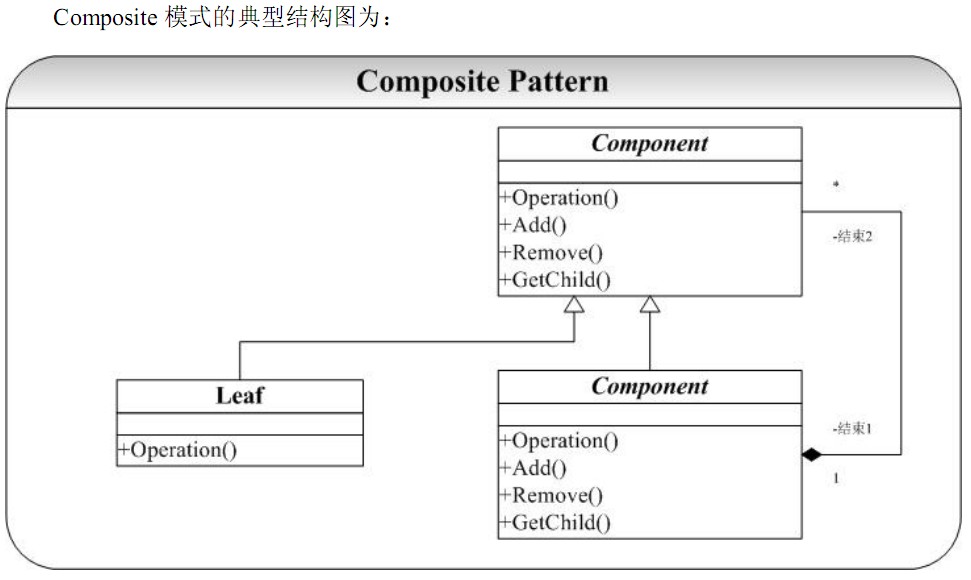
Composite 模式的实现
实现要点:
1.组合模式采用树形结构来实现普遍存在的对象容器,从而将“一对多”的关系转化“一对一”的关系,使得客户代码可以一致地处理对象和对象容器,无需关心处理的是单个的对象,还是组合的对象容器。
2.将“客户代码与复杂的对象容器结构”解耦是组合模式的核心思想,解耦之后,客户代码将与纯粹的抽象接口——而非对象容器的复内部实现结构——发生依赖关系,从而更能“应对变化”。
3.组合模式中,是将“Add和Remove等和对象容器相关的方法”定义在“表示抽象对象的Component类”中,还是将其定义在“表示对象容器的Composite类”中,是一个关乎“透明性”和“安全性”的两难问题,需要仔细权衡。这里有可能违背面向对象的“单一职责原则”,但是对于这种特殊结构,这又是必须付出的代价。
4.组合模式在具体实现中,可以让父对象中的子对象反向追溯;如果父对象有频繁的遍历需求,可使用缓存技巧来改善效率。
5. 客户端尽量不要直接调用树叶类的方法,而是借助其父类(Component)的多态性完成调用,这样可以增加代码的复用性。
使用场景:
以下情况下适用组合模式:
1.你想表示对象的部分-整体层次结构。
2.你希望用户忽略组合对象与单个对象的不同,用户将统一地使用组合结构中的所有对象。
/////////////////Component.h////////////////////////
#pragma once
class Component
{
public:
virtual ~Component();
Component();
virtual void Operation() = ;
virtual void Add( Component*);
virtual void Remove( Component*);
virtual Component* GetChild(int);
protected:
private:
};
/////////////////Component.cpp////////////////////////
#include "Component.h"
Component::Component()
{ }
Component::~Component()
{ }
void Component::Add( Component* com)
{ } void Component::Remove( Component* com)
{ }
void Component::Operation()
{ }
Component* Component::GetChild(int index)
{
return ;
}
/////////////////Composite.h////////////////////////
#pragma once
#include "Component.h"
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
class Composite : public Component
{
public:
Composite(const string&);
~Composite();
void Operation() ;
void Add( Component*);
void Remove( Component*);
Component* GetChild(int);
protected:
private:
vector<Component*> comVec ;
string _name ;
};
/////////////////Composite.cpp////////////////////////
#include "Composite.h"
#include "Component.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std; Composite::Composite(const string& name)
{
_name = name ;
}
Composite::~Composite()
{ }
void Composite::Operation()
{
cout<<"Composite operation : "<<_name<<endl;
vector<Component*>::iterator iter = comVec.begin();
for (;iter != comVec.end() ; iter++)
{ if (_name == "Com2")
{
cout<<"------";
}
if (_name == "Com1")
{
cout<<"---";
} (*iter)->Operation();
} }
void Composite::Add( Component* com)
{
comVec.push_back(com);
}
void Composite::Remove( Component* com)
{
for (vector<Component*>::iterator it = comVec.begin() ; it != comVec.end() ;)
{
if (com == *it)
{
it = comVec.erase(it);
}
else
{
it++;
}
}
} Component* Composite::GetChild(int index)
{
return comVec[index] ;
}
////////////////////Leaf.h///////////////////////
#pragma once
#include "Component.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Leaf : public Component
{
public:
Leaf(const string&);
~Leaf();
void Operation();
protected:
private:
string _name;
}; Leaf::Leaf(const string& name)
{
_name = name ;
}
Leaf::~Leaf()
{ }
void Leaf::Operation()
{
cout<<"Leaf operation : "<< _name <<endl;
}
/////////////////main////////////////////////////
#include "Component.h"
#include "Composite.h"
#include "Leaf.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std; int main()
{
Component* leaf1 = new Leaf("leaf1") ;
Component* leaf2 = new Leaf("leaf2") ;
Component* leaf3 = new Leaf("leaf3") ;
Component* com1 = new Composite("Com1");
com1->Add(leaf1);
com1->Add(leaf2);
com1->Add(leaf3); Component* leaf4 = new Leaf("leaf4") ;
Component* leaf5 = new Leaf("leaf5") ;
Component* com2 = new Composite("Com2");
com2->Add(leaf4);
com2->Add(leaf5); com1->Add(com2); com1->Operation(); getchar();
return ;
}

Composite 模式的实现的更多相关文章
- 组合模式/composite模式/对象结构型模式
组合模式/composite模式/对象结构型 意图 将对象组合成树形结构以表示"整体--部分"的层次结构.Composite使得用户对单个对象和组合对象的使用具有一致性. 动机 C ...
- C++基础——模拟事务 (2)Composite模式
=================================版权声明================================= 版权声明:原创文章 禁止转载 请通过右侧公告中的“联系邮 ...
- Composite模式
1 意图:将对象组成树形结构,以表示“部分——整体”的层次结构.Composite使得用户对单个对象和组合对象的使用具有一致性. 2 动机:同意处理图元对象和包含图元的容器对象.Composite通过 ...
- Java 实现组合(Composite)模式
类图 /** * 树 总体 * * @author stone * */ public class Tree { private TreeNode root; //根节点 public Tree(St ...
- 【结构型】Composite模式
组合模式意在将对象组合成树形结构以表示部分与整体的层次结构关系,并且用户对单个对象的操作以有对组合对象的操作都是一致的.即:组合对象 is-a 单个对象,同时又可以组合着 n 个的单个对象(甚至于其他 ...
- (原创)composite模式和bridge模式是天生的好朋友
composite模式的意图是:将对象组合成树形结构以表示“部分-整体”的层次结构.composite使得用户对单个对象和组合对象的使用具有一致性.它的类图如下: composite模式的实现分为透明 ...
- Java设计模式(8)组合模式(Composite模式)
Composite定义:将对象以树形结构组织起来,以达成“部分-整体” 的层次结构,使得客户端对单个对象和组合对象的使用具有一致性. Composite比较容易理解,想到Composite就应该想到树 ...
- 设计模式之——Composite模式
composite模式又叫做组合模式/复合模式. 它是一种能够使容器与内容具有一致性,创造出递归结构的模式. 示例程序是列出文件夹以及其内部文件与文件夹一览的功能: 可以由示例图看出,有一个电影文件夹 ...
- Composite模式 组合模式
Android的ViewGroup 和 View 的关系,即是采用组合模式 1. 概述 在数据结构里面,树结构是很重要,我们可以把树的结构应用到设计模式里面. 例子1:就是多级树形菜单. 例子2:文件 ...
- Composite模式(组合设计模式)
Composite 设计模式? 在计算机的文件系统中,有"文件夹"的概念(在有些操作系统(Linux操作系统)中,也称为"目录").文件夹里面既可以放入文件,也 ...
随机推荐
- WordPress Shareaholic 插件跨站请求伪造漏洞
漏洞名称: WordPress Shareaholic 插件跨站请求伪造漏洞 CNNVD编号: CNNVD-201308-250 发布时间: 2013-08-19 更新时间: 2013-08-19 危 ...
- 把这两天遇到的码(e)农(xin)题记下来
1019: [SHOI2008]汉诺塔 1858: [Scoi2010]序列操作 1058: [ZJOI2007]报表统计
- 如何配置jdk和tomcat 转
一.配置JDK1.解压JDK至D:\JDK1.5目录下(楼主可以自由选取目录).2.设置环境变量(右键我得电脑->属性->高级->环境变量),在系统变量中添加一个叫JAVA_HOME ...
- 51单片机的堆栈指针(SP)
堆栈指针(SP,Stack Pointer),专门用于指出堆栈顶部数据的地址. 那么51单片机的堆栈在什么地方呢?由于单片机中存放数据的区域有限,我们不能够专门分配一块地方做堆栈,所以就在内存(RAM ...
- 锐浪应用小插曲,asp.net下的使用
下午提前完成了今天的工作内容,整了下bs中的应用,嘿嘿,其中遇到不少问题,接下来说下大概会遇到哪些问题,1:grid++ 6.0插件下载安装之后ie浏览器无法打开,居然什么都没有显示,奇葩啊,系统版本 ...
- (转载)sinaeditor漏洞
SinaEditor简介 SinaEditor是基于新浪博客编辑器的开源编辑器.您可以用它来编辑富文本内容. 编辑器的核心是一个执行队列的调度系统,加入插件来实现功能,并通过事件来驱动编辑器的运行.我 ...
- lightoj 1030 概率dp
题目链接:http://lightoj.com/volume_showproblem.php?problem=1030 #include<cstdio> #include<cstri ...
- php异步请求模拟多进程
在A请求页面发起另一个B页面请求 不需要等待B页面执行结束再返回 直接往下执行A页面的请求 A页面代码 <?php $url = 'http://'.$_SERVER['HTTP_HOST']. ...
- c#基础语言编程-集合
引言 在c#常用的集合分为非泛型集合和泛型集合. 非泛型集合的类和接口位于System.Collections命名空间.这些接口和类定义各种对象(如列表.队列.位数组.哈希表和字典)的集合. 泛型集合 ...
- ODBC 中遇到的错误
直接贴解决办法的链接: http://zhidao.baidu.com/link?url=pyd2AiazzsZr4IlMpiCdXlLC6nnao908xmqmY9QI0yj8vIGCbRPRrqh ...
