QuantLib 金融计算——收益率曲线之构建曲线(4)
如果未做特别说明,文中的程序都是 C++11 代码。
QuantLib 金融计算——收益率曲线之构建曲线(4)
本文代码对应的 QuantLib 版本是 1.15。相关源代码可以在 QuantLibEx 找到。
概述
QuantLib 中提供了用三次 B 样条函数拟合期限结构的功能,但是,并未提供使用三次样条函数拟合期限结构的功能。本文展示了如何在 QuantLib 的框架内实现三次样条函数,并拟合期限结构。
示例所用的样本券交易数据来自专门进行期限结构分析的 R 包——termstrc。具体来说是数据集 govbonds 中的 GERMANY 部分,包含 2008-01-30 这一天德国市场上 52 只固息债的成交数据。
注意:为了适配 QuantLib,实际计算中删除了两只债券的数据,以保证所有样本券的到期时间均不相同。样本券数据在《收益率曲线之构建曲线(3)》的附录中列出。
三次样条函数与期限结构
用三次样条函数拟合期限结构,实质上是用若干三次样条函数的组合近似贴现因子曲线的形状,
\]
贴现因子 \(d(t,\beta)\) 表示为三次样条函数的线性组合,\(\beta_l\) 是最优化计算需要估计出的参数。
三次样条函数 \(c_l(t)\) 的形式基于文献 (Ferstl and Hayden, 2010),
& \text{ if } l=n, c_l(t)=t\\
& \text{ else }, c_{l}\left(t\right)=
\left\{\begin{array}{ll}
0 & {t<k_{l-1}} \\
{\frac{\left(t-k_{l-1}\right)^{3}}{6\left(k_{l}-k_{l-1}\right)}} & {k_{l-1} \leq t<k_{l}} \\
{\frac{\left(k_{l}-k_{l-1}\right)^{2}}{6}+\frac{\left(k_{l}-k_{l-1}\right)\left(t-k_{l}\right)}{2}+\frac{(t-k_l)^2}{2} -\frac{\left(t-k_{l}\right)^{3}}{6\left(k_{l+1}-k_{l}\right)}} & {k_{l} \leq t<k_{l+1}} \\
{\left(k_{l+1}-k_{l-1}\right)\left[\frac{2 k_{l+1}-k_{l}-k_{l-1}}{6}+\frac{t-k_{l+1}}{2}\right]} & {k_{l+1} \leq t}
\end{array}\right.
\end{cases}
\]
对于有 \(n\) 个参数的贴现因子曲线,用户需要提供 \(n-1\) 个 knots \(k_i(1\le i\lt n)\),并令 \(k_0 = 0\) 以及 \(k_n = k_{n-1}\)。
knots 的选择
knots 的选择基于文献 (McCulloch, 1975),也可以参考文献 (Ferstl and Hayden, 2010),
& \text{ if } l=1, k_l = 0\\
& \text{ else if } l=n-1,k_l=m_N \\
& \text{ else }, k_l = m_h + \theta(m_{h+1} - m_h)
\end{cases}
\]
其中,\(h=\left\lceil\frac{(l-1) k}{n-2}\right\rceil\),\(\theta=\frac{(l-1) k}{n-2}-h\),\(n = \left\lfloor\sqrt{k}+0.5 \right\rfloor\),\(m_i(1 \le i\le N)\) 是升序排列后样本券的剩余期限。
实现三次样条函数
三次样条函数类 CubicSpline 的实现仿照已存在的 BSpline 类,
CubicSpline.hpp
class CubicSpline {
public:
CubicSpline(const std::vector<Real>& knots);
~CubicSpline();
Real operator()(Natural i, Real x) const;
private:
Size n_;
std::vector<Real> knots_ex_;
};
CubicSpline.cpp
CubicSpline::CubicSpline(const std::vector<Real>& knots)
: n_(knots.size() + 1), knots_ex_(knots) {
knots_ex_.insert(knots_ex_.begin(), 0.0);
knots_ex_.insert(knots_ex_.end(), knots.back());
}
CubicSpline::~CubicSpline() {
}
Real CubicSpline::operator()(Natural i, Real x) const {
using namespace std;
if (i < n_) {
Real q = knots_ex_[i], q_minus = knots_ex_[i - 1], q_plus = knots_ex_[i + 1];
if (x < q_minus) {
return 0.0;
} else if (q_minus <= x and x < q) {
return pow(x - q_minus, 3) / (6.0 * (q - q_minus));
} else if (q <= x and x < q_plus) {
return pow(q - q_minus, 2) / 6.0
+ (q - q_minus) * (x - q) / 2.0
+ pow(x - q, 2) / 2.0
- pow(x - q, 3) / (6.0 * (q_plus - q));
} else {
return (q_plus - q_minus)
* ((2.0 * q_plus - q - q_minus) / 6.0
+ (x - q_plus) / 2.0);
}
} else {
return x;
}
}
实现拟合方法
拟合方法 CubicSplinesFitting 的实现仿照已存在的 CubicBSplinesFitting 类,两者均是 FittedBondDiscountCurve::FittingMethod 的派生类,
CubicSplinesFitting.hpp
class CubicSplinesFitting
: public FittedBondDiscountCurve::FittingMethod {
public:
CubicSplinesFitting(const std::vector<Time>& knotVector,
const Array& weights = Array(),
ext::shared_ptr<OptimizationMethod>
optimizationMethod = ext::shared_ptr<OptimizationMethod>(),
const Array& l2 = Array());
CubicSplinesFitting(const std::vector<Time>& knotVector,
const Array& weights,
const Array& l2);
//! cubic spline basis functions
Real basisFunction(Integer i, Time t) const;
static std::vector<Time> autoKnots(const std::vector<Time>& maturities);
#if defined(QL_USE_STD_UNIQUE_PTR)
std::unique_ptr<FittedBondDiscountCurve::FittingMethod> clone() const;
#else
std::auto_ptr<FittedBondDiscountCurve::FittingMethod> clone() const;
#endif
private:
Size size() const;
DiscountFactor discountFunction(const Array& x, Time t) const;
CubicSpline splines_;
Size size_;
//! N_th basis function coefficient to solve for when d(0)=1
Natural N_;
};
CubicSplinesFitting.cpp
CubicSplinesFitting::CubicSplinesFitting(const std::vector<Time>& knots,
const Array& weights,
ext::shared_ptr<OptimizationMethod> optimizationMethod,
const Array& l2)
: FittedBondDiscountCurve::FittingMethod(
false, weights, optimizationMethod, l2),
splines_(knots) {
Size basisFunctions = knots.size() + 1;
size_ = basisFunctions;
N_ = 0;
}
CubicSplinesFitting::CubicSplinesFitting(const std::vector<Time>& knots,
const Array& weights,
const Array& l2)
: FittedBondDiscountCurve::FittingMethod(
false, weights, ext::shared_ptr<OptimizationMethod>(), l2),
splines_(knots) {
Size basisFunctions = knots.size() + 1;
size_ = basisFunctions;
N_ = 0;
}
Real CubicSplinesFitting::basisFunction(Integer i,
Time t) const {
return splines_(i, t);
}
QL_UNIQUE_OR_AUTO_PTR<FittedBondDiscountCurve::FittingMethod> CubicSplinesFitting::clone() const {
return QL_UNIQUE_OR_AUTO_PTR<FittedBondDiscountCurve::FittingMethod>(
new CubicSplinesFitting(*this));
}
Size CubicSplinesFitting::size() const {
return size_;
}
DiscountFactor CubicSplinesFitting::discountFunction(const Array& x,
Time t) const {
DiscountFactor d = 1.0;
for (Size i = 0; i < size_; ++i) {
d += x[i] * splines_(i + 1, t);
}
return d;
}
std::vector<Time> CubicSplinesFitting::autoKnots(const std::vector<Time>& maturities) {
using namespace std;
vector<Time> m(maturities);
sort(m.begin(), m.end());
Size k = m.size();
Size n(floor(sqrt(k) + 0.5));
vector<Time> knots(n - 1);
knots[0] = 0.0;
knots[n - 1] = m.back();
for (Size l = 1; l < n - 1; ++l) {
Size h(ceil(Real(l * k) / Real(n - 2)));
Real theta = Real(l * k) / Real(n - 2) - h;
knots[l] = m[h - 1] + theta * (m[h] - m[h - 1]);
}
return knots;
}
测试
用上述两个类拟合样本券的期限结构,并和 termstrc 的结果做比较。
辅助函数 CubicSplineSpotRate 用于将样条函数表示的贴现因子转换成即期利率。
QuantLib::Real CubicSplineSpotRate(const std::vector<QuantLib::Real>& knots,
const QuantLib::Array& weights,
const QuantLib::Time& t) {
using namespace std;
using namespace QuantLib;
CubicSpline spline(knots);
Size s = weights.size();
Real d = 1.0, r;
for (Size i = 0; i < s; ++i) {
d += weights[i] * spline(i + 1, t);
}
r = -std::log(d) / t;
return r;
}
测试函数
void TestCubicSplineFitting() {
using namespace std;
using namespace QuantLib;
// 样本券数据,以及相关配置
Size bondNum = 50;
vector<Real> cleanPrice = {
100.002, 99.92, 99.805, 99.75, 100.305, 99.76, 99.75, 99.975, 100.0416, 100.0574,
99.5049, 101.0971, 101.137, 100.7199, 99.8883, 100.908, 103.3553, 99.5034, 103.913, 97.4229,
104.5636, 99.7527, 104.3708, 99.6051, 104.8603, 101.3415, 105.29, 102.4969, 103.7602, 100.2803,
102.6046, 102.5291, 99.4748, 95.9702, 97.1815, 114.2849, 100.2847, 112.23, 98.397, 102.0235,
99.8483, 121.2711, 125.9157, 114.5791, 103.2202, 123.4668, 113.4694, 103.1873, 91.5603, 95.4441};
vector<Handle<Quote>> priceHandle(bondNum);
for (Size i = 0; i < bondNum; ++i) {
ext::shared_ptr<Quote> q(
new SimpleQuote(cleanPrice[i]));
Handle<Quote> hq(q);
priceHandle[i] = hq;
}
vector<Year> issueYear = {
2002, 2006, 2003, 2006, 1998, 2006, 2003, 2006, 1999, 2007,
2004, 2007, 1999, 2007, 2004, 2007, 1999, 2005, 2000, 2005,
2000, 2006, 2001, 2006, 2001, 2007, 2002, 2007, 2002, 2003,
2003, 2004, 2004, 2005, 2005, 1986, 2006, 1986, 2006, 2007,
2007, 1993, 1997, 1998, 1998, 2000, 2000, 2003, 2004, 2006};
vector<Month> issueMonth = {
Aug, Mar, Apr, May, Jul, Aug, Sep, Nov, Jan, Feb,
Feb, May, Jul, Aug, Aug, Sep, Oct, Feb, May, Aug,
Sep, Feb, May, Aug, Dec, Feb, Jun, Aug, Dec, Jun,
Oct, Apr, Oct, Apr, Oct, Jun, Apr, Sep, Oct, Apr,
Sep, Dec, Jul, Jan, Oct, Jan, Oct, Jan, Dec, Dec};
vector<Day> issueDay = {
14, 8, 11, 30, 4, 30, 25, 30, 4, 28, 2, 30, 4, 24, 25, 21, 22,
24, 5, 26, 29, 26, 23, 30, 28, 28, 26, 24, 31, 24, 21, 25, 27, 28,
30, 20, 26, 20, 31, 27, 21, 29, 3, 4, 7, 4, 27, 22, 24, 28};
vector<Year> maturityYear = {
2008, 2008, 2008, 2008, 2008, 2008, 2008, 2008, 2009, 2009,
2009, 2009, 2009, 2009, 2009, 2009, 2010, 2010, 2010, 2010,
2011, 2011, 2011, 2011, 2012, 2012, 2012, 2012, 2013, 2013,
2014, 2014, 2015, 2015, 2016, 2016, 2016, 2016, 2017, 2017,
2018, 2024, 2027, 2028, 2028, 2030, 2031, 2034, 2037, 2039};
vector<Month> maturityMonth = {
Feb, Mar, Apr, Jun, Jul, Sep, Oct, Dec, Jan, Mar,
Apr, Jun, Jul, Sep, Oct, Dec, Jan, Apr, Jul, Oct,
Jan, Apr, Jul, Oct, Jan, Apr, Jul, Oct, Jan, Jul,
Jan, Jul, Jan, Jul, Jan, Jun, Jul, Sep, Jan, Jul,
Jan, Jan, Jul, Jan, Jul, Jan, Jan, Jul, Jan, Jul};
vector<Day> maturityDay = {
15, 14, 11, 13, 4, 12, 10, 12, 4, 13, 17, 12, 4, 11, 9, 11,
4, 9, 4, 8, 4, 8, 4, 14, 4, 13, 4, 12, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4,
20, 4, 20, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4};
vector<Date> issueDate(bondNum), maturityDate(bondNum);
for (Size i = 0; i < bondNum; ++i) {
Date idate(issueDay[i], issueMonth[i], issueYear[i]);
Date mdate(maturityDay[i], maturityMonth[i], maturityYear[i]);
issueDate[i] = idate;
maturityDate[i] = mdate;
}
vector<Real> couponRate = {
0.0425, 0.03, 0.03, 0.0325, 0.0475, 0.035, 0.035, 0.0375, 0.0375, 0.0375,
0.0325, 0.045, 0.045, 0.04, 0.035, 0.04, 0.05375, 0.0325, 0.0525, 0.025,
0.0525, 0.035, 0.05, 0.035, 0.05, 0.04, 0.05, 0.0425, 0.045, 0.0375, 0.0425,
0.0425, 0.0375, 0.0325, 0.035, 0.06, 0.04, 0.05625, 0.0375, 0.0425, 0.04,
0.0625, 0.065, 0.05625, 0.0475, 0.0625, 0.055, 0.0475, 0.04, 0.0425};
Frequency frequency = Annual;
Actual365Fixed dayCounter(Actual365Fixed::Standard);
BusinessDayConvention paymentConv = Unadjusted;
BusinessDayConvention terminationDateConv = Unadjusted;
BusinessDayConvention convention = Unadjusted;
Real redemption = 100.0;
Real faceAmount = 100.0;
Germany calendar(Germany::Eurex);
Date today = calendar.adjust(Date(30, Jan, 2008));
Settings::instance().evaluationDate() = today;
Natural bondSettlementDays = 0;
Date bondSettlementDate = calendar.advance(
today,
Period(bondSettlementDays, Days));
vector<ext::shared_ptr<BondHelper>> instruments(bondNum);
vector<Time> maturity(bondNum);
// 配置 helper
for (Size i = 0; i < bondNum; ++i) {
vector<Real> bondCoupon = {couponRate[i]};
Schedule schedule(
issueDate[i],
maturityDate[i],
Period(frequency),
calendar,
convention,
terminationDateConv,
DateGeneration::Backward,
false);
ext::shared_ptr<FixedRateBondHelper> helper(
new FixedRateBondHelper(
priceHandle[i],
bondSettlementDays,
faceAmount,
schedule,
bondCoupon,
dayCounter,
paymentConv,
redemption));
maturity[i] = dayCounter.yearFraction(
bondSettlementDate, helper->maturityDate());
instruments[i] = helper;
}
Real tolerance = 1.0e-6;
Natural max = 5000;
ext::shared_ptr<OptimizationMethod> optMethod(
new LevenbergMarquardt());
vector<Real> knots = CubicSplinesFitting::autoKnots(maturity);
vector<Real> termstrcKnotes = {
0.000000, 1.006027, 2.380274, 5.033425, 9.234521, 31.446575};
cout << "QuantLib knots:\t";
for (auto v : knots) {
cout << setprecision(6) << fixed << v << ", ";
}
cout << endl;
cout << "termstrc knots:\t";
for (auto v : termstrcKnotes) {
cout << setprecision(6) << fixed << v << ", ";
}
cout << endl;
cout << endl;
CubicSplinesFitting csf(
knots, Array(), optMethod);
FittedBondDiscountCurve tsCubicSplines(
bondSettlementDate,
instruments, dayCounter,
csf, tolerance, max);
Array weights = tsCubicSplines.fitResults().solution();
Array termstrcWeights(7);
termstrcWeights[0] = 1.9320e-02, termstrcWeights[1] = -8.4936e-05,
termstrcWeights[2] = -3.2009e-04, termstrcWeights[3] = -3.7101e-04,
termstrcWeights[4] = 7.2921e-04, termstrcWeights[5] = 2.0159e-03,
termstrcWeights[6] = -4.1632e-02;
cout << "QuantLib weights: \t" << weights << endl;
cout << "termstrc weights: \t" << termstrcWeights << endl;
cout << endl;
cout << "QuantLib final cost value:\t"
<< tsCubicSplines.fitResults().minimumCostValue() << endl;
cout << endl;
// 比较 QuantLib 和 termstrc 的结果
Real spotRate, termstrcSpot;
for (Size i = 0; i < bondNum; ++i) {
Time t = dayCounter.yearFraction(
bondSettlementDate, maturityDate[i]);
spotRate =
tsCubicSplines.zeroRate(t, Compounding::Continuous, frequency).rate() * 100.0;
termstrcSpot =
CubicSplineSpotRate(termstrcKnotes, termstrcWeights, t) * 100.0;
cout << setprecision(3) << fixed
<< t << ",\t"
<< spotRate << ",\t"
<< termstrcSpot << ",\t"
<< spotRate - termstrcSpot << endl;
}
}
部分结果:
QuantLib knots: 0.000000, 1.117808, 2.690411, 5.430137, 9.432877, 31.446575,
termstrc knots: 0.000000, 1.006027, 2.380274, 5.033425, 9.234521, 31.446575,
QuantLib weights: [ 0.005281; 0.004565; -0.002934; 0.000804; 0.000652; 0.001886; -0.038316 ]
termstrc weights: [ 0.019320; -0.000085; -0.000320; -0.000371; 0.000729; 0.002016; -0.041632 ]
QuantLib final cost value: 0.000338
0.044, 3.823, 4.125, -0.302
0.121, 3.809, 4.061, -0.253
0.197, 3.794, 4.001, -0.207
0.370, 3.761, 3.878, -0.116
...
..
.
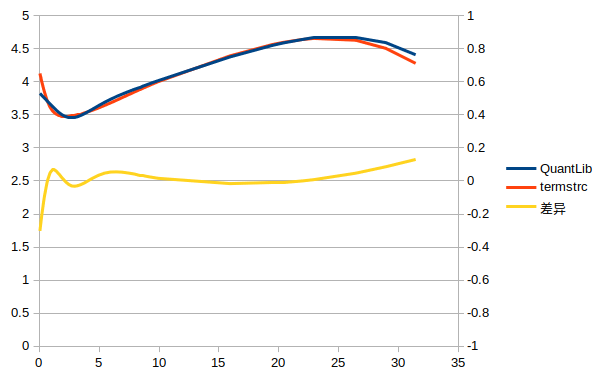
图 1:结果对比
注意:尽管以 termstrc 的结果作为基准,并不意味着基准就是正确答案。
由于样本券的数量不同(termstrc 使用了 52 只券),两者的 knots 差异较大。同时,因为优化方法的不同(termstrc 使用 OLS,QuantLib 使用 Levenberg-Marquardt 算法),估计出的参数也有差异。最终导致两个期限结构在两端差异较大。
不过,考虑到最终的 cost value,QuantLib 的结果可能更好一些。
参考文献
- Ferstl.R, Hayden.J (2010). "Zero-Coupon Yield Curve Estimation with the Package
termstrc." Journal of Statistical Software, Volume 36, Issue 1. - McCulloch JH (1975). "The Tax-Adjusted Yield Curve." The Journal of Finance, 30(3), 811–830.
QuantLib 金融计算——收益率曲线之构建曲线(4)的更多相关文章
- QuantLib 金融计算——收益率曲线之构建曲线(1)
目录 QuantLib 金融计算--收益率曲线之构建曲线(1) YieldTermStructure DiscountCurve DiscountCurve 对象的构造 ZeroCurve ZeroC ...
- QuantLib 金融计算——收益率曲线之构建曲线(2)
目录 QuantLib 金融计算--收益率曲线之构建曲线(2) YieldTermStructure 问题描述 Piecewise** 分段收益率曲线的原理 Piecewise** 对象的构造 Fit ...
- QuantLib 金融计算——收益率曲线之构建曲线(3)
目录 QuantLib 金融计算--收益率曲线之构建曲线(3) 概述 估算期限结构的步骤 读取样本券数据 一些基本配置 配置 *Helper 对象 配置期限结构 估算期限结构 汇总结果 当前实现存在的 ...
- QuantLib 金融计算——收益率曲线之构建曲线(5)
目录 QuantLib 金融计算--收益率曲线之构建曲线(5) 概述 Nelson-Siegel 模型家族的成员 Nelson-Siegel 模型 Svensson 模型 修正 Svensson 模型 ...
- QuantLib 金融计算
我的微信:xuruilong100 <Implementing QuantLib>译后记 QuantLib 金融计算 QuantLib 入门 基本组件之 Date 类 基本组件之 Cale ...
- QuantLib 金融计算——自己动手封装 Python 接口(1)
目录 QuantLib 金融计算--自己动手封装 Python 接口(1) 概述 QuantLib 如何封装 Python 接口? 自己封装 Python 接口 封装 Array 和 Matrix 类 ...
- QuantLib 金融计算——自己动手封装 Python 接口(2)
目录 QuantLib 金融计算--自己动手封装 Python 接口(2) 概述 如何封装一项复杂功能? 寻找最小功能集合的策略 实践 估计期限结构参数 修改官方接口文件 下一步的计划 QuantLi ...
- QuantLib 金融计算——数学工具之插值
目录 QuantLib 金融计算--数学工具之插值 概述 一维插值方法 二维插值方法 如果未做特别说明,文中的程序都是 Python3 代码. QuantLib 金融计算--数学工具之插值 载入模块 ...
- QuantLib 金融计算——高级话题之模拟跳扩散过程
目录 QuantLib 金融计算--高级话题之模拟跳扩散过程 跳扩散过程 模拟算法 面临的问题 "脏"的方法 "干净"的方法 实现 示例 参考文献 如果未做特别 ...
随机推荐
- vertx 异步编程指南 step8-使用RxJava进行反应式编程
vertx 异步编程指南 step8-使用RxJava进行反应式编程 2018-04-23 13:15:32 zyydecsdn 阅读数 1212 收藏 更多 分类专栏: vertx 到目前为止 ...
- webapi 返回类型
参考 大神;https://www.cnblogs.com/landeanfen/p/5501487.html
- disable_function绕过--利用LD_PRELOAD
0x00 前言 有时候直接执行命令的函数被ban了,那么有几种思路可以bypass 1.使用php本身自带的能够调用外部程序的函数 2.使用第三方插件入(如imagick) 但是这两种无非就是利用ph ...
- android studio学习----构建(gradle )依赖时使用动态依赖的问题
今天在看Dan Lew大神的博客发现最新的文章就是 “Don't use dynamic versions for your dependencies” Everyone, please, to st ...
- 安装Python,输入pip命令报错———pip Fatal error in launcher: Unable to create process using
今天把Python的安装位置也从C盘剪切到了D盘, 然后修改了Path环境变量中对应的盘符:D:\Python27\;D:\Python27\Scripts; 不管是在哪个目录,Python可以执行了 ...
- Cloud Alert 实现告警智能降噪,成功规避告警风暴
# 前言 睿象云前段时间发表了一篇[< Zabbix 实现电话.邮件.微信告警通知的实践分享>](https://www.toutiao.com/i6734876723126469127/ ...
- 旅游景点信息API接口大全
1.分享数据:“http://www.shareapi.cn/docs/api/id/127”,免费,次数1000次 返回JSON示例 { "SceneryID":10224,/* ...
- Linux进程管理之top
关于Linux进程查看,前面讲解了ps命令,下面拉介绍另一个命令top ps:静态查看 top:动态查看 动态查看进程的状态 # top [root@wei ~]# top top - 18:38:4 ...
- Linux命令——lsmod
参考:8 LSMOD, RMMOD, MODPROBE, AND MODINFO COMMAND EXAMPLES IN LINUX Linux lsmod command 简介 lsmod显示(或“ ...
- nbu虚拟机恢复样例(之后补图)
9.2.1进入Backup,Archive,and Restore管理器 9.2.2选择客户端和策略类型 9.2.3选择恢复的虚拟机 9.2.4恢复虚拟机到不同目录 9.2.5更改虚拟机名称和存储 因 ...
