思维题--code forces round# 551 div.2
思维题--code forces round# 551 div.2-D
题目
D. Serval and Rooted Tree
time limit per test
2 seconds
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Now Serval is a junior high school student in Japari Middle School, and he is still thrilled on math as before.
As a talented boy in mathematics, he likes to play with numbers. This time, he wants to play with numbers on a rooted tree.
A tree is a connected graph without cycles. A rooted tree has a special vertex called the root. A parent of a node vv is the last different from vv vertex on the path from the root to the vertex vv. Children of vertex vv are all nodes for which vv is the parent. A vertex is a leaf if it has no children.
The rooted tree Serval owns has nn nodes, node 11 is the root. Serval will write some numbers into all nodes of the tree. However, there are some restrictions. Each of the nodes except leaves has an operation maxmax or minmin written in it, indicating that the number in this node should be equal to the maximum or minimum of all the numbers in its sons, respectively.
Assume that there are kk leaves in the tree. Serval wants to put integers 1,2,…,k1,2,…,k to the kk leaves (each number should be used exactly once). He loves large numbers, so he wants to maximize the number in the root. As his best friend, can you help him?
Input
The first line contains an integer nn (2≤n≤3⋅1052≤n≤3⋅105), the size of the tree.
The second line contains nn integers, the ii-th of them represents the operation in the node ii. 00 represents minmin and 11represents maxmax. If the node is a leaf, there is still a number of 00 or 11, but you can ignore it.
The third line contains n−1n−1 integers f2,f3,…,fnf2,f3,…,fn (1≤fi≤i−11≤fi≤i−1), where fifi represents the parent of the node ii.
Output
Output one integer — the maximum possible number in the root of the tree.
Examples
input
Copy
6
1 0 1 1 0 1
1 2 2 2 2
output
Copy
1
input
Copy
5
1 0 1 0 1
1 1 1 1
output
Copy
4
input
Copy
8
1 0 0 1 0 1 1 0
1 1 2 2 3 3 3
output
Copy
4
input
Copy
9
1 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 1
1 1 2 2 3 3 4 4
output
Copy
5
Note
Pictures below explain the examples. The numbers written in the middle of the nodes are their indices, and the numbers written on the top are the numbers written in the nodes.
In the first example, no matter how you arrange the numbers, the answer is 11.
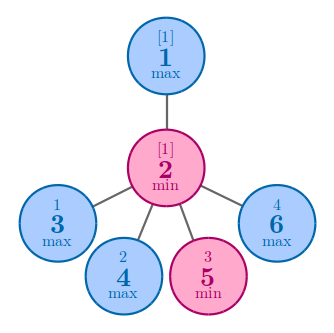
In the second example, no matter how you arrange the numbers, the answer is 44.
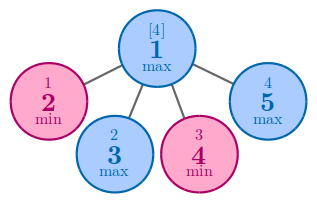
In the third example, one of the best solution to achieve 44 is to arrange 44 and 55 to nodes 44 and 55.
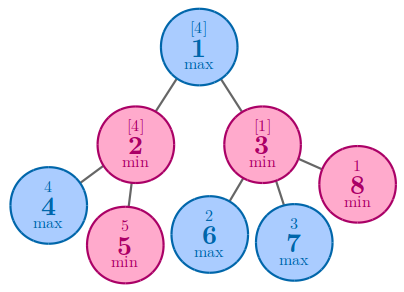
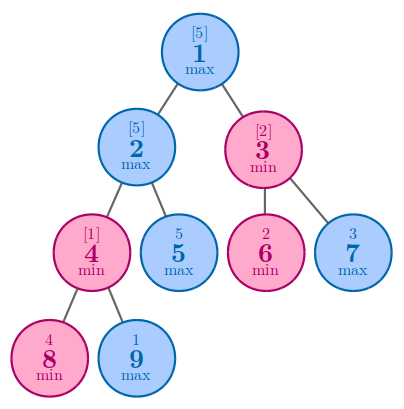
In the fourth example, the best solution is to arrange 55 to node 55.
题意易懂
思路
让所有叶子的值都为1
算的是必要的叶子个数,那么答案就是叶子个数 - 必要的叶子个数 + 1
如果是取max,那么该节点要取最大,那必要的叶子个数取决于该节点的所有子节点中,最小的必要叶子个数
如果是取min,那么该节点要取最大,必要的叶子个数为该节点的所有子节点中,所有的必要叶子个数的和
因为题目输入格式,可以知道父节点的输入一定在子节点前面,所以能遍历
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <sstream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <iomanip>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int N = 300000+50;
const int MOD = 1e9 + 9;
#define lson l, m, rt << 1
#define rson m + 1, r, rt << 1 | 1
#define F(i, l, r) for(int i = l;i <= (r);++i)
#define RF(i, l, r) for(int i = l;i >= (r);--i)
vector<int> v[N];
int a[N], c[N];
int n;
int main()
{
cin >> n;
F(i, 1, n) cin >> a[i];
F(i, 2, n)
{
int t;
cin >> t;
v[t].push_back(i);
}
int cnt = 0, ans = 0;
RF(i, n, 1)
{
if(v[i].size() == 0)
{
c[i] = 1;
cnt++;
}
else if(a[i])
{
c[i] = INF;
F(j, 0, v[i].size() - 1)
c[i] = min(c[i], c[v[i][j]]);
}
else
{
F(j, 0, v[i].size() - 1)
c[i] += c[v[i][j]];
}
}
cout << cnt + 1 - c[1] << endl;
return 0;
}
dfs写法
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <sstream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <iomanip>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int N = 300000+50;
const int MOD = 1e9 + 9;
#define lson l, m, rt << 1
#define rson m + 1, r, rt << 1 | 1
#define F(i, l, r) for(int i = l;i <= (r);++i)
#define RF(i, l, r) for(int i = l;i >= (r);--i)
vector<int> v[N];
int a[N], c[N];
int n, ant = 0, cnt;
void dfs(int now)
{
if(v[now].size() == 0)
{
c[now] = 1;
cnt++;
}
else if(a[now])
{
c[now] = INF;
F(j, 0, v[now].size() - 1)
{
dfs(v[now][j]);
c[now] = min(c[now], c[v[now][j]]);
}
}
else
{
F(j, 0, v[now].size() - 1)
{
dfs(v[now][j]);
c[now] += c[v[now][j]];
}
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> n;
F(i, 1, n) cin >> a[i];
F(i, 2, n)
{
int t;
cin >> t;
v[t].push_back(i);
}
dfs(1);
cout << cnt + 1 - c[1] << endl;
return 0;
}
思维题--code forces round# 551 div.2的更多相关文章
- 【Codeforces】Codeforces Round #551 (Div. 2)
Codeforces Round #551 (Div. 2) 算是放弃颓废决定好好打比赛好好刷题的开始吧 A. Serval and Bus 处理每个巴士最早到站且大于t的时间 #include &l ...
- CF Round #551 (Div. 2) D
CF Round #551 (Div. 2) D 链接 https://codeforces.com/contest/1153/problem/D 思路 不考虑赋值和贪心,考虑排名. 设\(dp_i\ ...
- 水题 Codeforces Beta Round #70 (Div. 2) A. Haiku
题目传送门 /* 水题:三个字符串判断每个是否有相应的元音字母,YES/NO 下午网速巨慢:( */ #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> ...
- Codeforces Round #551 (Div. 2) E. Serval and Snake (交互题)
人生第一次交互题ac! 其实比较水 容易发现如果查询的矩阵里面包含一个端点,得到的值是奇数:否则是偶数. 所以只要花2*n次查询每一行和每一列,找出其中查询答案为奇数的行和列,就表示这一行有一个端点. ...
- Codeforces Round #551 (Div. 2) 题解
CF1153A 直接做啊,分类讨论即可 #include<iostream> #include<string.h> #include<string> #includ ...
- C. Serval and Parenthesis Sequence 【括号匹配】 Codeforces Round #551 (Div. 2)
冲鸭,去刷题:http://codeforces.com/contest/1153/problem/C C. Serval and Parenthesis Sequence time limit pe ...
- 【做题】Codeforces Round #429 (Div. 2) E. On the Bench——组合问题+dp
题目大意是给你n个数,求相邻两数相乘不是完全平方数的排列数. 一开始看到这题的时候,本人便想给相乘为完全平方数的数对建边,然后就写萎了... 后来通过集体智慧发现这个重要性质:对于自然数a,b,c,若 ...
- Codeforces Round #551 (Div. 2) A~E题解
突然发现上一场没有写,那就补补吧 本来这场应该5题的,结果一念之差E fail了 A. Serval and Bus 基本数学不解释,假如你没有+1 -1真的不好意思见人了 #include<c ...
- 【思维题】TCO14 Round 2C InverseRMQ
全网好像就只有劼和manchery写了博客的样子……:正解可能是最大流?但是仔细特判也能过 题目描述 RMQ问题即区间最值问题是一个有趣的问题. 在这个问题中,对于一个长度为 n 的排列,query( ...
随机推荐
- 分布式事务,EventBus 解决方案:CAP【中文文档】(转)
出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/savorboard/p/cap-document.html 前言 很多同学想对CAP的机制以及用法等想有一个详细的了解,所以花了将近两周时间写了这 ...
- 马婕 2014MBA专硕考试 报刊选读 6(转)
http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_3e66af4601016udh.html Protecting the weakest保护最弱势群体The recession may ...
- 用Word2007写CSDN博客
目前大部分的博客作者在用Word写博客这件事情上都会遇到以下3个痛点: 1.所有博客平台关闭了文档发布接口,用户无法使用Word,Windows Live Writer等工具来发布博客.使用Word写 ...
- 从Objective-C到Swift,你必须会的(三)init的顺序
Objective-C的构造函数吧,就最后return一个self.里头你要初始化了什么都可以.在Swift的init函数里把super.init放在前面,然后再初始化你代码里的东西就会报错了. 所以 ...
- 看图说说Sun HotSpot虚拟机对象
- 创建 Android 项目
创建 Android 项目 上一页下一页 您也应该阅读 项目概览 本课向您介绍如何使用 Android Studio 创建新的 Android 项目并介绍该项目中的一些文件. 在 Android St ...
- 个人整理的一些iOS Entitlements
收集了不少Entitlement,当然也肯定有遗漏.有的就是key的字面意思,就不多做解释.不过有的虽然字面意思好理解,不过具体的用处不太清楚,就写的Unknown use.在替换entitlemen ...
- [LeetCode 题解]: Symmetric Tree
前言 [LeetCode 题解]系列传送门: http://www.cnblogs.com/double-win/category/573499.html 1.题目描述 Given a ...
- Debug就是Debug,Release就是Release
现在线上发布的时候使用的是增量发布,什么是增量发布呢,就是变化什么,上什么.最近把jenkins搭建上去了,发现每次dll文件大小不一样,已查询发现原来是两个模式debuge模式与release模式搞 ...
- win10 照片查看器
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00 ; Change Extension's File Type [HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Clas ...
