Codeforce 438D-The Child and Sequence 分类: Brush Mode 2014-10-06 20:20 102人阅读 评论(0) 收藏
4 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
At the children's day, the child came to Picks's house, and messed his house up. Picks was angry at him. A lot of important things were lost, in particular the favorite sequence of Picks.
Fortunately, Picks remembers how to repair the sequence. Initially he should create an integer array a[1], a[2], ..., a[n]. Then
he should perform a sequence of m operations. An operation can be one of the following:
- Print operation l, r. Picks should write down the value of
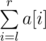 .
. - Modulo operation l, r, x. Picks should perform assignment a[i] = a[i] mod x for
each i (l ≤ i ≤ r). - Set operation k, x. Picks should set the value of a[k] to x (in
other words perform an assignment a[k] = x).
Can you help Picks to perform the whole sequence of operations?
The first line of input contains two integer: n, m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 105).
The second line contains n integers, separated by space:a[1], a[2], ..., a[n] (1 ≤ a[i] ≤ 109) —
initial value of array elements.
Each of the next m lines begins with a number type 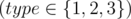 .
.
- If type = 1, there will be two integers more in the line: l, r (1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ n),
which correspond the operation 1. - If type = 2, there will be three integers more in the line: l, r, x (1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ n; 1 ≤ x ≤ 109),
which correspond the operation 2. - If type = 3, there will be two integers more in the line: k, x (1 ≤ k ≤ n; 1 ≤ x ≤ 109),
which correspond the operation 3.
For each operation 1, please print a line containing the answer. Notice that the answer may exceed the 32-bit integer.
5 5
1 2 3 4 5
2 3 5 4
3 3 5
1 2 5
2 1 3 3
1 1 3
8
5
10 10
6 9 6 7 6 1 10 10 9 5
1 3 9
2 7 10 9
2 5 10 8
1 4 7
3 3 7
2 7 9 9
1 2 4
1 6 6
1 5 9
3 1 10
49
15
23
1
9
Consider the first testcase:
- At first, a = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}.
- After operation 1, a = {1, 2, 3, 0, 1}.
- After operation 2, a = {1, 2, 5, 0, 1}.
- At operation 3, 2 + 5 + 0 + 1 = 8.
- After operation 4, a = {1, 2, 2, 0, 1}.
- At operation 5, 1 + 2 + 2 = 5.
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
struct node{
long long l, r, s, maxx;
}num[800005];
long long n, m, key; template <class T>
inline bool scan_d(T &ret) {
char c; int sgn;
if(c=getchar(),c==EOF) return 0; //EOF
while(c!='-'&&(c<'0'||c>'9')) c=getchar();
sgn=(c=='-')?-1:1;
ret=(c=='-')?0:(c-'0');
while(c=getchar(),c>='0'&&c<='9') ret=ret*10+(c-'0');
ret*=sgn;
return 1;
} inline void out(long long x) {
if(x>9) out(x/10);
putchar(x%10+'0');
} void build(int l,int r,int k)
{
num[k].l = l;
num[k].r = r;
num[k].s = 0;
num[k].maxx = 0;
if(l == r) return;
int mi = (l+r)>>1;
build(l,mi,k+k);
build(mi+1,r,k+k+1);
return;
} void update(int l, int r, int k)
{
if(num[k].l==num[k].r)
{
num[k].s = key;
num[k].maxx = key;
return;
}
int mi = (num[k].l+num[k].r)>>1;
if(l > mi) update(l,r,k+k+1);
else if(r <= mi) update(l,r,k+k);
else
{
update(l,mi,k+k);
update(mi+1,r,k+k+1);
}
num[k].s = num[k+k].s + num[k+k+1].s;
num[k].maxx = max(num[k+k].maxx,num[k+k+1].maxx);
return;
} void upmod(int l, int r, int k)
{
if(num[k].maxx<key) return;
if(num[k].l==num[k].r)
{
num[k].s%=key;
num[k].maxx = num[k].s;
return;
}
int mi = (num[k].l+num[k].r)>>1;
if(l > mi) upmod(l,r,k+k+1);
else if(r <= mi) upmod(l,r,k+k);
else
{
upmod(l,mi,k+k);
upmod(mi+1,r,k+k+1);
}
num[k].s = num[k+k].s + num[k+k+1].s;
num[k].maxx = max(num[k+k].maxx,num[k+k+1].maxx);
return;
} long long query(int k,int l,int r)
{
if(num[k].l==l && num[k].r==r)
{
return num[k].s;
}
else
{
int mi = (num[k].l+num[k].r)>>1;
if(r<=mi) return query(k+k,l,r);
else if(l>mi) return query(k+k+1,l,r);
else return query(k+k,l,mi)+query(k+k+1,mi+1,r);
}
} int main()
{
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0);
int Case;
int a, b, c;
memset(num,0,sizeof(num));
scan_d(n);
scan_d(m);
build(1,n,1);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
scan_d(key);
update(i,i,1);
}
while(m--)
{
scan_d(c);
switch(c)
{
case 1:
scan_d(a);
scan_d(b);
out(query(1,a,b));
putchar('\n');
break;
case 2:
scan_d(a);
scan_d(b);
scan_d(key);
upmod(a,b,1);
break;
case 3:
scan_d(a);
scan_d(key);
update(a,a,1);
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
另一种的线段树写法:
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string>
#include <deque>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <iomanip>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
#define lson l , m , rt << 1
#define rson m + 1 , r , rt << 1 | 1
const int maxn = 100010; LL sum[maxn<<2], ma[maxn<<2];
void PushUP(int rt) {
sum[rt] = sum[rt<<1] + sum[rt<<1|1];
}
void PushUP2(int rt) {
ma[rt] = max(ma[rt<<1], ma[rt<<1|1]);
}
void build(int l,int r,int rt) {
if (l == r) {
//scanf("%I64d",&sum[rt]);
cin >> sum[rt];
ma[rt] = sum[rt];
return ;
}
int m = (l + r) >> 1;
build(lson);
build(rson);
PushUP(rt);
PushUP2(rt);
}
//#define lson l , m , rt << 1
//#define rson m + 1 , r , rt << 1 | 1
void MOD(int L,int R,int l,int r,int rt, LL mod)
{
// if(R < l || L > r) return ;
// if(L <= l && r <= R && ma[rt] < mod) return ;
if(ma[rt] < mod) return ;
if(l == r) {sum[rt] %= mod; ma[rt] = sum[rt];return ;} int m = (l + r) >> 1;
if (L <= m) MOD(L, R , lson, mod);
if (R > m) MOD(L, R , rson, mod);
PushUP(rt);
PushUP2(rt);
} void update(int p,LL add,int l,int r,int rt) {
if (l == r) {
//sum[rt] += add;
sum[rt] = add;
ma[rt] = sum[rt];
return ;
}
int m = (l + r) >> 1;
if (p <= m) update(p , add , lson);
else update(p , add , rson);
PushUP(rt);
PushUP2(rt);
}
LL query(int L,int R,int l,int r,int rt) {
if (L <= l && r <= R) {
return sum[rt];
}
int m = (l + r) >> 1;
LL ret = 0;
if (L <= m) ret += query(L , R , lson);
if (R > m) ret += query(L , R , rson);
return ret;
}
int main() { int n, m, op, l, r, k;
LL x, mod;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
build(1, n, 1);
while(m--)
{
scanf("%d",&op);
if(op == 1)
{
//scanf("%d%d",&l, &r);
cin >> l >> r;
cout << query(l, r, 1, n, 1) << endl;
//printf("%I64d\n",query(l, r, 1, n, 1));
}
else if(op == 2)
{
cin >> l >> r >> mod;
//scanf("%d%d%I64d",&l, &r, &mod);
MOD(l, r, 1, n, 1, mod); }
else
{
cin >> k >> x;
//scanf("%d%d",&k,&x);
update(k, x, 1, n, 1);
}
} return 0;
}
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载。
Codeforce 438D-The Child and Sequence 分类: Brush Mode 2014-10-06 20:20 102人阅读 评论(0) 收藏的更多相关文章
- bzoj 1041 圆上的整点 分类: Brush Mode 2014-11-11 20:15 80人阅读 评论(0) 收藏
这里先只考虑x,y都大于0的情况 如果x^2+y^2=r^2,则(r-x)(r+x)=y*y 令d=gcd(r-x,r+x),r-x=d*u^2,r+x=d*v^2,显然有gcd(u,v)=1且u&l ...
- NYOJ 119 士兵杀敌(三)【ST算法】 分类: Brush Mode 2014-11-13 20:56 101人阅读 评论(0) 收藏
题目链接:http://acm.nyist.net/JudgeOnline/problem.php?pid=119 解题思路: RMQ算法. 不会的可以去看看我总结的RMQ算法. http://blo ...
- Poj 2559 最大矩形面积 v单调栈 分类: Brush Mode 2014-11-13 20:48 81人阅读 评论(0) 收藏
#include<iostream> #include<stack> #include<stdio.h> using namespace std; struct n ...
- DNA Sorting 分类: POJ 2015-06-23 20:24 9人阅读 评论(0) 收藏
DNA Sorting Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 10000K Total Submissions: 88690 Accepted: 35644 Descrip ...
- Binary Tree 分类: POJ 2015-06-12 20:34 17人阅读 评论(0) 收藏
Binary Tree Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 6355 Accepted: 2922 Descr ...
- Self Numbers 分类: POJ 2015-06-12 20:07 14人阅读 评论(0) 收藏
Self Numbers Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 10000K Total Submissions: 22101 Accepted: 12429 De ...
- 共享内存+互斥量实现linux进程间通信 分类: Linux C/C++ 2015-03-26 17:14 67人阅读 评论(0) 收藏
一.共享内存简介 共享内存是进程间通信中高效方便的方式之一.共享内存允许两个或更多进程访问同一块内存,就如同 malloc() 函数向不同进程返回了指向同一个物理内存区域的指针,两个进程可以对一块共享 ...
- OC基础知识总结 分类: ios学习 OC 2015-06-26 17:58 58人阅读 评论(0) 收藏
//OC: Objective-C, 面向对象的C语言 //OC与C的区别 //1.OC是C的超集, C语言的所有语法都可以在OC中使用 //2.OC是面向对象 //3.OC是一门运行时语言 //4. ...
- OC基础:类的扩展.协议 分类: ios学习 OC 2015-06-22 19:22 34人阅读 评论(0) 收藏
//再设计一个类的时候,有些方法需要对外公开(接口),有些仅供内部使用. 类的扩展:为类添加新的特征(属性)或者方法 对已知类: 1.直接添加 2.继承(在其子类中添加实例变量和方法) 3.使用ext ...
随机推荐
- qemu-kvm简单使用
qemu-kvm主要有以下几个选项: -snapshot: 创建快照 -m: 指定内存大小 -smp: 指定处理器个数 -cpu: 指定CPU类型 -name: 设置虚拟机名称 -vnc: 使用vnc ...
- 小鸟哥哥博客 For SAE
独立博客地址:http://www.zhujiawei.com.cn/ 辞职后出去玩了几个月,把积蓄都快花光了,打算熬到年底再找工作.最近闲来无聊,想起自己一年前趁着活动便宜,一口气买了10年的域名一 ...
- 二,CentOS minimal 网络配置及用yum安装所需软件
CentOS minimal在刚安装完成后,ifconfig一下没发现网卡,是因为使用最小安装的网卡默认没启动,设置配置文件很简单,如下: 1.打开配置文件 vi /etc/sysconfig/net ...
- C#通过WinAPI获取内存信息,32位64位可用
using System;using System.Collections.Generic;using System.Linq;using System.Text;using System.Runti ...
- R语言的日期运算
写hive SQL查询, 需要从导入的参数, 自动累加日期. 从而实现一个自动的,多个日期的统计过程 R语言的日期运算超级简单. > test<-Sys.Date() > test ...
- sublimeText OmniMarkupPreviewer 404
这个错误也是出现的莫名奇妙. "Error: 404 Not Found Sorry, the requested URL 'http://127.0.0.1:51004/view/29' ...
- 【javascript】随手记代码
//js实现的当前界面的刷新.前进.后退 <input type="button" value="刷新" onclick="window.loc ...
- [php]如何更改wamp默认的mysq空密码?
最近刚开始学php,爬坑中.上午看了会儿书,下了个源码,把文件部署到www下之后,也导入了sql文件,但是进入之后显示 = = 一开始不知道是什么.后来百度之后发现是mysql的问题,应该是源码中p ...
- eclipse集成maven
1.工具下载: Eclipse4.2 jee版本(这里使用最新的Eclipse版本,3.7以上版本按照以下步骤都可以) 下载地址:http://www.eclipse.org/downloads/do ...
- EMVTag系列3《持卡人基本信息数据》
Ø 9F61 持卡人证件号 L:2–26 R(需求):数据应存在,在读应用数据过程中,终端不检查: (PBOC2.0第五部分中规定)芯片中持卡人姓名 5F20与持卡人姓名扩展9F0B只能使用一 ...
