day-8 python自带库实现ID3决策树算法
前一天,我们基于sklearn科学库实现了ID3的决策树程序,本文将基于python自带库实现ID3决策树算法。
一、代码涉及基本知识
1、 为了绘图方便,引入了一个第三方treePlotter模块进行图形绘制。该模块使用方法简单,调用模块createPlot接口,传入一个树型结构对象,即可绘制出相应图像。
2、 在python中,如何定义一个树型结构对象
可以使用了python自带的字典数据类型来定义一个树型对象。例如下面代码,我们定义一个根节点和两个左右子节点:
rootNode = {'rootNode': {}}
leftNode = {'leftNode': {'yes':'yes'}}
rightNode = {'rightNode': {'no':'no'}}
rootNode['rootNode']['left'] = leftNode
rootNode['rootNode']['right'] = rightNode
treePlotter.createPlot(rootNode)
通过调用treePlotter模块,绘制出如下树的图像

2、 递归调用
为了求每个节点的各个子节点,要用到递归的方法来实现,基本思想和二叉树的遍历方法一致,后面我们还会用Python实现一个二叉树源码,此处不再进行介绍。
3、 此外,还需要对python常用的数据类型及其操作比较了解,例如字典、列表、集合等
二、程序主要流程
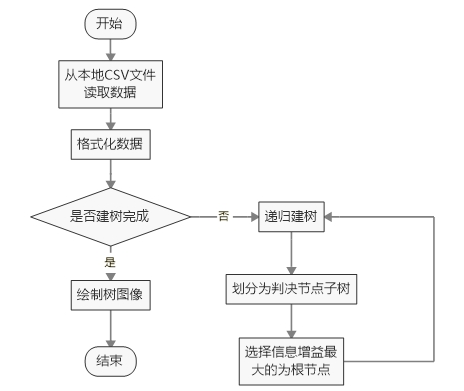
三、测试数据集
|
age |
income |
student |
credit_rating |
class_buys_computer |
|
youth |
high |
no |
fair |
no |
|
youth |
high |
no |
excellent |
no |
|
middle_aged |
high |
no |
fair |
yes |
|
senior |
medium |
no |
fair |
yes |
|
senior |
low |
yes |
fair |
yes |
|
senior |
low |
yes |
excellent |
no |
|
middle_aged |
low |
yes |
excellent |
yes |
|
youth |
medium |
no |
fair |
no |
|
youth |
low |
yes |
fair |
yes |
|
senior |
medium |
yes |
fair |
yes |
|
youth |
medium |
yes |
excellent |
yes |
|
middle_aged |
medium |
no |
excellent |
yes |
|
middle_aged |
high |
yes |
fair |
yes |
|
senior |
medium |
no |
excellent |
no |
四、程序代码
1、计算测试集熵及信息增益
# 求最优的根节点
def chooseBestFeatureToSplit(dataset,headerList):
# 定义一个初始值
bestInfoGainRate = 0.0
bestFeature = 0
# 求特征列项的数量
numFeatures = len(dataset[0]) -1
# 获取整个测试数据集的熵
baseShnnonEnt = calcShannonEnt(dataset)
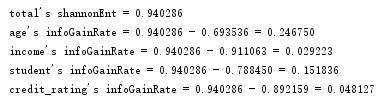
print("total's shannonEnt = %f" % (baseShnnonEnt))
# 遍历每一个特征列,求取信息增益
for i in range(numFeatures):
# 获取某一列所有特征值
featureList = [example[i] for example in dataset]
uniqueVals = set(featureList)
newEntropy = 0.0
# 求得某一列某一个特征值的概率和熵
newShannonEnt = 0.0
for value in uniqueVals:
# 计算熵
subDataset = splitDataSet(dataset,i,value)
newEntropy = calcShannonEnt(subDataset)
# 计算某一列某一个特征值的概率
newProbability = len(subDataset) / float(len(dataset))
newShannonEnt += newProbability*calcShannonEnt(subDataset)
infoGainRate = baseShnnonEnt - newShannonEnt
print("%s's infoGainRate = %f - %f = %f"%(headerList[i],baseShnnonEnt,newShannonEnt,infoGainRate))
if infoGainRate > bestInfoGainRate:
bestInfoGainRate = infoGainRate
bestFeature = i
return bestFeature
该结果和前一天计算结果一致,age特征对应信息增益最大,因此设为根节点:
2、程序源码
treePlotter.py
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # 定义决策树决策结果属性
descisionNode = dict(boxstyle='sawtooth', fc='0.8')
leafNode = dict(boxstyle='round4', fc='0.8')
arrow_args = dict(arrowstyle='<-') def plotNode(nodeTxt, centerPt, parentPt, nodeType):
# nodeTxt为要显示的文本,centerNode为文本中心点, nodeType为箭头所在的点, parentPt为指向文本的点
createPlot.ax1.annotate(nodeTxt, xy=parentPt, xycoords='axes fraction',
xytext=centerPt, textcoords='axes fraction',
va='center', ha='center', bbox=nodeType, arrowprops=arrow_args)
def getNumLeafs(myTree):
numLeafs = 0
firstStr = list(myTree.keys())[0]
secondDict = myTree[firstStr]
for key in secondDict.keys():
if type(secondDict[key]).__name__ == 'dict':
numLeafs += getNumLeafs(secondDict[key])
else:
numLeafs += 1
return numLeafs def getTreeDepth(myTree):
maxDepth = 0
firstStr = list(myTree.keys())[0] # 这个是改的地方,原来myTree.keys()返回的是dict_keys类,不是列表,运行会报错。有好几个地方这样
secondDict = myTree[firstStr]
for key in secondDict.keys():
if type(secondDict[key]).__name__ == 'dict':
thisDepth = 1 + getTreeDepth(secondDict[key])
else:
thisDepth = 1
if thisDepth > maxDepth:
maxDepth = thisDepth
return maxDepth def createPlot(inTree):
fig = plt.figure(1, facecolor='white')
fig.clf()
axprops = {'xticks': None, 'yticks': None}
createPlot.ax1 = plt.subplot(111, frameon=False)
plotTree.totalW = float(getNumLeafs(inTree)) # 全局变量宽度 = 叶子数目
plotTree.totalD = float(getTreeDepth(inTree)) # 全局变量高度 = 深度
plotTree.xOff = -0.5/plotTree.totalW
plotTree.yOff = 1.0
plotTree(inTree, (0.5, 1.0), '')
plt.show() def plotTree(myTree, parentPt, nodeTxt):
numLeafs = getNumLeafs(myTree)
depth = getTreeDepth(myTree)
firstStr = list(myTree.keys())[0]
# cntrPt文本中心点, parentPt指向文本中心的点
cntrPt = (plotTree.xOff + (1.0 + float(numLeafs))/2.0/plotTree.totalW, plotTree.yOff)
plotMidText(cntrPt, parentPt, nodeTxt)
plotNode(firstStr, cntrPt, parentPt, descisionNode)
seconDict = myTree[firstStr]
plotTree.yOff = plotTree.yOff - 1.0/plotTree.totalD
for key in seconDict.keys():
if type(seconDict[key]).__name__ == 'dict':
plotTree(seconDict[key], cntrPt, str(key))
else:
plotTree.xOff = plotTree.xOff + 1.0/plotTree.totalW
plotNode(seconDict[key], (plotTree.xOff, plotTree.yOff), cntrPt, leafNode)
plotMidText((plotTree.xOff, plotTree.yOff), cntrPt, str(key))
plotTree.yOff = plotTree.yOff + 1.0/plotTree.totalD def plotMidText(cntrPt, parentPt, txtString):
xMid = (parentPt[0] - cntrPt[0])/2.0 + cntrPt[0]
yMid = (parentPt[1] - cntrPt[1])/2.0 + cntrPt[1]
createPlot.ax1.text(xMid, yMid, txtString, va='center', ha='center', rotation=30)
decision_tree_ID3.py
# 导入库
import csv
import math
import operator
import treePlotter # 导入数据集
def readDataset(file_path,file_mode):
allElectronicsData = open(file_path, file_mode)
reader = csv.reader(allElectronicsData)
# 读取特征名称
headers = next(reader)
# 读取测试数据集
dataset = []
for row in reader:
dataset.append(row)
return headers,dataset # 求某个数据集的熵
def calcShannonEnt(dataset):
shannonEnt = 0.0
labelList = {}
for vec_now in dataset:
labelValue = vec_now[-1]
if vec_now[-1] not in labelList.keys():
labelList[labelValue] = 0
labelList[labelValue] += 1
for labelKey in labelList:
probability = float(labelList[labelKey] / len(dataset))
shannonEnt -= probability*math.log(probability,2)
return shannonEnt # 根据给定的列特征值,分理出给定的特征量
def splitDataSet(dataset,feature_seq,value):
new_dataset = []
for vec_row in dataset:
feature_Value = vec_row[feature_seq]
if feature_Value == value:
temp_vec = []
temp_vec = vec_row[:feature_seq]
temp_vec.extend(vec_row[feature_seq+1:])
new_dataset.append(temp_vec)
return new_dataset # 求最优的根节点
def chooseBestFeatureToSplit(dataset,headerList):
# 定义一个初始值
bestInfoGainRate = 0.0
bestFeature = 0
# 求特征列项的数量
numFeatures = len(dataset[0]) -1
# 获取整个测试数据集的熵
baseShnnonEnt = calcShannonEnt(dataset)
#print("total's shannonEnt = %f" % (baseShnnonEnt))
# 遍历每一个特征列,求取信息增益
for i in range(numFeatures):
# 获取某一列所有特征值
featureList = [example[i] for example in dataset]
uniqueVals = set(featureList)
newEntropy = 0.0
# 求得某一列某一个特征值的概率和熵
newShannonEnt = 0.0
for value in uniqueVals:
# 计算熵
subDataset = splitDataSet(dataset,i,value)
newEntropy = calcShannonEnt(subDataset)
# 计算某一列某一个特征值的概率
newProbability = len(subDataset) / float(len(dataset))
newShannonEnt += newProbability*calcShannonEnt(subDataset)
infoGainRate = baseShnnonEnt - newShannonEnt
#print("%s's infoGainRate = %f - %f = %f"%(headerList[i],baseShnnonEnt,newShannonEnt,infoGainRate))
if infoGainRate > bestInfoGainRate:
bestInfoGainRate = infoGainRate
bestFeature = i
return bestFeature # 标签判定,通过少数服从多数原则
def majorityCnt(classList):
classcount = {}
for cl in classList:
if cl not in classcount.keys():
classcount[cl] = 0
classcount[cl] += 1
sortedClassCount = sorted(classcount.items(),key = operator.itemgetter(1),reverse= True)
return sortedClassCount[0][0] # 创建一个决策树
def createTree(dataSet, labels):
classList = [example[-1] for example in dataSet]
# 1 所有特征值都是相同的时候直接返回
if classList.count(classList[0]) == len(classList):
return classList[0]
# 2 遍历完所有特征值,投票原则,返回出现次数最多的标签
if len(dataSet[0]) == 1:
return majorityCnt(classList)
# 3 如果不满足上面两者,求最优特征
bestFeature = chooseBestFeatureToSplit(dataSet,labels)
bestFeatureLabel = labels[bestFeature]
myTree = {bestFeatureLabel: {}}
del (labels[bestFeature])
featurValues = [example[bestFeature] for example in dataSet]
uniqueVals = set(featurValues)
# 使用递归的方法,获得整个树
for value in uniqueVals:
subLabels = labels[:]
myTree[bestFeatureLabel][value] = createTree(splitDataSet(dataSet, bestFeature, value), subLabels)
return myTree def classify(inputTree, featLabels, testVec):
firstStr = list(inputTree.keys())[0]
secondDict = inputTree[firstStr]
featIndex = featLabels.index(firstStr)
for key in secondDict.keys():
if testVec[featIndex] == key:
if type(secondDict[key]).__name__ == 'dict':
classLabel = classify(secondDict[key], featLabels, testVec)
else:
classLabel = secondDict[key]
return classLabel def classifyAll(inputTree, featLabels, testDataSet):
classLabelAll = []
for testVec in testDataSet:
classLabelAll.append(classify(inputTree, featLabels, testVec))
return classLabelAll def storeTree(inputTree, filename):
import pickle
fw = open(filename, 'wb')
pickle.dump(inputTree, fw)
fw.close() def grabTree(filename):
import pickle
fr = open(filename, 'rb')
return pickle.load(fr) def main():
# 读取数据集
labels, dataSet = readDataset(file_path=r'D:\test.csv', file_mode='r')
labels_tmp = labels[:] # 拷贝,createTree会改变labels
desicionTree = createTree(dataSet, labels_tmp)
storeTree(desicionTree, 'classifierStorage.txt')
desicionTree = grabTree('classifierStorage.txt')
treePlotter.createPlot(desicionTree)
testSet = [['youth', 'high', 'no', 'fair', 'no']]
print('classifyResult:\n', classifyAll(desicionTree, labels, testSet)) if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
五、测试结果及结论
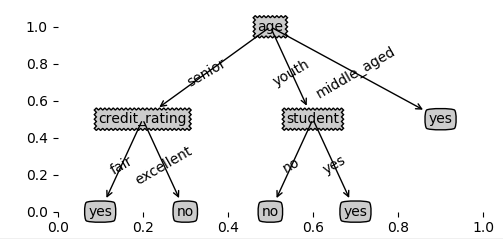
我们从上面求解信息增益的公式中,其实可以看出,信息增益准则其实是对可取值数目较多的属性有所偏好!
现在假如我们把数据集中的“编号”也作为一个候选划分属性。我们可以算出“编号”的信息增益是0.998
因为每一个样本的编号都是不同的(由于编号独特唯一,条件熵为0了,每一个结点中只有一类,纯度非常高啊),也就是说,来了一个预测样本,你只要告诉我编号,其它特征就没有用了,这样生成的决策树显然不具有泛化能力。
参考链接:
http://www.cnblogs.com/wsine/p/5180310.html
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/26760551
day-8 python自带库实现ID3决策树算法的更多相关文章
- day-9 sklearn库和python自带库实现最近邻KNN算法
K最近邻(k-Nearest Neighbor,KNN)分类算法,是一个理论上比较成熟的方法,也是最简单的机器学习算法之一.该方法的思路是:如果一个样本在特征空间中的k个最相似(即特征空间中最邻近)的 ...
- python机器学习笔记 ID3决策树算法实战
前面学习了决策树的算法原理,这里继续对代码进行深入学习,并掌握ID3的算法实践过程. ID3算法是一种贪心算法,用来构造决策树,ID3算法起源于概念学习系统(CLS),以信息熵的下降速度为选取测试属性 ...
- 机器学习-ID3决策树算法(附matlab/octave代码)
ID3决策树算法是基于信息增益来构建的,信息增益可以由训练集的信息熵算得,这里举一个简单的例子 data=[心情好 天气好 出门 心情好 天气不好 出门 心情不好 天气好 出门 心情不好 天气不好 ...
- python自带库及第三方库api察看
今天发现一个很有意思的功能,python自带了所有库的文档查看器,配置如下: 配置pydoc服务,cmd中输入如下代码: python –m pydoc –p 1234 回车后 ,使用过程中,该窗口不 ...
- ID3决策树算法原理及C++实现(其中代码转自别人的博客)
分类是数据挖掘中十分重要的组成部分.分类作为一种无监督学习方式被广泛的使用. 之前关于"数据挖掘中十大经典算法"中,基于ID3核心思想的分类算法C4.5榜上有名.所以不难看出ID3 ...
- day-11 python自带库实现2层简单神经网络算法
深度神经网络算法,是基于神经网络算法的一种拓展,其层数更深,达到多层,本文以简单神经网络为例,利用梯度下降算法进行反向更新来训练神经网络权重和偏向参数,文章最后,基于Python 库实现了一个简单神经 ...
- ID3决策树算法实现(Python版)
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- from numpy import * import numpy as np import pandas as pd from math import l ...
- 决策树算法——ID3
决策树算法是一种有监督的分类学习算法.利用经验数据建立最优分类树,再用分类树预测未知数据. 例子:利用学生上课与作业状态预测考试成绩. 上述例子包含两个可以观测的属性:上课是否认真,作业是否认真,并以 ...
- 机器学习回顾篇(7):决策树算法(ID3、C4.5)
.caret, .dropup > .btn > .caret { border-top-color: #000 !important; } .label { border: 1px so ...
随机推荐
- php中的变量作用域
<?php include_once $_SERVER['DOCUMENT_ROOT'].'/includes/db.inc.php'; function totalJokes() { try{ ...
- Restframework的认证,权限,节流
1.认证 流程:请求到达REST framework的时候,会对request进行二次封装,在封装的过程中会对客户端发送过来的request封装进认证,选择,解析等功能.request方法封装完成之后 ...
- 搭建Hadoop2.6.0+Eclipse开发调试环境
上一篇在win7虚拟机下搭建了hadoop2.6.0伪分布式环境.为了开发调试方便,本文介绍在eclipse下搭建开发环境,连接和提交任务到hadoop集群. 1. 环境 Eclipse版本Luna ...
- [SHOI2015]脑洞治疗仪(恶心的线段树,区间最大子段和)
题目描述: 曾经发明了自动刷题机的发明家 SHTSC 又公开了他的新发明:脑洞治疗仪--一种可以治疗他因为发明而日益增大的脑洞的神秘装置. 为了简单起见,我们将大脑视作一个 01 序列.11代表这个位 ...
- oracle-sql优化-通过分组和缓存减少不必要的读
环境:aix 7.1,oracle12.1.0.2 cdb 优化前SQL select * from (select row_.*, rownum rownum_ from (select '弱覆盖' ...
- Linux入门-第五周
1.磁盘lvm管理,完成下面要求,并写出详细过程: 1) 创建一个至少有两个PV组成的大小为20G的名为testvg的VG;要求PE大小 为16MB, 而后在卷组中创建大小为5G的逻辑卷testlv; ...
- centos7-mongodb3.4.6集群的搭建
0.需要环境 安装包:mongodb-linux-x86_64-3.4.6.tgz 安装路径:/usr/mongodb 服务器: 192.168.177.131/132/133 mongos 2000 ...
- js实现区县联动
1. 引入区县联动函数如下,将provinceList中数据改为需要联动的数据信息 var addressInit = function(_cmbProvince, _cmbCity, _cmbAre ...
- 开通CSDN博客的原因
为什么要写博客? 提供持续学习的动力 例如,我为自己设限每天 ...
- Python基本图形绘制
turtle的一个画布空间最小单位是像素 turtle的绘制窗体:turtle.stup(width,heigth,startx,starty) 四个参数中后两个可选 turtle空间坐标体系:tur ...
