Scala与Mongodb实践2-----图片、日期的存储读取
目的:在IDEA中实现图片、日期等相关的类型在mongodb存储读取
- 主要是Scala和mongodb里面的类型的转换。Scala里面的数据编码类型和mongodb里面的存储的数据类型各个不同。存在类型转换。
- 而图片和日期的转换如下图所示。

1、日期的存取
- 简单借助java.until.Calendar即可。
val ca=Calendar.getInstance()
ca.set()
ca.getTime
- 有多种具体的格式等,再直接应用mgoDateTime等方法
//显示各种格式
type MGODate = java.util.Date
def mgoDate(yyyy: Int, mm: Int, dd: Int): MGODate = {
val ca = Calendar.getInstance()
ca.set(yyyy,mm,dd)
ca.getTime()
}
def mgoDateTime(yyyy: Int, mm: Int, dd: Int, hr: Int, min: Int, sec: Int): MGODate = {
val ca = Calendar.getInstance()
ca.set(yyyy,mm,dd,hr,min,sec)
ca.getTime()
}
def mgoDateTimeNow: MGODate = {
val ca = Calendar.getInstance()
ca.getTime
}
def mgoDateToString(dt: MGODate, formatString: String): String = {
val fmt= new SimpleDateFormat(formatString)
fmt.format(dt)
}
2、图片的存取(看图片大小,一般都是如下,大于16M的图片即采用GridFS,分别将图片的属性存储)
借助Akka的FileStream
将File(图片)===》Array[Byte]代码格式,图片在mongodb中显示形式binary
具体代码如下:
FileStreaming.scala
package com.company.files import java.nio.file.Paths
import java.nio._
import java.io._
import akka.stream.{Materializer}
import akka.stream.scaladsl.{FileIO, StreamConverters} import scala.concurrent.{Await}
import akka.util._
import scala.concurrent.duration._ object FileStreaming {
def FileToByteBuffer(fileName: String, timeOut: FiniteDuration)(
implicit mat: Materializer):ByteBuffer = {
val fut = FileIO.fromPath(Paths.get(fileName)).runFold(ByteString()) { case (hd, bs) =>
hd ++ bs
}
(Await.result(fut, timeOut)).toByteBuffer
} def FileToByteArray(fileName: String, timeOut: FiniteDuration)(
implicit mat: Materializer): Array[Byte] = {
val fut = FileIO.fromPath(Paths.get(fileName)).runFold(ByteString()) { case (hd, bs) =>
hd ++ bs
}
(Await.result(fut, timeOut)).toArray
} def FileToInputStream(fileName: String, timeOut: FiniteDuration)(
implicit mat: Materializer): InputStream = {
val fut = FileIO.fromPath(Paths.get(fileName)).runFold(ByteString()) { case (hd, bs) =>
hd ++ bs
}
val buf = (Await.result(fut, timeOut)).toArray
new ByteArrayInputStream(buf)
} def ByteBufferToFile(byteBuf: ByteBuffer, fileName: String)(
implicit mat: Materializer) = {
val ba = new Array[Byte](byteBuf.remaining())
byteBuf.get(ba,0,ba.length)
val baInput = new ByteArrayInputStream(ba)
val source = StreamConverters.fromInputStream(() => baInput) //ByteBufferInputStream(bytes))
source.runWith(FileIO.toPath(Paths.get(fileName)))
} def ByteArrayToFile(bytes: Array[Byte], fileName: String)(
implicit mat: Materializer) = {
val bb = ByteBuffer.wrap(bytes)
val baInput = new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes)
val source = StreamConverters.fromInputStream(() => baInput) //ByteBufferInputStream(bytes))
source.runWith(FileIO.toPath(Paths.get(fileName)))
} def InputStreamToFile(is: InputStream, fileName: String)(
implicit mat: Materializer) = {
val source = StreamConverters.fromInputStream(() => is)
source.runWith(FileIO.toPath(Paths.get(fileName)))
}
}
- Helpers.scala
package com.company.lib import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit import scala.concurrent.Await
import scala.concurrent.duration.Duration
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat
import java.util.Calendar
import org.mongodb.scala._ object Helpers { implicit class DocumentObservable[C](val observable: Observable[Document]) extends ImplicitObservable[Document] {
override val converter: (Document) => String = (doc) => doc.toJson
} implicit class GenericObservable[C](val observable: Observable[C]) extends ImplicitObservable[C] {
override val converter: (C) => String = (doc) => doc.toString
} trait ImplicitObservable[C] {
val observable: Observable[C]
val converter: (C) => String def results(): Seq[C] = Await.result(observable.toFuture(), Duration(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS))
def headResult() = Await.result(observable.head(), Duration(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS))
def printResults(initial: String = ""): Unit = {
if (initial.length > 0) print(initial)
results().foreach(res => println(converter(res)))
}
def printHeadResult(initial: String = ""): Unit = println(s"${initial}${converter(headResult())}")
} type MGODate = java.util.Date
def mgoDate(yyyy: Int, mm: Int, dd: Int): MGODate = {
val ca = Calendar.getInstance()
ca.set(yyyy,mm,dd)
ca.getTime()
}
def mgoDateTime(yyyy: Int, mm: Int, dd: Int, hr: Int, min: Int, sec: Int): MGODate = {
val ca = Calendar.getInstance()
ca.set(yyyy,mm,dd,hr,min,sec)
ca.getTime()
}
def mgoDateTimeNow: MGODate = {
val ca = Calendar.getInstance()
ca.getTime
} def mgoDateToString(dt: MGODate, formatString: String): String = {
val fmt= new SimpleDateFormat(formatString)
fmt.format(dt)
} }
- Model.scala
模型中包含了两个具体的模型Person和Address,二者是包含关系,具体模型内含存取方法
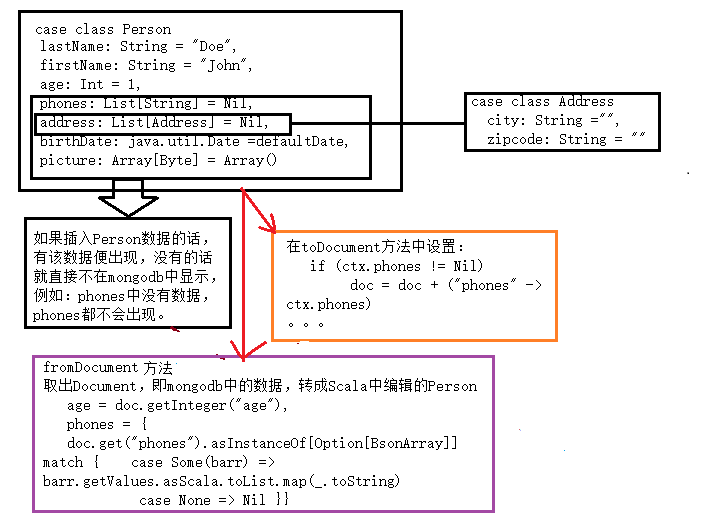
package com.company.demo import org.mongodb.scala._
import bson._
import java.util.Calendar
import com.company.files._ import akka.stream.ActorMaterializer object Models {
//Model可存在在不同的模型,下面存在一个拥有代表性的模型Person case class Address(
//Scala中的字段类型,且String的默认参数是“”
city: String ="",
zipcode: String = ""
) {
def toDocument: Document =
bson.Document(
//bson.Document是bson包里面的Document,其他包内有不同的Document
"city" -> city,
"zipcode" -> zipcode
)
def fromDocument(doc: Document): Address =
this.copy(
city = doc.getString("city"),
zipcode = doc.getString("zipcode")
)
}
//这是日期的设置
val ca = Calendar.getInstance()
ca.set(2001,10,23)
val defaultDate = ca.getTime
case class Person (
lastName: String = "Doe",
firstName: String = "John",
age: Int = 1,
phones: List[String] = Nil,
address: List[Address] = Nil,
birthDate: java.util.Date = defaultDate,
picture: Array[Byte] = Array()
) { ctx =>
def toDocument: Document = {
var doc = bson.Document(
"lastName" -> ctx.lastName,
"firstName" -> ctx.firstName,
"age" -> ctx.age,
"birthDate" -> ctx.birthDate
)
if (ctx.phones != Nil)
doc = doc + ("phones" -> ctx.phones)
if (ctx.address != Nil)
doc = doc + ("address" -> ctx.address.map(addr => addr.toDocument))
if (!ctx.picture.isEmpty)
doc = doc + ("picture" -> ctx.picture) doc }
import scala.collection.JavaConverters._
def fromDocument(doc: Document): Person = {
//keySet
val ks = doc.keySet
ctx.copy(
lastName = doc.getString("lastName"),
firstName = doc.getString("firstName"),
age = doc.getInteger("age"),
phones = {
doc.get("phones").asInstanceOf[Option[BsonArray]] match {
case Some(barr) => barr.getValues.asScala.toList.map(_.toString)
case None => Nil
}
},
address = {
if (ks.contains("address")) {
doc.get("address").asInstanceOf[Option[BsonArray]] match {
case Some(barr) => barr.getValues.asScala.toList.map (
ad => Address().fromDocument(ad.asDocument())
)
case None => Nil
}
}
else Nil
},
picture = {
if (ks.contains("picture")) {
doc.get("picture").asInstanceOf[Option[BsonBinary]] match {
case Some(ba) => ba.getData
case None => Array()
}
}
else Array()
}
)
}
//在控制台显示的格式。
def toSink()(implicit mat: ActorMaterializer) = {
println(s"LastName: ${ctx.lastName}")
println(s"firstName: ${ctx.firstName}")
println(s"age: ${ctx.age}")
println(s"phones: ${ctx.phones}")
println(s"address ${ctx.address}")
if(!ctx.picture.isEmpty) {
val path = s"/img/${ctx.firstName}.jpg"
FileStreaming.ByteArrayToFile(ctx.picture,path)
println(s"picture saved to: ${path}")
}
} } }
- PersonCRUD.scala简单测试
package com.company.demo import org.mongodb.scala._
import bson._
import java.util.Calendar
import scala.collection.JavaConverters._
import com.company.lib.Helpers._
import com.company.files.FileStreaming._
import akka.actor._
import akka.stream._
import scala.concurrent.duration._
import scala.util._ object PersonCRUD extends App {
import Models._ implicit val system = ActorSystem()
implicit val ec = system.dispatcher
implicit val mat = ActorMaterializer() // or provide custom MongoClientSettings
val settings: MongoClientSettings = MongoClientSettings.builder()
.applyToClusterSettings(b => b.hosts(List(new ServerAddress("localhost")).asJava))
.build()
val client: MongoClient = MongoClient(settings)
val mydb = client.getDatabase("mydb")
val mytable = mydb.getCollection("personal") val susan = Person(
lastName = "Wang",
firstName = "Susan",
age = 18,
phones = List("137110998","189343661"),
address = List(
Address("Sz","101992"),
Address(city = "gz", zipcode="231445")
),
birthDate = mgoDate(2001,5,8),
picture = FileToByteArray("/img/sc.jpg",3 seconds)
)
/*
val futResult = mytable.insertOne(susan.toDocument).toFuture() futResult.onComplete {
case Success(value) => println(s"OK! ${value}")
case Failure(err) => println(s"Boom!!! ${err.getMessage}")
} scala.io.StdIn.readLine() */
mytable.find().toFuture().andThen {
case Success(ps) => ps.foreach(Person().fromDocument(_).toSink())
case Failure(err) => println(s"ERROR: ${err.getMessage}")
}
scala.io.StdIn.readLine()
system.terminate()
}
Scala与Mongodb实践2-----图片、日期的存储读取的更多相关文章
- Scala与Mongodb实践4-----数据库操具体应用
目的:在实践3中搭建了运算环境,这里学会如何使用该环境进行具体的运算和相关的排序组合等. 由数据库mongodb操作如find,aggregate等可知它们的返回类型是FindObservable.A ...
- Scala与Mongodb实践3-----运算环境的搭建
目的:使的在IDEA中编辑代码,令代码实现mongodb运算,且转换较为便捷 由实验2可知,运算环境的搭建亦需要对数据进行存储和计算,故需要实现类型转换,所以在实验2的基础上搭建环境. 由菜鸟教程可得 ...
- Scala与Mongodb实践1-----mongodbCRUD
目的:如何使用MongoDB之前提供有关Scala驱动程序及其异步API. 1.现有条件 IDEA中的:Scala+sbt+SDK mongodb-scala-driver的网址:http://mon ...
- Python中使用Flask、MongoDB搭建简易图片服务器
主要介绍了Python中使用Flask.MongoDB搭建简易图片服务器,本文是一个详细完整的教程,需要的朋友可以参考下 1.前期准备 通过 pip 或 easy_install 安装了 pymong ...
- 使用Scala操作Mongodb
介绍 Scala是一种功能性面向对象语言.它融汇了很多前所未有的特性.而同一时候又执行于JVM之上.随着开发人员对Scala的兴趣日增,以及越来越多的工具支持,无疑Scala语言将成为你手上一件不可缺 ...
- Scala对MongoDB的增删改查操作
=========================================== 原文链接: Scala对MongoDB的增删改查操作 转载请注明出处! ==================== ...
- 【Scala】Scala多线程-并发实践
Scala多线程-并发实践 scala extends Thread_百度搜索 scala多线程 - 且穷且独立 - 博客园 Scala和并发编程 - Andy Tech Talk - ITeye博客 ...
- 一个从MongoDB中导出给定日期范围内数据的shell脚本
#!/bin/sh ver=`date "+%Y%m%d"` #d1, the beginning date, eg:2017-06-28 d1=$1 d1=`date -d $d ...
- Scala操作MongoDB
Scala操作MongoDB // Maven <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.mongodb</group ...
随机推荐
- 基于BERT预训练的中文命名实体识别TensorFlow实现
BERT-BiLSMT-CRF-NERTensorflow solution of NER task Using BiLSTM-CRF model with Google BERT Fine-tuni ...
- html手机端全屏显示和溢出问题
<meta name="viewport" content="width=1200, initial-scale=0.3"> initial-sca ...
- H3C HDLC协议特点
- Codeforces 1100F(离线 or 在线)
传送门 •参考资料 [1]:在线线性基 [2]:离线线性基 [3]:离线线性基 •题意 给你 n 个数,m 次询问: 每次询问给定一个区间 $l,r$,求 $a_{l \cdots r}$ 异或的最大 ...
- UVa 1354 Mobile Computing[暴力枚举]
**1354 Mobile Computing** There is a mysterious planet called Yaen, whose space is 2-dimensional. Th ...
- vue 使用webpack打包后路径报错以及 alias 的使用
一.vue 使用webpack打包后路径报错(两步解决) 1. config文件夹 ==> index.js ==> 把assetsPublicPath的 '/ '改为 './' 2. b ...
- C# 从零开始写 SharpDx 应用 绘制基础图形
本文告诉大家通过 SharpDx 画出简单的 2D 界面 本文属于 SharpDx 系列 博客,建议从头开始读 本文分为两步,第一步是初始化,第二步才是画界面 初始化 先创建 RenderForm 用 ...
- Linux 字节序
小心不要假设字节序. PC 存储多字节值是低字节为先(小端为先, 因此是小端), 一些高 级的平台以另一种方式(大端)工作. 任何可能的时候, 你的代码应当这样来编写, 它不在 乎它操作的数据的字节序 ...
- Github上的英文解释
1.AFAIK: As far as I know. 据我所知 2.SPOF: Single point of failure. 单节点崩溃 3.ASAP: As soon as possible. ...
- JS闭包机制实现为DOM元素循环添加事件
HTML代码: <button type='button' class='btn' id='1'>按钮1</button> <button type='button' c ...
