asp.net mvc源码分析-Route的GetRouteData
我知道Route这里东西应该算路由,这里把它放到mvc里面有些不怎么合适,但是我想大家多数遇到路由都是在mvc的时候吧.首先我们还是来看看GetRouteData方法吧
[csharp]
public override RouteData GetRouteData(HttpContextBase httpContext)
{
string virtualPath = httpContext.Request.AppRelativeCurrentExecutionFilePath.Substring() + httpContext.Request.PathInfo;
RouteValueDictionary values = this._parsedRoute.Match(virtualPath, this.Defaults);
if (values == null)
{
return null;
}
RouteData data = new RouteData(this, this.RouteHandler);
if (!this.ProcessConstraints(httpContext, values, RouteDirection.IncomingRequest))
{
return null;
}
foreach (KeyValuePair<string, object> pair in values)
{
data.Values.Add(pair.Key, pair.Value);
}
if (this.DataTokens != null)
{
foreach (KeyValuePair<string, object> pair2 in this.DataTokens)
{
data.DataTokens[pair2.Key] = pair2.Value;
}
}
return data;
} public override RouteData GetRouteData(HttpContextBase httpContext)
{
string virtualPath = httpContext.Request.AppRelativeCurrentExecutionFilePath.Substring() + httpContext.Request.PathInfo;
RouteValueDictionary values = this._parsedRoute.Match(virtualPath, this.Defaults);
if (values == null)
{
return null;
}
RouteData data = new RouteData(this, this.RouteHandler);
if (!this.ProcessConstraints(httpContext, values, RouteDirection.IncomingRequest))
{
return null;
}
foreach (KeyValuePair<string, object> pair in values)
{
data.Values.Add(pair.Key, pair.Value);
}
if (this.DataTokens != null)
{
foreach (KeyValuePair<string, object> pair2 in this.DataTokens)
{
data.DataTokens[pair2.Key] = pair2.Value;
}
}
return data;
}
我还是沿用以前的思路,已一个demo来便说明吧,现在假设我的路由信息是:
routes.IgnoreRoute("{resource}.axd/{*pathInfo}");
routes.IgnoreRoute("{*favicon}", new { favicon = @"(.*/)?favicon.ico(/.*)?" });
routes.MapRoute(
"Default", // 路由名称
"{controller}/{action}/{id}", // 带有参数的 URL
new { controller = "Home", action = "Index", id = UrlParameter.Optional }, // 参数默认值
new { controller="([A-Za-z])*" },
new string[] { "MvcApp.Controllers" }
);
我们知道httpContext.Request.AppRelativeCurrentExecutionFilePath的返回值都是以~/打头的,这里httpContext.Request.PathInfo为空,多数情况下该属性也是空的,所以这里的virtualPath=Home/index。
有关MapRoute的代码可以参照
[csharp]
public static Route MapRoute(this RouteCollection routes, string name, string url, object defaults, object constraints, string[] namespaces) {
if (routes == null) {
throw new ArgumentNullException("routes");
}
if (url == null) {
throw new ArgumentNullException("url");
} Route route = new Route(url, new MvcRouteHandler()) {
Defaults = new RouteValueDictionary(defaults),
Constraints = new RouteValueDictionary(constraints),
DataTokens = new RouteValueDictionary()
}; if ((namespaces != null) && (namespaces.Length > )) {
route.DataTokens["Namespaces"] = namespaces;
} routes.Add(name, route); return route;
} public static Route MapRoute(this RouteCollection routes, string name, string url, object defaults, object constraints, string[] namespaces) {
if (routes == null) {
throw new ArgumentNullException("routes");
}
if (url == null) {
throw new ArgumentNullException("url");
} Route route = new Route(url, new MvcRouteHandler()) {
Defaults = new RouteValueDictionary(defaults),
Constraints = new RouteValueDictionary(constraints),
DataTokens = new RouteValueDictionary()
}; if ((namespaces != null) && (namespaces.Length > )) {
route.DataTokens["Namespaces"] = namespaces;
} routes.Add(name, route); return route;
}
首先调用_parsedRoute.Match(virtualPath, this.Defaults)获取一个RouteValueDictionary ,至于这个方法的具体实现放到后面来说,然后实例化一个RouteData ,并且把先前的RouteValueDictionary的值添加到先前实例化的 RouteData中,如果DataTokens有元素的话也加入到RouteData的DataTokens中来。不过这个过程有个约束的处理
if (!this.ProcessConstraints(httpContext, values, RouteDirection.IncomingRequest))
{
return null;
}
其中RouteDirection的定义如下:
public enum RouteDirection
{
IncomingRequest,
UrlGeneration
}
约束检查失败而返回null,现在我们来看看ProcessConstraints方法:
private bool ProcessConstraints(HttpContextBase httpContext, RouteValueDictionary values, RouteDirection routeDirection)
{
if (this.Constraints != null)
{
foreach (KeyValuePair<string, object> pair in this.Constraints)
{
if (!this.ProcessConstraint(httpContext, pair.Value, pair.Key, values, routeDirection))
{
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
如果Constraints有元素,依次检查每个成员,检查方法主要是调用ProcessConstraint方法,
[csharp]
protected virtual bool ProcessConstraint(HttpContextBase httpContext, object constraint, string parameterName, RouteValueDictionary values, RouteDirection routeDirection)
{
object obj2;
IRouteConstraint constraint2 = constraint as IRouteConstraint;
if (constraint2 != null)
{
return constraint2.Match(httpContext, this, parameterName, values, routeDirection);
}
string str = constraint as string;
if (str == null)
{
throw new InvalidOperationException(string.Format(CultureInfo.CurrentUICulture, SR.GetString("Route_ValidationMustBeStringOrCustomConstraint"), new object[] { parameterName, this.Url }));
}
values.TryGetValue(parameterName, out obj2);
string input = Convert.ToString(obj2, CultureInfo.InvariantCulture);
string pattern = "^(" + str + ")$";
return Regex.IsMatch(input, pattern, RegexOptions.CultureInvariant | RegexOptions.Compiled | RegexOptions.IgnoreCase);
} protected virtual bool ProcessConstraint(HttpContextBase httpContext, object constraint, string parameterName, RouteValueDictionary values, RouteDirection routeDirection)
{
object obj2;
IRouteConstraint constraint2 = constraint as IRouteConstraint;
if (constraint2 != null)
{
return constraint2.Match(httpContext, this, parameterName, values, routeDirection);
}
string str = constraint as string;
if (str == null)
{
throw new InvalidOperationException(string.Format(CultureInfo.CurrentUICulture, SR.GetString("Route_ValidationMustBeStringOrCustomConstraint"), new object[] { parameterName, this.Url }));
}
values.TryGetValue(parameterName, out obj2);
string input = Convert.ToString(obj2, CultureInfo.InvariantCulture);
string pattern = "^(" + str + ")$";
return Regex.IsMatch(input, pattern, RegexOptions.CultureInvariant | RegexOptions.Compiled | RegexOptions.IgnoreCase);
}
这里首先检查我们的约束类型,如果它是IRouteConstraint那么就直接调用它的Match方法,约束不是IRouteConstraint那么就转化为字符串,再把约束验证的值从RouteValueDictionary 中取出来转化为字符串,最后在用正则表达式来验证我们的值是否通过。
好,现在让我们来看看this._parsedRoute.Match(virtualPath, this.Defaults);这个方法是然后获取RouteValueDictionary的:
[csharp]
public RouteValueDictionary Match(string virtualPath, RouteValueDictionary defaultValues)
{
IList<string> source = RouteParser.SplitUrlToPathSegmentStrings(virtualPath);
if (defaultValues == null)
{
defaultValues = new RouteValueDictionary();
}
RouteValueDictionary matchedValues = new RouteValueDictionary();
bool flag = false;
bool flag2 = false;
for (int i = ; i < this.PathSegments.Count; i++)
{
PathSegment segment = this.PathSegments[i];
if (source.Count <= i)
{
flag = true;
}
string a = flag ? null : source[i];
if (segment is SeparatorPathSegment)
{
if (!flag && !string.Equals(a, "/", StringComparison.Ordinal))
{
return null;
}
}
else
{
ContentPathSegment contentPathSegment = segment as ContentPathSegment;
if (contentPathSegment != null)
{
if (contentPathSegment.IsCatchAll)
{
this.MatchCatchAll(contentPathSegment, source.Skip<string>(i), defaultValues, matchedValues);
flag2 = true;
}
else if (!this.MatchContentPathSegment(contentPathSegment, a, defaultValues, matchedValues))
{
return null;
}
}
}
}
if (!flag2 && (this.PathSegments.Count < source.Count))
{
for (int j = this.PathSegments.Count; j < source.Count; j++)
{
if (!RouteParser.IsSeparator(source[j]))
{
return null;
}
}
}
if (defaultValues != null)
{
foreach (KeyValuePair<string, object> pair in defaultValues)
{
if (!matchedValues.ContainsKey(pair.Key))
{
matchedValues.Add(pair.Key, pair.Value);
}
}
}
return matchedValues;
} public RouteValueDictionary Match(string virtualPath, RouteValueDictionary defaultValues)
{
IList<string> source = RouteParser.SplitUrlToPathSegmentStrings(virtualPath);
if (defaultValues == null)
{
defaultValues = new RouteValueDictionary();
}
RouteValueDictionary matchedValues = new RouteValueDictionary();
bool flag = false;
bool flag2 = false;
for (int i = ; i < this.PathSegments.Count; i++)
{
PathSegment segment = this.PathSegments[i];
if (source.Count <= i)
{
flag = true;
}
string a = flag ? null : source[i];
if (segment is SeparatorPathSegment)
{
if (!flag && !string.Equals(a, "/", StringComparison.Ordinal))
{
return null;
}
}
else
{
ContentPathSegment contentPathSegment = segment as ContentPathSegment;
if (contentPathSegment != null)
{
if (contentPathSegment.IsCatchAll)
{
this.MatchCatchAll(contentPathSegment, source.Skip<string>(i), defaultValues, matchedValues);
flag2 = true;
}
else if (!this.MatchContentPathSegment(contentPathSegment, a, defaultValues, matchedValues))
{
return null;
}
}
}
}
if (!flag2 && (this.PathSegments.Count < source.Count))
{
for (int j = this.PathSegments.Count; j < source.Count; j++)
{
if (!RouteParser.IsSeparator(source[j]))
{
return null;
}
}
}
if (defaultValues != null)
{
foreach (KeyValuePair<string, object> pair in defaultValues)
{
if (!matchedValues.ContainsKey(pair.Key))
{
matchedValues.Add(pair.Key, pair.Value);
}
}
}
return matchedValues;
}
这里RouteParser的SplitUrlToPathSegmentStrings方法很简单,就是把url字符串按照”/“来分割
[csharp] view plaincopyprint?internal static IList<string> SplitUrlToPathSegmentStrings(string url)
{
List<string> list = new List<string>();
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(url))
{
int index;
for (int i = ; i < url.Length; i = index + )
{
index = url.IndexOf('/', i);
if (index == -)
{
string str = url.Substring(i);
if (str.Length > )
{
list.Add(str);
}
return list;
}
string item = url.Substring(i, index - i);
if (item.Length > )
{
list.Add(item);
}
list.Add("/");
}
}
return list;
} internal static IList<string> SplitUrlToPathSegmentStrings(string url)
{
List<string> list = new List<string>();
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(url))
{
int index;
for (int i = ; i < url.Length; i = index + )
{
index = url.IndexOf('/', i);
if (index == -)
{
string str = url.Substring(i);
if (str.Length > )
{
list.Add(str);
}
return list;
}
string item = url.Substring(i, index - i);
if (item.Length > )
{
list.Add(item);
}
list.Add("/");
}
}
return list;
}
所以Match方法中的source 是成员是很好明白的,我的示例中它的值是:
在ParsedRoute的Match方法中用到了一个PathSegments属性。该属性定义为:private IList<PathSegment> PathSegments { get; set; }真正该改属性复制的是ParsedRoute的构造函数。而Route中的_parsedRoute的获取是在Url属性中
public string Url
{
get
{
return (this._url ?? string.Empty);
}
set
{
this._parsedRoute = RouteParser.Parse(value);
this._url = value;
}
}
在我们这个例子中url的value={controller}/{action}/{id}。
其中RouteParser的Parse方法如下:
[csharp]
public static ParsedRoute Parse(string routeUrl)
{
if (routeUrl == null)
{
routeUrl = string.Empty;
}
if ((routeUrl.StartsWith("~", StringComparison.Ordinal) || routeUrl.StartsWith("/", StringComparison.Ordinal)) || (routeUrl.IndexOf('?') != -))
{
throw new ArgumentException(SR.GetString("Route_InvalidRouteUrl"), "routeUrl");
}
IList<string> pathSegments = SplitUrlToPathSegmentStrings(routeUrl);
Exception exception = ValidateUrlParts(pathSegments);
if (exception != null)
{
throw exception;
}
return new ParsedRoute(SplitUrlToPathSegments(pathSegments));
} public static ParsedRoute Parse(string routeUrl)
{
if (routeUrl == null)
{
routeUrl = string.Empty;
}
if ((routeUrl.StartsWith("~", StringComparison.Ordinal) || routeUrl.StartsWith("/", StringComparison.Ordinal)) || (routeUrl.IndexOf('?') != -))
{
throw new ArgumentException(SR.GetString("Route_InvalidRouteUrl"), "routeUrl");
}
IList<string> pathSegments = SplitUrlToPathSegmentStrings(routeUrl);
Exception exception = ValidateUrlParts(pathSegments);
if (exception != null)
{
throw exception;
}
return new ParsedRoute(SplitUrlToPathSegments(pathSegments));
}
在这里我们知道url不能以~ /打头,也不能含有?。这里的pathSegments也很好理解,其值:

这里的ValidateUrlParts主要就是验证这里的pathSegments集合,ValidateUrlParts这里的具体是怎么验证的很是复杂,这里就忽略了它吧。
有关SplitUrlToPathSegments的方法比较复杂,分为两部分,把urlParts中的"/" 变成SeparatorPathSegment对象作为站位,像{controller}这样转换为ContentPathSegment对象,其中它的subsegments是一个List<PathSubsegment>实例,
[csharp]
private static IList<PathSegment> SplitUrlToPathSegments(IList<string> urlParts)
{
List<PathSegment> list = new List<PathSegment>();
foreach (string str in urlParts)
{
if (IsSeparator(str))
{
list.Add(new SeparatorPathSegment());
}
else
{
Exception exception;
IList<PathSubsegment> subsegments = ParseUrlSegment(str, out exception);
list.Add(new ContentPathSegment(subsegments));
}
}
return list;
} internal static bool IsSeparator(string s)
{
return string.Equals(s, "/", StringComparison.Ordinal);
} private static IList<PathSubsegment> ParseUrlSegment(string segment, out Exception exception)
{
int startIndex = ;
List<PathSubsegment> list = new List<PathSubsegment>();
while (startIndex < segment.Length)
{
int num2 = IndexOfFirstOpenParameter(segment, startIndex);
if (num2 == -)
{
string str = GetLiteral(segment.Substring(startIndex));
if (str == null)
{
exception = new ArgumentException(string.Format(CultureInfo.CurrentUICulture, SR.GetString("Route_MismatchedParameter"), new object[] { segment }), "routeUrl");
return null;
}
if (str.Length > )
{
list.Add(new LiteralSubsegment(str));
}
break;
}
int index = segment.IndexOf('}', num2 + );
if (index == -)
{
exception = new ArgumentException(string.Format(CultureInfo.CurrentUICulture, SR.GetString("Route_MismatchedParameter"), new object[] { segment }), "routeUrl");
return null;
}
string literal = GetLiteral(segment.Substring(startIndex, num2 - startIndex));
if (literal == null)
{
exception = new ArgumentException(string.Format(CultureInfo.CurrentUICulture, SR.GetString("Route_MismatchedParameter"), new object[] { segment }), "routeUrl");
return null;
}
if (literal.Length > )
{
list.Add(new LiteralSubsegment(literal));
}
string parameterName = segment.Substring(num2 + , (index - num2) - );
list.Add(new ParameterSubsegment(parameterName));
startIndex = index + ;
}
exception = null;
return list;
} private static int IndexOfFirstOpenParameter(string segment, int startIndex)
{
while (true)
{
startIndex = segment.IndexOf('{', startIndex);
if (startIndex == -)
{
return -;
}
if (((startIndex + ) == segment.Length) || (((startIndex + ) < segment.Length) && (segment[startIndex + ] != '{')))
{
return startIndex;
}
startIndex += ;
}
} private static string GetLiteral(string segmentLiteral)
{
string str = segmentLiteral.Replace("{{", "").Replace("}}", "");
if (!str.Contains("{") && !str.Contains("}"))
{
return segmentLiteral.Replace("{{", "{").Replace("}}", "}");
}
return null;
} internal sealed class LiteralSubsegment : PathSubsegment
{
// Methods
public LiteralSubsegment(string literal)
{
this.Literal = literal;
} // Properties
public string Literal { get; private set; }
}
internal sealed class ParameterSubsegment : PathSubsegment
{
// Methods
public ParameterSubsegment(string parameterName)
{
if (parameterName.StartsWith("*", StringComparison.Ordinal))
{
this.ParameterName = parameterName.Substring();
this.IsCatchAll = true;
}
else
{
this.ParameterName = parameterName;
}
} // Properties
public bool IsCatchAll { get; private set; } public string ParameterName { get; private set; }
}
internal sealed class ContentPathSegment : PathSegment
{
// Methods
public ContentPathSegment(IList<PathSubsegment> subsegments)
{
this.Subsegments = subsegments;
} // Properties
public bool IsCatchAll
{
get
{
return this.Subsegments.Any<PathSubsegment>(seg => ((seg is ParameterSubsegment) && ((ParameterSubsegment)seg).IsCatchAll));
}
} public IList<PathSubsegment> Subsegments { get; private set; }
} private static IList<PathSegment> SplitUrlToPathSegments(IList<string> urlParts)
{
List<PathSegment> list = new List<PathSegment>();
foreach (string str in urlParts)
{
if (IsSeparator(str))
{
list.Add(new SeparatorPathSegment());
}
else
{
Exception exception;
IList<PathSubsegment> subsegments = ParseUrlSegment(str, out exception);
list.Add(new ContentPathSegment(subsegments));
}
}
return list;
} internal static bool IsSeparator(string s)
{
return string.Equals(s, "/", StringComparison.Ordinal);
} private static IList<PathSubsegment> ParseUrlSegment(string segment, out Exception exception)
{
int startIndex = ;
List<PathSubsegment> list = new List<PathSubsegment>();
while (startIndex < segment.Length)
{
int num2 = IndexOfFirstOpenParameter(segment, startIndex);
if (num2 == -)
{
string str = GetLiteral(segment.Substring(startIndex));
if (str == null)
{
exception = new ArgumentException(string.Format(CultureInfo.CurrentUICulture, SR.GetString("Route_MismatchedParameter"), new object[] { segment }), "routeUrl");
return null;
}
if (str.Length > )
{
list.Add(new LiteralSubsegment(str));
}
break;
}
int index = segment.IndexOf('}', num2 + );
if (index == -)
{
exception = new ArgumentException(string.Format(CultureInfo.CurrentUICulture, SR.GetString("Route_MismatchedParameter"), new object[] { segment }), "routeUrl");
return null;
}
string literal = GetLiteral(segment.Substring(startIndex, num2 - startIndex));
if (literal == null)
{
exception = new ArgumentException(string.Format(CultureInfo.CurrentUICulture, SR.GetString("Route_MismatchedParameter"), new object[] { segment }), "routeUrl");
return null;
}
if (literal.Length > )
{
list.Add(new LiteralSubsegment(literal));
}
string parameterName = segment.Substring(num2 + , (index - num2) - );
list.Add(new ParameterSubsegment(parameterName));
startIndex = index + ;
}
exception = null;
return list;
} private static int IndexOfFirstOpenParameter(string segment, int startIndex)
{
while (true)
{
startIndex = segment.IndexOf('{', startIndex);
if (startIndex == -)
{
return -;
}
if (((startIndex + ) == segment.Length) || (((startIndex + ) < segment.Length) && (segment[startIndex + ] != '{')))
{
return startIndex;
}
startIndex += ;
}
} private static string GetLiteral(string segmentLiteral)
{
string str = segmentLiteral.Replace("{{", "").Replace("}}", "");
if (!str.Contains("{") && !str.Contains("}"))
{
return segmentLiteral.Replace("{{", "{").Replace("}}", "}");
}
return null;
} internal sealed class LiteralSubsegment : PathSubsegment
{
// Methods
public LiteralSubsegment(string literal)
{
this.Literal = literal;
} // Properties
public string Literal { get; private set; }
}
internal sealed class ParameterSubsegment : PathSubsegment
{
// Methods
public ParameterSubsegment(string parameterName)
{
if (parameterName.StartsWith("*", StringComparison.Ordinal))
{
this.ParameterName = parameterName.Substring();
this.IsCatchAll = true;
}
else
{
this.ParameterName = parameterName;
}
} // Properties
public bool IsCatchAll { get; private set; } public string ParameterName { get; private set; }
}
internal sealed class ContentPathSegment : PathSegment
{
// Methods
public ContentPathSegment(IList<PathSubsegment> subsegments)
{
this.Subsegments = subsegments;
} // Properties
public bool IsCatchAll
{
get
{
return this.Subsegments.Any<PathSubsegment>(seg => ((seg is ParameterSubsegment) && ((ParameterSubsegment)seg).IsCatchAll));
}
} public IList<PathSubsegment> Subsegments { get; private set; }
}
ParseUrlSegment方法主要就是获取代码是:
string parameterName = segment.Substring(num2 + , (index - num2) - );
list.Add(new ParameterSubsegment(parameterName));
例如我们传进来的字符串是{controller},那么这里parameterName就会处理为controller。如果传入的参数没有{、}如Channel,那么ParseUrlSegment将处理为
if (str.Length > )
{
list.Add(new LiteralSubsegment(str));
}
break;
现在是时候回到ParsedRoute的Match方法了,首先我们来看看这个方法用到的PathSegments是个什么东东,我的url是{controller}/{action}/{id}它对应的PathSegments如图:
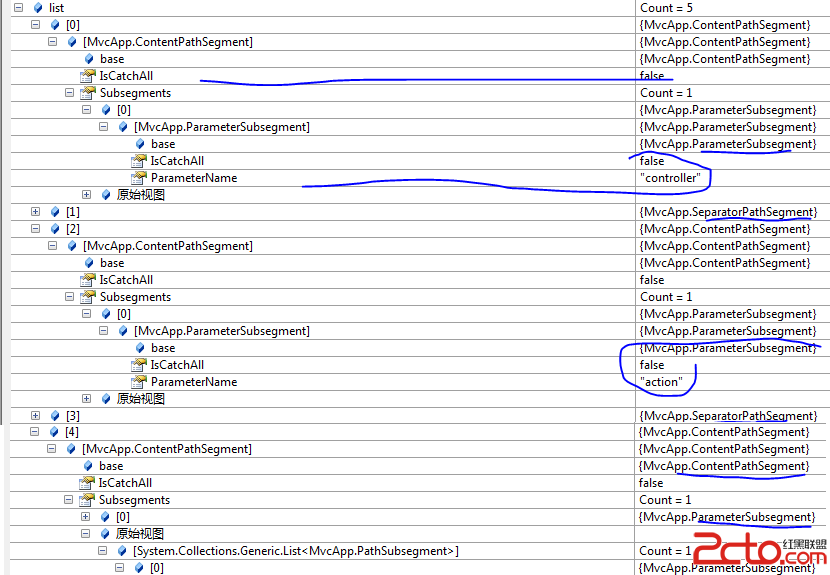
着了我们看看几次循环的主要变量取值:
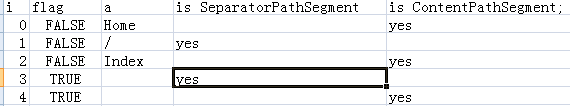
当前ContentPathSegment的IsCatchAll为false。那么我们现在主要关心的是MatchContentPathSegment方法了
[csharp]
private bool MatchContentPathSegment(ContentPathSegment routeSegment, string requestPathSegment, RouteValueDictionary defaultValues, RouteValueDictionary matchedValues)
{
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(requestPathSegment))
{
if (routeSegment.Subsegments.Count <= )
{
object obj2;
ParameterSubsegment subsegment = routeSegment.Subsegments[] as ParameterSubsegment;
if (subsegment == null)
{
return false;
}
if (defaultValues.TryGetValue(subsegment.ParameterName, out obj2))
{
matchedValues.Add(subsegment.ParameterName, obj2);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
int length = requestPathSegment.Length;
int num2 = routeSegment.Subsegments.Count - ;
ParameterSubsegment subsegment2 = null;
LiteralSubsegment subsegment3 = null;
while (num2 >= )
{
int num3 = length;
ParameterSubsegment subsegment4 = routeSegment.Subsegments[num2] as ParameterSubsegment;
if (subsegment4 != null)
{
subsegment2 = subsegment4;
}
else
{
LiteralSubsegment subsegment5 = routeSegment.Subsegments[num2] as LiteralSubsegment;
if (subsegment5 != null)
{
subsegment3 = subsegment5;
int startIndex = length - ;
if (subsegment2 != null)
{
startIndex--;
}
if (startIndex < )
{
return false;
}
int num5 = requestPathSegment.LastIndexOf(subsegment5.Literal, startIndex, StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase);
if (num5 == -)
{
return false;
}
if ((num2 == (routeSegment.Subsegments.Count - )) && ((num5 + subsegment5.Literal.Length) != requestPathSegment.Length))
{
return false;
}
num3 = num5;
}
}
if ((subsegment2 != null) && (((subsegment3 != null) && (subsegment4 == null)) || (num2 == )))
{
int num6;
int num7;
if (subsegment3 == null)
{
if (num2 == )
{
num6 = ;
}
else
{
num6 = num3 + subsegment3.Literal.Length;
}
num7 = length;
}
else if ((num2 == ) && (subsegment4 != null))
{
num6 = ;
num7 = length;
}
else
{
num6 = num3 + subsegment3.Literal.Length;
num7 = length - num6;
}
string str = requestPathSegment.Substring(num6, num7);
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(str))
{
return false;
}
matchedValues.Add(subsegment2.ParameterName, str);
subsegment2 = null;
subsegment3 = null;
}
length = num3;
num2--;
}
if (length != )
{
return (routeSegment.Subsegments[] is ParameterSubsegment);
}
return true;
} private bool MatchContentPathSegment(ContentPathSegment routeSegment, string requestPathSegment, RouteValueDictionary defaultValues, RouteValueDictionary matchedValues)
{
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(requestPathSegment))
{
if (routeSegment.Subsegments.Count <= )
{
object obj2;
ParameterSubsegment subsegment = routeSegment.Subsegments[] as ParameterSubsegment;
if (subsegment == null)
{
return false;
}
if (defaultValues.TryGetValue(subsegment.ParameterName, out obj2))
{
matchedValues.Add(subsegment.ParameterName, obj2);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
int length = requestPathSegment.Length;
int num2 = routeSegment.Subsegments.Count - ;
ParameterSubsegment subsegment2 = null;
LiteralSubsegment subsegment3 = null;
while (num2 >= )
{
int num3 = length;
ParameterSubsegment subsegment4 = routeSegment.Subsegments[num2] as ParameterSubsegment;
if (subsegment4 != null)
{
subsegment2 = subsegment4;
}
else
{
LiteralSubsegment subsegment5 = routeSegment.Subsegments[num2] as LiteralSubsegment;
if (subsegment5 != null)
{
subsegment3 = subsegment5;
int startIndex = length - ;
if (subsegment2 != null)
{
startIndex--;
}
if (startIndex < )
{
return false;
}
int num5 = requestPathSegment.LastIndexOf(subsegment5.Literal, startIndex, StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase);
if (num5 == -)
{
return false;
}
if ((num2 == (routeSegment.Subsegments.Count - )) && ((num5 + subsegment5.Literal.Length) != requestPathSegment.Length))
{
return false;
}
num3 = num5;
}
}
if ((subsegment2 != null) && (((subsegment3 != null) && (subsegment4 == null)) || (num2 == )))
{
int num6;
int num7;
if (subsegment3 == null)
{
if (num2 == )
{
num6 = ;
}
else
{
num6 = num3 + subsegment3.Literal.Length;
}
num7 = length;
}
else if ((num2 == ) && (subsegment4 != null))
{
num6 = ;
num7 = length;
}
else
{
num6 = num3 + subsegment3.Literal.Length;
num7 = length - num6;
}
string str = requestPathSegment.Substring(num6, num7);
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(str))
{
return false;
}
matchedValues.Add(subsegment2.ParameterName, str);
subsegment2 = null;
subsegment3 = null;
}
length = num3;
num2--;
}
if (length != )
{
return (routeSegment.Subsegments[] is ParameterSubsegment);
}
return true;
}
这个方法就是真正把路由参数和路由的值给关联起来,如果参数requestPathSegment为null则参数值从defaultValues中获取,
if (defaultValues.TryGetValue(subsegment.ParameterName, out obj2))
{
matchedValues.Add(subsegment.ParameterName, obj2);
return true;
}
否则从我们传递进来的requestPathSegment获取。
string str = requestPathSegment.Substring(num6, num7);
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(str))
{
return false;
}
matchedValues.Add(subsegment2.ParameterName, str);
Match方法在结束之前会检查我们的defaultValues字典,把defaultValues中的key(matchedValues不存在对应的key)加到matchedValues中来。整个match方法及结束了,结合前面的东西我们也就可以明白Route类的GetRouteData方法了。
为了跟好的理解上面个方法,我这里再举一个demo:
路由信息: routes.MapRoute("Default", "{ChannelName}/{action}", new { controller = "Home", action = "Index" });
调用Match方法的 virtualPath=men/index,
source取值:
PathSegments取值:
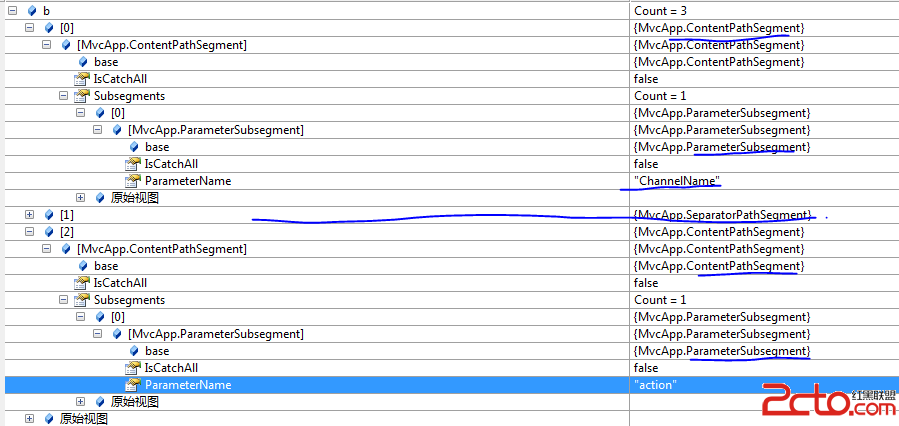
至于Match方法中的有一种路径是调用MatchCatchAll方法,
[csharp]
private void MatchCatchAll(ContentPathSegment contentPathSegment, IEnumerable<string> remainingRequestSegments, RouteValueDictionary defaultValues, RouteValueDictionary matchedValues)
{
object obj2;
string str = string.Join(string.Empty, remainingRequestSegments.ToArray<string>());
ParameterSubsegment subsegment = contentPathSegment.Subsegments[] as ParameterSubsegment;
if (str.Length > )
{
obj2 = str;
}
else
{
defaultValues.TryGetValue(subsegment.ParameterName, out obj2);
}
matchedValues.Add(subsegment.ParameterName, obj2);
} private void MatchCatchAll(ContentPathSegment contentPathSegment, IEnumerable<string> remainingRequestSegments, RouteValueDictionary defaultValues, RouteValueDictionary matchedValues)
{
object obj2;
string str = string.Join(string.Empty, remainingRequestSegments.ToArray<string>());
ParameterSubsegment subsegment = contentPathSegment.Subsegments[] as ParameterSubsegment;
if (str.Length > )
{
obj2 = str;
}
else
{
defaultValues.TryGetValue(subsegment.ParameterName, out obj2);
}
matchedValues.Add(subsegment.ParameterName, obj2);
}
它要求contentPathSegment.IsCatchAll为true。从 ParameterSubsegment类的定义可以知道当且仅当传进来parameterName以*打头才是True。parameterName是从url中来的,也就是说url中要含有*,IsCatchAll才为true。在前面提到的ValidateUrlParts方法会验证url的,其主要代码如下:
private static Exception ValidateUrlParts(IList<string> pathSegments)
{
HashSet<string> usedParameterNames = new HashSet<string>(StringComparer.OrdinalIgnoreCase);
bool? nullable = null;
bool flag = false;
foreach (string str in pathSegments)
{
bool flag2;
if (flag)
{
return new ArgumentException(string.Format(CultureInfo.CurrentUICulture, SR.GetString("Route_CatchAllMustBeLast"), new object[]), "routeUrl");
} if (!flag2)
{
Exception exception;
IList<PathSubsegment> pathSubsegments = ParseUrlSegment(str, out exception); flag = pathSubsegments.Any<PathSubsegment>(seg => (seg is ParameterSubsegment) && ((ParameterSubsegment) seg).IsCatchAll);
}
}
return null;
}
所以以上的那个MatchCatchAll执行的条件也很明显就是url中带有*号,并且是最后一个参数带有*,希望大家注意一下。大家看到这里相信对Route类的GetRouteData方法有个大致的了解了吧。
asp.net mvc源码分析-Route的GetRouteData的更多相关文章
- ASP.NET MVC源码分析
MVC4 源码分析(Visual studio 2012/2013) HttpModule中重要的UrlRoutingModule 9:this.OnApplicationPostResolveReq ...
- ASP.NET MVC 源码分析(一)
ASP.NET MVC 源码分析(一) 直接上图: 我们先来看Core的设计: 从项目结构来看,asp.net.mvc.core有以下目录: ActionConstraints:action限制相关 ...
- asp.net mvc源码分析-DefaultModelBinder 自定义的普通数据类型的绑定和验证
原文:asp.net mvc源码分析-DefaultModelBinder 自定义的普通数据类型的绑定和验证 在前面的文章中我们曾经涉及到ControllerActionInvoker类GetPara ...
- asp.net mvc源码分析-ModelValidatorProviders 客户端的验证
几年写过asp.net mvc源码分析-ModelValidatorProviders 当时主要是考虑mvc的流程对,客户端的验证也只是简单的提及了一下,现在我们来仔细看一下客户端的验证. 如图所示, ...
- asp.net MVC 源码分析
先上一张图吧 asp.net请求机制的图 by传智播客邹华栋老师 然后是 邹老师添加MVC请求过程的图 其实MVC 是在.netframework上加了一个过滤器 HttpModule 在C:\W ...
- ASP.NET MVC 源码分析(二) —— 从 IRouteBuilder认识路由构建
我们来看IRouteBuilder的定义: public interface IRouteBuilder { IRouter DefaultHandler { get; set; } IService ...
- asp.net mvc源码分析-Action篇 IModelBinder
我们首先还是看看ReflectedParameterBindingInfo的Binder属性吧: public override IModelBinder Binder { ge ...
- ASP.NET MVC源码分析系列
Controller下的JsonResult的ExecuteResult方法 public override void ExecuteResult(ControllerContext context) ...
- ASP.NET WebForm / MVC 源码分析
浏览器 Url:https//localhost:6565/Home/Index ,https//localhost:6565/WebForm1.aspx,请求服务器(构建请求报文,并且将请求报文发送 ...
随机推荐
- delphi DBgrid应用大全
Delphi 语言的数据库编程中,DBGrid 是显示数据的主要手段之一.但是 DBGrid 缺省的外观未免显得单调和缺乏创意.其实,我们完全可以在我们的程序中通过编程来达到美化DBGrid 外观的目 ...
- AnsiIO
1.文件数据内容,元数据内容 i节点ls -l err.txt-rw-rw-r-- 1 csgec csgec 50 Jun 23 11:19 err.txt-:普通文件(文件类型)rw-:属主用户拥 ...
- 【翻译】在Visual Studio中使用Asp.Net Core MVC创建第一个Web Api应用(二)
运行应用 In Visual Studio, press CTRL+F5 to launch the app. Visual Studio launches a browser and navigat ...
- php中二维数组如何使用
最近需要使用PHP中的二维数组,就用一个简单的例子来说明PHP中二数组是如何使用 <?php $a=array('a','b','c'); $c=array('a1','b1','c1'); $ ...
- Canvas createRadialGradient API
Canvas createRadialGradient API <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> ...
- python中将两个list合并为字典
两个list合并为字典的代码如下: def Run(): list2 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5 ]; list3 = ["a", "b", " ...
- KB奇遇记(4):困难重重的选型
在以往的工作经历中,虽然也会出现公司的一些规章制度,但我鲜少与其打交道,也极少听说.但是来KB这里,突然发现公司居然并没有给我配备电脑!!原因是制度上并没有写IT人员入职需要配备电脑,尔后通过特批流程 ...
- easyui datagrid的json格式
easyui datagrid的json格式: {"columns":[[{"field":"one","title": ...
- 开源OSS.Social微信项目解析
前言:OSS.Social是个开源的社交网站接口集成项目,当前也有很多其他不错的项目,不过始终没有我想要的那种简单清晰,只能撸起袖子,从头打造一个.当前正在进行的是对微信项目的开发,这里把对接口的整 ...
- Codeforce 712A Memory and Crow
A. Memory and Crow time limit per test:2 seconds memory limit per test:256 megabytes input:standard ...

