“一切都是消息”--MSF(消息服务框架)之【请求-响应】模式
MSF的名字是 Message Service Framework 的简称,由于目前框架主要功能在于处理即时(immediately)消息,所以iMSF就是 immediately Message Service Framework,中文名称:即时消息服务框架,它是PDF.NET框架的一部分。
在后续的文章中,iMSF跟MSF是一个意思,或者你也可以给它取一个好听的中文名称:爱美XX :)
在前一篇, “一切都是消息”--MSF(消息服务框架)入门简介, 我们介绍了MSF基于异步通信,支持请求-响应通信模式和发布-订阅通信模式,并且介绍了如何获取MSF。今天,我们来看看如何使用MSF来做一个请求-响应通信模式的例子。
MSF封装了WCF,所以使用MSF不能像使用WCF那样直接在客户端添加服务引用,你需要手工编写客户端代理类,这样有一个好处就是代理类写的更简单,使用更灵活。我们可以看看网友写的这篇文章《不引用服务而使用WCF,手动编写客户端代理类》,看看直接使用WCF是如何手动编写客户端代理类的。我对作者文中有一句话很认同:
--我们应当把WCF理解为一种通信技术,而不只是服务。
这正是MSF的设计理念!
回到MSF,我们来看看实现请求-响应通信模式的步骤。
一,编写iMSF服务类
在上一篇文中搭建好的MSF解决方案中,我们创建了一个名字为 TestService的项目,首先,添加Nuget 的MSF服务端引用,
Install-Package PDF.Net.MSF.Service
现在添加一个类 Service1,让它继承MSF的IService 接口。具体代码如下:
using PWMIS.EnterpriseFramework.Service.Runtime;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text; namespace TestService
{
public class Service1:IService
{
public void CompleteRequest(IServiceContext context)
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
} public bool IsUnSubscribe
{
get { throw new NotImplementedException(); }
} public bool ProcessRequest(IServiceContext context)
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
}
}
然后,将上面方法中的异常信息注释掉,并且添加一个 SayHello 方法,具体修改如下:
public class Service1:IService
{
public string SayHello(string who)
{
return string.Format("Hello {0} ,I am MSF Server.", who);
} public void CompleteRequest(IServiceContext context)
{
//throw new NotImplementedException();
} public bool IsUnSubscribe
{
//get { throw new NotImplementedException(); }
get
{
//返回True ,表示当前服务不执行系统后续的服务方法的订阅处理过程,而是由用户自己输出结果数据
return false;
}
} public bool ProcessRequest(IServiceContext context)
{
//throw new NotImplementedException();
return true;
}
}
可以看到,实现MSF服务类,不需要先定义一个WCF服务契约接口,也没用其它WCF的代码影子,不过有点类似 ASP.NET 的HTTP处理过程:
- 首先,每个MSF服务类都会执行 ProcessRequest 方法,它有一个IServiceContext 对象,通过它可以知道请求相关的上下文信息;
- 然后,会有一个 IsUnSubscribe 属性,表示本次请求是否是一个自定义的服务订阅而不再继续执行系统的服务订阅,虽然本次的示例是演示“请求-响应”的通信模式的,但是MSF本质上对此种通信模式还是通过“发布-订阅”通信模式实现的,也就是说,MSF的消息通信,始终是面向长连接的;
- 如果IsUnSubscribe 属性返回为False,紧接着,MSF会调用您真正的服务方法,比如这里的 SayHello 方法;
- 最后,你可以在 CompleteRequest 中执行一些本次服务处理的收尾工作。
二,编写iMSF客户端
我们在上一篇文中说的TestClient 项目中,来编写今天的MSF客户端代码,在原有代码基础上,做适当的修改。
MSF客户端调用可以分为多种方式:
2.1,使用服务请求的URI模式:
本质上,MSF的客户端请求服务端的时候,是将请求的服务信息转换成MSF固有的URI地址参数信息的,类似RESTfull WebAPI 的URI一样,本次请求的URI地址如下:
Service://Service1/SayHello/System.String=bluedoctor1
它表示我们请求的服务类名称是 Service1,请求的服务方法名称是 SayHello,有一个String类型的参数并且给它赋值为 bluedoctor 。
MSF请求服务的时候,服务方法的参数是不用区分参数名的,只跟参数的顺序,参数的类型和参数的数量有关系,这根我们使用委托方法调用一个实际的方法一样的方式。
相关调用代码如下:
client.RequestService<string>("Service://Service1/SayHello/System.String=bluedoctor1",
PWMIS.EnterpriseFramework.Common.DataType.Text,
s =>
{
Console.WriteLine("1,Server Response:【{0}】", s);
});
如果调用服务成功,将输出结果:
1,Server Response:【Hello bluedoctor1 ,I am is MSF Server.】
2.2,使用ServiceRequest 对象来封装服务请求信息
前面通过服务请求的URI模式虽然比较直观简洁,但使用对象来封装请求信息可能更可靠,对前面例子改写成 ServiceRequest 对象的代码如下:
ServiceRequest request = new ServiceRequest();
request.ServiceName = "Service1";
request.MethodName = "SayHello";
request.Parameters = new object[] { "bluedoctor23" };
client.RequestService<string>(request,
PWMIS.EnterpriseFramework.Common.DataType.Text,
s =>
{
Console.WriteLine("2,Server Response:【{0}】", s);
});
2.3,使用异步调用方法
前面两个调用示例,其实都是传入一个委托方法给RequestService 方法,然后服务端回调此委托方法的,而此委托方法的回调时机是不确定的,相对于调用线程它是异步执行的,所以我们称呼前面2种调用方式为“异步委托方法”。这种方式的一大缺点就是我们的代码中会有大量的难以阅读和调试的异步回调代码。.NET 4.0之后提供了Task对象它可以简化这种调用过程,使得代码写起来就跟同步调用代码一样。这种异步调用方式,MSF也提供了支持,使用服务请求的Async后缀的方法即可:
string serverMsg= client.RequestServiceAsync<string>(request).Result;
Console.WriteLine("3,Server Response:【{0}】", serverMsg);
调用 RequestServiceAsync 方法返回结果的 Result方法,能够同步阻塞调用结果,使得后续代码按照我们预期的顺序执行。
三、注册iMSF服务类
运行上面编写的服务端和客户端,调用并不成功,在服务端出现了下面的异常:
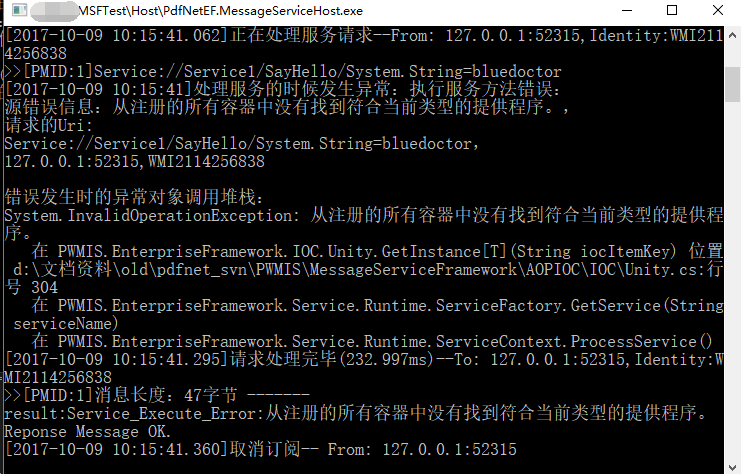
上面截图中显示的错误信息是 :“从注册的所有容器中没有找到符合当前类型的提供程序。”
这个错误信息会返回到客户端:
处理服务时错误:从注册的所有容器中没有找到符 合当前类型的提供程序。
这个错误提示我们没有注册我们的MSF服务类,因为MSF会通过IOC容器去寻找我们调用的服务类,所以需要注册下。
MSF采用了一个简单的IOC工具,它支持通过XML配置文件类注册我们自定义的MSF服务类。
在解决方案中,看到引用了MSF Host的主项目 MSFTest,nuget添加MSF Host的时候,已经添加了一个IOC配置文件:IOCConfig.xml
这个文件的使用,在MSF Host的配置文件 PdfNetEF.MessageServiceHost.exe.config 中做了配置:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<configuration>
<appSettings>
<add key="IOCConfigFile" value=".\IOCConfig.xml" />
<add key="ServerIP" value="127.0.0.1" />
<add key="ServerPort" value="8888" />
</appSettings>
... 其它配置内容略
IOCConfig.xml 文件已经配置了MSF必要的内容和一些示例的测试配置,具体内容为:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<IOCConfig>
<!--
IOC 依赖注入容器配置
ver 1.0 注:PDF.NET MSF Servic Host 使用
PWMIS 消息服务框架,2011.12.7 创建
-->
<GroupConfig>
<Group ID="1" ParentID="0" Name="ServiceRuntime" >分布式服务运行时</Group>
<Group ID="2" ParentID="0" Name="ServiceModel" >服务模型</Group>
<Group ID="3" ParentID="0" Name="TestService" >示例服务</Group>
</GroupConfig>
<SystemInterface>
<Add Name="IService" Interface="PWMIS.EnterpriseFramework.Service.IService" Assembly="PWMIS.EnterpriseFramework.Service.Runtime"/>
</SystemInterface>
<GroupSet>
<IOC Name="ServiceRuntime">
<Add Key="CacheServer" InterfaceName="IService" FullClassName="PWMIS.EnterpriseFramework.Service.Runtime.CacheService" Assembly="PWMIS.EnterpriseFramework.Service.Runtime" />
<Add Key="RegService" InterfaceName="IService" FullClassName="PWMIS.EnterpriseFramework.Service.Group.RegService" Assembly="PWMIS.EnterpriseFramework.Service.Group" />
<Add Key="ManageService" InterfaceName="IService" FullClassName="TranstarAuction.Service.Runtime.ManageService" Assembly="TranstarAuctionServiceRuntime" />
</IOC>
<IOC Name="TestService">
<Add Key="Calculator" InterfaceName="IService" FullClassName="ServiceSample.TestCalculatorService" Assembly="ServiceSample" />
<Add Key="TestTimeService" InterfaceName="IService" FullClassName="ServiceSample.TestTimeService" Assembly="ServiceSample" />
<Add Key="AlarmClockService" InterfaceName="IService" FullClassName="ServiceSample.AlarmClockService" Assembly="ServiceSample" />
<Add Key="Service1" InterfaceName="IService" FullClassName="TestService.Service1" Assembly="TestService" />
</IOC>
<IOC Name="ServiceModel">
<Add Key="TimeCount" InterfaceName="" FullClassName="Model.TimeCount" Assembly="Model" />
<!-- 下面4个是消息服务框架必须的ServiceModel -->
<Add Key="ServiceIdentity" InterfaceName="" FullClassName="PWMIS.EnterpriseFramework.Service.Runtime.Principal.ServiceIdentity" Assembly="PWMIS.EnterpriseFramework.Service.Runtime" />
<Add Key="CacheItemPolicy" InterfaceName="" FullClassName="System.Runtime.Caching.CacheItemPolicy" Assembly="System.Runtime.Caching, Version=4.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=b03f5f7f11d50a3a" />
<Add Key="ServiceRegModel" InterfaceName="" FullClassName="PWMIS.EnterpriseFramework.Service.Client.Model.ServiceRegModel" Assembly="PWMIS.EnterpriseFramework.Service.Client" />
<Add Key="ServiceHostInfo" InterfaceName="" FullClassName="PWMIS.EnterpriseFramework.Service.Client.Model.ServiceHostInfo" Assembly="PWMIS.EnterpriseFramework.Service.Client" />
</IOC>
</GroupSet>
</IOCConfig>
其中,Key=“Service1” 配置节,便是我们今天需要配置的Service1 服务类的内容。
四、返回复杂类型的服务方法
4.1,编写iMSF服务类
在前面的示中,服务类 Service1 的服务方法 SayHello 返回的是String 类型这样的简单类型,很多时候,我们需要服务方法返回结构复杂的自定义业务类型。在本次示例中,我们定义一个邮件消息类,我们新建一个C# 类库项目 TestDto,然后如下定义它:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace TestDto
{
public class MailMessage
{
public string Sender { get; set; }
public string Reply { get; set; }
public string Message { get; set; } public DateTime RevoveryTime { get; set; }
}
}
然后,回到TestService项目的Service1服务类,增加一个GetMailMessage 方法:
public MailMessage GetMailMessage(string who)
{
MailMessage mail = new MailMessage();
mail.Reply = who;
mail.Sender = "MSF Server";
mail.Message = string.Format("Hello {0} ,I am MSF Server.", who);
mail.RevoveryTime = DateTime.Now;
return mail;
}
4.2,编写iMSF客户端代码
最后,我们在TestClient中添加调用此服务的客户端代码:
client.RequestService<MailMessage>("Service://Service1/GetMailMessage/System.String=bluedoctor4",
PWMIS.EnterpriseFramework.Common.DataType.Json,
mail =>
{
Console.WriteLine("4,Server Response:【{0}】,\r\n Revovery Time:{1}", mail.Message,mail.RevoveryTime);
});
调用结果将输出:
4,Server Response:【Hello bluedoctor4 ,I am is MSF Server.】
同样,我们也可以使用ServiceRequest 对象来调用这个服务:
ServiceRequest request2 = new ServiceRequest();
request2.ServiceName = "Service1";
request2.MethodName = "GetMailMessage";
request2.Parameters = new object[] { "bluedoctor567" }; client.RequestService<MailMessage>(request2,
PWMIS.EnterpriseFramework.Common.DataType.Json,
mail =>
{
Console.WriteLine("5,Server Response:【{0}】,\r\n Revovery Time:{1}", mail.Message, mail.RevoveryTime);
});
4.3,使用客户端自定义结果类型
我们调用服务方法的时候,客户端调用服务方法返回值的对象类型,可以跟服务方法定义的返回类型名字不一样,比如GetMailMessage 方法调用,我们可以在本地定义一个结构相同的不同的类:
namespace TestClient
{
public class MailMessage2
{
public string Sender { get; set; }
public string Reply { get; set; }
public string Message { get; set; } public DateTime RevoveryTime { get; set; }
}
}
然后在客户端调用,使用这个新的在客户端定义的类型作为服务方法调用的返回值:
client.RequestService<MailMessage2>(request2,
PWMIS.EnterpriseFramework.Common.DataType.Json,
mail =>
{
Console.WriteLine("6,Server Response:【{0}】,\r\n Revovery Time:{1}", mail.Message, mail.RevoveryTime);
});
输出结果跟上面是一样的。这是因为服务端和客户端使用的都是JSON序列化,它是不关心类型的名字的只关心内部数据结构是否一致。
五、小结
上面的过程演示了MSF编写服务端和客户端代码的简单过程,对MSF而言,服务是本质上都是异步调用和返回的,服务方法返回结果不仅支持简单类型,还支持复杂类型;客户端支持多种调用代码书写方式。
虽然MSF是基于WCF构建的,但是从本文的示例过程看,仅使用MSF,无需掌握任何WCF的知识。
下面是完整的MSF服务端代码:
namespace TestService
{
public class Service1 : IService
{
public string SayHello(string who)
{
return string.Format("Hello {0} ,I am MSF Server.", who);
} public MailMessage GetMailMessage(string who)
{
MailMessage mail = new MailMessage();
mail.Reply = who;
mail.Sender = "MSF Server";
mail.Message = string.Format("Hello {0} ,I am MSF Server.", who);
mail.RevoveryTime = DateTime.Now;
return mail;
} public void CompleteRequest(IServiceContext context)
{
//throw new NotImplementedException();
} public bool IsUnSubscribe
{
//get { throw new NotImplementedException(); }
get
{
//返回True ,表示当前服务不执行系统后续的服务方法的订阅处理过程,而是由用户自己输出结果数据
return false;
}
} public bool ProcessRequest(IServiceContext context)
{
//throw new NotImplementedException();
return true;
}
}
}
下面是完整的客户端代码:
namespace MSFTest
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("******** PDF.NET MSF 客户端测试程序 *********");
Console.WriteLine();
Proxy client = new Proxy();
client.ErrorMessage += client_ErrorMessage;
Console.Write("请输入服务器的主机名或者IP地址(默认 127.0.0.1):");
string host = Console.ReadLine();
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(host))
host = "127.0.0.1";
Console.WriteLine("服务地址:{0}",host); Console.Write("请输入服务的端口号(默认 8888):");
string port = Console.ReadLine();
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(port))
port = "";
Console.WriteLine("服务端口号:{0}", port); client.ServiceBaseUri = string.Format("net.tcp://{0}:{1}", host, port);
Console.WriteLine("当前客户端代理的服务基础地址是:{0}",client.ServiceBaseUri);
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine("MSF 请求-响应 模式调用示例:"); client.RequestService<string>("Service://Service1/SayHello/System.String=bluedoctor1",
PWMIS.EnterpriseFramework.Common.DataType.Text,
s =>
{
Console.WriteLine("1,Server Response:【{0}】", s);
}); ServiceRequest request = new ServiceRequest();
request.ServiceName = "Service1";
request.MethodName = "SayHello";
request.Parameters = new object[] { "bluedoctor23" };
client.RequestService<string>(request,
PWMIS.EnterpriseFramework.Common.DataType.Text,
s =>
{
Console.WriteLine("2,Server Response:【{0}】", s);
}); string serverMsg= client.RequestServiceAsync<string>(request).Result;
Console.WriteLine("3,Server Response:【{0}】", serverMsg); client.RequestService<MailMessage>("Service://Service1/GetMailMessage/System.String=bluedoctor4",
PWMIS.EnterpriseFramework.Common.DataType.Json,
mail =>
{
Console.WriteLine("4,Server Response:【{0}】,\r\n Revovery Time:{1}", mail.Message,mail.RevoveryTime);
}); ServiceRequest request2 = new ServiceRequest();
request2.ServiceName = "Service1";
request2.MethodName = "GetMailMessage";
request2.Parameters = new object[] { "bluedoctor567" }; client.RequestService<MailMessage>(request2,
PWMIS.EnterpriseFramework.Common.DataType.Json,
mail =>
{
Console.WriteLine("5,Server Response:【{0}】,\r\n Revovery Time:{1}", mail.Message, mail.RevoveryTime);
}); client.RequestService<MailMessage2>(request2,
PWMIS.EnterpriseFramework.Common.DataType.Json,
mail =>
{
Console.WriteLine("6,Server Response:【{0}】,\r\n Revovery Time:{1}", mail.Message, mail.RevoveryTime);
}); MailMessage mail2 = client.RequestServiceAsync<MailMessage>(request2).Result;
Console.WriteLine("7,Server Response:【{0}】,\r\n Revovery Time:{1}", mail2.Message, mail2.RevoveryTime); Console.WriteLine("按回车键继续");
Console.ReadLine(); Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine("MSF 发布-订阅 模式调用示例:");
string repMsg = "你好!"; client.SubscribeTextMessage("我是客户端", serverMessage => {
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine("[来自服务器的消息]::{0}", serverMessage);
}); while (repMsg != "")
{
Console.Write("回复服务器(输入为空,则退出):>>");
repMsg = Console.ReadLine();
client.SendTextMessage(repMsg);
} Console.WriteLine("测试完成,退出"); } static void client_ErrorMessage(object sender, MessageSubscriber.MessageEventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("---处理服务时错误:{0}",e.MessageText);
}
}
}
下面是运行客户端输出的结果示例:
******** PDF.NET MSF 客户端测试程序 ********* 请输入服务器的主机名或者IP地址(默认 127.0.0.1):
服务地址:127.0.0.1
请输入服务的端口号(默认 8888):
服务端口号:8888
当前客户端代理的服务基础地址是:net.tcp://127.0.0.1:8888 MSF 请求-响应 模式调用示例:
1,Server Response:【Hello bluedoctor1 ,I am MSF Server.】
3,Server Response:【Hello bluedoctor23 ,I am MSF Server.】
2,Server Response:【Hello bluedoctor23 ,I am MSF Server.】
7,Server Response:【Hello bluedoctor567 ,I am MSF Server.】,
Revovery Time:2017-10-9 15:50:33
按回车键继续
4,Server Response:【Hello bluedoctor4 ,I am MSF Server.】,
Revovery Time:2017-10-9 15:50:33
5,Server Response:【Hello bluedoctor567 ,I am MSF Server.】,
Revovery Time:2017-10-9 15:50:33
6,Server Response:【Hello bluedoctor567 ,I am MSF Server.】,
Revovery Time:2017-10-9 15:50:33
在下一篇,我们将演示MSF的“发布-订阅”通信模式。
本篇测试程序全部源码,已经上传到GitHub:
https://github.com/bluedoctor/MSFTest
欢迎加入我们的QQ群讨论MSF框架的使用,群号:敏思(PWMIS) .NET 18215717,加群请注明:PDF.NET技术交流,否则可能被拒。
“一切都是消息”--MSF(消息服务框架)之【请求-响应】模式的更多相关文章
- WCF消息交换模式之请求-响应模式
WCF的消息交换模式(MEP)有三种:请求/响应.单向模式和双工模式.WCF的默认MEP是请求/响应模式. 请求/响应模式操作签名代码如下,无需指定模式,默认就是. [OperationContrac ...
- 一: WCF的服务端与客户端在通信时有三种模式:请求响应模式、数据报模式和双工通讯模式。
说一下基本知识, 1.如果想要将当前接口作为wcf服务器,则一定要加上[ServiceContract] 契约 2.要想将方法作为wcf服务方法发布给外部调用,则一定要加上 [Operatio ...
- “一切都是消息”--MSF(消息服务框架)之【发布-订阅】模式
在上一篇,“一切都是消息”--MSF(消息服务框架)之[请求-响应]模式 ,我们演示了MSF实现简单的请求-响应模式的示例,今天来看看如何实现[发布-订阅]模式.简单来说,该模式的工作过程是: 客户端 ...
- “一切都是消息”--iMSF(即时消息服务框架)之【发布-订阅】模式
MSF的名字是 Message Service Framework 的简称,由于目前框架主要功能在于处理即时(immediately)消息,所以iMSF就是 immediately Message S ...
- “一切都是消息”--iMSF(即时消息服务框架)之【请求-响应】模式(点对点)
MSF的名字是 Message Service Framework 的简称,由于目前框架主要功能在于处理即时(immediately)消息,所以iMSF就是 immediately Message S ...
- WCF把书读薄(2)——消息交换、服务实例、会话与并发
上一篇:WCF把书读薄(1)——终结点与服务寄宿 八.消息交换模式 WCF服务的实现是基于消息交换的,消息交换模式一共有三种:请求回复模式.单向模式与双工模式. 请求回复模式很好理解,比如int Ad ...
- 高性能的分布式服务框架 Dubbo
我思故我在,提问启迪思考! 1. 什么是Dubbo? 官网:http://dubbo.io/,DUBBO是一个分布式服务框架,致力于提供高性能和透明化的RPC远程服务调用方案,以及作为SOA服务治理的 ...
- 【转】Dubbo是Alibaba开源的分布式服务框架
Dubbo是Alibaba开源的分布式服务框架,它最大的特点是按照分层的方式来架构,使用这种方式可以使各个层之间解耦合(或者最大限度地松耦合).从服务模型的角度来看,Dubbo采用的是一种非常简单的模 ...
- 基于.NET CORE微服务框架 -浅析如何使用surging
1.前言 surging受到大家这么强烈的关注,我感到非常意外,比如有同僚在公司的分享会上分享surging, 还有在博客拿其它的RPC框架,微服务做对比等等,这些举动都让我感觉压力很大,毕竟作为个人 ...
随机推荐
- MySql数据库导入导出
1.导出整个数据库 mysqldump -u 用户名 -p 数据库名 > 存放位置 比如: mysqldump -u root -p project > c:/a. ...
- ActiveMQ笔记——技术点汇总
目录 · Introduction to ActiveMQ · Installing ActiveMQ · Message-oriented middleware · JMS specificatio ...
- indexOf和lastIndexOf方法
lastIndexOf 方法: 返回 String 对象中子字符串最后出现的位置. strObj.lastIndexOf(substring[startindex]) 参数:strObj必选项.Str ...
- poj3463 最短路和比最短路长1的路径数
这题需要很好的理解Dij. 在Dij的基础上,每个点多一个次短路的长度和数量进行控制. 那么在队列中,最短路控制时出现n次,次短路控制出现n次.注意松弛条件中val值和最短路.次短路的关系. 这题需要 ...
- zabbix 问题汇总
1.Zabbix agent on Zabbix server is unreachable for 5 minutes 查看日志sudo tailf /var/log/zabbix/zabbix_a ...
- 团队作业8——第二次项目冲刺(Beta阶段)Day7——5.26
展开圆桌式会议: 会议内容:1.汇总BETA阶段的成果.2.针对BETA阶段的大家的获得的收获进行了讨论.3.对整个团队项目的过程进行了总结.每个人的工作分配: 队员 今日任务 贡献比 林燕 做最后测 ...
- C++学习笔记——STL(标准模板库)
1.首先.需要学习C++ 模板的概念 2.C++ STL(标准模板库)是一套功能强大的 C++ 模板类,提供了通用的模板类和函数,这些模板类和函数可以实现多种流行和常用的算法和数据结构,如向量.链表. ...
- 201521123051《Java程序设计》第七周学习总结
1. 本周学习总结 以你喜欢的方式(思维导图或其他)归纳总结集合相关内容. 使用工具:百度脑图 2. 书面作业 1.ArrayList代码分析 1.1 解释ArrayList的contains源代码 ...
- 201521123105 第四周Java学习总结
1. 本周学习总结 1.1 尝试使用思维导图总结有关继承的知识点. 1.2 使用常规方法总结其他上课内容. 继承与多态的概念与实现父类与之类的关系解决代码复用的办法 2. 书面作业 2.1 将在网上商 ...
- 201521123112《Java程序设计》第2周学习总结
1.本周学习总结 本周在课堂面授课粗略讲了<Java学习笔记>中的第三章,其内容大部分都与上学期学习的数据结构差不多,所以只是粗略的复习了一下就带过,然后通过将PTA上的实验便于我们本周的 ...
