全排列12 · Permutations
无重复
[抄题]:
Given a collection of numbers, return all possible permutations.
For example,
[1,2,3] have the following permutations:
[1,2,3], [1,3,2], [2,1,3], [2,3,1], [3,1,2], and [3,2,1].
[思维问题]:
不知道回溯法:和求子集一样-[1],[1,2]-只剩[1]
123用了2,312又要用2。反复用,所以叫回溯法
[一句话思路]:
[输入量]:空: 正常情况:特大:特小:程序里处理到的特殊情况:异常情况(不合法不合理的输入):
[画图]:

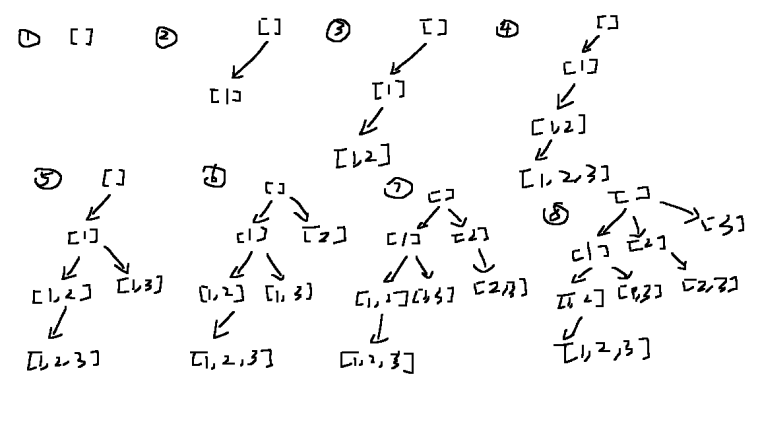
[一刷]:
- 递归退出用return;表示 递归推出的出口在helper函数中,不在每个点加进permutation的过程中
- 结果是复数数组,返回results 如果nums == null,返回[] 如果nums.length == 0, 返回[[]](result中添加一个空数组,返回result)
- ist.size()的效果等于nums.length
- helper调用整个数组时,参数是数组名
[二刷]:
[三刷]:
[四刷]:
[五刷]:
[五分钟肉眼debug的结果]:
[总结]:
- 搜索递归的三个步骤:新参数、递归、去掉新参数
- 不知道回溯法:和求子集一样-[1],[1,2]-只剩[1]
[复杂度]:Time complexity: O() Space complexity: O()
[英文数据结构或算法,为什么不用别的数据结构或算法]:
[其他解法]:
[Follow Up]:
[LC给出的题目变变变]:
public class Solution {
/*
* @param nums: A list of integers.
* @return: A list of permutations.
*/
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {
//corner case
List<List<Integer>> results = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> permutations = new ArrayList<>();
HashSet<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
if (nums == null) {
return null;
}
if (nums.length == 0) {
//return new ArrayList<>();
results.add(new ArrayList<>());
return results;
}
//helper
helper(nums, permutations, set, results);
//return
return results;
}
//helper
public void helper (int[] nums, List<Integer> permutations,
HashSet<Integer> set, List<List<Integer>> results) {
if (permutations.size() == nums.length) {
results.add(new ArrayList<>(permutations));
return ;//
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (set.contains(nums[i])) {
continue;
}
permutations.add(nums[i]);
set.add(nums[i]);
helper(nums, permutations, set, results);
set.remove(nums[i]);
permutations.remove(permutations.size() - 1);
}
}
}
有重复
[抄题]:
[思维问题]:
有重复元素不知道是默认不排序的,要先排序
[一句话思路]:
排序后用visited数组来控制
[输入量]:空: 正常情况:特大:特小:程序里处理到的特殊情况:异常情况(不合法不合理的输入):
[画图]:

((i != 0 && visited[i - 1] == 0) &&
nums[i - 1] == nums[i]//
)
在不是第零位(没有前一位)的前提下,如果两数字相同,前面一个数却没有访问,此时不可
[一刷]:
- 有数组要先排序
- 设置visited数组默认为0
[二刷]:
[三刷]:
[四刷]:
[五刷]:
[五分钟肉眼debug的结果]:
不要把visited nums数组名写错了
[总结]:
代码风格:太长可以换行、不要用很多的&& ||符号
[复杂度]:Time complexity: O(分支的深度次方) Space complexity: O(深度*分支)

[英文数据结构或算法,为什么不用别的数据结构或算法]:
[其他解法]:
[Follow Up]:
[LC给出的题目变变变]:
31. Next Permutation 如果不是要求找出全部排列的,就几乎都是做数组调整 玩文字游戏
public class Solution {
/*
* @param nums: A list of integers.
* @return: A list of permutations.
*/
public List<List<Integer>> permuteUnique(int[] nums) {
//corner case
List<List<Integer>> results = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> permutations = new ArrayList<>();
int[] visited = new int[nums.length];
if (nums == null) {
return null;
}
if (nums.length == 0) {
results.add(new ArrayList<>());
return results;
}
//helper
Arrays.sort(nums);
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
visited[i] = 0;
}
helper(nums, permutations, visited, results);
//return
return results;
}
//helper
public void helper (int[] nums, List<Integer> permutations,
int[] visited, List<List<Integer>> results) {
if (permutations.size() == nums.length) {
results.add(new ArrayList<>(permutations));
return ;//
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (visited[i] == 1) {
continue;
}
if ((i != 0 && visited[i - 1] == 0) &&
nums[i - 1] == nums[i]//
) {
continue;
}
visited[i] = 1;
permutations.add(nums[i]);
helper(nums, permutations, visited, results);
permutations.remove(permutations.size() - 1);
visited[i] = 0;
}
}
}
全排列12 · Permutations的更多相关文章
- Leetcode之回溯法专题-46. 全排列(Permutations)
Leetcode之回溯法专题-46. 全排列(Permutations) 给定一个没有重复数字的序列,返回其所有可能的全排列. 示例: 输入: [1,2,3] 输出: [ [1,2,3], [1,3, ...
- [Swift]LeetCode47. 全排列 II | Permutations II
Given a collection of numbers that might contain duplicates, return all possible unique permutations ...
- LeetCode 46. 全排列(Permutations)
题目描述 给定一个没有重复数字的序列,返回其所有可能的全排列. 示例: 输入: [1,2,3] 输出: [ [1,2,3], [1,3,2], [2,1,3], [2,3,1], [3,1,2], [ ...
- 刷题——有重复元素的全排列(Permutations II)
题目如上所示. 我的解决方法(参考了九章的答案!): class Solution { public: /* * @param : A list of integers * @return: A li ...
- [CareerCup] 9.5 Permutations 全排列
9.5 Write a method to compute all permutations of a string. LeetCode上的原题,请参加我之前的博客Permutations 全排列和P ...
- LeetCode 046 Permutations
题目要求:Permutations(全排列) Given a collection of numbers, return all possible permutations. For example, ...
- HDOJ-ACM1016(JAVA) 字典序全排列,并剪枝
转载声明:原文转自http://www.cnblogs.com/xiezie/p/5576273.html 题意: 一个环是用图中所示的n个圆组成的.把自然数1.2.…….n分别放入每个圆中,并在相邻 ...
- 给定一个正整数,实现一个方法求出离该整数最近的大于自身的 换位数 <把一个整数各个数位进行全排列>
"""给定一个正整数,实现一个方法求出离该整数最近的大于自身的 换位数 -> 把一个整数各个数位进行全排列""" # 使用 permu ...
- UVALive 6909 Kevin's Problem 数学排列组合
Kevin's Problem 题目连接: https://icpcarchive.ecs.baylor.edu/index.php?option=com_onlinejudge&Itemid ...
随机推荐
- Java内部类引用外部类中的局部变量为何必须是final问题解析
今天编写一个多线程程序,发现在方法内定义内部类时,如果内部类调用了方法中的变量,那么该变量必须申明为final类型,百思不得其解,后来想到应该是生命周期的原因,因为方法内定义的变量是局部变量,离开该方 ...
- C# AtomicInt
using System; using System.Threading; /// <summary> /// Provides lock-free atomic read/write u ...
- 洛谷::P1972 [SDOI2009]HH的项链
题目背景 无 题目描述 HH 有一串由各种漂亮的贝壳组成的项链.HH 相信不同的贝壳会带来好运,所以每次散步完后,他都会随意取出一段贝壳,思考它们所表达的含义.HH 不断地收集新的贝壳,因此,他的项链 ...
- python基础补充内容
知识内容: 1.三元运算表达式 2.python代码编写规范 3.模块导入与使用 4.python文件名 5.python脚本的"__name__"属性 6.python之禅 一. ...
- UnicodeEncodeError: 'gbk' codec can't encode character '\xbb' in position
python实现爬虫遇到编码问题: error:UnicodeEncodeError: 'gbk' codec can't encode character '\xXX' in position XX ...
- 28. centos 5.6添加用户时报copydir(): preserving permissions for /home/xxx/.mozilla: Operation not supported错
当执行useradd xxx报如下错:copydir(): preserving permissions for /home/xxx/.mozilla: Operation not supported ...
- Asp.net MVC重要
1.asp.net mvc百度解释 2.asp.net mvc各版本特点 3.asp.net mvc知多少 4.asp.net mvc4入门到精通系列目录汇总(邹琼俊)[重要] 5.新年奉献MVC+E ...
- ansible之条件语句when
注册变量: 变量的另一个用途是将一条命令的运行结果保存到变量中,供后面的playbook使用.例如: - hosts: webservers tasks: - shell: /usr/bin/foo ...
- Rquest对象代码练习
1.代码练习 <%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="utf-8 ...
- SPARK数据类型
转自: http://www.cnblogs.com/tuitui1989/p/5331113.html 一.本地向量 有如下几个类: Vector(基类),DenseVector,SparseVec ...
