Machine learning吴恩达第三周 Logistic Regression
1. Sigmoid function
function g = sigmoid(z)
%SIGMOID Compute sigmoid function
% g = SIGMOID(z) computes the sigmoid of z. % You need to return the following variables correctly
g = zeros(size(z)); % ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Compute the sigmoid of each value of z (z can be a matrix,
% vector or scalar). g=1./(1+exp(-z)); % ============================================================= end

2. Logistic Regression Cost & Logistic Regression Gradient

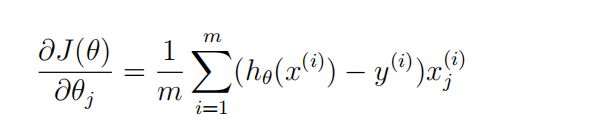
首先可以将h(x)表示出来----sigmoid函数
然后对于gredient(j)来说,
可以现在草稿纸上把矩阵画出来,然后观察,用向量来解决;
function [J, grad] = costFunction(theta, X, y)
%COSTFUNCTION Compute cost and gradient for logistic regression
% J = COSTFUNCTION(theta, X, y) computes the cost of using theta as the
% parameter for logistic regression and the gradient of the cost
% w.r.t. to the parameters. % Initialize some useful values
m = length(y); % number of training examples % You need to return the following variables correctly
J = 0;
grad = zeros(size(theta)); % ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Compute the cost of a particular choice of theta.
% You should set J to the cost.
% Compute the partial derivatives and set grad to the partial
% derivatives of the cost w.r.t. each parameter in theta
%
% Note: grad should have the same dimensions as theta
%
h=sigmoid(X*theta); for i=1:m,
J=J+1/m*(-y(i)*log(h(i))-(1-y(i))*log(1-h(i)));
endfor grad=1/m*X'*(h.-y); % ============================================================= end
3. Predict
function p = predict(theta, X)
%PREDICT Predict whether the label is 0 or 1 using learned logistic
%regression parameters theta
% p = PREDICT(theta, X) computes the predictions for X using a
% threshold at 0.5 (i.e., if sigmoid(theta'*x) >= 0.5, predict 1) m = size(X, 1); % Number of training examples % You need to return the following variables correctly
p = zeros(m, 1); % ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Complete the following code to make predictions using
% your learned logistic regression parameters.
% You should set p to a vector of 0's and 1's
% p=sigmoid(X*theta);
for i=1:m
if(p(i)>=0.5)p(i)=1;
else p(i)=0;
end
endfor % ========================================================================= end
4.Regularized Logistic Regression Cost & Regularized Logistic Regression Gradient

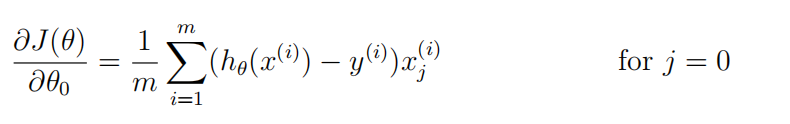

要注意的是:
Octave中,下标是从1开始的;
其次:
对于gradient(j)而言;
我们可以用X(:,j)的方式获取第j列的所有元素;
function [J, grad] = costFunctionReg(theta, X, y, lambda)
%COSTFUNCTIONREG Compute cost and gradient for logistic regression with regularization
% J = COSTFUNCTIONREG(theta, X, y, lambda) computes the cost of using
% theta as the parameter for regularized logistic regression and the
% gradient of the cost w.r.t. to the parameters. % Initialize some useful values
m = length(y); % number of training examples % You need to return the following variables correctly
J = 0;
grad = zeros(size(theta)); % ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Compute the cost of a particular choice of theta.
% You should set J to the cost.
% Compute the partial derivatives and set grad to the partial
% derivatives of the cost w.r.t. each parameter in theta h=sigmoid(X*theta); for i=1:m
J=J+1/m*(-y(i)*log(h(i))-(1-y(i))*log(1-h(i)));
endfor for i=2:length(theta)
J=J+lambda/(2*m)*theta(i)^2;
endfor grad(1)=1/m*(h-y)'*X(:,1);
for i=2:length(theta)
grad(i)=1/m*(h-y)'*X(:,i)+lambda/m*theta(i);
endfor % ============================================================= end
Machine learning吴恩达第三周 Logistic Regression的更多相关文章
- Machine Learning——吴恩达机器学习笔记(酷
[1] ML Introduction a. supervised learning & unsupervised learning 监督学习:从给定的训练数据集中学习出一个函数(模型参数), ...
- Machine learning吴恩达第二周coding作业(选做)
1.Feature Normalization: 归一化的处理 function [X_norm, mu, sigma] = featureNormalize(X) %FEATURENORMALIZE ...
- Machine learning 吴恩达第二周coding作业(必做题)
1.warmUpExercise: function A = warmUpExercise() %WARMUPEXERCISE Example function in octave % A = WAR ...
- 吴恩达+neural-networks-deep-learning+第二周作业
Logistic Regression with a Neural Network mindset v4 简单用logistic实现了猫的识别,logistic可以被看做一个简单的神经网络结构,下面是 ...
- Deap Learning (吴恩达) 第一章深度学习概论 学习笔记
Deap Learning(Ng) 学习笔记 author: 相忠良(Zhong-Liang Xiang) start from: Sep. 8st, 2017 1 深度学习概论 打字太麻烦了,索性在 ...
- 吴恩达机器学习笔记 —— 7 Logistic回归
http://www.cnblogs.com/xing901022/p/9332529.html 本章主要讲解了逻辑回归相关的问题,比如什么是分类?逻辑回归如何定义损失函数?逻辑回归如何求最优解?如何 ...
- Github | 吴恩达新书《Machine Learning Yearning》完整中文版开源
最近开源了周志华老师的西瓜书<机器学习>纯手推笔记: 博士笔记 | 周志华<机器学习>手推笔记第一章思维导图 [博士笔记 | 周志华<机器学习>手推笔记第二章&qu ...
- 我在 B 站学机器学习(Machine Learning)- 吴恩达(Andrew Ng)【中英双语】
我在 B 站学机器学习(Machine Learning)- 吴恩达(Andrew Ng)[中英双语] 视频地址:https://www.bilibili.com/video/av9912938/ t ...
- Coursera课程《Machine Learning》吴恩达课堂笔记
强烈安利吴恩达老师的<Machine Learning>课程,讲得非常好懂,基本上算是无基础就可以学习的课程. 课程地址 强烈建议在线学习,而不是把视频下载下来看.视频中间可能会有一些问题 ...
随机推荐
- p2408 不同子串个数
传送门 分析 首先我们不难求出一共有多少子串 之后我们只需要减掉重复个数即可 于是我们对于每个后缀减去它跟它前一名的最长公共前缀即可 代码 #include<iostream> #incl ...
- c#反射泛型方法
private void GetByEnumType() { var EnumType = Context.Request["EnumType"] ?? ""; ...
- 取得MapReduce的Thread Dump
====2016/5/20: 经过上级指示,为了MR性能调优,需要截取MR的服务器的线程堆栈(Thread Dump) 战友介绍的方法是这样的: ①.使用ps命令[ps -ef | grep java ...
- VWAP算法(成交量加权平均价)
算法交易其实主要是用在基金公司.券商量化比较多.例如我已经选好股,要大量买入,但是单凭交易员的操作海量单而且要完成买入100万股这些的操作是有点的困难的.那么这时候怎样解决拆单,防止冲击成本的问题呢? ...
- 两款JSON类库Jackson与JSON-lib的性能对比(新增第三款测试)
本篇文章主要介绍了"两款JSON类库Jackson与JSON-lib的性能对比(新增第三款测试)",主要涉及到两款JSON类库Jackson与JSON-lib的性能对比(新增第三款 ...
- 启动Hadoop HDFS时的“Incompatible clusterIDs”错误原因分析
"Incompatible clusterIDs"的错误原因是在执行"hdfs namenode -format"之前,没有清空DataNode节点的data目 ...
- Python 通过配置文件 读取参数,执行测试用例,生成测试报告并发送邮件
#-*-coding:utf-8-*- #测试用例配置参数 #XXXXX_Uitest->baseinfo->__init__.py base_url = "http://XXX ...
- python-接口测试(思路)
案例:接口发送post请求 步骤1:编写方法,用于提交post请求 步骤2:编写测试数据对象,用户提交测试数据 步骤3:调用方法和数据,进行测试 实例展示: 步骤1:编写方法checkapi_post ...
- Android-ContentProvider原理图
ContentProvider的设计思想是模仿了Web里面的架构思想: Web服务器 对外暴露数据(提供被访问的地址Uri,并允许给客户端访问,也可以只让客户端访问某些行为) ContentPro ...
- [LeetCode 题解]:Path Sum
前言 [LeetCode 题解]系列传送门: http://www.cnblogs.com/double-win/category/573499.html 1.题目描述 Given a bi ...
