POJ 3177 (Redundant Paths) —— (有重边,边双联通,无向图缩点)
做到这里以后,总算是觉得tarjan算法已经有点入门了。
这题的题意是,给出若干个点和若干条边连接他们,在这个无向图中,问至少增加多少条边可以使得这个图变成边双联通图(即任意两点间都有至少两条没有重复边的路径可以到达,可以经过同一个点。这个条件等价于每一条边都至少在一个环中)。
方法:将无向图缩点以后,找出那些度为1的点的个数cnt,那么答案就是(cnt+1)/2。这么一看,好像就是缩点以后使它变成强连通图的意思?大概强连通图是有向图才有的名词吧。。
和有向图缩点类似,只要把if(!belong[v])改成if(v != fa)即可,这样,就可以防止同一条边的方向性关系了,而a到b如果是间接到达的话,是没有问题的。还有,通过这题,我明白了为什么tarjan算法里面有一个是用dfn来更新的了。这里来回顾一下:找割点或者桥的时候有low[v]和dfn[u]的比较,如果都是用low更新的话,那么low可能会变小导致漏掉割点或者桥的情况。举割点那篇中的图当例子:http://www.cnblogs.com/zzyDS/p/5629021.html 如这个图,
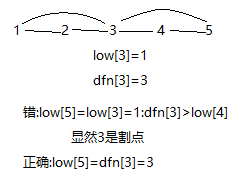
图(v,e)点为1,2,3,4,5,边有(1,2),(2,3),(1,3),(3,4),(4,5),(3,5),令1为树根。显然3为割点。不妨假设搜索顺序是(1,2),(2,3),(3,1),(3,4),(4,5),(5,3),搜索到(3,1)的时候,更新low[3] = dfn[1] = 1,然后搜索(3,4)、(4,5),(5,3),发现3已经遍历,那么如果此时采用low[u] = min(low[u], low[v])的话,会更新low[5] = low[3] = 1,回溯到4,low[4] = low[5] = 1,回溯到3,low[3] = low[4] = 1,然后比较发现low[4] < dfn[3],判断出3不是割点,算法错误。反正以后都用dfn更新应该就对了- -还有一点想说的是,用dfn的好处在于,不需要belong数组了,只要low一样的那么他们缩点以后都属于一个点(这个说法是错误的!上面这个图就是反例,上面那个图缩点以后还是只有一个点了,所以还是老老实实的用belong数组吧)。
另外,这题比较有意思的地方在于,题目给定,两个点之间如果有重边,只算一条。那么就引发了一大堆有意思的讨论了。
先给出最初的代码(WA的,因为没判断重边):
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stack>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string.h>
#include <vector>
using namespace std; const int N = +; stack<int> S;
int dfs_clock;
int dfn[N];
int low[N];
vector<int> G[N];
int n,r;
int du[N]; void dfs(int u,int fa)
{
dfn[u] = low[u] = ++dfs_clock;
for(int i=;i<G[u].size();i++)
{
int v = G[u][i];
if(!dfn[v])
{
dfs(v,u);
low[u] = min(low[u],low[v]);
}
else if(v != fa)
{
low[u] = min(low[u],dfn[v]);
}
}
} void solve()
{
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
if(!dfn[i]) dfs(i,-);
} for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
for(int j=;j<G[i].size();j++)
{
int v = G[i][j];
if(low[i]!=low[v]) du[low[i]]++;
}
} int cnt=;
for(int i=;i<=dfs_clock;i++) if(du[i]==) cnt++;
printf("%d\n",(cnt+)/);
} void init()
{
for(int i=;i<=n;i++) G[i].clear();
dfs_clock=;
memset(dfn,,sizeof(dfn));
memset(du,,sizeof(du));
} int main()
{
while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&r)==)
{
init(); for(int i=;i<=r;i++)
{
int u,v;
scanf("%d%d",&u,&v);
G[u].push_back(v);
G[v].push_back(u);
}
solve();
}
return ;
}
然后由于这题给的边是5000,可以用邻接矩阵来做,但是要注意用bool数组,不然超内存。代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stack>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string.h>
#include <vector>
using namespace std; const int N = +; int dfs_clock;
int dfn[N];
int low[N];
int n,r;
int du[N];
bool mp[N][N]; void dfs(int u,int fa)
{
dfn[u] = low[u] = ++dfs_clock;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
if(!mp[u][i]) continue;
if(!dfn[i])
{
dfs(i,u);
low[u] = min(low[u],low[i]);
}
else if(i != fa)
{
low[u] = min(low[u],dfn[i]);
}
}
} void solve()
{
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
if(!dfn[i]) dfs(i,-);
} for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
for(int j=;j<=n;j++)
{
if(!mp[i][j]) continue;
if(low[i]!=low[j]) du[low[i]]++;
}
} int cnt=;
for(int i=;i<=dfs_clock;i++) if(du[i]==) cnt++;
printf("%d\n",(cnt+)/);
} void init()
{
memset(mp,,sizeof(mp));
dfs_clock=;
memset(dfn,,sizeof(dfn));
memset(du,,sizeof(du));
} int main()
{
while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&r)==)
{
init(); for(int i=;i<=r;i++)
{
int u,v;
scanf("%d%d",&u,&v);
if(mp[u][v]) continue;
mp[u][v]=mp[v][u]=;
}
solve();
}
return ;
}
然后要判重的话,可以用大力学长的set法,把边用pair记录然后全部丢进set里面用find来查找即可,代码如下:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<string>
#include<cstring>
#include<map>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
#include<set>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef long long LL;
#define MP make_pair
#define PII pair<int,int>
#define PFI pair<double,int>
#define F first
#define S second
#define lson l,mid,rt<<1
#define rson mid+1,r,rt<<1|1
const int INF = 0x7f7f7f7f;
const int MOD = ;
const double eps = 1e-;
const int maxn = + ; const int N = + ;
int n,m;
vector<vector<int> > G(N);
int scc_cnt,dfs_clock,belong[N],dfn[N],low[N];
bool instack[N];
stack<int> S;
set<pair<int,int> > st;
void dfs(int u,int fa){
low[u] = dfn[u] = ++ dfs_clock;
S.push(u);
for(int i = ; i < G[u].size() ; i ++){
int v = G[u][i];
if(v == fa) continue; // 无向图 a-b: 防止b访问a(父亲)
if(!dfn[v]){
dfs(v,u);
low[u] = min(low[u],low[v]);
}else if(!belong[v]){
low[u] = min(low[u],dfn[v]);
}
}
if(low[u] == dfn[u]){
scc_cnt ++;
for(;;){
int x = S.top(); S.pop();
belong[x] = scc_cnt; // 缩点。
if(x == u) break;
}
}
}
void scc(){
scc_cnt = dfs_clock = ;
memset(belong,,sizeof(belong));
memset(dfn,,sizeof(dfn));
memset(low,,sizeof(low));
memset(instack,false,sizeof(instack));
while(!S.empty()) S.pop();
for(int i = ; i <= n ; i ++){
if(!dfn[i]) dfs(i,-);
}
int deg[N];
memset(deg,,sizeof(deg));
for(int i = ; i <= n ; i ++){
for(int j = ; j < G[i].size() ; j ++){
int v = G[i][j];
if(belong[i] != belong[v]){
deg[ belong[i] ] ++;
deg[ belong[v] ] ++;
}
}
}
int cnt = ;
for(int i = ; i <= n ; i++){
if(deg[i] / == ) cnt ++;
}
cout << (cnt + ) / << endl;
}
int main(){
while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&m) != EOF){
for(int i = ; i <= n ; i ++) G[i].clear();
st.clear();
for(int i = ; i < m ; i ++){
int u,v;
scanf("%d%d",&u,&v);
// 判重边。
if(st.find(MP(u,v)) != st.end()) continue;
if(st.find(MP(v,u)) != st.end()) continue;
st.insert(MP(u,v));
st.insert(MP(v,u));
G[u].push_back(v);
G[v].push_back(u);
}
scc();
}
return ;
}
最后,我想,既然要判重,干脆不用vector了,直接用set吧- -!代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stack>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string.h>
#include <vector>
#include <set>
using namespace std; const int N = +; stack<int> S;
int dfs_clock;
int dfn[N];
int low[N];
set<int> G[N];
int n,r;
int du[N]; void dfs(int u,int fa)
{
dfn[u] = low[u] = ++dfs_clock;
for(set<int>::iterator it=G[u].begin();it!=G[u].end();it++)
{
int v = *it;
if(!dfn[v])
{
dfs(v,u);
low[u] = min(low[u],low[v]);
}
else if(v != fa)
{
low[u] = min(low[u],dfn[v]);
}
}
} void solve()
{
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
if(!dfn[i]) dfs(i,-);
} for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
for(set<int>::iterator it=G[i].begin();it!=G[i].end();it++)
{
int v = *it;
if(low[i]!=low[v]) du[low[i]]++;
}
} int cnt=;
for(int i=;i<=dfs_clock;i++) if(du[i]==) cnt++;
printf("%d\n",(cnt+)/);
} void init()
{
for(int i=;i<=n;i++) G[i].clear();
dfs_clock=;
memset(dfn,,sizeof(dfn));
memset(du,,sizeof(du));
} int main()
{
while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&r)==)
{
init(); for(int i=;i<=r;i++)
{
int u,v;
scanf("%d%d",&u,&v);
G[u].insert(v);
G[v].insert(u);
}
solve();
}
return ;
}
POJ 3177 (Redundant Paths) —— (有重边,边双联通,无向图缩点)的更多相关文章
- POJ 3177 Redundant Paths (tarjan边双连通分量)
题目连接:http://poj.org/problem?id=3177 题目大意是给定一些牧场,牧场和牧场之间可能存在道路相连,要求从一个牧场到另一个牧场要有至少两条以上不同的路径,且路径的每条pat ...
- POJ 3177 Redundant Paths(重边标记法,有重边的边双连通分支)
大致题意: 为了保护放牧环境,避免牲畜过度啃咬同一个地方的草皮,牧场主决定利用不断迁移牲畜进行喂养的方法去保护牧草.然而牲畜在迁移过程中也会啃食路上的牧草,所以如果每次迁移都用同一条道路,那么该条道路 ...
- POJ 3177 Redundant Paths (桥,边双连通分量,有重边)
题意:给一个无向图,问需要补多少条边才可以让整个图变成[边双连通图],即任意两个点对之间的一条路径全垮掉,这两个点对仍可以通过其他路径而互通. 思路:POJ 3352的升级版,听说这个图会给重边.先看 ...
- poj 3177 Redundant Paths(tarjan边双连通)
题目链接:http://poj.org/problem?id=3177 题意:求最少加几条边使得没对点都有至少两条路互通. 题解:边双连通顾名思义,可以先求一下连通块显然连通块里的点都是双连通的,然后 ...
- tarjan算法求桥双连通分量 POJ 3177 Redundant Paths
POJ 3177 Redundant Paths Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 12598 Accept ...
- POJ 3177 Redundant Paths POJ 3352 Road Construction(双连接)
POJ 3177 Redundant Paths POJ 3352 Road Construction 题目链接 题意:两题一样的.一份代码能交.给定一个连通无向图,问加几条边能使得图变成一个双连通图 ...
- POJ 3177 Redundant Paths(边双连通的构造)
Redundant Paths Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 13717 Accepted: 5824 ...
- 洛谷P2860 [USACO06JAN]冗余路径Redundant Paths(tarjan求边双联通分量)
题目描述 In order to get from one of the F (1 <= F <= 5,000) grazing fields (which are numbered 1. ...
- POJ 3177——Redundant Paths——————【加边形成边双连通图】
Redundant Paths Time Limit:1000MS Memory Limit:65536KB 64bit IO Format:%I64d & %I64u Sub ...
- poj 3177 Redundant Paths 求最少添加几条边成为双联通图: tarjan O(E)
/** problem: http://poj.org/problem?id=3177 tarjan blog: https://blog.csdn.net/reverie_mjp/article/d ...
随机推荐
- Spring实战(三)Spring中装配Bean的三种方式---XML、JavaConfig、AutoWire
创建应用对象之间协作关系的行为称为装配(wiring),这也是依赖注入的本质. Spring容器负责创建应用程序中的bean并通过DI来协调这些对象之间的关系,而开发者需要告诉Spring需要创建哪些 ...
- ButterKnife8.5.1最新版本使用详细步骤
android studio中使用方法: 1.build.gradle(Modul: app) 添加dependencies{ compile 'com.jakewharton:butterknife ...
- netstat用法详解
netstat用法详解 知识,netstat用法详解 图片 netstat用法详解 内容,netstat用法详介绍,netstat用法详正文 netstat命令是一个监控TCP/IP网络的非常有用的工 ...
- 【转】SpringBoot+SpringCloud实现登录用户信息在微服务之间的传递
实现思路: 1:准备一个ThreadLocal变量,供线程之间共享. 2:每个微服务对所有过来的Feign调用进行过滤,然后从请求头中获取User用户信息,并存在ThreadLocal变量中. 3:每 ...
- Java基础加强-日志
/*日志*/ 从功能上来说,日志API本身所需求的功能非常简单,只需要能够记录一段文本即可 API的使用者在需要记录时,根据当前的上下文信息构造出相应的文本信息,调用API完成记录.一般来说,日志AP ...
- 前端基础(八):Font Awesome(图标)
一.font awesome简介 目前图标总数共有519个; 不依赖Javascript 矢量图形,无限缩放 免费,可用于商业 CSS控制样式,自定义图标颜色,大小,阴影,一切可能实现的效果 支持re ...
- JQuery初始加载时注册文本框失去焦点事件
在JQuery初始加载时注册文本框失去焦点事件 $(function(){ $('#文本框ID').blur(function(){ //对文本框内容进行处理 }); });
- Spark(一)wordcount
Spark(一)wordcount 一.新建一个scala项目 在maven中导入 <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.spar ...
- SQLite3学习笔记(3)
SQLite 表达式 表达式是一个或多个值.运算符和计算值的 SQL函数的组合. SQL表达式与公式类似,都写在查询语言中.您还可以使用特定的数据集来查询数据库. SELECT语句的基本语法如下: S ...
- GDB调试器教程
启动和退出GDBGDB(GNU Project Debugger)几乎适用于所有类Unix系统,小巧方便且不失功能强大,Linux/Unix程序员经常用它来调试程序. 总的来说有几下几种方法启动GDB ...
