【译】x86程序员手册03 - 2.1内存组织和分段
2.1 Memory Organization and Segmentation 内存组织和分段
The physical memory of an 80386 system is organized as a sequence of 8-bit bytes. Each byte is assigned a unique address that ranges from zero to a maximum of 2^(32) -1 (4 gigabytes).
80386系统的物理内存被看做8位的流。每一位分配一个唯一的地址,这样就有了从0到最大2^(32)-1(4G)。
80386 programs, however, are independent of the physical address space. This means that programs can be written without knowledge of how much physical memory is available and without knowledge of exactly where in physical memory the instructions and data are located.
然而,80386的程序不依赖于物理地址空间。这意味着程序并不需要知道有多少物理内存可以使用也不需要知道指令和数据被准确地存在放哪些物理内存中。
The model of memory organization seen by applications programmers is determined by systems-software designers. The architecture of the 80386 gives designers the freedom to choose a model for each task. The model of memory organization can range between the following extremes:
程序设计者看到的内存组织模式由操作系统设计者决定。80386的架构给设计者为每个任务选择模式的自由。这种内存组织模式可以导致下列的极端行为:
- A "flat" address space consisting of a single array of up to 4 gigabytes. 一个由4G大小的单个数组来构成的扁平地址空间。
- A segmented address space consisting of a collection of up to 16,383 linear address spaces of up to 4 gigabytes each. 由每4G都是由16383个线性地址空间(最大到4T)集合构成的分段地址空间。
Both models can provide memory protection. Different tasks may employ different models of memory organization. The criteria that designers use to determine a memory organization model and the means that systems programmers use to implement that model are covered in Part -- Programming.
两种模式都可以提供内在保护。不同任务应该有不同的内存组织形式。设计者决定一个内存组织模式的标准和系统程序员实现这些模式的意义将在程序部分涉及。
2.1.1 The "Flat" Model 扁平模式
In a "flat" model of memory organization, the applications programmer sees a single array of up to 2^(32) bytes (4 gigabytes). While the physical memory can contain up to 4 gigabytes, it is usually much smaller; the processor maps the 4 gigabyte flat space onto the physical address space by the address translation mechanisms described in Chapter 5 . Applications programmers do not need to know the details of the mapping.
在扁平的内在组织模式中,应用程序员看到的是一个最大到4G的单个数组。物理内存可以访问到4G大小,但通常没有那么多。处理器映射4G扁平空间到物理地址空间是通过一个在第5章描述的地址转换机制来实现的。应用程序设计人员不需要知道映射细节。
A pointer into this flat address space is a 32-bit ordinal number that may range from 0 to 2^(32) -1. Relocation of separately-compiled modules in this space must be performed by systems software (e.g., linkers, locators, binders, loaders).
扁平地址空间的指针是一个32位的普通数字,其范围为0到2^(32)-1。独立的编译模块对空间的重定位必须由系统软件实现(如:linkers,locators,binders,loaders)。
2.1.2 The Segmented Model 分段模式
In a segmented model of memory organization, the address space as viewed by an applications program (called the logical address space) is a much larger space of up to 2^(46) bytes (64 terabytes). The processor maps the 64 terabyte logical address space onto the physical address space (up to 4 gigabytes ) by the address translation mechanisms described in Chapter 5 . Applications programmers do not need to know the details of this mapping.
在分段的内存组织模式中,应用程序可以看到的地址空间(也叫逻辑地址空间)是一个大到2^(46)字节的空间。处理器通过地址转换机制(第5章会讲到)来映射64T的逻辑地址空间到物理地址空间(最大4G)。应用程序不需要知道映射细节。
Applications programmers view the logical address space of the 80386 as a collection of up to 16,383 one-dimensional subspaces, each with a specified length. Each of these linear subspaces is called a segment. A segment is a unit of contiguous address space. Segment sizes may range from one byte up to a maximum of 2^(32) bytes (4 gigabytes).
应用程序将80386的逻辑地址空间视做一个最大下标为16383的集合,每个项都有相同的指定的长度。每个线性子空间被称作一个段。每个段都是一个连续的地址空间单元。段大小可以从一个字节到最大2^(32)字节(4G)。
A complete pointer in this address space consists of two parts (see Figure 2-1 ):
在这种地址空间下指针由两部分构成(见表2-1):
- A segment selector, which is a 16-bit field that identifies a segment.
一个段选择子,包含16位,表示一个段。
- An offset, which is a 32-bit ordinal that addresses to the byte level within a segment.
一个偏移量,包含32位,表示在段内的位移。
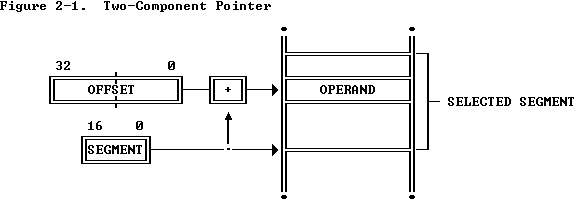
During execution of a program, the processor associates with a segment selector the physical address of the beginning of the segment. Separately compiled modules can be relocated at run time by changing the base address of their segments. The size of a segment is variable; therefore, a segment can be exactly the size of the module it contains.
在执行一个程序时,处理器将一个段选择子和该段的起始物理地址相关联。分享编译的模块可以在运行时通过改变他们的段基址被重新分配。段大小是可变化的;因此,一个段可以是包含的模块的准确大小。
【译】x86程序员手册03 - 2.1内存组织和分段的更多相关文章
- 【译】x86程序员手册02 - 基本的程序模式
Chapter 2 -- Basic Programming Model: 基本的程序模式 Introduces the models of memory organization. Defines ...
- 【译】x86程序员手册01
Intel 80386 Reference Programmer's Manual 80386程序员参考手册 Chapter 1 -- Introduction to the 80386 第1章 - ...
- 【译】x86程序员手册29-第8章 输入输出
Chapter 8 Input/Output 输入/输出 This chapter presents the I/O features of the 80386 from the following ...
- 【译】x86程序员手册07 - 2.5操作数选择
2.5 Operand Selection 操作数选择 An instruction can act on zero or more operands, which are the data mani ...
- 【译】x86程序员手册05 - 2.3寄存器
2.3 Registers 寄存器 The 80386 contains a total of sixteen registers that are of interest to the applic ...
- 【译】x86程序员手册04 - 2.2数据类型
2.2 Data Types 数据类型 Bytes, words, and doublewords are the fundamental data types (refer to Figure 2- ...
- 【译】x86程序员手册00 - 翻译起因
从上一次学习MIT的操作系统课程又过去了一年.上次学习并没有坚持下去.想来虽有种种原因,其还在自身无法坚持罢了.故此次再鼓起勇气重新学习,发现课程都已由2014改版为2016了.但大部分内容并没有改变 ...
- 【译】x86程序员手册38-10.2实在址模式下的软件初始化
10.2 Software Initialization for Real-Address Mode 实地址模式的软件初始化 In real-address mode a few structur ...
- 【译】x86程序员手册09-第3章程序指令集
注:觉得本章内容与理解操作系统不直接相关,所以本章并未看完,也就没有翻译完,放在这里中是为了保证手册的完整.有兴趣的人可以去原址查看. https://pdos.csail.mit.edu/6.828 ...
随机推荐
- Ubuntu 16.04下FireFox安装Flash插件
下载: https://get.adobe.com/flashplayer/ 选择tar.gz包 解压 sudo tar zxvf flash_player_npapi_linux.x86_64.ta ...
- wsgi初探
大半夜的不睡觉,起来看技术文档,我这是什么精神啊~ ok 本文的大部分内容都是阅读 http://wsgi.readthedocs.org/en/latest/ 得来的.下面开始研究 wsgi wsg ...
- python基础学习之02 序列
#encoding=utf-8 import math a=[1,23,4,5,6] print a a[1:1]=[2,3,5] print a a a[1]='a' print a a[1]={1 ...
- TI C66x DSP 系统events及其应用 - 5.11(中断控制寄存器)
C66x DSP运行中断的简要流程: 1.使能了全局中断和子中断.假设硬件检測到中断发生,那么CPU就要跳转. 2.软件把CPU内部的A,B类寄存器的值等推入堆栈保存,把当前PC寄存器的值放入IRP寄 ...
- iOS中xib与storyboard原理,与Android界面布局的异同
用文本标记语言来进行布局,用的最多的应该是HTML语言.HTML能够理解为有一组特殊标记的XML语言. 一.iOS中xib与storyboard显示原理 在iOS中基本的布置界面的方式有3种:代码.x ...
- Hadoop AWS Word Count 样例
在AWS里用Elastic Map Reduce 开一个Cluster 然后登陆master node并编译下面程序: import java.io.IOException; import java. ...
- iOS常用的宏定义总结
字符串是否为空 1 #define kStringIsEmpty(str) ([str isKindOfClass:[NSNull class]] || str == nil || [str le ...
- 项目构建之maven篇:1.环境搭建
maven下载: 下载地址 环境变量设置 watermark/2/text/aHR0cDovL2Jsb2cuY3Nkbi5uZXQvd29iZW5kaWFua3Vu/font/5a6L5L2T/fon ...
- 关于C语言指针的一些新认识(2)
在使用C语言编程的过程中,遇到了很多关于指针使用的小问题,这里总结一下就当做是编程的小技巧啦 Q1. 如何用printf( )输出指针 这个问题相当于如何用printf( )输出地址,答案是:用"%p ...
- error: 'Can't connect to local MySQL server through socket '/var/lib/mysql/mysql.sock' (2)'
[root@luozhonghua ~]# /usr/bin/mysqladmin -u root password 'aaaaaa' /usr/bin/mysqladmin: connect t ...
