database---many to many relationships(多对多关系型数据库)
Many to many Relationships
A many-to-many relationship occurs when multiple records in a table are associated with multiple records in another table. For example, a many-to-many relationship exists between customers and products: customers can purchase various products, and products can be purchased by many customers.
Relational database systems usually don't allow you to implement a direct many-to-many relationship between two tables. Consider the example of keeping track of invoices. If there were many invoices with the same invoice number and one of your customers inquired about that invoice number, you wouldn’t know which number they were referring to. This is one reason for assigning a unique value to each invoice.
To avoid this problem, you can break the many-to-many relationship into two one-to-many relationships by using a third table, called a join table. Each record in a join table includes a match field that contains the value of the primary keys of the two tables it joins. (In the join table, these match fields are foreign keys.) These foreign key fields are populated with data as records in the join table are created from either table it joins.
A typical example of a many-to many relationship is one between students and classes. A student can register for many classes, and a class can include many students.
The following example includes a Students table, which contains a record for each student, and a Classes table, which contains a record for each class. A join table, Enrollments, creates two one-to-many relationships—one between each of the two tables.
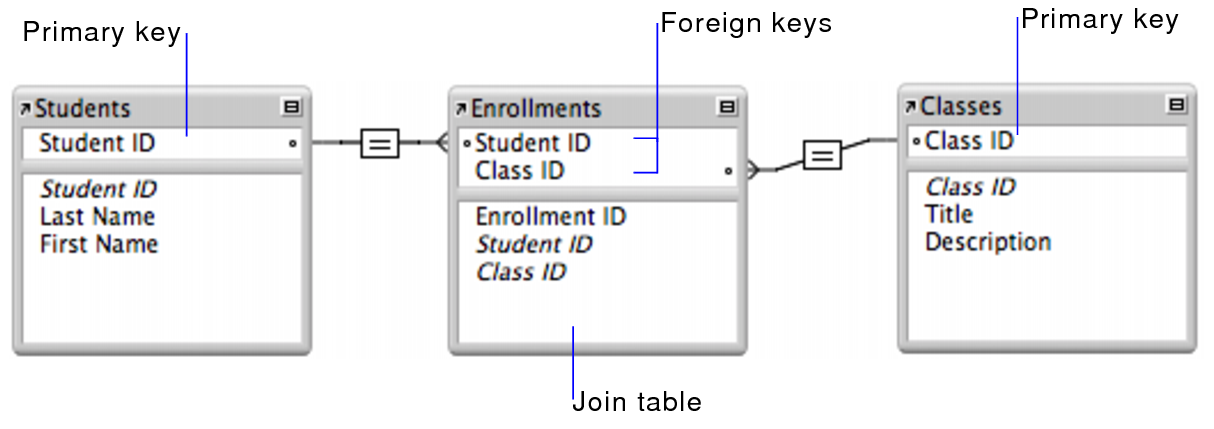
The primary key Student ID uniquely identifies each student in the Students table. The primary key Class ID uniquely identifies each class in the Classes table. The Enrollments table contains the foreign keys Student ID and Class ID.
To set up a join table for a many-to-many relationship:
Using the example above, create a table named Enrollments. This will be the join table.
In the Enrollments table, create a Student ID field and a Class ID field.
Join tables typically hold fields that might not make sense to have in any other table. You can add fields to the Enrollments table, such as a Date field to keep track of when someone started a class, and a Cost field to track how much a student paid to take a class.
- Create a relationship between the two Student ID fields in the tables. Then create a relationship between the two Class ID fields in the tables.
Using this design, if a student registers for three classes, that student will have one record in the Students table and three records in the Enrollments table—one record for each class the student enrolled in.
Notes
- Join tables can access fields and data across tables without having to create a separate relationship. For example, to display a list of all the classes a student enrolled in, create a portal on a layout based on the Students table. Design the portal to show related records from the Classes table. Then add the appropriate fields from Classes to the portal. As you browse through records in the Students layout, the portal displays all the classes a particular student is enrolled in.
database---many to many relationships(多对多关系型数据库)的更多相关文章
- Node的关系型数据库ORM库:bookshelf
NodeJs 关系数据库ORM库:Bookshelf.js bookshelf.js是基于knex的一个关系型数据库的ORM库.简单易用,内置了Promise的支持.这里主要罗列一些使用的例子,例子就 ...
- 关系型数据库之Mysql
简介 主要知识点包括:能够与mysql建立连接,创建数据库.表,分别从图形界面与脚本界面两个方面讲解 相关的知识点包括:E-R关系模型,数据库的3范式,mysql中数据字段的类型,字段约束 数据库的操 ...
- Oracle之关系型数据库
什么是关系型数据库? (1)关系型数据库是依据关系模型来创建的数据库. (2)所谓关系模型就是"一对一.一对多.多对多"等关系模型,关系模型就是指二维表格模型,因而一个关系型数据库 ...
- MongoDB学习笔记(二:入门环境配置及与关系型数据库区别总结)
一.下载及安装MongoDB MongoDB下载官网链接:http://www.mongodb.org/downloads 具体安装步骤教程:http://www.shouce.ren/api/vie ...
- Sqoop2入门之导入关系型数据库数据到HDFS上(sqoop2-1.99.4版本)
sqoop2-1.99.4和sqoop2-1.99.3版本操作略有不同:新版本中使用link代替了老版本的connection,其他使用类似. sqoop2-1.99.4环境搭建参见:Sqoop2环境 ...
- Google的分布式关系型数据库F1和Spanner
F1是Google开发的分布式关系型数据库,主要服务于Google的广告系统.Google的广告系统以前使用MySQL,广告系统的用户经常需要使用复杂的query和join操作,这就需要设计shard ...
- 大数据时代的数据存储,非关系型数据库MongoDB
在过去的很长一段时间中,关系型数据库(Relational Database Management System)一直是最主流的数据库解决方案,他运用真实世界中事物与关系来解释数据库中抽象的数据架构. ...
- 非关系型数据库SequoiaDB虚拟机下应用初探
SequoiaDB是广州巨杉软件有限公司开发的一款新型分布式非关系型数据库.可应用于linux操作系统下.在虚拟机下试用了一下(操作系统Ubuntu),感觉不错,操控简单易上手,在此分享一下心得. 下 ...
- ORMBase对象/关系型数据库映射在MVC中的应用
ORM这个字眼在我们操作数据库的时候,是我们使用频率最高的.它到底是个什么东西呢,我们先来看看一些对它的含义解释. 对象/关系数据库映射(object/relational mapping(ORM)) ...
随机推荐
- wordcloud 的常规方法
wordcloud 库把词云当作一个WordCloud对象 ——wordcloud.WordCloud() 代表一个文本对应的词云 ——可以根据文本中词语出现的频率等参数绘制词云 ——绘制词云的形状. ...
- SQL COUNT DISTINCT 函数
定义和用法 可以一同使用 DISTINCT 和 COUNT 关键词,来计算非重复结果的数目. 语法 SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT column(s)) FROM table 例子 注意: ...
- Python-1-基础
获取用户输入 >>> x = input("x: ") x: 34 >>> y = input("y: ") y: 42 & ...
- 选择提示框UIAlertController 和网络状态判断AFNetworking
// 选择提示框 DownloadView *vc = [[DownloadView alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectMake(, , SCREEN_WIDTH, SCREEN_ ...
- a标签中href=""的几种用法
http://blog.csdn.net/u010297791/article/details/52784879 这是分页上的 <?php function pages($page,$e_pag ...
- 解决Centos下SSH登录慢的问题
产生这个问题的原因是:server的sshd会去DNS查找访问client IP的hostname,如果DNS不可用或者没有相关的记录就会花费大量的时间. 1.在server上/etc/hosts文件 ...
- 转 open_cursors参数设置调优
https://www.cnblogs.com/Peyton-for-2012/archive/2013/05/07/3065058.html
- 74HC14D(6反向施密特触发器)
74HC14D:6反向施密特触发器:延迟特性,反向特性,整形特点. 施密特触发器是具有特殊功能的非门,当加在它的输入端A的电压逐渐上升到某个值时(正阈值电压),输出端Y会突然从高电平跳到低电平,而当输 ...
- vuex 使用方法
1.安装vuex扩展 : npm install vuex 2.在componets目录下新建 store.js 文件 import Vue from 'vue' import Vuex from ' ...
- nodejs Async 使用方法(解决多层回调嵌套)
由于nodejs是异步处理的,有时我们想同步从mysql里取出数据,最后在处理逻辑 就需要用到此扩展: 此扩展可以避免多层回调: 安装方法: npm install async 使用方法: 1.par ...
