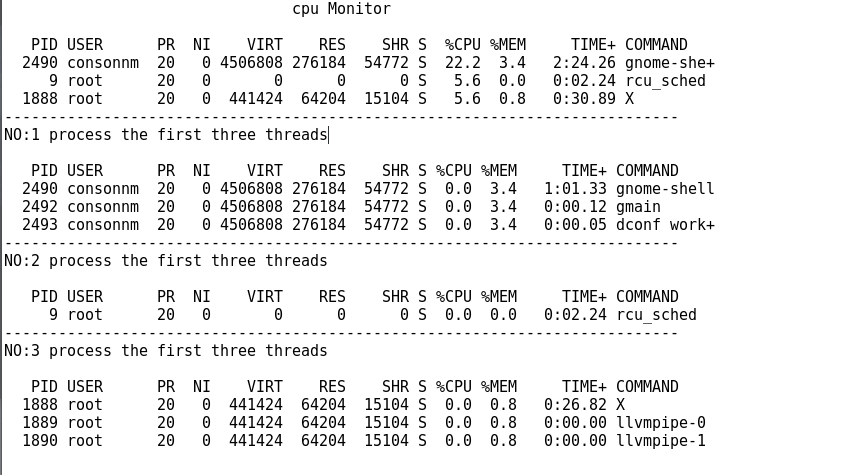
5.结构体数组相加
(1)编译器自动进行内存对齐
第一个成员的偏移量为0.
每个成员的首地址是自身大小的整数倍
结构体的总大小,为其成员中所含最大类型的整数倍。
结构体中改变声明变量的顺序可以节约内存
内存对齐的意义
cpu访问内存的时候,在不同的平台上已2,4,8,16,32字节存取来访问内存,如果对其可能增加访问次数。
提高程序在不同平台上的可移植性
宏声明 (超过结构体中最大成员(类型)的size无效)
#pragma pack(n)
对变量、结构或者联合,设定一个指定大小的对齐格式
__attribute__((aligned(n)))
(2)指令的使用
官方手册
[intel Intrinsics Guide] https://www.laruence.com/sse/#techs=AVX,AVX2注意编译的时候要根据不同的指令加上
CPUID Flags
用几种不同的指令优化了一下似乎差距不大以double型为例
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <immintrin.h>
#include<omp.h>
using namespace std;
const int N =100;
struct A{
int a;
float b;
double c;
char d;
}a[N+5];
union B{
int a;
float b;
double c;
char d;
}b[N+5];
int main(){
//第一种
__m128i h=_mm_set_epi32(9,6,3,0);
__m128i h1=_mm_set_epi32(3,2,1,0);
for(int i=1;i<=N/4*4;i+=4){
__m256d a1=_mm256_i32gather_pd(&a[i].c,h,8);
__m256d b1=_mm256_i32gather_pd(&b[i].c,h1,8);
a1=_mm256_add_pd(a1,b1);
a[i].c=a1[0],a[i+1].c=a1[1],a[i+2].c=a1[2],a[i+3].c=a1[3];
}
for(int i=N/4*4+1;i<=N;i++)
a[i].c+=b[i].c;
//第二种
for(int i=1;i<=N/4*4;i++){
__attribute__((aligned(32))) double c[4]={a[i].c,a[i+1].c,a[i+2].c,a[i+3].c};
__attribute__((aligned(32))) double d[4]={b[i].c,b[i+1].c,b[i+2].c,b[i+3].c};
__m256d a1=_mm256_load_pd(c);
__m256d b1=_mm256_load_pd(d);
a1=_mm256_add_pd(a1,b1);
a[i].c=a1[0],a[i+1].c=a1[1],a[i+2].c=a1[2],a[i+3].c=a1[3];
}
for(int i=N/4*4+1;i<=N;i++)
a[i].c+=b[i].c;
}
6.Dijkstar算法优化
用堆优化了一下,暂时没想好的并行方法
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <immintrin.h>
using namespace std;
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define endl '\n'
typedef long long ll;
int n,m,x,y,v,s,size,head[2000005],flag,dis[2000005],vis[2000005];
struct node{
int to,next,v;
}p[2000006];
struct node1{
int x,v;
}q[2000005];
void add(int x,int y,int v){
p[++flag].to=y;
p[flag].v=v;
p[flag].next=head[x];
head[x]=flag;
}
void push(int x,int v){
q[++size].x=x;
q[size].v=v;
int flag=size;
while((flag>>1)>=1){
int h=flag>>1;
if(q[flag].v<q[h].v){
swap(q[flag],q[h]);
flag=h;
}
else break;
}
}
void pop(){
swap(q[1],q[size--]);
int flag=1;
while((flag<<1)<=size){
int h=flag<<1;
if((h|1)<=size&&q[h].v>q[h|1].v) h=h|1;
if(q[flag].v>q[h].v){
swap(q[flag],q[h]);
flag=h;
}
else break;
}
}
void dijk(){
push(s,0);
while(size){
int x=q[1].x;
pop();
if(vis[x]) continue;
vis[x]=1;
for(int i=head[x];i;i=p[i].next){
if(dis[x]+p[i].v<dis[p[i].to]&&!vis[p[i].to]){
dis[p[i].to]=dis[x]+p[i].v;
push(p[i].to,dis[p[i].to]);
}
}
}
}
int main(int argc,char* argv[]){
cin>>n>>m>>s;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
dis[i]=INF;
dis[s]=0;
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){
cin>>x>>y>>v;
add(x,y,v);
}
dijk();
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
cout<<dis[i]<<" ";
}
HPL Study 2的更多相关文章
- HPL Study 1
1.安装Linux系统 在虚拟机Vmware上安装CentOS 7系统 2.安装OneApi 安装的时候将文件从桌面拖动到虚拟机安装的时候报错:archive corrupted 解决方法:大文件应采 ...
- Improve Your Study Habits
1.Plan your time carefully. Make a list of your weekly tasks.Then make a schedule or chart of your t ...
- HPL/SQL与CDH5.4.7集成
1.下载hplsql-0.3.13到本地并解压 2.修改plsql,为如下内容 #!/bin/bash export "HADOOP_CLASSPATH=/opt/cloudera/parc ...
- RSA Study
These days I study the RSA Algorithm. It is a little complex, but not very. Also, my study has not f ...
- Machine Learning Algorithms Study Notes(3)--Learning Theory
Machine Learning Algorithms Study Notes 高雪松 @雪松Cedro Microsoft MVP 本系列文章是Andrew Ng 在斯坦福的机器学习课程 CS 22 ...
- Machine Learning Algorithms Study Notes(2)--Supervised Learning
Machine Learning Algorithms Study Notes 高雪松 @雪松Cedro Microsoft MVP 本系列文章是Andrew Ng 在斯坦福的机器学习课程 CS 22 ...
- Machine Learning Algorithms Study Notes(1)--Introduction
Machine Learning Algorithms Study Notes 高雪松 @雪松Cedro Microsoft MVP 目 录 1 Introduction 1 1.1 ...
- jar tvf study.war jar命令查看war/jar包的内容
jar tvf study.war 0 Thu Oct 20 14:01:18 CST 2016 META-INF/ 137 Thu Oct 20 14:01:16 CST 2016 META-INF ...
- Mongo DB Study: first face with mongo DB
Mongo DB Study: first face with mongo DB 1. study methods: 1. Translate: I am the mongo DB organiz ...
随机推荐
- [CSharpTips]判断两条线段是否相交
判断两条线段是否相交 主要用到了通过向量积的正负判断两个向量位置关系 向量a×向量b(×为向量叉乘),若结果小于0,表示向量b在向量a的顺时针方向:若结果大于0,表示向量b在向量a的逆时针方向:若等于 ...
- 坚守自主创新,璞华HawkEye IETM系统惠及国计民生
可上九天揽月,可下五洋捉鳖,这是我们很多年的梦想.而要实现这样的梦想,不仅需要安全可靠的技术装备,还需要让这些技术装备处于良好的维保状态.于是,作为装备维保过程中必须的知识创作.管理.发布.浏览工具, ...
- winform,隐藏窗体
public Form1() { InitializeComponent(); this.WindowState = FormWindowSt ...
- SpringBoot Xml转Json对象
一.导入需要的依赖 <dependency> <groupId>maven</groupId> <artifactId>dom4j</artifa ...
- keycloak~资源的远程授权
17.1远程资源授权准备 17.1.1认证和访问流程图 参考:http://www.zyiz.net/tech/detail-141309.html 17.1.2为用户指定角色 可以使用ROLE_US ...
- MySQL8更改数据存储目录
- 2.第一篇 k8s组件版本及功能简介
文章转载自:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzI1MDgwNzQ1MQ==&mid=2247483772&idx=1&sn=a693d8a9 ...
- DirectPV-----文章内容有待进一步实践完善
GitHub文档地址:https://github.com/minio/directpv DirectPV是用于直连存储的CSI驱动程序.从更简单的意义上讲,它是一个分布式持久卷管理器,而不是像SAN ...
- 使用 Skywalking Agent,这里使用sidecar 模式挂载 agent
文章转载自:https://bbs.huaweicloud.com/blogs/315037 方法汇总 Java 中使用 agent ,提供了以下三种方式供你选择 使用官方提供的基础镜像 将 agen ...
- win10系统恢复默认的照片查看器
新建一个TXT文本文档,把以下代码复制粘贴到其中: 注:你可以根据需要按同样的格式增减或修改其中的图片格式代码 Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00 ; Chang ...
