Spring Boot实战笔记(二)-- Spring常用配置(Scope、Spring EL和资源调用)
一、Bean的Scope
Scope描述的是Spring容器如何新建Bean实例的。Spring的Scope有以下几种,通过@Scope注解来实现。
(1)Singleton:一个Spring容器中只有一个Bean的实例,此为Spring的默认配置,全容器共享一个实例。
(2)Prototype:每次调用新建一个Bean实例。
(3)Request:Web项目中,给每一个 http request 新建一个Bean实例。
(4)Session:Web项目中,给每一个 http session 新建一个Bean实例。
(5)GlobalSession:这个只在portal应用中有用,给每一个 global http session 新建一个Bean实例。
另外,在Spring Batch中还有一个Scope是使用@StepScope,我们将在批处理介绍这个Scope。
接下来简单演示默认的 Singleton 和 Prototype,分别从Spring容器中获取两次Bean,判断Bean的实例是否相等。
1.编写Singleton的Bean。
package com.ecworking.scope; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; @Service //默认为Singleton,相当于@Scope("singleton")。
public class DemoSingletonService {
}
2.编写Prototype的Bean。
package com.ecworking.scope; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; @Service
@Scope("prototype") //声明Scopew为Prototype。
public class DemoPrototypeService {
}
3.配置类。
package com.ecworking.scope; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.ecworking.scope")
public class ScopeConfig {
}
4.运行。
package com.ecworking.scope;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(ScopeConfig.class);
DemoSingletonService s1 = context.getBean(DemoSingletonService.class);
DemoSingletonService s2 = context.getBean(DemoSingletonService.class);
DemoPrototypeService p1 = context.getBean(DemoPrototypeService.class);
DemoPrototypeService p2 = context.getBean(DemoPrototypeService.class);
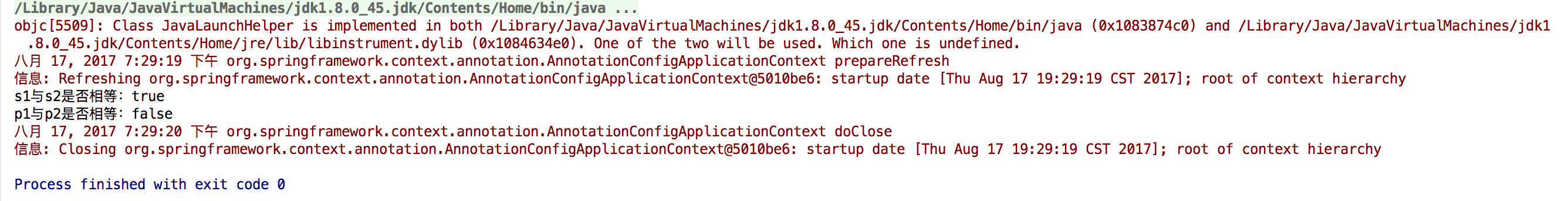
System.out.println("s1与s2是否相等:" + s1.equals(s2));
System.out.println("p1与p2是否相等:" + p1.equals(p2));
context.close();
}
}
运行结果:
二、Spring EL和资源调用
Spring EL-Spring表达式语言,支持在xml和注解中使用表达式,类似于JSP的EL表达式语言。
Spring 开发中经常涉及调用各种资源的情况,包含普通文件、网址、配置文件、系统环境变量等,我们可以使用Spring表达式语言实现资源的注入。
Spring 主要在注解@Value的参数中使用表达式。
本节演示实现以下几种情况:
(1)注入普通字符;
(2)注入操作系统属性;
(3)注入表达式运算结果;
(4)注入其他Bean的属性;
(5)注入文件内容;
(6)注入网址内容;
(7)注入属性文件;
1. 准备,增加commons-io可简化文件相关操作。
本例中使用commons-io将file转换成字符串:
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-io</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-io</artifactId>
<version>2.3</version>
</dependency>
在com.ecworking.el.source包下新建test.txt,内容随意。
在com.ecworking.el.source包下新建test.propertise,内容如下:
book.author = dongyp
book.name = spring boot
2. 需要被注入的Bean。
package com.ecworking.el; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; @Service
public class DemoService {
@Value("其他类的属性") //此处为注入普通字符串
private String another; public String getAnother() {
return another;
} public void setAnother(String another) {
this.another = another;
}
}
3. 演示类Bean。
package com.ecworking.el; import org.apache.commons.io.IOUtils;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import org.springframework.context.support.PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.core.io.Resource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import java.io.IOException; @Service
@PropertySource("classpath:test.properties")
//注入配置文件需使用@PropertySource指定文件地址,若使用@Value注入,则要配置一个PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer的Bean。注意@Value("${book.name}"),使用的是$而不是#。
//注入 Properties 还可以从 Environment 中获得。
public class DemoElService {
@Value("I LOVE YOU!") //注入普通字符串
private String normal; @Value("#{systemProperties['os.name']}") //注入操作系统属性
private String osName; @Value("#{T(java.lang.Math).random() * 100.0}") //注入表达式结果
private String randomNumber; @Value("#{demoService.another}") //注入其他Bean属性
private String fromAnother; @Value("classpath:/test.txt") //注入文件资源
private Resource testFile; @Value("http://www.baidu.com") //注入网址资源
private Resource testUrl; @Value("${book.name}") // 注入配置文件
private String bookName; @Autowired // 注入配置文件
private Environment environment; @Bean // 注入配置文件
public static PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer propertyConfigurer(){
return new PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer();
} public void outputResource(){
try {
System.out.println(normal);
System.out.println(osName);
System.out.println(randomNumber);
System.out.println(fromAnother);
System.out.println(IOUtils.toString(testFile.getInputStream()));
System.out.println(IOUtils.toString(testUrl.getInputStream()));
System.out.println(bookName);
System.out.println(environment.getProperty("book.author"));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
4.配置类。
package com.ecworking.el; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.ecworking.el")
public class ElConfig {
}
5.运行。
package com.ecworking.el;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(ElConfig.class);
DemoElService demoElService = context.getBean(DemoElService.class);
demoElService.outputResource();
context.close();
}
}
运行结果:

Spring Boot实战笔记(二)-- Spring常用配置(Scope、Spring EL和资源调用)的更多相关文章
- spring boot实战(第十三篇)自动配置原理分析
前言 spring Boot中引入了自动配置,让开发者利用起来更加的简便.快捷,本篇讲利用RabbitMQ的自动配置为例讲分析下Spring Boot中的自动配置原理. 在上一篇末尾讲述了Spring ...
- Spring Boot学习笔记二
Spring Boot入门第二篇 第一天的详见:https://www.cnblogs.com/LBJLAKERS/p/12001253.html 同样是新建一个pring Initializer快速 ...
- Spring Boot实战系列(7)集成Consul配置中心
本篇主要介绍了 Spring Boot 如何与 Consul 进行集成,Consul 只是服务注册的一种实现,还有其它的例如 Zookeeper.Etcd 等,服务注册发现在微服务架构中扮演这一个重要 ...
- Spring Boot实战笔记(一)-- Spring简介
一.Spring 概述 Spring框架是一个轻量级的企业级开发的一站式解决方案.所谓的解决方案就是可以基于Spring解决所有的Java EE开发的所有问题. Spring框架主要提供了Ioc(In ...
- JavaEE开发的颠覆者 Spring Boot实战--笔记
1.Spring boot的三种启动模式 Spring 的问题 Spring boot的特点,没有特别的地方 1.Spring 基础 PS:关于spring配置 PS: 现在都已经使用 java配置, ...
- Spring Boot学习笔记(二二) - 与Mybatis集成
Mybatis集成 Spring Boot中的JPA部分默认是使用的hibernate,而如果想使用Mybatis的话就需要自己做一些配置.使用方式有两种,第一种是Mybatis官方提供的 mybat ...
- spring boot 实战笔记(一)
spring 概述: Bean :每一个被 Spring 管理的 JAVA对象,都称之为 Bean.Spring提供一个IoC容器来初始化对象,负责创建Bean, 解决对象之间的依赖管理和对象的使用. ...
- Spring Boot实战笔记(九)-- Spring高级话题(组合注解与元注解)
一.组合注解与元注解 从Spring 2开始,为了响应JDK 1.5推出的注解功能,Spring开始大量加入注解来替代xml配置.Spring的注解主要用来配置注入Bean,切面相关配置(@Trans ...
- Spring Boot实战笔记(五)-- Spring高级话题(Spring Aware)
一.Spring Aware Spring 依赖注入的最大亮点就是你所有的 Bean 对 Spring容器的存在是没有意识的.即你可以将你的容器替换成其他的容器,如Google Guice,这时 Be ...
随机推荐
- andrid面试题
下面的题目都是楼主在android交流群大家面试时遇到的,如果大家有好的题目或者好的见解欢迎分享,楼主将长期维护此帖. 某公司高级面试题(2015-03-14)[感谢helder分享] 1.详述And ...
- 【算法导论】图的深度优先搜索遍历(DFS)
关于图的存储在上一篇文章中已经讲述,在这里不在赘述.下面我们介绍图的深度优先搜索遍历(DFS). 深度优先搜索遍历实在访问了顶点vi后,访问vi的一个邻接点vj:访问vj之后,又访问vj的一个邻接点, ...
- 使用API获取(默认付款条件和到期日)
1. 目的:使用API取到应收事务处理的付款条件(实现标准功能的付款条件和到期日)2. 实现方法:调用 ARP_TRX_DEFAULTS_3.get_term_default获得付款条件 3.实现代码 ...
- linux grep 和 sed使用
http://www.cnblogs.com/zhuyp1015/archive/2012/07/01/2572289.html 听说过sed 和 awk 比较强大,专门学习了一下. 使用这些shel ...
- shim & polyfill
在JavaScript中,经常提到shim和polyfill,polyfill是shim的一种.shim 是将不同 api 封装成一种,比如 jQuery 的 $.ajax 封装了 XMLHttpRe ...
- iOS苹果自带UIMenuController
一.UIMenuController认识 1.默认情况下,UITextView / UITextFiled / UIWebView 都有苹果自带的有UIMenuController功能 2.UITex ...
- mysql之数据库的增删改查
一.DDL 1.创建数据库 create database 数据库名 *数据库名不能中文, 不能数字正常英文 , 关键字会自动变大写 2.删除数据库 drop database 数据库名 3.使用数据 ...
- 别跟我谈EF抵抗并发,敢问你到底会不会用EntityFramework
前言 一直以来写的博文都是比较温婉型的博文,今天这篇博文算是一篇批判性博文,有问题欢迎探讨,如标题,你到底会不会用EntityFramework啊. 你到底会不会用EntityFramework啊 面 ...
- Elasticsearch——起步
1.下载 地址:https://www.elastic.co/downloads/elasticsearch 2.解压 unzip elasticsearch-1.7.0.zip 3.启动 mv el ...
- java并发包分析之———AQS框架
一.什么是同步器 多线程并发的执行,之间通过某种 共享 状态来同步,只有当状态满足 xxxx 条件,才能触发线程执行 xxxx . 这个共同的语义可以称之为同步器.可以认为以上所有的锁机制都可以基 ...
