CF #305 (Div. 2) C. Mike and Frog(扩展欧几里得&&当然暴力is also no problem)
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Mike has a frog and a flower. His frog is named Xaniar and his flower is named Abol. Initially(at time 0), height of Xaniar is h1 and height of Abol is h2. Each second, Mike waters Abol and Xaniar.

So, if height of Xaniar is h1 and height of Abol is h2, after one second height of Xaniar will become  and height of Abol will become
and height of Abol will become  where x1, y1, x2 and y2 are some integer numbers and
where x1, y1, x2 and y2 are some integer numbers and  denotes the remainder of amodulo b.
denotes the remainder of amodulo b.
Mike is a competitive programmer fan. He wants to know the minimum time it takes until height of Xania is a1 and height of Abol is a2.
Mike has asked you for your help. Calculate the minimum time or say it will never happen.
The first line of input contains integer m (2 ≤ m ≤ 106).
The second line of input contains integers h1 and a1 (0 ≤ h1, a1 < m).
The third line of input contains integers x1 and y1 (0 ≤ x1, y1 < m).
The fourth line of input contains integers h2 and a2 (0 ≤ h2, a2 < m).
The fifth line of input contains integers x2 and y2 (0 ≤ x2, y2 < m).
It is guaranteed that h1 ≠ a1 and h2 ≠ a2.
Print the minimum number of seconds until Xaniar reaches height a1 and Abol reaches height a2 or print -1 otherwise.
5
4 2
1 1
0 1
2 3
3
1023
1 2
1 0
1 2
1 1
-1
题解:
In this editorial, consider p = m, a = h1, a′ = a1, b = h2 and b′ = a2.
First of all, find the number of seconds it takes until height of Xaniar becomes a′ (starting from a) and call it q. Please note that q ≤ pand if we don't reach a′ after p seconds, then answer is - 1.
If after q seconds also height of Abol will become equal to b′ then answer if q.
Otherwise, find the height of Abdol after q seconds and call it e.
Then find the number of seconds it takes until height of Xaniar becomes a′ (starting from a′) and call it c. Please note that c ≤ p and if we don't reach a′ after p seconds, then answer is - 1.
if g(x) = Xx + Y, then find f(x) = g(g(...(g(x)))) (c times). It is really easy:
c = 1, d = 0
for i = 1 to c
c = (cX) % p
d = (dX + Y) % pThen,
f(x)
return (cx + d) % p
Actually, if height of Abol is x then, after c seconds it will be f(x).
Then, starting from e, find the minimum number of steps of performing e = f(e) it takes to reach b′ and call it o. Please note thato ≤ p and if we don't reach b′ after p seconds, then answer is - 1.
Then answer is x + c × o.
Time Complexity: 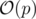
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<algorithm>
typedef long long ll ;
ll mod ;
ll a , a1 ;
ll x , y ;
ll b , b1 ;
ll _x , _y ;
ll A , T ;
ll B , _T ; ll exgcd (ll a,ll b,ll& x,ll &y)
{
if(b==){
x=;
y=;
return a;
}
ll d = exgcd ( b , a % b , x , y ) ;
ll tmp = x ;
x = y ;
y = tmp - a / b * y ;
return d;
}
//用扩展欧几里得算法解线性方程ax+by=c;
void __exgcd(ll a , ll b , ll c )
{
ll x , y ;
ll d = exgcd ( a , b , x , y ) ;
if(c % d) {
puts ("-1") ;
return ;
} ll k = c / d ;
x *= k ; y *= k ;//求的只是其中一个解
if (d < ) d = -d ;
ll t1 = T / d , t2 = _T / d ;
// printf ("t1 = %I64d , t2 = %I64d\n" , t1 , t2 ) ;
//printf ("x = %I64d , y = %I64d\n" , x , y ) ;
if (x < || y < ) {
while (x < || y < ) {
x += t1 ;
y += t2 ;
}
}
else {
while (x >= && y >= ) {
x -= t1 ;
y -= t2 ;
}
x += t1 ;
y += t2 ;
}
//printf ("x = %I64d , y = %I64d\n" , x , y ) ;
printf ("%I64d\n" , A + T * y) ;
} bool workA ()
{
ll cnt = ;
ll c = a ;
while () {
cnt ++ ;
c = (c * x + y) % mod ;
if (c == a1) {
A = cnt ;
return true ;
}
if (cnt > mod) break ;
}
return false ;
} bool workB ()
{
ll cnt = ;
ll c = b ;
while () {
cnt ++ ;
c = (c * _x + _y) % mod ;
if (c == b1) {
B = cnt ;
return true ;
}
if (cnt > mod) break ;
}
return false ;
} bool workT ()
{
T = ;
ll cnt = ;
ll c = a1 ;
while () {
cnt ++ ;
c = (c * x + y) % mod ;
if (c == a1) {
T = cnt ;
return true ;
}
if (cnt > mod) break ;
}
return false ;
} bool work_T ()
{
_T = ;
ll cnt = ;
ll c = b1 ;
while () {
cnt ++ ;
c = (c * _x + _y) % mod ;
if (c == b1) {
_T = cnt ;
return true ;
}
if (cnt > mod) break ;
}
return false ;
} int main ()
{
//freopen ("a.txt" , "r" , stdin ) ;
while (~ scanf ("%I64d" , &mod)) {
scanf ("%I64d%I64d%I64d%I64d" , &a , &a1 , &x , &y) ;
scanf ("%I64d%I64d%I64d%I64d" , &b , &b1 , &_x , &_y) ;
if (!workA ()) puts ("-1") ;
else {
if (!workB ()) puts ("-1") ;
else if (A == B) printf ("%I64d\n" , A) ;
else {
workT () ;
work_T () ;
if (T == || _T == ) {
if (T == && _T == ) puts ("-1") ;
else if (T == ) {
if (A - B >= && (A - B) % _T == ) printf ("%I64d\n" , A) ;
else puts ("-1") ;
}
else if (_T == ) {
if (B - A >= && (B - A) % T == ) printf ("%I64d\n" , B) ;
else puts ("-1") ;
}
} else {
ll a = _T , b = -T , c = A - B ;
__exgcd (a , b , c) ;
}
}
}
}
return ;
}
题解:
一般情况:我们能用暴力求出a-->a1所需时间A , b-->b1所需时间B,a1-->a1时间Ta , b1-->b1时间Tb;
注意:A , B , Ta , Tb 都会在 “mod 时间”内完成,若没在这段时间内找到,则不存在。
所以为了达到目标显然需要满足一下等式:A + x * Ta = B + y * Tb ---- ①---> A - B = - Ta * x + Tb * y ----②;
那么问题就转变成了求该方程是否有整数解(这道题有整数解,就必有正整数解)。
根据扩展欧几里得算法:
c = a * x + b * y ;
只要满足gcd (a , b) | c (及a,b的gcd为c的约数)时,该方程必有解,我们令 d = gcd (a , b) ;
则存在解时:(下面的_x , _y都假定为执行完 exgcd(a , b , x , y)后产生的 _x , _y)
其中一组特解:x' = _x * c / d ;(c = A - B)
y' = _y * c / d ;
递推式:
x = x' + Ta / fabs (d) * k ;( k 为 参数)
y = y' + Tb / fabs (d) * k ;
然后我们只要暴力求出可行解(x , y)中与0最接近的即可 , A + x * Ta 及为答案。
暴力枚举:(简洁,大神的)
#include <cstring>
#include <map>
#include <deque>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <sstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
#include <math.h>
#include <ctime>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <set>
#include <list>
#include <climits>
#include <cctype>
#include <bitset>
#include <iostream>
#include <complex> using namespace std; typedef stringstream ss;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<ll, ll> ii;
typedef vector<vector<ii> > vii;
typedef vector<string> vs;
typedef vector<ll> vi;
typedef vector<double> vd;
typedef long double ld;
typedef vector<vector<ll> > matrix;
typedef complex<double> point; #define all(v) v.begin(), v.end()
#define rall(v) v.rbegin(), v.rend()
#define sz(v) ((ll)v.size())
#define clr(v, d) memset(v, d, sizeof(v))
#define polar(r,t) ((r)*exp(point(0,(t))))
#define length(a) hypot((a).real(),(a).imag())
#define angle(a) atan2((a).imag() , (a).real())
#define vec(a,b) ((b)-(a))
#define dot(a,b) ((conj(a)*(b)).real())
#define cross(a,b) ((conj(a)*(b)).imag())
#define lengthSqr(a) dot(a,a)
#define rotate(v,t) ((v)*exp(point(0,t)))
#define rotateAbout(v,t,a) (rotate(vec(a,v),t)+(a))
#define reflect(v,m) (conj((v)/(m))*m)
#define dist(a,b) (sqrt(pow((a).real()-(b).real(),2.0)+pow((a).imag()-(b).imag(),2.0)))
#define normalize(a) ((a)/length(a)) int dx[] = { , -, , };
int dy[] = { , , , - };
double PI = 3.1415926535897932384626433832795; const ll oo = (ll) 1e9 + ;
const double eps = 1e-;
const ll mod = ; int main() {
//freopen("a.txt", "r", stdin);
ios_base::sync_with_stdio();
ll m, h1, a1, x1, y1, h2, a2, x2, y2;
cin >> m >> h1 >> a1 >> x1 >> y1 >> h2 >> a2 >> x2 >> y2;
ll idx1 = -, idx2 = -;
for (int i = ; i <= m; i++) {
h1 = (x1 * h1 + y1) % m;
if (h1 == a1) {
idx1 = i;
break;
}
}
for (int i = ; i <= m; i++) {
h2 = (x2 * h2 + y2) % m;
if (h2 == a2) {
idx2 = i;
break;
}
} if (idx1 == - || idx2 == -) {
cout << "-1" << endl;
return ;
} ll step1, step2;
for (int i = ; i <= m; i++) {
h1 = (x1 * h1 + y1) % m;
if (h1 == a1) {
step1 = i;
break;
}
}
for (int i = ; i <= m; i++) {
h2 = (x2 * h2 + y2) % m;
if (h2 == a2) {
step2 = i;
break;
}
}
//printf ("idx1 = %I64d , idx2 = %I64d , step1 = %I64d, step2 = %I64d\n" , idx1 , idx2 , step1 , step2 ) ;
for (int i = ; i <= * m; i++) {
if (idx1 == idx2) {
cout << idx1 << endl;
return ;
}
if (idx1 > idx2) {
idx2 += step2;
} else {
idx1 += step1;
}
}
cout << "-1" << endl;
return ;
}
CF #305 (Div. 2) C. Mike and Frog(扩展欧几里得&&当然暴力is also no problem)的更多相关文章
- 数论/暴力 Codeforces Round #305 (Div. 2) C. Mike and Frog
题目传送门 /* 数论/暴力:找出第一次到a1,a2的次数,再找到完整周期p1,p2,然后以2*m为范围 t1,t2为各自起点开始“赛跑”,谁落后谁加一个周期,等到t1 == t2结束 详细解释:ht ...
- Codeforces Round #305 (Div. 1) A. Mike and Frog 暴力
A. Mike and Frog Time Limit: 20 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB 题目连接 http://codeforces.com/contest/547/pr ...
- CF #305(Div.2) D. Mike and Feet(数学推导)
D. Mike and Feet time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard inp ...
- set+线段树 Codeforces Round #305 (Div. 2) D. Mike and Feet
题目传送门 /* 题意:对于长度为x的子序列,每个序列存放为最小值,输出长度为x的子序列的最大值 set+线段树:线段树每个结点存放长度为rt的最大值,更新:先升序排序,逐个添加到set中 查找左右相 ...
- 暴力 Codeforces Round #305 (Div. 2) B. Mike and Fun
题目传送门 /* 暴力:每次更新该行的num[],然后暴力找出最优解就可以了:) */ #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #includ ...
- 字符串处理 Codeforces Round #305 (Div. 2) A. Mike and Fax
题目传送门 /* 字符串处理:回文串是串联的,一个一个判断 */ #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <iostr ...
- Codeforces Round #305 (Div. 2) B. Mike and Fun 暴力
B. Mike and Fun Time Limit: 20 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB 题目连接 http://codeforces.com/contest/548/pro ...
- Codeforces Round #305 (Div. 2) A. Mike and Fax 暴力回文串
A. Mike and Fax Time Limit: 20 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB 题目连接 http://codeforces.com/contest/548/pro ...
- Codeforces Round #305 (Div. 2) D. Mike and Feet 单调栈
D. Mike and Feet time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard inp ...
随机推荐
- OC冒泡排序
NSMutableArray *p = [[NSMutableArray alloc] initWithObjects:@"3",@"5",@"4&q ...
- hdu 2037 - 今年暑假不AC(区间调度问题)
题意:区间调度问题 解法:应用贪心算法,贪心的规则: 在可选的节目中,选取结束时间早的节目. 1: #include<stdlib.h> 2: #include<string.h&g ...
- CSS3的transition动画功能
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head> <meta charset="UTF-8" ...
- windows系统下安装MySQL
可以运行在本地windows版本的MySQL数据库程 序自从3.21版以后已经可以从MySQL AB公司获得,而且 MYSQL每日的下载百分比非常大.这部分描述在windows上安装MySQL的过程. ...
- CentOS7 Mini安装Oracle后用PL/SQL连接数据库(图形化安装)
1.本来是安装完数据库后,本地可以访问了,而Win10下Oracle客户端配置Oracle Net Manager时报连接超时 解决方法: 这种连接超时,让我想到telnet连接问题,就用telnet ...
- IP-Address TextBox
http://www.codeproject.com/Articles/4693/IP-Address-TextBox 可以下载试用效果.个人感觉功能很强大,但输入时让人不太舒服.可以参考. ntro ...
- shiro 更改登录的用户名
ShiroUser user = (ShiroUser) SecurityUtils.getSubject().getPrincipal(); user.name = newName;
- Java国际化程序
根据不同的国家配置不同的资源文件(资源文件有时也称为属性文件,后缀为.properties),所有的资源文件以键值对的形式出现. Locale类 ResourceBundle类 //========= ...
- Java 组播
MulticastSocketServer.java package cn.edu.buaa.multicast; import java.io.IOException; import java.ne ...
- Visual Studio的调试技巧
Visual Studio的调试技巧 [原文地址] Debugging Tips with Visual Studio 2010 [原文发表日期] 2010/8/19 10:48 AM 这是我写的关于 ...
