Tensorflow学习(练习)—CPU训练模型
Mask R-CNN - Train on Shapes Dataset
This notebook shows how to train Mask R-CNN on your own dataset. To keep things simple we use a synthetic dataset of shapes (squares, triangles, and circles) which enables fast training. You'd still need a GPU, though, because the network backbone is a Resnet101, which would be too slow to train on a CPU. On a GPU, you can start to get okay-ish results in a few minutes, and good results in less than an hour.
The code of the Shapes dataset is included below. It generates images on the fly, so it doesn't require downloading any data. And it can generate images of any size, so we pick a small image size to train faster.
--------------------------------------------------------------------
import os
import sys
import random
import math
import re
import time
import numpy as np
import cv2
import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Root directory of the project
ROOT_DIR = os.path.abspath("../../")
# Import Mask RCNN
sys.path.append(ROOT_DIR) # To find local version of the library
from mrcnn.config import Config
from mrcnn import utils
import mrcnn.model as modellib
from mrcnn import visualize
from mrcnn.model import log
%matplotlib inline
# Directory to save logs and trained model
MODEL_DIR = os.path.join(ROOT_DIR, "logs")
# Local path to trained weights file
COCO_MODEL_PATH = os.path.join(ROOT_DIR, "mask_rcnn_coco.h5")
# Download COCO trained weights from Releases if needed
if not os.path.exists(COCO_MODEL_PATH):
utils.download_trained_weights(COCO_MODEL_PATH)
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Configurations
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
class ShapesConfig(Config):
"""Configuration for training on the toy shapes dataset.
Derives from the base Config class and overrides values specific
to the toy shapes dataset.
"""
# Give the configuration a recognizable name
NAME = "shapes"
# Train on 1 GPU and 8 images per GPU. We can put multiple images on each
# GPU because the images are small. Batch size is 8 (GPUs * images/GPU).
GPU_COUNT = 1
IMAGES_PER_GPU = 8
# Number of classes (including background)
NUM_CLASSES = 1 + 3 # background + 3 shapes
# Use small images for faster training. Set the limits of the small side
# the large side, and that determines the image shape.
IMAGE_MIN_DIM = 128
IMAGE_MAX_DIM = 128
# Use smaller anchors because our image and objects are small
RPN_ANCHOR_SCALES = (8, 16, 32, 64, 128) # anchor side in pixels
# Reduce training ROIs per image because the images are small and have
# few objects. Aim to allow ROI sampling to pick 33% positive ROIs.
TRAIN_ROIS_PER_IMAGE = 32
# Use a small epoch since the data is simple
STEPS_PER_EPOCH = 100
# use small validation steps since the epoch is small
VALIDATION_STEPS = 5
config = ShapesConfig()
config.display()
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
运行结果:
Configurations:
BACKBONE resnet101
BACKBONE_STRIDES [4, 8, 16, 32, 64]
BATCH_SIZE 8
BBOX_STD_DEV [0.1 0.1 0.2 0.2]
COMPUTE_BACKBONE_SHAPE None
DETECTION_MAX_INSTANCES 100
DETECTION_MIN_CONFIDENCE 0.7
DETECTION_NMS_THRESHOLD 0.3
FPN_CLASSIF_FC_LAYERS_SIZE 1024
GPU_COUNT 1
GRADIENT_CLIP_NORM 5.0
IMAGES_PER_GPU 8
IMAGE_MAX_DIM 128
IMAGE_META_SIZE 16
IMAGE_MIN_DIM 128
IMAGE_MIN_SCALE 0
IMAGE_RESIZE_MODE square
IMAGE_SHAPE [128 128 3]
LEARNING_MOMENTUM 0.9
LEARNING_RATE 0.001
LOSS_WEIGHTS {'rpn_class_loss': 1.0, 'rpn_bbox_loss': 1.0, 'mrcnn_class_loss': 1.0, 'mrcnn_bbox_loss': 1.0, 'mrcnn_mask_loss': 1.0}
MASK_POOL_SIZE 14
MASK_SHAPE [28, 28]
MAX_GT_INSTANCES 100
MEAN_PIXEL [123.7 116.8 103.9]
MINI_MASK_SHAPE (56, 56)
NAME shapes
NUM_CLASSES 4
POOL_SIZE 7
POST_NMS_ROIS_INFERENCE 1000
POST_NMS_ROIS_TRAINING 2000
ROI_POSITIVE_RATIO 0.33
RPN_ANCHOR_RATIOS [0.5, 1, 2]
RPN_ANCHOR_SCALES (8, 16, 32, 64, 128)
RPN_ANCHOR_STRIDE 1
RPN_BBOX_STD_DEV [0.1 0.1 0.2 0.2]
RPN_NMS_THRESHOLD 0.7
RPN_TRAIN_ANCHORS_PER_IMAGE 256
STEPS_PER_EPOCH 100
TOP_DOWN_PYRAMID_SIZE 256
TRAIN_BN False
TRAIN_ROIS_PER_IMAGE 32
USE_MINI_MASK True
USE_RPN_ROIS True
VALIDATION_STEPS 5
WEIGHT_DECAY 0.0001
--------------------------------------------------------
Notebook Preferences
def get_ax(rows=1, cols=1, size=8):
"""Return a Matplotlib Axes array to be used in
all visualizations in the notebook. Provide a
central point to control graph sizes.
Change the default size attribute to control the size
of rendered images
"""
_, ax = plt.subplots(rows, cols, figsize=(size*cols, size*rows))
return ax
--------------------------------------------------------------------
Dataset
Create a synthetic dataset
Extend the Dataset class and add a method to load the shapes dataset, load_shapes(), and override the following methods:
- load_image()
- load_mask()
- image_reference()
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
class ShapesDataset(utils.Dataset):
"""Generates the shapes synthetic dataset. The dataset consists of simple
shapes (triangles, squares, circles) placed randomly on a blank surface.
The images are generated on the fly. No file access required.
"""
def load_shapes(self, count, height, width):
"""Generate the requested number of synthetic images.
count: number of images to generate.
height, width: the size of the generated images.
"""
# Add classes
self.add_class("shapes", 1, "square")
self.add_class("shapes", 2, "circle")
self.add_class("shapes", 3, "triangle")
# Add images
# Generate random specifications of images (i.e. color and
# list of shapes sizes and locations). This is more compact than
# actual images. Images are generated on the fly in load_image().
for i in range(count):
bg_color, shapes = self.random_image(height, width)
self.add_image("shapes", image_id=i, path=None,
width=width, height=height,
bg_color=bg_color, shapes=shapes)
def load_image(self, image_id):
"""Generate an image from the specs of the given image ID.
Typically this function loads the image from a file, but
in this case it generates the image on the fly from the
specs in image_info.
"""
info = self.image_info[image_id]
bg_color = np.array(info['bg_color']).reshape([1, 1, 3])
image = np.ones([info['height'], info['width'], 3], dtype=np.uint8)
image = image * bg_color.astype(np.uint8)
for shape, color, dims in info['shapes']:
image = self.draw_shape(image, shape, dims, color)
return image
def image_reference(self, image_id):
"""Return the shapes data of the image."""
info = self.image_info[image_id]
if info["source"] == "shapes":
return info["shapes"]
else:
super(self.__class__).image_reference(self, image_id)
def load_mask(self, image_id):
"""Generate instance masks for shapes of the given image ID.
"""
info = self.image_info[image_id]
shapes = info['shapes']
count = len(shapes)
mask = np.zeros([info['height'], info['width'], count], dtype=np.uint8)
for i, (shape, _, dims) in enumerate(info['shapes']):
mask[:, :, i:i+1] = self.draw_shape(mask[:, :, i:i+1].copy(),
shape, dims, 1)
# Handle occlusions
occlusion = np.logical_not(mask[:, :, -1]).astype(np.uint8)
for i in range(count-2, -1, -1):
mask[:, :, i] = mask[:, :, i] * occlusion
occlusion = np.logical_and(occlusion, np.logical_not(mask[:, :, i]))
# Map class names to class IDs.
class_ids = np.array([self.class_names.index(s[0]) for s in shapes])
return mask.astype(np.bool), class_ids.astype(np.int32)
def draw_shape(self, image, shape, dims, color):
"""Draws a shape from the given specs."""
# Get the center x, y and the size s
x, y, s = dims
if shape == 'square':
cv2.rectangle(image, (x-s, y-s), (x+s, y+s), color, -1)
elif shape == "circle":
cv2.circle(image, (x, y), s, color, -1)
elif shape == "triangle":
points = np.array([[(x, y-s),
(x-s/math.sin(math.radians(60)), y+s),
(x+s/math.sin(math.radians(60)), y+s),
]], dtype=np.int32)
cv2.fillPoly(image, points, color)
return image
def random_shape(self, height, width):
"""Generates specifications of a random shape that lies within
the given height and width boundaries.
Returns a tuple of three valus:
* The shape name (square, circle, ...)
* Shape color: a tuple of 3 values, RGB.
* Shape dimensions: A tuple of values that define the shape size
and location. Differs per shape type.
"""
# Shape
shape = random.choice(["square", "circle", "triangle"])
# Color
color = tuple([random.randint(0, 255) for _ in range(3)])
# Center x, y
buffer = 20
y = random.randint(buffer, height - buffer - 1)
x = random.randint(buffer, width - buffer - 1)
# Size
s = random.randint(buffer, height//4)
return shape, color, (x, y, s)
def random_image(self, height, width):
"""Creates random specifications of an image with multiple shapes.
Returns the background color of the image and a list of shape
specifications that can be used to draw the image.
"""
# Pick random background color
bg_color = np.array([random.randint(0, 255) for _ in range(3)])
# Generate a few random shapes and record their
# bounding boxes
shapes = []
boxes = []
N = random.randint(1, 4)
for _ in range(N):
shape, color, dims = self.random_shape(height, width)
shapes.append((shape, color, dims))
x, y, s = dims
boxes.append([y-s, x-s, y+s, x+s])
# Apply non-max suppression wit 0.3 threshold to avoid
# shapes covering each other
keep_ixs = utils.non_max_suppression(np.array(boxes), np.arange(N), 0.3)
shapes = [s for i, s in enumerate(shapes) if i in keep_ixs]
return bg_color, shapes
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Training dataset
dataset_train = ShapesDataset()
dataset_train.load_shapes(500, config.IMAGE_SHAPE[0], config.IMAGE_SHAPE[1])
dataset_train.prepare()
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
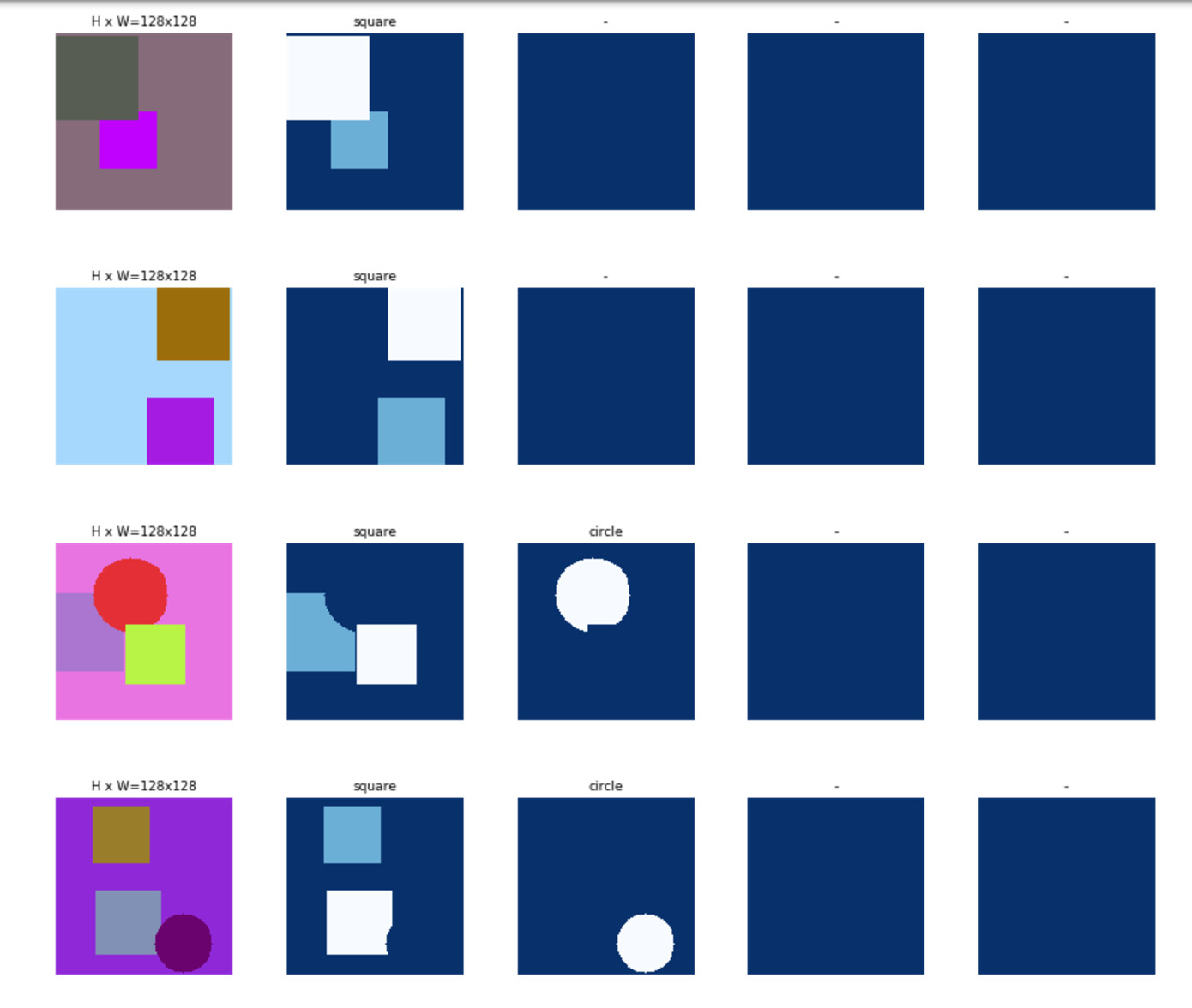
# Load and display random samples
image_ids = np.random.choice(dataset_train.image_ids, 4)
for image_id in image_ids:
image = dataset_train.load_image(image_id)
mask, class_ids = dataset_train.load_mask(image_id)
visualize.display_top_masks(image, mask, class_ids, dataset_train.class_names)
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Ceate Model
------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Create model in training mode
model = modellib.MaskRCNN(mode="training", config=config,model_dir=MODEL_DIR)
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
----------------------------------------------------------------------
# Which weights to start with?
init_with = "coco" # imagenet, coco, or last
if init_with == "imagenet":
model.load_weights(model.get_imagenet_weights(), by_name=True)
elif init_with == "coco":
# Load weights trained on MS COCO, but skip layers that
# are different due to the different number of classes
# See README for instructions to download the COCO weights
model.load_weights(COCO_MODEL_PATH, by_name=True,
exclude=["mrcnn_class_logits", "mrcnn_bbox_fc",
"mrcnn_bbox", "mrcnn_mask"])
elif init_with == "last":
# Load the last model you trained and continue training
model.load_weights(model.find_last(), by_name=True)
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Training¶
Train in two stages:
Only the heads. Here we're freezing all the backbone layers and training only the randomly initialized layers (i.e. the ones that we didn't use pre-trained weights from MS COCO). To train only the head layers, pass
layers='heads'to thetrain()function.Fine-tune all layers. For this simple example it's not necessary, but we're including it to show the process. Simply pass
layers="allto train all layers.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Train the head branches
# Passing layers="heads" freezes all layers except the head
# layers. You can also pass a regular expression to select
# which layers to train by name pattern.
model.train(dataset_train, dataset_val,
learning_rate=config.LEARNING_RATE,
epochs=1,
layers='heads')
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
Starting at epoch 0. LR=0.001
Checkpoint Path: C:\Users\luo\tensorflow\Mask_RCNN-master\logs\shapes20180817T1409\mask_rcnn_shapes_{epoch:04d}.h5
Selecting layers to train
fpn_c5p5 (Conv2D)
fpn_c4p4 (Conv2D)
fpn_c3p3 (Conv2D)
fpn_c2p2 (Conv2D)
fpn_p5 (Conv2D)
fpn_p2 (Conv2D)
fpn_p3 (Conv2D)
fpn_p4 (Conv2D)
In model: rpn_model
rpn_conv_shared (Conv2D)
rpn_class_raw (Conv2D)
rpn_bbox_pred (Conv2D)
mrcnn_mask_conv1 (TimeDistributed)
mrcnn_mask_bn1 (TimeDistributed)
mrcnn_mask_conv2 (TimeDistributed)
mrcnn_mask_bn2 (TimeDistributed)
mrcnn_class_conv1 (TimeDistributed)
mrcnn_class_bn1 (TimeDistributed)
mrcnn_mask_conv3 (TimeDistributed)
mrcnn_mask_bn3 (TimeDistributed)
mrcnn_class_conv2 (TimeDistributed)
mrcnn_class_bn2 (TimeDistributed)
mrcnn_mask_conv4 (TimeDistributed)
mrcnn_mask_bn4 (TimeDistributed)
mrcnn_bbox_fc (TimeDistributed)
mrcnn_mask_deconv (TimeDistributed)
mrcnn_class_logits (TimeDistributed)
mrcnn_mask (TimeDistributed)
E:\Anaconda3\install1\lib\site-packages\tensorflow\python\ops\gradients_impl.py:97: UserWarning: Converting sparse IndexedSlices to a dense Tensor of unknown shape. This may consume a large amount of memory.
"Converting sparse IndexedSlices to a dense Tensor of unknown shape. "
Epoch 1/1
100/100 [==============================] - 2824s 28s/step - loss: 1.5765 - rpn_class_loss: 0.0302 - rpn_bbox_loss: 0.5675 - mrcnn_class_loss: 0.3577 - mrcnn_bbox_loss: 0.3586 - mrcnn_mask_loss: 0.2625 - val_loss: 0.9420 - val_rpn_class_loss: 0.0130 - val_rpn_bbox_loss: 0.4263 - val_mrcnn_class_loss: 0.1708 - val_mrcnn_bbox_loss: 0.1679 - val_mrcnn_mask_loss: 0.1640
-------------------------------------------------------------------
# Fine tune all layers
# Passing layers="all" trains all layers. You can also
# pass a regular expression to select which layers to
# train by name pattern.
model.train(dataset_train, dataset_val,
learning_rate=config.LEARNING_RATE / 10,
epochs=1,
layers="all")
-------------------------------------------------------------------
Starting at epoch 1. LR=0.0001
Checkpoint Path: C:\Users\luo\tensorflow\Mask_RCNN-master\logs\shapes20180817T1409\mask_rcnn_shapes_{epoch:04d}.h5
Selecting layers to train
conv1 (Conv2D)
bn_conv1 (BatchNorm)
res2a_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn2a_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res2a_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn2a_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res2a_branch2c (Conv2D)
res2a_branch1 (Conv2D)
bn2a_branch2c (BatchNorm)
bn2a_branch1 (BatchNorm)
res2b_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn2b_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res2b_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn2b_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res2b_branch2c (Conv2D)
bn2b_branch2c (BatchNorm)
res2c_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn2c_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res2c_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn2c_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res2c_branch2c (Conv2D)
bn2c_branch2c (BatchNorm)
res3a_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn3a_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res3a_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn3a_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res3a_branch2c (Conv2D)
res3a_branch1 (Conv2D)
bn3a_branch2c (BatchNorm)
bn3a_branch1 (BatchNorm)
res3b_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn3b_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res3b_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn3b_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res3b_branch2c (Conv2D)
bn3b_branch2c (BatchNorm)
res3c_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn3c_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res3c_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn3c_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res3c_branch2c (Conv2D)
bn3c_branch2c (BatchNorm)
res3d_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn3d_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res3d_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn3d_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res3d_branch2c (Conv2D)
bn3d_branch2c (BatchNorm)
res4a_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn4a_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res4a_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn4a_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res4a_branch2c (Conv2D)
res4a_branch1 (Conv2D)
bn4a_branch2c (BatchNorm)
bn4a_branch1 (BatchNorm)
res4b_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn4b_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res4b_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn4b_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res4b_branch2c (Conv2D)
bn4b_branch2c (BatchNorm)
res4c_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn4c_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res4c_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn4c_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res4c_branch2c (Conv2D)
bn4c_branch2c (BatchNorm)
res4d_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn4d_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res4d_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn4d_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res4d_branch2c (Conv2D)
bn4d_branch2c (BatchNorm)
res4e_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn4e_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res4e_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn4e_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res4e_branch2c (Conv2D)
bn4e_branch2c (BatchNorm)
res4f_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn4f_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res4f_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn4f_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res4f_branch2c (Conv2D)
bn4f_branch2c (BatchNorm)
res4g_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn4g_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res4g_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn4g_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res4g_branch2c (Conv2D)
bn4g_branch2c (BatchNorm)
res4h_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn4h_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res4h_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn4h_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res4h_branch2c (Conv2D)
bn4h_branch2c (BatchNorm)
res4i_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn4i_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res4i_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn4i_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res4i_branch2c (Conv2D)
bn4i_branch2c (BatchNorm)
res4j_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn4j_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res4j_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn4j_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res4j_branch2c (Conv2D)
bn4j_branch2c (BatchNorm)
res4k_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn4k_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res4k_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn4k_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res4k_branch2c (Conv2D)
bn4k_branch2c (BatchNorm)
res4l_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn4l_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res4l_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn4l_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res4l_branch2c (Conv2D)
bn4l_branch2c (BatchNorm)
res4m_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn4m_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res4m_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn4m_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res4m_branch2c (Conv2D)
bn4m_branch2c (BatchNorm)
res4n_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn4n_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res4n_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn4n_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res4n_branch2c (Conv2D)
bn4n_branch2c (BatchNorm)
res4o_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn4o_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res4o_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn4o_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res4o_branch2c (Conv2D)
bn4o_branch2c (BatchNorm)
res4p_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn4p_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res4p_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn4p_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res4p_branch2c (Conv2D)
bn4p_branch2c (BatchNorm)
res4q_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn4q_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res4q_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn4q_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res4q_branch2c (Conv2D)
bn4q_branch2c (BatchNorm)
res4r_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn4r_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res4r_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn4r_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res4r_branch2c (Conv2D)
bn4r_branch2c (BatchNorm)
res4s_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn4s_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res4s_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn4s_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res4s_branch2c (Conv2D)
bn4s_branch2c (BatchNorm)
res4t_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn4t_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res4t_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn4t_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res4t_branch2c (Conv2D)
bn4t_branch2c (BatchNorm)
res4u_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn4u_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res4u_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn4u_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res4u_branch2c (Conv2D)
bn4u_branch2c (BatchNorm)
res4v_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn4v_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res4v_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn4v_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res4v_branch2c (Conv2D)
bn4v_branch2c (BatchNorm)
res4w_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn4w_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res4w_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn4w_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res4w_branch2c (Conv2D)
bn4w_branch2c (BatchNorm)
res5a_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn5a_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res5a_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn5a_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res5a_branch2c (Conv2D)
res5a_branch1 (Conv2D)
bn5a_branch2c (BatchNorm)
bn5a_branch1 (BatchNorm)
res5b_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn5b_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res5b_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn5b_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res5b_branch2c (Conv2D)
bn5b_branch2c (BatchNorm)
res5c_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn5c_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res5c_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn5c_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res5c_branch2c (Conv2D)
bn5c_branch2c (BatchNorm)
fpn_c5p5 (Conv2D)
fpn_c4p4 (Conv2D)
fpn_c3p3 (Conv2D)
fpn_c2p2 (Conv2D)
fpn_p5 (Conv2D)
fpn_p2 (Conv2D)
fpn_p3 (Conv2D)
fpn_p4 (Conv2D)
In model: rpn_model
rpn_conv_shared (Conv2D)
rpn_class_raw (Conv2D)
rpn_bbox_pred (Conv2D)
mrcnn_mask_conv1 (TimeDistributed)
mrcnn_mask_bn1 (TimeDistributed)
mrcnn_mask_conv2 (TimeDistributed)
mrcnn_mask_bn2 (TimeDistributed)
mrcnn_class_conv1 (TimeDistributed)
mrcnn_class_bn1 (TimeDistributed)
mrcnn_mask_conv3 (TimeDistributed)
mrcnn_mask_bn3 (TimeDistributed)
mrcnn_class_conv2 (TimeDistributed)
mrcnn_class_bn2 (TimeDistributed)
mrcnn_mask_conv4 (TimeDistributed)
mrcnn_mask_bn4 (TimeDistributed)
mrcnn_bbox_fc (TimeDistributed)
mrcnn_mask_deconv (TimeDistributed)
mrcnn_class_logits (TimeDistributed)
mrcnn_mask (TimeDistributed)
E:\Anaconda3\install1\lib\site-packages\tensorflow\python\ops\gradients_impl.py:97: UserWarning: Converting sparse IndexedSlices to a dense Tensor of unknown shape. This may consume a large amount of memory.
"Converting sparse IndexedSlices to a dense Tensor of unknown shape. "
# Save weights
# Typically not needed because callbacks save after every epoch
# Uncomment to save manually
# model_path = os.path.join(MODEL_DIR, "mask_rcnn_shapes.h5")
# model.keras_model.save_weights(model_path)
Detection
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
class InferenceConfig(ShapesConfig):
GPU_COUNT = 1
IMAGES_PER_GPU = 1
inference_config = InferenceConfig()
# Recreate the model in inference mode
model = modellib.MaskRCNN(mode="inference",
config=inference_config,
model_dir=MODEL_DIR)
# Get path to saved weights
# Either set a specific path or find last trained weights
# model_path = os.path.join(ROOT_DIR, ".h5 file name here")
model_path = model.find_last()
# Load trained weights
print("Loading weights from ", model_path)
model.load_weights(model_path, by_name=True)
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
运行结果:
Loading weights from C:\Users\luo\tensorflow\Mask_RCNN-master\logs\shapes20180817T1459\mask_rcnn_shapes_0001.h5 ----------------------------------------------------
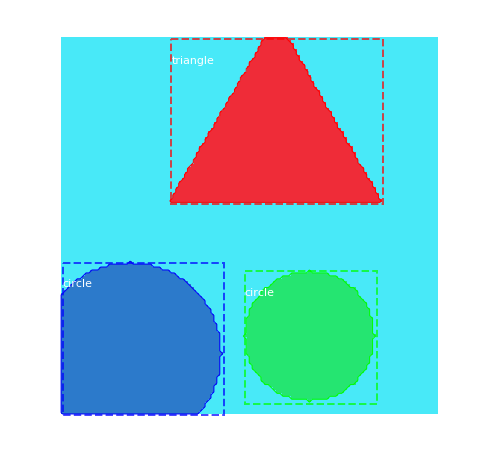
# Test on a random image
image_id = random.choice(dataset_val.image_ids)
original_image, image_meta, gt_class_id, gt_bbox, gt_mask =\
modellib.load_image_gt(dataset_val, inference_config,
image_id, use_mini_mask=False)
log("original_image", original_image)
log("image_meta", image_meta)
log("gt_class_id", gt_class_id)
log("gt_bbox", gt_bbox)
log("gt_mask", gt_mask)
visualize.display_instances(original_image, gt_bbox, gt_mask, gt_class_id, dataset_train.class_names, figsize=(8, 8))
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
original_image shape: (128, 128, 3) min: 72.00000 max: 248.00000 uint8
image_meta shape: (16,) min: 0.00000 max: 128.00000 int32
gt_class_id shape: (3,) min: 2.00000 max: 3.00000 int32
gt_bbox shape: (3, 4) min: 0.00000 max: 128.00000 int32
gt_mask shape: (128, 128, 3) min: 0.00000 max: 1.00000 bool
Evaluation
-----------------------------------------------------
# Compute VOC-Style mAP @ IoU=0.5 # Running on 10 images. Increase for better accuracy. image_ids = np.random.choice(dataset_val.image_ids, 10) APs = [] for image_id in image_ids: # Load image and ground truth data image, image_meta, gt_class_id, gt_bbox, gt_mask =\ modellib.load_image_gt(dataset_val, inference_config, image_id, use_mini_mask=False) molded_images = np.expand_dims(modellib.mold_image(image, inference_config), 0) # Run object detection results = model.detect([image], verbose=0) r = results[0] # Compute AP AP, precisions, recalls, overlaps =\ utils.compute_ap(gt_bbox, gt_class_id, gt_mask, r["rois"], r["class_ids"], r["scores"], r['masks']) APs.append(AP) print("mAP: ", np.mean(APs))
----------------------------------------------------
运行结果:
mAP: 0.966666667163372

train_shapesLast Checkpoint: 1 小时前(autosaved) Logout
Logout
Code
Markdown
Raw NBConvert
Heading
-
Mask R-CNN - Train on Shapes Dataset
This notebook shows how to train Mask R-CNN on your own dataset. To keep things simple we use a synthetic dataset of shapes (squares, triangles, and circles) which enables fast training. You'd still need a GPU, though, because the network backbone is a Resnet101, which would be too slow to train on a CPU. On a GPU, you can start to get okay-ish results in a few minutes, and good results in less than an hour.
The code of the Shapes dataset is included below. It generates images on the fly, so it doesn't require downloading any data. And it can generate images of any size, so we pick a small image size to train faster.
import os
import sys
import random
import math
import re
import time
import numpy as np
import cv2
import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Root directory of the project
ROOT_DIR = os.path.abspath("../../")
# Import Mask RCNN
sys.path.append(ROOT_DIR) # To find local version of the library
from mrcnn.config import Config
from mrcnn import utils
import mrcnn.model as modellib
from mrcnn import visualize
from mrcnn.model import log
%matplotlib inline
# Directory to save logs and trained model
MODEL_DIR = os.path.join(ROOT_DIR, "logs")
# Local path to trained weights file
COCO_MODEL_PATH = os.path.join(ROOT_DIR, "mask_rcnn_coco.h5")
# Download COCO trained weights from Releases if needed
if not os.path.exists(COCO_MODEL_PATH):
utils.download_trained_weights(COCO_MODEL_PATH)
Configurations
class ShapesConfig(Config):
"""Configuration for training on the toy shapes dataset.
Derives from the base Config class and overrides values specific
to the toy shapes dataset.
"""
# Give the configuration a recognizable name
NAME = "shapes"
# Train on 1 GPU and 8 images per GPU. We can put multiple images on each
# GPU because the images are small. Batch size is 8 (GPUs * images/GPU).
GPU_COUNT = 1
IMAGES_PER_GPU = 8
# Number of classes (including background)
NUM_CLASSES = 1 + 3 # background + 3 shapes
# Use small images for faster training. Set the limits of the small side
# the large side, and that determines the image shape.
IMAGE_MIN_DIM = 128
IMAGE_MAX_DIM = 128
# Use smaller anchors because our image and objects are small
RPN_ANCHOR_SCALES = (8, 16, 32, 64, 128) # anchor side in pixels
# Reduce training ROIs per image because the images are small and have
# few objects. Aim to allow ROI sampling to pick 33% positive ROIs.
TRAIN_ROIS_PER_IMAGE = 32
# Use a small epoch since the data is simple
STEPS_PER_EPOCH = 100
# use small validation steps since the epoch is small
VALIDATION_STEPS = 5
config = ShapesConfig()
config.display()
Configurations:
BACKBONE resnet101
BACKBONE_STRIDES [4, 8, 16, 32, 64]
BATCH_SIZE 8
BBOX_STD_DEV [0.1 0.1 0.2 0.2]
COMPUTE_BACKBONE_SHAPE None
DETECTION_MAX_INSTANCES 100
DETECTION_MIN_CONFIDENCE 0.7
DETECTION_NMS_THRESHOLD 0.3
FPN_CLASSIF_FC_LAYERS_SIZE 1024
GPU_COUNT 1
GRADIENT_CLIP_NORM 5.0
IMAGES_PER_GPU 8
IMAGE_MAX_DIM 128
IMAGE_META_SIZE 16
IMAGE_MIN_DIM 128
IMAGE_MIN_SCALE 0
IMAGE_RESIZE_MODE square
IMAGE_SHAPE [128 128 3]
LEARNING_MOMENTUM 0.9
LEARNING_RATE 0.001
LOSS_WEIGHTS {'rpn_class_loss': 1.0, 'rpn_bbox_loss': 1.0, 'mrcnn_class_loss': 1.0, 'mrcnn_bbox_loss': 1.0, 'mrcnn_mask_loss': 1.0}
MASK_POOL_SIZE 14
MASK_SHAPE [28, 28]
MAX_GT_INSTANCES 100
MEAN_PIXEL [123.7 116.8 103.9]
MINI_MASK_SHAPE (56, 56)
NAME shapes
NUM_CLASSES 4
POOL_SIZE 7
POST_NMS_ROIS_INFERENCE 1000
POST_NMS_ROIS_TRAINING 2000
ROI_POSITIVE_RATIO 0.33
RPN_ANCHOR_RATIOS [0.5, 1, 2]
RPN_ANCHOR_SCALES (8, 16, 32, 64, 128)
RPN_ANCHOR_STRIDE 1
RPN_BBOX_STD_DEV [0.1 0.1 0.2 0.2]
RPN_NMS_THRESHOLD 0.7
RPN_TRAIN_ANCHORS_PER_IMAGE 256
STEPS_PER_EPOCH 100
TOP_DOWN_PYRAMID_SIZE 256
TRAIN_BN False
TRAIN_ROIS_PER_IMAGE 32
USE_MINI_MASK True
USE_RPN_ROIS True
VALIDATION_STEPS 5
WEIGHT_DECAY 0.0001
Notebook Preferences
def get_ax(rows=1, cols=1, size=8):
"""Return a Matplotlib Axes array to be used in
all visualizations in the notebook. Provide a
central point to control graph sizes.
Change the default size attribute to control the size
of rendered images
"""
_, ax = plt.subplots(rows, cols, figsize=(size*cols, size*rows))
return ax
Dataset
Create a synthetic dataset
Extend the Dataset class and add a method to load the shapes dataset, load_shapes(), and override the following methods:
- load_image()
- load_mask()
- image_reference()
class ShapesDataset(utils.Dataset):
"""Generates the shapes synthetic dataset. The dataset consists of simple
shapes (triangles, squares, circles) placed randomly on a blank surface.
The images are generated on the fly. No file access required.
"""
def load_shapes(self, count, height, width):
"""Generate the requested number of synthetic images.
count: number of images to generate.
height, width: the size of the generated images.
"""
# Add classes
self.add_class("shapes", 1, "square")
self.add_class("shapes", 2, "circle")
self.add_class("shapes", 3, "triangle")
# Add images
# Generate random specifications of images (i.e. color and
# list of shapes sizes and locations). This is more compact than
# actual images. Images are generated on the fly in load_image().
for i in range(count):
bg_color, shapes = self.random_image(height, width)
self.add_image("shapes", image_id=i, path=None,
width=width, height=height,
bg_color=bg_color, shapes=shapes)
def load_image(self, image_id):
"""Generate an image from the specs of the given image ID.
Typically this function loads the image from a file, but
in this case it generates the image on the fly from the
specs in image_info.
"""
info = self.image_info[image_id]
bg_color = np.array(info['bg_color']).reshape([1, 1, 3])
image = np.ones([info['height'], info['width'], 3], dtype=np.uint8)
image = image * bg_color.astype(np.uint8)
for shape, color, dims in info['shapes']:
image = self.draw_shape(image, shape, dims, color)
return image
def image_reference(self, image_id):
"""Return the shapes data of the image."""
info = self.image_info[image_id]
if info["source"] == "shapes":
return info["shapes"]
else:
super(self.__class__).image_reference(self, image_id)
def load_mask(self, image_id):
"""Generate instance masks for shapes of the given image ID.
"""
info = self.image_info[image_id]
shapes = info['shapes']
count = len(shapes)
mask = np.zeros([info['height'], info['width'], count], dtype=np.uint8)
for i, (shape, _, dims) in enumerate(info['shapes']):
mask[:, :, i:i+1] = self.draw_shape(mask[:, :, i:i+1].copy(),
shape, dims, 1)
# Handle occlusions
occlusion = np.logical_not(mask[:, :, -1]).astype(np.uint8)
for i in range(count-2, -1, -1):
mask[:, :, i] = mask[:, :, i] * occlusion
occlusion = np.logical_and(occlusion, np.logical_not(mask[:, :, i]))
# Map class names to class IDs.
class_ids = np.array([self.class_names.index(s[0]) for s in shapes])
return mask.astype(np.bool), class_ids.astype(np.int32)
def draw_shape(self, image, shape, dims, color):
"""Draws a shape from the given specs."""
# Get the center x, y and the size s
x, y, s = dims
if shape == 'square':
cv2.rectangle(image, (x-s, y-s), (x+s, y+s), color, -1)
elif shape == "circle":
cv2.circle(image, (x, y), s, color, -1)
elif shape == "triangle":
points = np.array([[(x, y-s),
(x-s/math.sin(math.radians(60)), y+s),
(x+s/math.sin(math.radians(60)), y+s),
]], dtype=np.int32)
cv2.fillPoly(image, points, color)
return image
def random_shape(self, height, width):
"""Generates specifications of a random shape that lies within
the given height and width boundaries.
Returns a tuple of three valus:
* The shape name (square, circle, ...)
* Shape color: a tuple of 3 values, RGB.
* Shape dimensions: A tuple of values that define the shape size
and location. Differs per shape type.
"""
# Shape
shape = random.choice(["square", "circle", "triangle"])
# Color
color = tuple([random.randint(0, 255) for _ in range(3)])
# Center x, y
buffer = 20
y = random.randint(buffer, height - buffer - 1)
x = random.randint(buffer, width - buffer - 1)
# Size
s = random.randint(buffer, height//4)
return shape, color, (x, y, s)
def random_image(self, height, width):
"""Creates random specifications of an image with multiple shapes.
Returns the background color of the image and a list of shape
specifications that can be used to draw the image.
"""
# Pick random background color
bg_color = np.array([random.randint(0, 255) for _ in range(3)])
# Generate a few random shapes and record their
# bounding boxes
shapes = []
boxes = []
N = random.randint(1, 4)
for _ in range(N):
shape, color, dims = self.random_shape(height, width)
shapes.append((shape, color, dims))
x, y, s = dims
boxes.append([y-s, x-s, y+s, x+s])
# Apply non-max suppression wit 0.3 threshold to avoid
# shapes covering each other
keep_ixs = utils.non_max_suppression(np.array(boxes), np.arange(N), 0.3)
shapes = [s for i, s in enumerate(shapes) if i in keep_ixs]
return bg_color, shapes
# Training dataset
dataset_train = ShapesDataset()
dataset_train.load_shapes(500, config.IMAGE_SHAPE[0], config.IMAGE_SHAPE[1])
dataset_train.prepare()
# Validation dataset
dataset_val = ShapesDataset()
dataset_val.load_shapes(50, config.IMAGE_SHAPE[0], config.IMAGE_SHAPE[1])
dataset_val.prepare()
# Load and display random samples
image_ids = np.random.choice(dataset_train.image_ids, 4)
for image_id in image_ids:
image = dataset_train.load_image(image_id)
mask, class_ids = dataset_train.load_mask(image_id)
visualize.display_top_masks(image, mask, class_ids, dataset_train.class_names)
Ceate Model
# Create model in training mode
model = modellib.MaskRCNN(mode="training", config=config,
model_dir=MODEL_DIR)
# Which weights to start with?
init_with = "coco" # imagenet, coco, or last
if init_with == "imagenet":
model.load_weights(model.get_imagenet_weights(), by_name=True)
elif init_with == "coco":
# Load weights trained on MS COCO, but skip layers that
# are different due to the different number of classes
# See README for instructions to download the COCO weights
model.load_weights(COCO_MODEL_PATH, by_name=True,
exclude=["mrcnn_class_logits", "mrcnn_bbox_fc",
"mrcnn_bbox", "mrcnn_mask"])
elif init_with == "last":
# Load the last model you trained and continue training
model.load_weights(model.find_last(), by_name=True)
Training
Train in two stages:
Only the heads. Here we're freezing all the backbone layers and training only the randomly initialized layers (i.e. the ones that we didn't use pre-trained weights from MS COCO). To train only the head layers, pass
layers='heads'to thetrain()function.Fine-tune all layers. For this simple example it's not necessary, but we're including it to show the process. Simply pass
layers="allto train all layers.
# Train the head branches
# Passing layers="heads" freezes all layers except the head
# layers. You can also pass a regular expression to select
# which layers to train by name pattern.
model.train(dataset_train, dataset_val,
learning_rate=config.LEARNING_RATE,
epochs=1,
layers='heads')
Starting at epoch 0. LR=0.001
Checkpoint Path: C:\Users\luo\tensorflow\Mask_RCNN-master\logs\shapes20180817T1409\mask_rcnn_shapes_{epoch:04d}.h5
Selecting layers to train
fpn_c5p5 (Conv2D)
fpn_c4p4 (Conv2D)
fpn_c3p3 (Conv2D)
fpn_c2p2 (Conv2D)
fpn_p5 (Conv2D)
fpn_p2 (Conv2D)
fpn_p3 (Conv2D)
fpn_p4 (Conv2D)
In model: rpn_model
rpn_conv_shared (Conv2D)
rpn_class_raw (Conv2D)
rpn_bbox_pred (Conv2D)
mrcnn_mask_conv1 (TimeDistributed)
mrcnn_mask_bn1 (TimeDistributed)
mrcnn_mask_conv2 (TimeDistributed)
mrcnn_mask_bn2 (TimeDistributed)
mrcnn_class_conv1 (TimeDistributed)
mrcnn_class_bn1 (TimeDistributed)
mrcnn_mask_conv3 (TimeDistributed)
mrcnn_mask_bn3 (TimeDistributed)
mrcnn_class_conv2 (TimeDistributed)
mrcnn_class_bn2 (TimeDistributed)
mrcnn_mask_conv4 (TimeDistributed)
mrcnn_mask_bn4 (TimeDistributed)
mrcnn_bbox_fc (TimeDistributed)
mrcnn_mask_deconv (TimeDistributed)
mrcnn_class_logits (TimeDistributed)
mrcnn_mask (TimeDistributed)
E:\Anaconda3\install1\lib\site-packages\tensorflow\python\ops\gradients_impl.py:97: UserWarning: Converting sparse IndexedSlices to a dense Tensor of unknown shape. This may consume a large amount of memory.
"Converting sparse IndexedSlices to a dense Tensor of unknown shape. "
Epoch 1/1
100/100 [==============================] - 2824s 28s/step - loss: 1.5765 - rpn_class_loss: 0.0302 - rpn_bbox_loss: 0.5675 - mrcnn_class_loss: 0.3577 - mrcnn_bbox_loss: 0.3586 - mrcnn_mask_loss: 0.2625 - val_loss: 0.9420 - val_rpn_class_loss: 0.0130 - val_rpn_bbox_loss: 0.4263 - val_mrcnn_class_loss: 0.1708 - val_mrcnn_bbox_loss: 0.1679 - val_mrcnn_mask_loss: 0.1640
# Fine tune all layers
# Passing layers="all" trains all layers. You can also
# pass a regular expression to select which layers to
# train by name pattern.
model.train(dataset_train, dataset_val,
learning_rate=config.LEARNING_RATE / 10,
epochs=1,
layers="all")
Starting at epoch 1. LR=0.0001
Checkpoint Path: C:\Users\luo\tensorflow\Mask_RCNN-master\logs\shapes20180817T1409\mask_rcnn_shapes_{epoch:04d}.h5
Selecting layers to train
conv1 (Conv2D)
bn_conv1 (BatchNorm)
res2a_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn2a_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res2a_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn2a_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res2a_branch2c (Conv2D)
res2a_branch1 (Conv2D)
bn2a_branch2c (BatchNorm)
bn2a_branch1 (BatchNorm)
res2b_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn2b_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res2b_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn2b_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res2b_branch2c (Conv2D)
bn2b_branch2c (BatchNorm)
res2c_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn2c_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res2c_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn2c_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res2c_branch2c (Conv2D)
bn2c_branch2c (BatchNorm)
res3a_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn3a_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res3a_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn3a_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res3a_branch2c (Conv2D)
res3a_branch1 (Conv2D)
bn3a_branch2c (BatchNorm)
bn3a_branch1 (BatchNorm)
res3b_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn3b_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res3b_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn3b_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res3b_branch2c (Conv2D)
bn3b_branch2c (BatchNorm)
res3c_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn3c_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res3c_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn3c_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res3c_branch2c (Conv2D)
bn3c_branch2c (BatchNorm)
res3d_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn3d_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res3d_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn3d_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res3d_branch2c (Conv2D)
bn3d_branch2c (BatchNorm)
res4a_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn4a_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res4a_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn4a_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res4a_branch2c (Conv2D)
res4a_branch1 (Conv2D)
bn4a_branch2c (BatchNorm)
bn4a_branch1 (BatchNorm)
res4b_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn4b_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res4b_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn4b_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res4b_branch2c (Conv2D)
bn4b_branch2c (BatchNorm)
res4c_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn4c_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res4c_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn4c_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res4c_branch2c (Conv2D)
bn4c_branch2c (BatchNorm)
res4d_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn4d_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res4d_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn4d_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res4d_branch2c (Conv2D)
bn4d_branch2c (BatchNorm)
res4e_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn4e_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res4e_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn4e_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res4e_branch2c (Conv2D)
bn4e_branch2c (BatchNorm)
res4f_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn4f_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res4f_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn4f_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res4f_branch2c (Conv2D)
bn4f_branch2c (BatchNorm)
res4g_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn4g_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res4g_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn4g_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res4g_branch2c (Conv2D)
bn4g_branch2c (BatchNorm)
res4h_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn4h_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res4h_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn4h_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res4h_branch2c (Conv2D)
bn4h_branch2c (BatchNorm)
res4i_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn4i_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res4i_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn4i_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res4i_branch2c (Conv2D)
bn4i_branch2c (BatchNorm)
res4j_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn4j_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res4j_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn4j_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res4j_branch2c (Conv2D)
bn4j_branch2c (BatchNorm)
res4k_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn4k_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res4k_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn4k_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res4k_branch2c (Conv2D)
bn4k_branch2c (BatchNorm)
res4l_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn4l_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res4l_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn4l_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res4l_branch2c (Conv2D)
bn4l_branch2c (BatchNorm)
res4m_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn4m_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res4m_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn4m_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res4m_branch2c (Conv2D)
bn4m_branch2c (BatchNorm)
res4n_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn4n_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res4n_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn4n_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res4n_branch2c (Conv2D)
bn4n_branch2c (BatchNorm)
res4o_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn4o_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res4o_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn4o_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res4o_branch2c (Conv2D)
bn4o_branch2c (BatchNorm)
res4p_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn4p_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res4p_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn4p_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res4p_branch2c (Conv2D)
bn4p_branch2c (BatchNorm)
res4q_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn4q_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res4q_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn4q_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res4q_branch2c (Conv2D)
bn4q_branch2c (BatchNorm)
res4r_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn4r_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res4r_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn4r_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res4r_branch2c (Conv2D)
bn4r_branch2c (BatchNorm)
res4s_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn4s_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res4s_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn4s_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res4s_branch2c (Conv2D)
bn4s_branch2c (BatchNorm)
res4t_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn4t_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res4t_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn4t_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res4t_branch2c (Conv2D)
bn4t_branch2c (BatchNorm)
res4u_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn4u_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res4u_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn4u_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res4u_branch2c (Conv2D)
bn4u_branch2c (BatchNorm)
res4v_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn4v_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res4v_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn4v_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res4v_branch2c (Conv2D)
bn4v_branch2c (BatchNorm)
res4w_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn4w_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res4w_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn4w_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res4w_branch2c (Conv2D)
bn4w_branch2c (BatchNorm)
res5a_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn5a_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res5a_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn5a_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res5a_branch2c (Conv2D)
res5a_branch1 (Conv2D)
bn5a_branch2c (BatchNorm)
bn5a_branch1 (BatchNorm)
res5b_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn5b_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res5b_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn5b_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res5b_branch2c (Conv2D)
bn5b_branch2c (BatchNorm)
res5c_branch2a (Conv2D)
bn5c_branch2a (BatchNorm)
res5c_branch2b (Conv2D)
bn5c_branch2b (BatchNorm)
res5c_branch2c (Conv2D)
bn5c_branch2c (BatchNorm)
fpn_c5p5 (Conv2D)
fpn_c4p4 (Conv2D)
fpn_c3p3 (Conv2D)
fpn_c2p2 (Conv2D)
fpn_p5 (Conv2D)
fpn_p2 (Conv2D)
fpn_p3 (Conv2D)
fpn_p4 (Conv2D)
In model: rpn_model
rpn_conv_shared (Conv2D)
rpn_class_raw (Conv2D)
rpn_bbox_pred (Conv2D)
mrcnn_mask_conv1 (TimeDistributed)
mrcnn_mask_bn1 (TimeDistributed)
mrcnn_mask_conv2 (TimeDistributed)
mrcnn_mask_bn2 (TimeDistributed)
mrcnn_class_conv1 (TimeDistributed)
mrcnn_class_bn1 (TimeDistributed)
mrcnn_mask_conv3 (TimeDistributed)
mrcnn_mask_bn3 (TimeDistributed)
mrcnn_class_conv2 (TimeDistributed)
mrcnn_class_bn2 (TimeDistributed)
mrcnn_mask_conv4 (TimeDistributed)
mrcnn_mask_bn4 (TimeDistributed)
mrcnn_bbox_fc (TimeDistributed)
mrcnn_mask_deconv (TimeDistributed)
mrcnn_class_logits (TimeDistributed)
mrcnn_mask (TimeDistributed)
E:\Anaconda3\install1\lib\site-packages\tensorflow\python\ops\gradients_impl.py:97: UserWarning: Converting sparse IndexedSlices to a dense Tensor of unknown shape. This may consume a large amount of memory.
"Converting sparse IndexedSlices to a dense Tensor of unknown shape. "
# Save weights
# Typically not needed because callbacks save after every epoch
# Uncomment to save manually
# model_path = os.path.join(MODEL_DIR, "mask_rcnn_shapes.h5")
# model.keras_model.save_weights(model_path)
Detection
class InferenceConfig(ShapesConfig):
GPU_COUNT = 1
IMAGES_PER_GPU = 1
inference_config = InferenceConfig()
# Recreate the model in inference mode
model = modellib.MaskRCNN(mode="inference",
config=inference_config,
model_dir=MODEL_DIR)
# Get path to saved weights
# Either set a specific path or find last trained weights
# model_path = os.path.join(ROOT_DIR, ".h5 file name here")
model_path = model.find_last()
# Load trained weights
print("Loading weights from ", model_path)
model.load_weights(model_path, by_name=True)
Loading weights from C:\Users\luo\tensorflow\Mask_RCNN-master\logs\shapes20180817T1459\mask_rcnn_shapes_0001.h5
# Test on a random image
image_id = random.choice(dataset_val.image_ids)
original_image, image_meta, gt_class_id, gt_bbox, gt_mask =\
modellib.load_image_gt(dataset_val, inference_config,
image_id, use_mini_mask=False)
log("original_image", original_image)
log("image_meta", image_meta)
log("gt_class_id", gt_class_id)
log("gt_bbox", gt_bbox)
log("gt_mask", gt_mask)
visualize.display_instances(original_image, gt_bbox, gt_mask, gt_class_id,
dataset_train.class_names, figsize=(8, 8))
original_image shape: (128, 128, 3) min: 72.00000 max: 248.00000 uint8
image_meta shape: (16,) min: 0.00000 max: 128.00000 int32
gt_class_id shape: (3,) min: 2.00000 max: 3.00000 int32
gt_bbox shape: (3, 4) min: 0.00000 max: 128.00000 int32
gt_mask shape: (128, 128, 3) min: 0.00000 max: 1.00000 bool
results = model.detect([original_image], verbose=1)
r = results[0]
visualize.display_instances(original_image, r['rois'], r['masks'], r['class_ids'],
dataset_val.class_names, r['scores'], ax=get_ax())
Processing 1 images
image shape: (128, 128, 3) min: 72.00000 max: 248.00000 uint8
molded_images shape: (1, 128, 128, 3) min: -51.70000 max: 144.10000 float64
image_metas shape: (1, 16) min: 0.00000 max: 128.00000 int32
anchors shape: (1, 4092, 4) min: -0.71267 max: 1.20874 float32
Evaluation
# Compute VOC-Style mAP @ IoU=0.5
# Running on 10 images. Increase for better accuracy.
image_ids = np.random.choice(dataset_val.image_ids, 10)
APs = []
for image_id in image_ids:
# Load image and ground truth data
image, image_meta, gt_class_id, gt_bbox, gt_mask =\
modellib.load_image_gt(dataset_val, inference_config,
image_id, use_mini_mask=False)
molded_images = np.expand_dims(modellib.mold_image(image, inference_config), 0)
# Run object detection
results = model.detect([image], verbose=0)
r = results[0]
# Compute AP
AP, precisions, recalls, overlaps =\
utils.compute_ap(gt_bbox, gt_class_id, gt_mask,
r["rois"], r["class_ids"], r["scores"], r['masks'])
APs.append(AP)
print("mAP: ", np.mean(APs))
mAP: 0.966666667163372
Tensorflow学习(练习)—CPU训练模型的更多相关文章
- Tensorflow学习教程------读取数据、建立网络、训练模型,小巧而完整的代码示例
紧接上篇Tensorflow学习教程------tfrecords数据格式生成与读取,本篇将数据读取.建立网络以及模型训练整理成一个小样例,完整代码如下. #coding:utf-8 import t ...
- 用tensorflow学习贝叶斯个性化排序(BPR)
在贝叶斯个性化排序(BPR)算法小结中,我们对贝叶斯个性化排序(Bayesian Personalized Ranking, 以下简称BPR)的原理做了讨论,本文我们将从实践的角度来使用BPR做一个简 ...
- Tensorflow学习笔记2019.01.22
tensorflow学习笔记2 edit by Strangewx 2019.01.04 4.1 机器学习基础 4.1.1 一般结构: 初始化模型参数:通常随机赋值,简单模型赋值0 训练数据:一般打乱 ...
- Tensorflow学习笔记2019.01.03
tensorflow学习笔记: 3.2 Tensorflow中定义数据流图 张量知识矩阵的一个超集. 超集:如果一个集合S2中的每一个元素都在集合S1中,且集合S1中可能包含S2中没有的元素,则集合S ...
- 深度学习-tensorflow学习笔记(2)-MNIST手写字体识别
深度学习-tensorflow学习笔记(2)-MNIST手写字体识别超级详细版 这是tf入门的第一个例子.minst应该是内置的数据集. 前置知识在学习笔记(1)里面讲过了 这里直接上代码 # -*- ...
- tensorflow学习笔记(2)-反向传播
tensorflow学习笔记(2)-反向传播 反向传播是为了训练模型参数,在所有参数上使用梯度下降,让NN模型在的损失函数最小 损失函数:学过机器学习logistic回归都知道损失函数-就是预测值和真 ...
- tensorflow学习笔记——使用TensorFlow操作MNIST数据(2)
tensorflow学习笔记——使用TensorFlow操作MNIST数据(1) 一:神经网络知识点整理 1.1,多层:使用多层权重,例如多层全连接方式 以下定义了三个隐藏层的全连接方式的神经网络样例 ...
- tensorflow学习笔记——自编码器及多层感知器
1,自编码器简介 传统机器学习任务很大程度上依赖于好的特征工程,比如对数值型,日期时间型,种类型等特征的提取.特征工程往往是非常耗时耗力的,在图像,语音和视频中提取到有效的特征就更难了,工程师必须在这 ...
- tensorflow学习笔记——使用TensorFlow操作MNIST数据(1)
续集请点击我:tensorflow学习笔记——使用TensorFlow操作MNIST数据(2) 本节开始学习使用tensorflow教程,当然从最简单的MNIST开始.这怎么说呢,就好比编程入门有He ...
- TensorFlow学习笔记(1)—— 基本概念与框架
入门框架时的常见问题 学习框架的原因? 方便.易用 学习框架的哪些知识点? 掌握一个项目的基本流程,就知道需要学习哪些知识点了 迅速学习框架的方法 根据项目每块流程的需要针对性的学 可以看官方的入门教 ...
随机推荐
- ubuntu 上查看文件的内容,二进制形式展现
Vim 可以用来查看和编辑二进制文件 vim -b egenea-base.ko 加上-b参数,以二进制打开 然后输入命令 :%!xxd -g 1 切换到十六进制模式显示
- 【数据库】MongoDB学习
http://www.w3cschool.cc/mongodb/mongodb-tutorial.html http://api.mongodb.org/python/2.7rc0/examples/ ...
- 如何加快MyEclipse的启动速度
学习java开发的朋友对Myeclipse应该不陌生,MyEclipse企业级工作平台(MyEclipseEnterprise Workbench ,简称MyEclipse)是对EclipseIDE的 ...
- bzoj 3173 最长上升子序列
Written with StackEdit. Description 给定一个序列,初始为空.现在我们将\(1\)到\(N\)的数字插入到序列中,每次将一个数字插入到一个特定的位置.每插入一个数字, ...
- Python 函数 min()
min() 函数 作用: min() 方法返回给定参数的最小值,参数可以为序列.x-数值表达式.y-数值表达式.z-数值表达式.返回给定参数的最小值. 语法: min( x, y, z, .... ...
- COGS 2259 异化多肽——生成函数+多项式求逆
题目:http://cogs.pro:8080/cogs/problem/problem.php?pid=2259 详见:https://www.cnblogs.com/Zinn/p/10054569 ...
- RK3288 模块单独编译
模块以Email为例: 1.执行build目录下的脚本文件envsetup.sh $ source ./build/envsetup.sh 2.选择版本(user为用户版本 eng为工程版本) $ ...
- delphi xe5 安卓 配置sqlite
本篇我们介绍一下在android手机上怎样使用sqlite数据库,这里用Navigator实现 增删改查. 1.新建firemonkey mobile application 2.选择blank ap ...
- shell中字体变色
在linux中给字体使用数字代码变色 字体颜色代码:重置0 ,黑色30,红色31,绿色32,黄色33,蓝色34,洋红35,青色36,浅灰37 效果代码:1m加粗 2m加下划线 5m闪动效果 7m ...
- 安装nagios-plugins插件make时遇到的error
安装nagios-plugins插件make时遇到的error error内容: check_http.c: In function ‘process_arguments’: check_http.c ...
