java子类对象和成员变量的隐写&方法重写
1、子类继承的方法只能操作子类继承和隐藏的成员变量名字类新定义的方法可以操作子类继承和子类新生命的成员变量,但是无法操作子类隐藏的成员变量(需要适用super关键字操作子类隐藏的成员变量。)
public class ChengYuanBianLing {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
CheapGoods cheap=new CheapGoods();
// cheap.weight=192.32;//非法
cheap.newSetWeight(23);
System.out.println(cheap.weight);
System.out.println(cheap.newGetPrice());
cheap.oldSetWight(3.32);
System.out.println(cheap.oldGetPrice());
}
}
class Goods{
public double weight;
public void oldSetWight(double w){
weight=w;
System.out.println("double型de weight="+weight);
}
public double oldGetPrice(){
double price=weight*10;
return price;
}
}
class CheapGoods extends Goods{
public int weight;
public void newSetWeight(int w){
weight=w;
System.out.println("新的weight="+weight);
}
public double newGetPrice(){
double price=weight*10;
return price;
}
}
2、方法重写 override method override
方法重写就是子类继承父类,子类方法中使用相同的方法名字和参数个数以及参数类型。子类通过重写父类的方法,可以隐藏父类的方法,重写父类的状态和行为改变为自己的状态和行为。
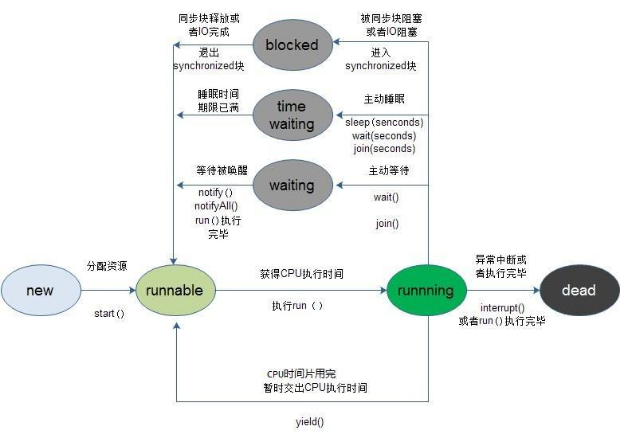
1、java线程就是一个object类,其实例继承类java.lang.Thread或其子类,创建编写线程运行时执行的代码有两种方式,一种是创建Thread子类的一个实例并重写run方法,一种是创建类的时候实现几口Runnable接口,如下展示的是run和start的区别。通过 调用start就会创建一个新的线程,但是run方法不会。run方法只会在当前的线程中运行。跟普通方法没有任何区别。
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("主线程ID:"+Thread.currentThread().getId()); MyThread thread1 = new MyThread("thread1"); thread1.start(); MyThread thread2 = new MyThread("thread2"); thread2.run(); }}class MyThread extends Thread{ private String name; public MyThread(String name){ this.name = name; } @Override public void run() { System.out.println("name:"+name+" 子线程ID:"+Thread.currentThread().getId()); }} |
运行结果:

public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Bank bank=new Bank();
bank.setMoney(300);
Thread account, chsher;
account=new Thread(bank);
chsher=new Thread(bank);
account.setName("读者");
chsher.setName("写者");
account.start();
chsher.start();
}
}
class Bank implements Runnable{
int money=200;
public void setMoney(int n){
money=n;
}
public void run(){
if(Thread.currentThread().getName().equals("读者"))
saveOrTake(200);
else if(Thread.currentThread().getName().equals("写者"))
saveOrTake(300);
}
public synchronized void saveOrTake(int amount){
if(Thread.currentThread().getName().equals("读者")){
// while(true){
for(int i=1;i<=1;i++){
money+=amount/3;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"开始工作"+"有这么多字"+amount);
try{
Thread.sleep(1000);
}catch(InterruptedException ex){
}
}
}else if(Thread.currentThread().getName().equals("写者")){
for(int i=1;i<=1;i++){
money+=amount/3;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"开始工作"+"有这么多字"+amount);
try{
Thread.sleep(1000);
}catch(InterruptedException ex){
}
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
TicketHouse officer=new TicketHouse();
Thread Tian, Ya;
Tian=new Thread(officer);
Tian.setName("田亚明");
Ya=new Thread(officer);
Ya.setName("倩倩");
Tian.start();
Ya.start();
}
}
class TicketHouse implements Runnable{
int fiveAmount=2,tenAmount=0,twentyAmount=0;
public void run(){
if(Thread.currentThread().getName().equals("田亚明")){
saleTicket(20);
}
else if(Thread.currentThread().getName().equals("倩倩")){
saleTicket(29);
}
}
private synchronized void saleTicket(int money){
if(money==20){
fiveAmount+=1;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"真好合适");
}
else if(money==29){
while(fiveAmount<=3){
try{
System.out.println("\n"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"等待");
wait();
}catch(InterruptedException ex){
}
fiveAmount-=3;
twentyAmount-=1;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
notifyAll();
}
}
}
java子类对象和成员变量的隐写&方法重写的更多相关文章
- java中使用反射做一个工具类,来为指定类中的成员变量进行赋值操作,使用与多个类对象的成员变量的赋值。
//------------------------------------------------我是代码的分割线 // 首选是一个工具类,在该工具类里面,定义了一个方法,public void s ...
- Java 访问限制符 在同一包中或在不同包中:使用类创建对象的权限 & 对象访问成员变量与方法的权限 & 继承的权限 & 深入理解protected权限
一.实例成员与类成员 1. 当类的字节码被加载到内存, 类中类变量.类方法即被分配了相应内存空间.入口地址(所有对象共享). 2. 当该类创建对象后,类中实例变量被分配内存(不同对象的实例变量互不相同 ...
- 假如java类里的成员变量是自身的对象
假如java类里的成员变量是自身的对象,则新建该类对象时内存中怎么分配空间,我感觉似乎死循环了. 不过我想的肯定是错的,因为很多类的成员变量是自身对象,并且绝对无错,举个例子: Class A{ pr ...
- Java学习日记基础篇(四)——类,对象之成员变量,成员方法,构造方法
面向对象(Object Oriented) 一.面向对象杂谈 面向对象(Object Oriented),我的翻译是以物体为目标的,就是说编程的时候是建立一个物体,然后对这个物体进行操作. Java语 ...
- java类里的成员变量是自身的对象问题
今晚看单例模式饿汉时想到一个问题:假如java类里的成员变量是自身的对象,则新建该类对象时内存中怎么分配空间,我感觉似乎死循环了.于是上网搜索了下,哈哈,果然有人早就思考过这个问题了,站在巨人的肩膀上 ...
- java基础疑难点总结之成员变量的继承,方法重载与重写的区别,多态与动态绑定
1.成员变量的继承 1.1要点 子类用extends关键字继承父类.子类中可以提供新的方法覆盖父类中的方法.子类中的方法不能直接访问父类中的私有域,子类可以用super关键字调用父类中的方法.在子类中 ...
- JAVA中局部变量 和 成员变量有哪些区别
JAVA中局部变量 和 成员变量有哪些区别 1.定义的位置不一样<重点>***局部变量:在方法的内部成员变量:在方法的外部,直接写在类当中 2.作用范围不一样<重点>***局部 ...
- 只用@property定义一个属性speed,子类不能直接用_speed,需要在interface的成员变量列表里写上_speed
//写法一: @interface Person : NSObject { } @property (nonatomic, strong) NSString *name; @end @implemen ...
- java笔记13之成员变量与局部变量
成员变量和局部变量的区别 1在类中的位置不同 局部变量:类的方法体内 成员变量:类的方法之外 2内存的不同位置 局部变量:在栈内存中 成员位置:在堆内存 3生命周期不同 局部变量:随着方法的调用而存在 ...
随机推荐
- struts2简单入门-Action的三种配置方式
普通的配置方式 优点:可读性高 缺点:重复的配置太多. 使用情况 一个actian只有一个方法,只需要处理一种请求. 代码演示 <action name="voteResult&quo ...
- 【blog】SpringBoot如何搭建聚合项目
以我的博客为例 blog --blog-common --blog-entity --blog-repo --blog-service --blog-web SpringBoot聚合项目推荐 http ...
- 前端html1.
HTML介绍 转载http://www.cnblogs.com/liwenzhou/p/7988087.html Web服务本质 import socket sk = socket.socket() ...
- LightOJ - 1245 Harmonic Number (II) 求同值区间的和
题目大意:对下列代码进行优化 long long H( int n ) { long long res = 0; for( int i = 1; i <= n; i++ ) ...
- Zookeeper客户端Curator基本API
在使用zookeper的时候一般不使用原生的API,Curator,解决了很多Zookeeper客户端非常底层的细节开发工作,包括连接重连.反复注册Watcher和NodeExistsExceptio ...
- MBA(它是指营销策划,领导力和影响力,财务会计,战略和转型的IT,企业融资,用于决策的数据分析识别市场趋势获得业务优势,全球商业战略)
推荐阅读者:玩股票的,创业的,管理者,吃货的商人,老板,管理层以及这方面的爱好者. 知识来源:https://www.edx.org/micromasters/USMx-UMD-MBA-Core-Cu ...
- Java 类加载机制(阿里面试题)-何时初始化类
(1)阿里的面试官问我,可以不可以自己写个String类 答案:不可以,因为 根据类加载的双亲委派机制,会去加载父类,父类发现冲突了String就不再加载了; (2)能否在加载类的时候,对类的字节码进 ...
- opencv处理验证码python代码
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # @Time : 2019-02-11 09:39 # @Author : cxa # @File : bgr2gry.py # @Software: ...
- 【转】细说new与malloc的10点区别
1.申请的内存所在位置 new操作符从自由存储区(free store)上为对象动态分配内存空间,而malloc函数从堆上动态分配内存.自由存储区是C++基于new操作符的一个抽象概念,凡是通过new ...
- TechnoSoftware OPCDA client(1.2.1) Error Codes
OPCDA.NET Client Interface WrapperSummary of OPC Error Codes We have attempted to minimize the numbe ...
