HDU4719-Oh My Holy FFF(DP线段树优化)
Oh My Holy FFF
Time Limit: 5000/2500 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65535/65535 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 606 Accepted Submission(s): 141
o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o
/F\ /F\ /F\ /F\ /F\ /F\ /F\ /F\ /F\ /F\ /F\ /F\ /F\ /F\ /F\ /F\ /F\ /F\
/ \ / \ / \ / \ / \ / \ / \ / \ / \ / \ / \ / \ / \ / \ / \ / \ / \ / \
You, as the captain of *FFF*, want to divide them into smaller groups, but each group should still be continous in the original line. Like this:
o o o | o o o o | o o o o o o | o o o o o
/F\ /F\ /F\ | /F\ /F\ /F\ /F\ | /F\ /F\ /F\ /F\ /F\ /F\ | /F\ /F\ /F\ /F\ /F\
/ \ / \ / \ | / \ / \ / \ / \ | / \ / \ / \ / \ / \ / \ | / \ / \ / \ / \ / \
In your opinion, the number of soldiers in each group should be no more than L.
Meanwhile, you want your division be "holy". Since the soldier may have different heights, you decide that for each group except the first one, its last soldier(which is the rightmost one) should be strictly taller than the previous group's last soldier. That
is, if we set bi as the height of the last soldier in group i. Then for i >= 2, there should be bi > bi-1.
You give your division a score, which is calculated as 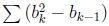 , b0 = 0 and 1 <= k <= M, if there are M groups in total. Note that M can equal to 1.
, b0 = 0 and 1 <= k <= M, if there are M groups in total. Note that M can equal to 1.
Given the heights of all soldiers, please tell us the best score you can get, or declare the division as impossible.
For each test case, first line has two numbers N and L (1 <= L <= N <= 105), as described above.
Then comes a single line with N numbers, from H1 to Hn, they are the height of each soldier in the line, from left to right. (1 <= Hi <= 105)
2
5 2
1 4 3 2 5
5 2
5 4 3 2 1
Case #1: 31
Case #2: No solution
的每一个人的身高都是比自己矮的? 能够进行先排序。让矮的人先选,假设身高一样就让序号在后的先选,这样就不会有冲突了(单点更新的时候)。 每次查询的时候单点更新就可以。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define REP(_,a,b) for(int _=(a); _<=(b);++_)
#define sz(s) (int)((s).size())
typedef long long ll;
const int maxn = 1e5+10;
int n,l;
ll dp[maxn];
struct Num{
ll h;
int idx;
Num(ll h = 0,int idx = 0):h(h),idx(idx){}
friend bool operator < (Num a,Num b){
if(a.h!=b.h) return a.h < b.h;
else return a.idx > b.idx;
}
};
vector<Num> vN;
struct node{
int lson,rson;
ll maxx;
int mid(){
return (lson+rson)>>1;
}
}tree[maxn*4];
void pushUp(int rt){
tree[rt].maxx = max(tree[rt<<1].maxx,tree[rt<<1|1].maxx);
} void build(int L,int R,int rt){
tree[rt].lson = L;
tree[rt].rson = R;
tree[rt].maxx = -1;
if(L==R){
return;
}
int mid = tree[rt].mid();
build(L,mid,rt<<1);
build(mid+1,R,rt<<1|1);
}
void init(){
vN.clear();
memset(dp,-1,sizeof dp);
}
void update(int pos,int l,int r,int rt,ll x){
if(l==r){
tree[rt].maxx = x;
return;
}
int mid = tree[rt].mid();
if(pos<=mid){
update(pos,l,mid,rt<<1,x);
}else{
update(pos,mid+1,r,rt<<1|1,x);
}
pushUp(rt);
}
ll query(int L,int R,int l,int r,int rt){
if(L <=l && R >= r){
return tree[rt].maxx;
}
int mid = tree[rt].mid();
ll ret;
bool flag = false;
if(L <= mid){
ret = query(L,R,l,mid,rt<<1);
flag = true;
}
if(R > mid){
if(flag){
ret = max(ret,query(L,R,mid+1,r,rt<<1|1));
}else{
ret = query(L,R,mid+1,r,rt<<1|1);
}
}
return ret;
}
void input(){
scanf("%d%d",&n,&l);
REP(_,1,n){
ll h;
scanf("%I64d",&h);
vN.push_back(Num(h,_));
}
sort(vN.begin(),vN.end());
build(0,n,1);
}
void solve(){
update(0,0,n,1,0);
REP(_,0,sz(vN)-1) {
int ni = vN[_].idx;
ll nh = vN[_].h;
ll tm = query(max(ni-l,0),ni-1,0,n,1);
if(tm>=0){
dp[ni] = tm+nh*nh;
update(ni,0,n,1,dp[ni]-nh);
}
if(ni==n) break;
}
if(dp[n]<=0){
printf("No solution\n");
}else{
printf("%I64d\n",dp[n]);
}
}
int main(){
int ncase,T=1;
cin >> ncase;
while(ncase--){
init();
input();
printf("Case #%d: ",T++);
solve();
}
return 0;
}
HDU4719-Oh My Holy FFF(DP线段树优化)的更多相关文章
- [USACO2005][POJ3171]Cleaning Shifts(DP+线段树优化)
题目:http://poj.org/problem?id=3171 题意:给你n个区间[a,b],每个区间都有一个费用c,要你用最小的费用覆盖区间[M,E] 分析:经典的区间覆盖问题,百度可以搜到这个 ...
- UVA-1322 Minimizing Maximizer (DP+线段树优化)
题目大意:给一个长度为n的区间,m条线段序列,找出这个序列的一个最短子序列,使得区间完全被覆盖. 题目分析:这道题不难想,定义状态dp(i)表示用前 i 条线段覆盖区间1~第 i 线段的右端点需要的最 ...
- zoj 3349 dp + 线段树优化
题目:给出一个序列,找出一个最长的子序列,相邻的两个数的差在d以内. /* 线段树优化dp dp[i]表示前i个数的最长为多少,则dp[i]=max(dp[j]+1) abs(a[i]-a[j])&l ...
- 完美字符子串 单调队列预处理+DP线段树优化
题意:有一个长度为n的字符串,每一位只会是p或j.你需要取出一个子串S(注意不是子序列),使得该子串不管是从左往右还是从右往左取,都保证每时每刻已取出的p的个数不小于j的个数.如果你的子串是最长的,那 ...
- hdu3698 Let the light guide us dp+线段树优化
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=3698 Let the light guide us Time Limit: 5000/2000 MS (Java ...
- 题解 HDU 3698 Let the light guide us Dp + 线段树优化
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=3698 Let the light guide us Time Limit: 5000/2000 MS (Java ...
- 【uva1502/hdu4117-GRE Words】DP+线段树优化+AC自动机
这题我的代码在hdu上AC,在uva上WA. 题意:按顺序输入n个串以及它的权值di,要求在其中选取一些串,前一个必须是后一个的子串.问d值的和最大是多少. (1≤n≤2×10^4 ,串的总长度< ...
- Contest20140906 ProblemA dp+线段树优化
Problem A 内存限制 256MB 时间限制 5S 程序文件名 A.pas/A.c/A.cpp 输入文件 A.in 输出文件 A.out 你有一片荒地,为了方便讨论,我们将这片荒地看成一条直线, ...
- POJ 3171.Cleaning Shifts-区间覆盖最小花费-dp+线段树优化(单点更新、区间查询最值)
Cleaning Shifts Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 4721 Accepted: 1593 D ...
随机推荐
- How to search a table in a store proc and open the store proc
1. select*fromdba_dependencieswherereferenced_name='CNTL_ISSUE'andTYPE='PROCEDURE' 2. selecttextfrom ...
- Socket 心跳包机制总结
跳包之所以叫心跳包是因为:它像心跳一样每隔固定时间发一次,以此来告诉服务器,这个客户端还活着.事实上这是为了保持长连接,至于这个包的内容,是没有什么特别规定的,不过一般都是很小的包,或者只包含包头的一 ...
- hdu 4712 Hamming Distance bfs
我的做法,多次宽搜,因为后面的搜索扩展的节点会比较少,所以复杂度还是不需要太悲观的,然后加上一开始对答案的估计,用估计值来剪枝,就可以ac了. #include <iostream> #i ...
- LeetCode--Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock (贪心策略 or 动态规划)
Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock Total Accepted: 14044 Total Submissions: 45572My Submissions Say you ...
- SpringMVC批量上传
@RequestMapping(value = "/upload") public String handleFormUpload(MultipartHttpServletRequ ...
- POJ1422 最小路径覆盖入门
题意:DAG求最小路径覆盖. 注意:二分匹配只试用于求DAG的最小路径覆盖, 有环就不行,具体可以理解证明. 对n个点进行拆点,分成左右两排点,对于边<u, v> 建 <u', v ...
- Hibernate(五)——经典解析一对一关联映射
前面两篇介绍了多对一.一对多的映射.今天分享下一对一的关联映射关系.有两种策略可以实现一对一的关联映射:主键关联.唯一外键关联. 主键关联——两个表有完全相同的主键值,来表示它们的一对一的关系.数据库 ...
- 人事管理系统 c语言版
int menu(){ printf("请按提示输入完毕操作!\n"); printf("1.查询员工信息\n"); printf("2.统计 ...
- Swift - 属性观察者(willSet与didSet)
属性观察者,类似于触发器.用来监视属性的除初始化之外的属性值变化,当属性值发生改变时可以对此作出响应.有如下特点: 1,不仅可以在属性值改变后触发didSet,也可以在属性值改变前触发willSet. ...
- 地大邀请赛d
Problem D: Tetrahedron Inequality Time Limit: 1 Sec Memory Limit: 128 MB Submit: 15 Solved: 3 [ ...
