Mounting File Systems
1.Mounting File Systems
Just creating a partition and putting a file system on it is not enough to start using it. To use a partition, you have to mount it as well. By mounting a partition (or better, the file system on it), you make its contents accessible through a specific directory.
To mount a file system, some information is needed:
■ What to mount: This information is mandatory and specifies the name of the device that needs to be mounted.
■ Where to mount it: This is also mandatory information which specifies the directory on which the device should be mounted.
■ What file system to mount: Optionally, you can specify the file system type. In most cases, this is not necessary. The mount command will detect which file system is used on the device and make sure the correct driver is used.
■ Mount options: Many mount options can be used when mounting a device. Using options is optional and depends on the needs you may have with the file system.
Manually Mounting File Systems To manually mount a file system, the mount command is used. To disconnect a mounted file system, the umount command is used. Using these commands is relatively easy. To mount the file system that is on /dev/vda5 on the directory /mnt, use the following command:
mount /dev/vda5 /mnt
To disconnect the mount, you can use umount with either the name of the device or the name of the mount point you want to disconnect. So, both of the following commands will work: umount /dev/vda5 umount /mnt
Using Device Names, UUIDs, or Disk Labels
To mount a device, the name of the device can be used, as in the command /dev/ vda5. If your server is used in an environment where a dynamic storage topology is used, this is not always the best approach. You may today have a storage device /dev/ sda5, which after changes in the storage topology can be /dev/sdb5 after the next reboot of your server. This is why on a default RHEL 7 installation UUIDs are used instead of device names. Every file system by default has a UUID associated to it, not just file systems that are used to store files but also special file systems such as the swap file system. You can use the blkid command to get an overview of the current file systems on your system and the UUID that is used by that file system.
[root@rhel7 ~]# blkid
/dev/sda1: UUID="2f8b9056-1129-4bea-bb94-bc2f7f8de206" TYPE="xfs"
/dev/sda2: UUID="OjqvZk-KS1b-YegW-zb4b-uaNV-zGt7-npfsjU" TYPE="LVM2_member"
/dev/sdb1: UUID="f4a212cd-211f-4ddd-84ed-18ede66505ff" TYPE="ext4"
/dev/sdc1: UUID="b74fbc00-3f2e-4dea-99da-a17de3f798c3" TYPE="swap"
/dev/mapper/rhel-root: UUID="4119798b-4939-48f4-be1a-3f3de1f8e934" TYPE="xfs"
/dev/mapper/rhel-swap: UUID="8a1f616f-989d-4846-a961-ee5ea2bc32bf" TYPE="swap"
mount UUID="42f419c4-633f-4ed7-b161-519a4dadd3da" /mnt --使用uuid挂载设备
Manually mounting devices using the UUID is not exactly easier. If mounts are automated as discussed in the next section, however, it does make sense using UUIDs instead of device names.
2. Automating File System Mounts Through /etc/fstab
[root@rhel7 ~]# cat /etc/fstab #
# /etc/fstab
# Created by anaconda on Tue Jun ::
#
# Accessible filesystems, by reference, are maintained under '/dev/disk'
# See man pages fstab(), findfs(), mount() and/or blkid() for more info
#
/dev/mapper/rhel-root / xfs defaults
UUID=2f8b9056--4bea-bb94-bc2f7f8de206 /boot xfs defaults
/dev/mapper/rhel-swap swap swap defaults #added by rusky:used for testing.
/dev/sdb1 /testdisk ext4 defaults
In the /etc/fstab file, everything is specified to mount the file system automatically. For this purpose, every line has six fields, as summarized in Table 14.5 .
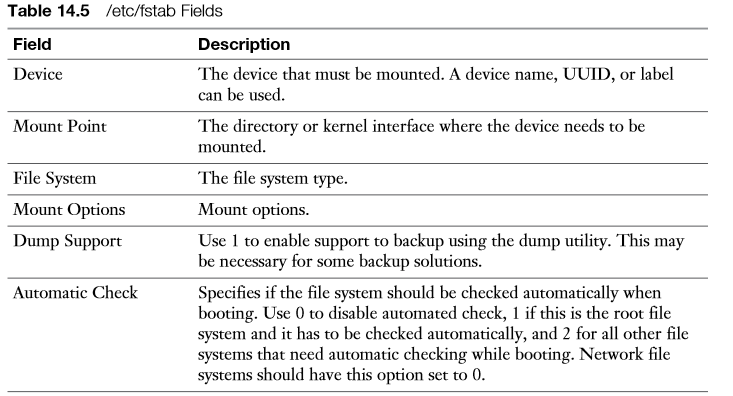
Notice that in the mount point not all file systems use a directory name. Some system devices such as swap are not mounted on a directory, but on a kernel interface. It is easy to recognize when a kernel interface is used; its name does not start with a / (and does not exist in the file system on your server). The Mount Options field defines specific mount options that can be used. If no specific options are required, this line will just read “defaults.” To offer specific functionality, a large number of mount options can be specified here. Table 14.6 gives an overview of some of the more common mount options.

The fifth column of /etc/fstab specifies support for the dump utility. This is a utility that was developed to create file system backups. It is good practice to switch this feature on by specifying a 1 for all real file systems, and switch it off by specifying 0 for all system mounts . The last column indicates if the file system integrity needs to be checked while booting. Put a 0 if you do not want to check the file system at all, a 1 if this is the root file system which needs to be checked before anything else, and a 2 if this is a nonroot file system that needs to be checked while booting.
Mounting File Systems的更多相关文章
- Introducing Microsoft Sync Framework: Sync Services for File Systems
https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/sync/bb887623 Introduction to Microsoft Sync Framework File Synchro ...
- centos重启报错Umounting file systems:umount:/opt:device is busy
系统重启报错: Umounting file systems:umount:/opt:device is busy 只能硬关机,回想一下最近刚安装了nod32 for linux x64的杀毒软件,开 ...
- centos 7 系统启动不了 出现报错dependency failed for /mnt , dependency failed for local file systems
阿里云一台Ecs重启后启动不了,出现报错 dependency failed for /mnt , dependency failed for local file systems , 报错的原因 ...
- Log-structured File Systems
换到博客园排版有问题,原版在这里:http://xubenbenhit.github.io/LogStructureFileSystem.html Log-structured File System ...
- 程序员的智囊库系列之3--分布式文件系统(Distributed file systems)
程序员的智囊库系列之3--分布式文件系统(Distributed file systems) 这是程序员的智囊库系列的第三篇文章.上一篇文章本来打算介绍几个搭建网站的框架,但由于这部分的内容较多,还需 ...
- enable user-defined extended attributes for ext3 file systems; 增加ext3 文件系统的扩展属性;
To enable user-defined extended attributes for ext3 file systems (i.e. device), use: tune2fs -o user ...
- “df: cannot read table of mounted file systems”.
“df: cannot read table of mounted file systems”.“df -l” returned an error: “df: cannot read table of ...
- Understanding Manycore Scalability of File Systems
多核场景下,不同文件系统,文件操作的性能评估.
- NFS(Network File System)服务配置和使用
Sun公司开发NFS (Network File System)之初就是为了在不同linux/Unix系统之间共享文件或者文件夹.可以在本地通过网络挂载远程主机的共享文件,和远程主机交互.NFS共享存 ...
随机推荐
- JavaScript--函数-01
函数的本质: function:创建一个函数对象的意思 什么是函数对象: 专门封装一个函数定义的存储空间 其实,函数是一个引用类型的对象 函数名,其实是一个引用函数对象的变量 函数只有在调用时才执行, ...
- mktime性能问题
#include <time.h> int main() { for (int i = 0; i < 100000; ++i) { struct tm tm = {}; tm.tm_ ...
- linux c下几种定时器实现
1.alarm n秒后触发一次,不是循环的2.setitimer 可以发出3种信号给自己,3.timerfd 这个接口基于文件描述符,通过文件描述符类似epoll那种的可读事件进行超时通知,能够被用于 ...
- CSS 去除浏览器默认 轮廓外框
在默认情况下,点击 a 标签,input,或者添加click事件的时候,浏览器留下一个轮廓外框(chrome之下为蓝色)~ 然而这些默认的轮廓外框,有时候很影响美观,并不是我们想保留的. 我们应如何消 ...
- php中json_decode()和json_encode()
1.json_decode() json_decode (PHP 5 >= 5.2.0, PECL json >= 1.2.0) json_decode — 对 JSON 格式的字符串进行 ...
- SCJP_104——题目分析(3)
11. what is reserved words in java?A. run B. default C. implement D. import Java 中,给标识符取名的时候,不能使用关键字 ...
- MVC中的区域
authour: chenboyi updatetime: 2015-05-03 08:26:30 friendly link: 目录: 1,思维导图 2,AreaRegistration类的Re ...
- 实验三:gdb跟踪调试内核从start_kernel到init进程启动
原创作品转载请注明出处<Linux内核分析>MOOC课程http://mooc.study.163.com/course/USTC-1000029000 如果我写的不好或者有误的地方请留言 ...
- spinner 下拉框控件
spinnerMode=dropdown时,为下拉模式spinnerMode=dialog时,会在界面中间弹出Android:popupBackground=”#f0000000”,可以去除spinn ...
- UE标签排列方式
UE是一款很顺手的文件编辑软件.打开文本,都会有个标签.根据个人喜好,我喜欢标签都展开,方便快速选取指定文本. 设置如下: 高级>配置>应用程序布局>可停靠窗口>类型 ...
