3.Netty的粘包、拆包(二)
Netty提供的TCP数据拆包、粘包解决方案
1.前言
关于TCP的数据拆包、粘包的介绍,我在上一篇文章里面已经有过介绍。
想要了解一下的,请点击这里 Chick Here!
今天我们要讲解的是Netty提供的两种解决方案:
- DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder
- FixedLengthFrameDecoder
2.关于Decoder
先观察下两段代码的不同
(1)使用StringDecoder之前
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception { try { ByteBuf in = (ByteBuf) msg;
String str = in.toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8);
System.out.println("Client:"+str); } finally {
ReferenceCountUtil.release(msg);
}
}
(2)使用StringDecoder之后
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception { try {
String str = (String) msg;
System.out.println("Client:"+str); } finally {
ReferenceCountUtil.release(msg);
}
}
关于Decoder
decoder:n. 解码器
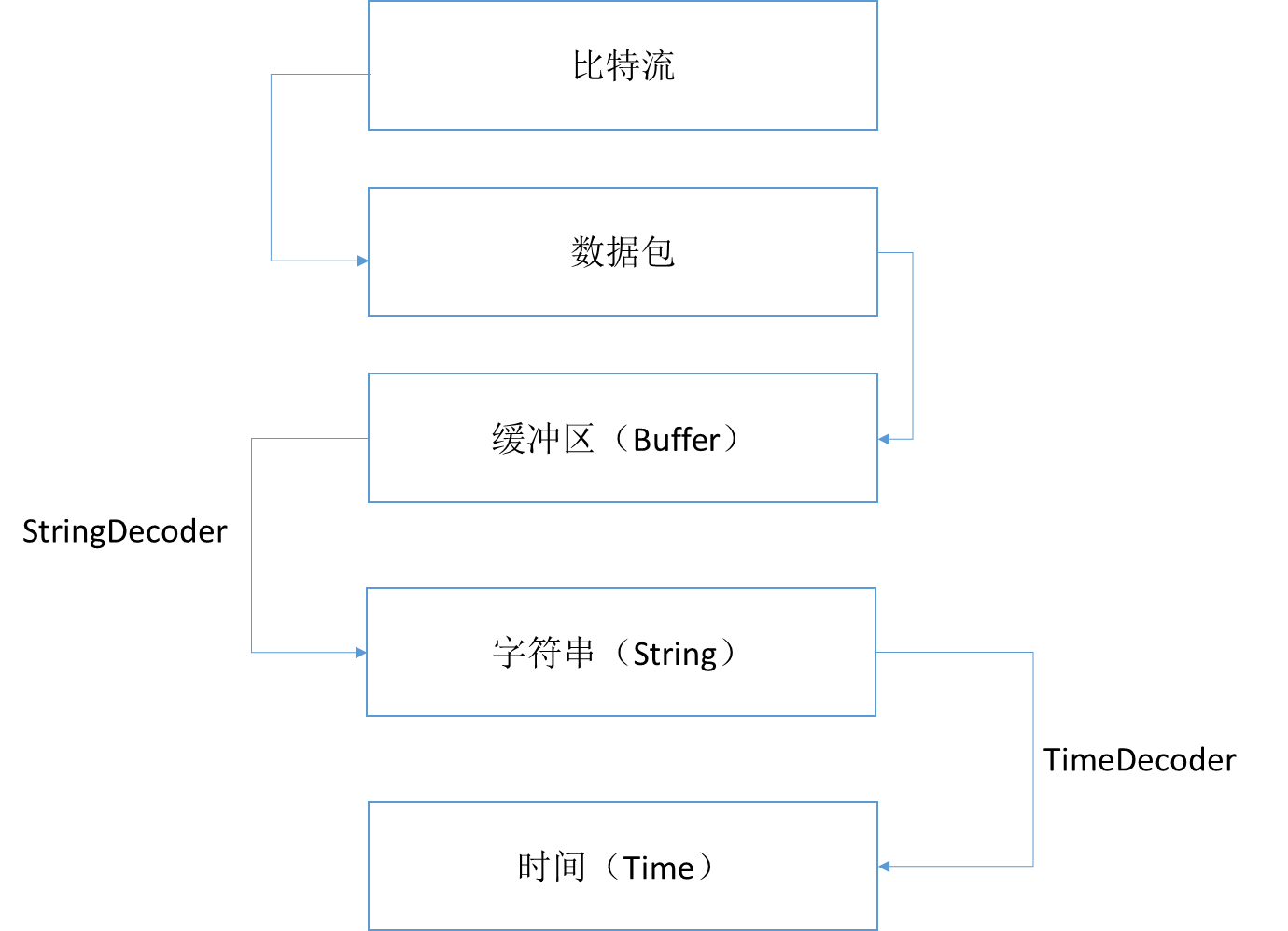
在我看来,Netty数据的解析方式大概为:
发送过程:Buffer------>数据报------>比特流
接受过程:Buffer<------数据报<------比特流
所以我们接受到的msg是一个ButeBuf
使用了Decoder(这里使用StringDecoder举例)之后:
发送过程:Buffer------>数据报------>比特流
接受过程:String<------Buffer<------数据报<------比特流
相当于ByteBuf按照StringDecoder的解码规则,把msg翻译成为了一个字符串。
如何使用Decoder
(1)实际代码演示:
package com.xm.netty.demo02; import java.net.InetSocketAddress; import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.Channel;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder; public class Server { private final int port; public Server(int port) {
this.port = port;
} public static void main(String[] args) { int port = 8989;
try {
new Server(port).start();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} } private void start() throws InterruptedException {
EventLoopGroup g1 = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup g2 = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
bootstrap
.group(g1,g2)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.localAddress(new InetSocketAddress( port))
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringDecoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ServerHandler());
}
});
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.bind().sync();
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
g1.shutdownGracefully().sync();
g2.shutdownGracefully().sync();
}
} }
代码改动:
ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringDecoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ServerHandler());
(2)多个Decoder的使用顺序:
从前往后,依次解码
假设我们有个通过字符串变化为时间的TimeDecoder:
ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringDecoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new TimeDecoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ServerHandler());
解析规则为:
3.DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder
关于DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder
其实很简单,就是在一个缓冲区的末尾添加一个结束字符。
在规定了最大长度的缓冲区里,遇到一个特殊字符,就截取一次。
原理类似于String的split()方法。
代码实现
(1)服务端Server
package com.xm.netty.demo03; import java.net.InetSocketAddress; import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.Channel;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder; public class Server { private final int port; public Server(int port) {
this.port = port;
} public static void main(String[] args) { int port = 8989;
try {
new Server(port).start();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} } private void start() throws InterruptedException {
EventLoopGroup g1 = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup g2 = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
bootstrap
.group(g1,g2)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.localAddress(new InetSocketAddress( port))
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception {
ByteBuf buf = Unpooled.copiedBuffer("$".getBytes());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder(1024,buf));
ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringDecoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ServerHandler());
}
});
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.bind().sync();
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
g1.shutdownGracefully().sync();
g2.shutdownGracefully().sync();
}
} }
(2)服务端ServerHandler
package com.xm.netty.demo03; import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter; import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.util.CharsetUtil; public class ServerHandler extends ChannelHandlerAdapter { @Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception { String str = (String) msg;
System.out.println("Server:"+str);
str = "服务器返回--->"+ str+"$";
ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer(str.getBytes()));
} @Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
} @Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
System.out.println(DateTimeFormatter.ISO_LOCAL_DATE_TIME.format(LocalDateTime.now())+"一个客户端连接上服务器!");
} }(3)客户端Client
package com.xm.netty.demo03; import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter; import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder; public class Client { private final int port;
private final String host; public Client(int port, String host) {
this.port = port;
this.host = host;
} public static void main(String[] args) {
String host = "127.0.0.1";
int port = 8989;
try {
new Client(port, host).start();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
} private void start() throws InterruptedException { EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap
.group(group)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.remoteAddress(host, port)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { @Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ByteBuf buf = Unpooled.copiedBuffer("$".getBytes());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder(1024,buf));
ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringDecoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ClientHandler());
} }); ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.connect().sync(); for(int i=10;i<20;i++) {
String str = DateTimeFormatter.ISO_LOCAL_DATE_TIME.format(LocalDateTime.now()) + "---- " +i+"<<<$";
future.channel().write(Unpooled.copiedBuffer(str.getBytes()));
} future.channel().flush(); //future.channel().writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("Hello Netty!".getBytes())); future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
group.shutdownGracefully().sync();
} } }(4)客户端ClientHandler
package com.xm.netty.demo03; import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter; import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.util.CharsetUtil;
import io.netty.util.ReferenceCountUtil; public class ClientHandler extends ChannelHandlerAdapter { @Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception { try {
String str = (String) msg;
System.out.println("Client:"+str); } finally {
ReferenceCountUtil.release(msg);
}
} @Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
} @Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
System.out.println(DateTimeFormatter.ISO_LOCAL_DATE_TIME.format(LocalDateTime.now())+"已连接服务器!");
} }运行结果截图
(1)服务端运行结果:
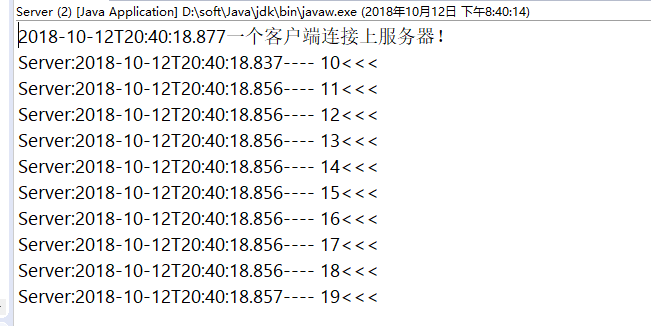
(2)客户端运行结果:

4.FixedLengthFrameDecoder
关于FixedLengthFrameDecoder
其实很简单,就是对规定的发送的数据进行限制长度,
当符合这个长度的情况下,就可以解析。
假设你发送一个’123456‘,’654321‘
那么解析的状况为’12345‘,’66543‘
代码实现
(1)服务端Server
package com.xm.netty.demo04; import java.net.InetSocketAddress; import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.Channel;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.FixedLengthFrameDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder; public class Server { private final int port; public Server(int port) {
this.port = port;
} public static void main(String[] args) { int port = 8989;
try {
new Server(port).start();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} } private void start() throws InterruptedException {
EventLoopGroup g1 = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup g2 = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
bootstrap
.group(g1,g2)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.localAddress(new InetSocketAddress( port))
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new FixedLengthFrameDecoder(5));
ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringDecoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ServerHandler());
}
});
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.bind().sync();
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
g1.shutdownGracefully().sync();
g2.shutdownGracefully().sync();
}
} }
(2)服务端ServerHandler
package com.xm.netty.demo04; import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter; import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.util.CharsetUtil; public class ServerHandler extends ChannelHandlerAdapter { @Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception { String str = (String) msg;
System.out.println("Server:"+str);
ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer(str.getBytes()));
} @Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
} @Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
System.out.println(DateTimeFormatter.ISO_LOCAL_DATE_TIME.format(LocalDateTime.now())+"一个客户端连接上服务器!");
} }(3)客户端Client
package com.xm.netty.demo04; import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter; import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.FixedLengthFrameDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder; public class Client { private final int port;
private final String host; public Client(int port, String host) {
this.port = port;
this.host = host;
} public static void main(String[] args) {
String host = "127.0.0.1";
int port = 8989;
try {
new Client(port, host).start();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
} private void start() throws InterruptedException { EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap
.group(group)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.remoteAddress(host, port)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { @Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new FixedLengthFrameDecoder(5));
ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringDecoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ClientHandler());
} }); ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.connect().sync(); for(int i=123450;i<123460;i++) {
String str = ""+i;
future.channel().write(Unpooled.copiedBuffer(str.getBytes()));
}
future.channel().flush(); //future.channel().writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("Hello Netty!".getBytes())); future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
group.shutdownGracefully().sync();
} } }(4)客户端ClientHandler
package com.xm.netty.demo04; import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter; import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.util.CharsetUtil;
import io.netty.util.ReferenceCountUtil; public class ClientHandler extends ChannelHandlerAdapter { @Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception { try {
String str = (String) msg;
System.out.println("Client:"+str); } finally {
ReferenceCountUtil.release(msg);
}
} @Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
} @Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
System.out.println(DateTimeFormatter.ISO_LOCAL_DATE_TIME.format(LocalDateTime.now())+"已连接服务器!");
} }运行结果截图
(1)服务端运行结果:
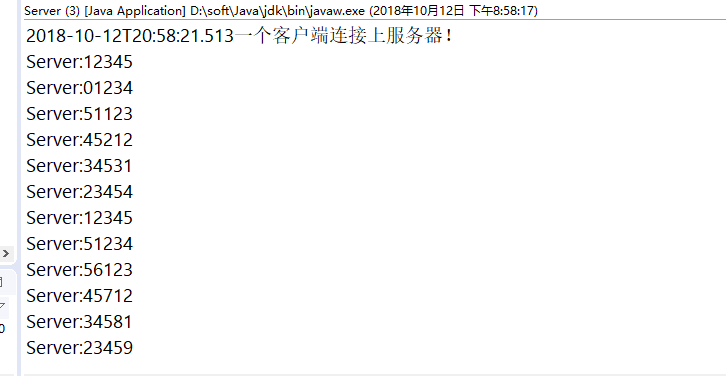
(2)客户端运行结果:

3.Netty的粘包、拆包(二)的更多相关文章
- Netty TCP粘包/拆包问题《二》
1.DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder:是以分隔符作为结束标志进行解决粘包/拆包问题 代码: EchoClient:客户端 /* * Copyright 2012 The Netty ...
- netty 解决粘包拆包问题
netty server TimeServer package com.zhaowb.netty.ch4_3; import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap; i ...
- Netty TCP粘包/拆包问题《一》
1.使用LineBasedFrameDecoder,StringDecoder解析器进行解决TCP粘包/拆包问题 2.代码搞起: TimeClient:客户端 /* * Copyright 2013- ...
- netty: 解决粘包拆包: 分隔符DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder,定长消息FixedLengthFrameDecoder
DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder 自定义分隔符 给Server发送多条信息,但是server会讲多条信息合并为一条.这时候我们需要对发生的消息指定分割,让client和server ...
- Netty入门系列(2) --使用Netty解决粘包和拆包问题
前言 上一篇我们介绍了如果使用Netty来开发一个简单的服务端和客户端,接下来我们来讨论如何使用解码器来解决TCP的粘包和拆包问题 TCP为什么会粘包/拆包 我们知道,TCP是以一种流的方式来进行网络 ...
- 《精通并发与Netty》学习笔记(14 - 解决TCP粘包拆包(二)Netty自定义协议解决粘包拆包)
一.Netty粘包和拆包解决方案 Netty提供了多个解码器,可以进行分包的操作,分别是: * LineBasedFrameDecoder (换行) LineBasedFrameDecoder是回 ...
- Netty(二)——TCP粘包/拆包
转载请注明出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/Joanna-Yan/p/7814644.html 前面讲到:Netty(一)--Netty入门程序 主要内容: TCP粘包/拆包的基础知 ...
- 1. Netty解决Tcp粘包拆包
一. TCP粘包问题 实际发送的消息, 可能会被TCP拆分成很多数据包发送, 也可能把很多消息组合成一个数据包发送 粘包拆包发生的原因 (1) 应用程序一次写的字节大小超过socket发送缓冲区大小 ...
- TCP粘包/拆包 ByteBuf和channel 如果没有Netty? 传统的多线程服务器,这个也是Apache处理请求的模式
通俗地讲,Netty 能做什么? - 知乎 https://www.zhihu.com/question/24322387 谢邀.netty是一套在java NIO的基础上封装的便于用户开发网络应用程 ...
- 《精通并发与Netty》学习笔记(13 - 解决TCP粘包拆包(一)概念及实例演示)
一.粘包/拆包概念 TCP是一个“流”协议,所谓流,就是没有界限的一长串二进制数据.TCP作为传输层协议并不不了解上层业务数据的具体含义,它会根据TCP缓冲区的实际情况进行数据包的划分,所以在业务上认 ...
随机推荐
- 2019.03.20 读书笔记 关于Reflect与Emit的datatable转list的效率对比
Reflect public static List<T> ToListByReflect<T>(this DataTable dt) where T : new() { Li ...
- GET和POST区别和用法
很多人都分不清GET与POST的区别,以及什么时候用GET?什么时候用POST? GET和POST两种方法都是将数据送到服务器,但你该用哪一种呢? HTTP标准包含这两种方法是为了达到不同的目的.PO ...
- machine learning 线性回归实战
matlab 线性回归实战 统一 输入时列向量 输出也是列向量 中间的过程可以出现行向量或者列向量,但是不能影响输入和输出为列向量 参数运算的输入都不会只是一个实数,要么是列向量,要么是一个矩阵 对于 ...
- Python常用模块一
一. os模块 os.getcwd() 获取当前工作目录,即当前python脚本工作的目录路径 os.chdir("dirname") 改变当前脚本工作目录:相当于shell下cd ...
- Win2D 官方文章系列翻译 - 调整控件分辨率
本文为个人博客备份文章,原文地址: http://validvoid.net/win2d-choosing-control-resolution/ 本文旨在讲解如何配置 Win2D XAML 控件使用 ...
- <Android 基础(六)> ActionBar
介绍 Action Bar是一种新増的导航栏功能,在Android 3.0之后加入到系统的API当中,它标识了用户当前操作界面的位置,并提供了额外的用户动作.界面导航等功能.使用ActionBar的好 ...
- Android 5.0 以上监听网络变化
大家好,大概有一个多月没有更新博客了,我是干什么去了呢?很明显,程序员当然要加班……这一次跟大家分享一下新项目的一些心得. 监听网络变化在开发中是经常用到的,例如我们断网有一些友好的提示,或者根据不同 ...
- 【起航计划 004】2015 起航计划 Android APIDemo的魔鬼步伐 03 App->Activity->Animation Activity跳转动画 R.anim.×× overridePendingTransition ActivityOptions类
App->Activity->Animation示例用于演示不同Activity切换时动态效果. android 5.0例子中定义了6种动画效果: 渐变Fade In 缩放Zoom In ...
- ASP.NET设置母版页
母版页允许开发人员创建具有指定的可编辑区域的站点级模板.随后,此模板可应用到网站中的 ASP.NET 页面上.这些 ASP.NET 页面只需为母版页中指定的可编辑区域提供相应内容 – 在使用母版页的所 ...
- 还是要精简开发呀,VS2015太大,VS2010不想装
公司电脑配置没有很好,所以对于我就是一个挑战. vs2015装上了,但是一打开就卡卡卡,基本没法办公. 公布能用记事本吧,太多不方便: Notepad++做辅助的局部修改还是很好用的,装上插件就智能提 ...
