Android--UI之Button
前言
最近一直在讲androidUI控件的使用方式,这篇博客讲解一下基本上属于用处最广泛的控件之一的Button控件。如果有过其他平台开发经验的程序员,对按钮是不会陌生的。本篇博客首先讲解一下Android的Button控件的常用事件以及事件绑定和触发,再在Button控件中通过设定属性值来实现图文混排,这个功能是在项目中常用到的。
Button控件
Button继承了TextView。它的功能就是提供一个按钮,这个按钮可以供用户点击,当用户对按钮进行操作的时候,触发相应事件,如点击,触摸。
还有一个ImageButton,它继承自Button,可以在ImageButton中显示一个图片展示给用户看,并且对其Text属性设置值的时候是无效的,其它功能与Button一样。
常用事件
一般对于一个按钮而言,用的最多的就是点击事件,Button间接继承自View,而AndroidUI中的所有事件,都是定义在View中的。在本篇博客中,示例讲解的点击事件、触摸事件,其他事件的使用方式与此类似,只是触发的时机不同而已。此处分别需要实现View.OnClickListener、View.OnTouchListener接口的方法。
- View.OnClickListener,需要实现onClick(View v)方法,其中v为当前触发事件的控件。
- View.OnTouchListener,需要实现onTouch(View v , MotionEvent event),其中v为当前触发事件的控件,event包括了触摸时的具体内容,如移动、按下等。
下面使用一个示例讲解一下事件的绑定及触发,在示例中显示两个按钮控件,一个为普通按钮,一个为填充图片的按钮,为它们绑定click事件,当点击事件触发的时候,对其尺寸进行修改,为图片按钮绑定触摸事件,当触摸的时候触发,切换图片显示。
布局代码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" > <Button
android:id="@+id/btnChangeSize"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="点击修改尺寸"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnChangeImg"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@drawable/image1"
/>
</LinearLayout>
实现代码:
package com.bgxt.buttondemo; import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.MotionEvent;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.view.View.OnTouchListener;
import android.widget.Button; //通过实现接口,对其进行click、touch事件的支持
public class ButtonListener extends Activity implements OnClickListener,
OnTouchListener { private Button btnChangeSize;
private Button btnChangeImg;
private int flag = 1; @Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.btn_listener); btnChangeSize = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnChangeSize);
btnChangeImg = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnChangeImg); // 对两个按钮进行事件绑定
btnChangeSize.setOnClickListener(this);
btnChangeImg.setOnClickListener(this);
btnChangeImg.setOnTouchListener(this);
} @Override
public boolean onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event) {
// 获取触发事件的Button控件
Button btn = (Button) v;
if (event.getAction() == MotionEvent.ACTION_UP) {
// 当触摸时按下,则替换展示图片为image1
btn.setBackgroundResource(R.drawable.image1);
} else {
btn.setBackgroundResource(R.drawable.image2);
}
return false;
} @Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Button btn = (Button) v;
if (flag == 1
&& btn.getWidth() == getWindowManager().getDefaultDisplay()
.getWidth()) {
// 如果等于屏幕的宽度,则修改标识flag为-1
flag = -1;
} else if (flag == -1 && btn.getWidth() < 100) {
flag = 1;
}
// 设置button控件尺寸
btn.setWidth(btn.getWidth() + (int) (btn.getWidth() * 0.1) * flag);
btn.setHeight(btn.getHeight() + (int) (btn.getHeight() * 0.1) * flag);
}
}
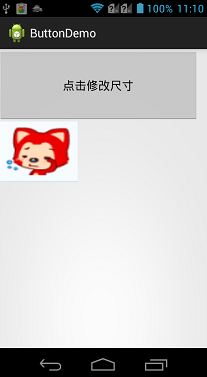
展示效果图:
当点击按钮的时候,按钮被放大,当放大到屏幕宽度时,开始缩小。
当触摸图标按钮的时候,图像改变。
图文混排
对于在实际项目中,经常会需要设置按钮展示为图文混排的效果,这样可以通过图表更直观的把按钮的功能展示给用户,又可以有简短的文字说明。虽然ImageButton也可以实现图片按钮的效果,但是对于ImageButton而言,设置Text属性是没有作用的,所以这里不讲解ImageButton的使用。对于Button控件,图文混排需要用到一个android:drawableXxx属性(Xxx为图片所在按钮的方向),这个属性配合android:text,就可以实现图文混排的效果。
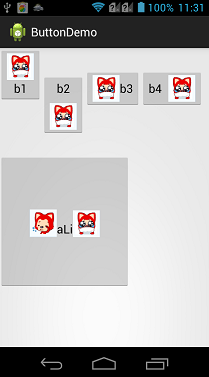
下面一个示例,分别展示了上下左右四个方位的图标按钮,并且生成一个通过Java代码动态生成图文混排按钮的。因为Button是继承自TextView的,所以通过代码设置图文混排的方式与TextView类似,都需要用到SpannableString类,关于SpannableString的详细讲解可以参见我的另外一篇博客,Android--UI之TextView,这里就不再详细讲解了。
布局代码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" > <LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="150dp"
android:orientation="horizontal" >
<!-- 图片在上,项目中常用这样的设置 -->
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:drawableTop="@drawable/image2"
android:text="b1" />
<!-- 图片在下 -->
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:drawableBottom="@drawable/image2"
android:drawablePadding="10dp"
android:text="b2" />
<!-- 图片在左 -->
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:drawableLeft="@drawable/image2"
android:text="b3" />
<!-- 图片在右 -->
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:drawablePadding="10dp"
android:drawableRight="@drawable/image2"
android:text="b4" />
</LinearLayout>
<!-- 声明一个空的按钮,用于进行代码设置 -->
<Button android:layout_width="200dp" android:layout_height="200dp" android:id="@+id/btnSty" android:layout_marginTop="10dp"/>
</LinearLayout>
Java实现代码:
package com.bgxt.buttondemo; import android.app.Activity;
import android.graphics.Bitmap;
import android.graphics.BitmapFactory;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.text.SpannableString;
import android.text.Spanned;
import android.text.style.ImageSpan;
import android.widget.Button; public class ButtonStyle extends Activity { private Button btnSty;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.btn_style);
//获取按钮控件
btnSty=(Button)findViewById(R.id.btnSty);
//生成SpannableString,用于图片的载体
SpannableString spannebleLeft=new SpannableString("left");
Bitmap bitmapleft=BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), R.drawable.image1);
ImageSpan imageSpanLeft=new ImageSpan(ButtonStyle.this,bitmapleft);
spannebleLeft.setSpan(imageSpanLeft,0,4,Spanned.SPAN_EXCLUSIVE_EXCLUSIVE); SpannableString spannebleRight=new SpannableString("right");
Bitmap bitmapRight=BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), R.drawable.image2);
ImageSpan imageSpanRight=new ImageSpan(ButtonStyle.this,bitmapRight);
spannebleRight.setSpan(imageSpanRight,0,5,Spanned.SPAN_EXCLUSIVE_EXCLUSIVE); //把生成的SpannableString追加到按钮上
btnSty.append(spannebleLeft);
btnSty.append("aLi");
btnSty.append(spannebleRight);
}
}
效果展示:
总结
对于实际项目而言,一般按钮的样式都会通过额外的XML样式文件包装一下,这个之后再介绍,这里只是介绍一下Button的简单使用。按钮的最多用处就是供用户点击从而触发相应时间,没有什么难点。
请支持原创,尊重原创,转载请注明出处。谢谢。

Android--UI之Button的更多相关文章
- Android经常使用UI组件 - Button
button(Button)是Android其中一个经常使用的UI组件.非常小可是在开发中最经常使用到.一般通过与监听器结合使用.从而触发一些特定事件. Button继承了TextView.它的功能就 ...
- Android UI 统一修改Button控件的样式,以及其它系统控件的默认样式
先介绍下修改原理:首先打开位于android.widget包下面的Button.java文件,这里有一句关键的代码如下: public Button(Context context, Attribut ...
- Android UI 绘制过程浅析(五)自定义View
前言 这已经是Android UI 绘制过程浅析系列文章的第五篇了,不出意外的话也是最后一篇.再次声明一下,这一系列文章,是我在拜读了csdn大牛郭霖的博客文章<带你一步步深入了解View> ...
- 【Android UI】Android开发之View的几种布局方式及实践
引言 通过前面两篇: Android 开发之旅:又见Hello World! Android 开发之旅:深入分析布局文件&又是“Hello World!” 我们对Android应用程序运行原理 ...
- 【Android UI设计与开发】第05期:引导界面(五)实现应用程序只启动一次引导界面
[Android UI设计与开发]第05期:引导界面(五)实现应用程序只启动一次引导界面 jingqing 发表于 2013-7-11 14:42:02 浏览(229501) 这篇文章算是对整个引导界 ...
- Android UI系列-----时间、日期、Toasts和进度条Dialog
您可以通过点击 右下角 的按钮 来对文章内容作出评价, 也可以通过左下方的 关注按钮 来关注我的博客的最新动态. 如果文章内容对您有帮助, 不要忘记点击右下角的 推荐按钮 来支持一下哦 如果您对文章内 ...
- [Android UI] shape和selector的结合使用
shape和selector是Android UI设计中经常用到的,比如我们要自定义一个圆角Button,点击Button有些效果的变化,就要用到shape和selector.可以这样说,shape和 ...
- android UI库
https://github.com/wasabeef/awesome-android-ui List of Android UI/UX Libraries A curated list of awe ...
- 十二、Android UI开发专题(转)
http://dev.10086.cn/cmdn/bbs/viewthread.php?tid=18736&page=1#pid89255Android UI开发专题(一) 之界面设计 近期很 ...
- Android UI -- 布局介绍(布局包括FrameLayout, LinearLayout, RelativeLayout, GridLayout)
首先介绍常用布局类 FrameLayout 最简单的布局管理器. 这个布局管理类有几个特性: 添加组件默认在左上角的. 如果添加多个组件会叠加到一起,并且都在左上角.(可以通过一gravity属性改变 ...
随机推荐
- Mysql双主互备+keeplived高可用架构介绍
一.Mysql双主互备+keeplived高可用架构介绍 Mysql主从复制架构可以在很大程度保证Mysql的高可用,在一主多从的架构中还可以利用读写分离将读操作分配到从库中,减轻主库压力.但是在这种 ...
- 浅谈nodejs和php
现在,Web开发公司和开发人员可以选择多种技术栈来构建Web应用程序.早期网络发展,不同的技术被用于前端和后端开发.但是,随着Node.js的发布,布局发生了变化,因为它允许开发人员使用 JavaSc ...
- sjms-4 行为型模式
行为型模式 责任链模式 内容:使多个对象都有机会处理请求,从而避免请求的发送者和接收者之间的耦合关系.将这些对象连成一条链,并沿着这条链传递该请求,直到有一个对象处理它为止.角色:抽象处理者(Hand ...
- OpenGL ES中MRT应用
Demo涵盖了OpenGL ES 3.0 的一系列新特性: 1.VAO和VBO 2.帧缓冲对象 3.MRT 效果: 代码: //yf's version #define STB_IMAGE_IMPLE ...
- intent和手势探测
一.三种启动方法 setComponent ComponentName comp = new ComponentName( this, SecondActivity.class); Intent in ...
- OpenGIS
OpenGIS(Open Geodata Interoperation Specification,OGIS-开放的地理数据互操作规范)由美国OGC(OpenGIS协会,Open Geospatial ...
- HDU 2147 P/N博弈
点这里去做题 如图 找必胜点和必败点, 1.终点为必胜点 2.所有能一步走到必胜点的都是必败点 3.每一步都只能走到必败点的是必胜点 #include<bits/stdc++.h> usi ...
- 自由拖拽DIV实现
最近在做的项目有个效果是要实现div随意拖拽改变大小,前端框架选择的是vue.js,UI用的是element,拖拽效果可以很简单的实现,但是在拖拽过程中发现会对其他元素实现全选效果,因此最后选择使用元 ...
- HDU5813 Elegant Construction
Elegant Construction Time Li ...
- 人工智能之一般合一算法Java实现之
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.List; import java.util.Scanner ...